Spring(五)之Bean定义继承和依赖注入
一、Bean定义继承
bean定义可以包含许多配置信息,包括构造函数参数,属性值和特定于容器的信息,例如初始化方法,静态工厂方法名称等。
子bean定义从父定义继承配置数据。子定义可以根据需要覆盖某些值或添加其他值。
Spring Bean定义继承与Java类继承无关,但继承概念是相同的。您可以将父bean定义定义为模板,其他子bean可以从父bean继承所需的配置。
使用基于XML的配置元数据时,可以使用parent属性指定子bean定义,并将父bean指定为此属性的值。
演示示例:
(1)编写HelloWorld.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class HelloWorld {
private String message1;
private String message2; public void setMessage1(String message){
this.message1 = message;
}
public void setMessage2(String message){
this.message2 = message;
}
public void getMessage1(){
System.out.println("World Message1 : " + message1);
}
public void getMessage2(){
System.out.println("World Message2 : " + message2);
}
}
(2)编写HelloIndea.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class HelloIndia {
private String message1;
private String message2;
private String message3;
public void setMessage1(String message){
this.message1 = message;
}
public void setMessage2(String message){
this.message2 = message;
}
public void setMessage3(String message){
this.message3 = message;
}
public void getMessage1(){
System.out.println("India Message1 : " + message1);
}
public void getMessage2(){
System.out.println("India Message2 : " + message2);
}
public void getMessage3(){
System.out.println("India Message3 : " + message3);
}
}
(3)编写MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); HelloWorld objA = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
objA.getMessage1();
objA.getMessage2(); HelloIndia objB = (HelloIndia) context.getBean("helloIndia");
objB.getMessage1();
objB.getMessage2();
objB.getMessage3();
}
}
(4)Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> <bean id = "helloWorld" class = "com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld">
<property name = "message1" value = "Hello World!"/>
<property name = "message2" value = "Hello Second World!"/>
</bean> <bean id ="helloIndia" class = "com.tutorialspoint.HelloIndia" parent = "helloWorld">
<property name = "message1" value = "Hello India!"/>
<property name = "message3" value = "Namaste India!"/>
</bean> </beans>
(5)运行MainApp.java中的main方法

二、依赖注入
每个基于Java的应用程序都有一些对象可以协同工作,以呈现最终用户所看到的工作应用程序。在编写复杂的Java应用程序时,应用程序类应尽可能独立于其他Java类,以增加重用这些类的可能性,并在单元测试时独立于其他类测试它们。依赖注入(或称为布线)有助于将这些类粘合在一起,同时保持它们的独立性。
依赖注入常用两种形式:
1.set注入(比较常用)
2.构造函数注入
set注入示例:
(1)编写TextEditor.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class TextEditor {
private SpellChecker spellChecker;
// a setter method to inject the dependency.
public void setSpellChecker(SpellChecker spellChecker) {
System.out.println("Inside setSpellChecker." );
this.spellChecker = spellChecker;
}
// a getter method to return spellChecker
public SpellChecker getSpellChecker() {
return spellChecker;
}
public void spellCheck() {
spellChecker.checkSpelling();
}
}
(2)编写SpellChecker.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class SpellChecker {
public SpellChecker(){
System.out.println("Inside SpellChecker constructor." );
}
public void checkSpelling(){
System.out.println("Inside checkSpelling." );
}
}
(3)编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> <!-- Definition for textEditor bean using inner bean -->
<bean id = "textEditor" class = "com.tutorialspoint.TextEditor">
<property name = "spellChecker">
<bean id = "spellChecker" class = "com.tutorialspoint.SpellChecker"/>
</property>
</bean> </beans>
(4)编写MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
TextEditor te = (TextEditor) context.getBean("textEditor");
te.spellCheck();
}
}
(5)运行MainApp.java中的main方法
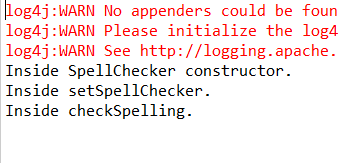
2.注入集合
Spring提供四种集合注入方式:
(1)Set;(2)List;(3)Map;(4)Props;
演示示例如下:
(1)编写JavaCollection
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.*; public class JavaCollection {
List addressList;
Set addressSet;
Map addressMap;
Properties addressProp; // a setter method to set List
public void setAddressList(List addressList) {
this.addressList = addressList;
} // prints and returns all the elements of the list.
public List getAddressList() {
System.out.println("List Elements :" + addressList);
return addressList;
} // a setter method to set Set
public void setAddressSet(Set addressSet) {
this.addressSet = addressSet;
} // prints and returns all the elements of the Set.
public Set getAddressSet() {
System.out.println("Set Elements :" + addressSet);
return addressSet;
} // a setter method to set Map
public void setAddressMap(Map addressMap) {
this.addressMap = addressMap;
} // prints and returns all the elements of the Map.
public Map getAddressMap() {
System.out.println("Map Elements :" + addressMap);
return addressMap;
} // a setter method to set Property
public void setAddressProp(Properties addressProp) {
this.addressProp = addressProp;
} // prints and returns all the elements of the Property.
public Properties getAddressProp() {
System.out.println("Property Elements :" + addressProp);
return addressProp;
}
}
(2)编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> <!-- Definition for javaCollection -->
<bean id = "javaCollection" class = "com.tutorialspoint.JavaCollection"> <!-- results in a setAddressList(java.util.List) call -->
<property name = "addressList">
<list>
<value>INDIA</value>
<value>Pakistan</value>
<value>USA</value>
<value>USA</value>
</list>
</property> <!-- results in a setAddressSet(java.util.Set) call -->
<property name = "addressSet">
<set>
<value>INDIA</value>
<value>Pakistan</value>
<value>USA</value>
<value>USA</value>
</set>
</property> <!-- results in a setAddressMap(java.util.Map) call -->
<property name = "addressMap">
<map>
<entry key = "1" value = "INDIA"/>
<entry key = "2" value = "Pakistan"/>
<entry key = "3" value = "USA"/>
<entry key = "4" value = "USA"/>
</map>
</property> <!-- results in a setAddressProp(java.util.Properties) call -->
<property name = "addressProp">
<props>
<prop key = "one">INDIA</prop>
<prop key = "one">INDIA</prop>
<prop key = "two">Pakistan</prop>
<prop key = "three">USA</prop>
<prop key = "four">USA</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean> </beans>
(3)编写MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
JavaCollection jc=(JavaCollection)context.getBean("javaCollection"); jc.getAddressList();
jc.getAddressSet();
jc.getAddressMap();
jc.getAddressProp();
}
}
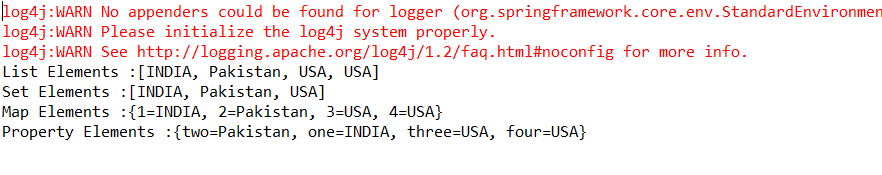
(4)运行MainApp.java中的main方法
结果如下:
Spring(五)之Bean定义继承和依赖注入的更多相关文章
- spring学习五:Spring Bean 定义继承
Bean 定义继承 bean 定义可以包含很多的配置信息,包括构造函数的参数,属性值,容器的具体信息例如初始化方法,静态工厂方法名,等等. 子 bean 的定义继承父定义的配置数据.子定义可以根据需要 ...
- 品Spring:负责bean定义注册的两个“排头兵”
别看Spring现在玩的这么花,其实它的“筹码”就两个,“容器”和“bean定义”. 只有先把bean定义注册到容器里,后续的一切可能才有可能成为可能. 所以在进阶的路上如果要想走的顺畅些,彻底搞清楚 ...
- Spring IOC源代码具体解释之容器依赖注入
Spring IOC源代码具体解释之容器依赖注入 上一篇博客中介绍了IOC容器的初始化.通过源代码分析大致了解了IOC容器初始化的一些知识.先简单回想下上篇的内容 加载bean定义文件的过程.这个过程 ...
- Spring升级案例之IOC介绍和依赖注入
Spring升级案例之IOC介绍和依赖注入 一.IOC的概念和作用 1.什么是IOC 控制反转(Inversion of Control, IoC)是一种设计思想,在Java中就是将设计好的对象交给容 ...
- Spring-初识Spring框架-IOC控制反转(DI依赖注入)
---恢复内容开始--- IOC :控制反转 (DI:依赖注入)使用ioc模式开发 实体类必须有无参构造方法1.搭建Spring环境下载jarhttp://maven.springframework. ...
- 三大框架 之 Spring(IOC控制反转、DI依赖注入)
目录 常用词汇 left join与left outer join的区别 Struts2的标签库导入 Spring Spring概述 什么是Spring spring特点 下载 IOC 什么IOC 传 ...
- spring接口多实现类,该依赖注入哪一个?
一.问题的描述 在实际的系统应用开发中我经常会遇到这样的一类需求,相信大家在工作中也会经常遇到: 同一个系统在多个省份部署. 一个业务在北京是一种实现方式,是基于北京用户的需求. 同样的业务在上海是另 ...
- Spring详解(三)------DI依赖注入
上一篇博客我们主要讲解了IOC控制反转,也就是说IOC 让程序员不在关注怎么去创建对象,而是关注与对象创建之后的操作,把对象的创建.初始化.销毁等工作交给spring容器来做.那么创建对象的时候,有可 ...
- Java框架spring 学习笔记(五):Bean定义继承
子 bean 的定义继承父定义的配置数据.子定义可以根据需要重写一些值,或者添加其他值. 编写HelloWorld.java package com.example.spring; public cl ...
随机推荐
- grpc的数据包监控
CommView是一个专门为网络管理员,安全专家,网络程序员,以及任何想要全面了解一台个人电脑或一个网段中的网络通信量的用户设计的强大的网络监控器和分析器,不过它支持Win系统. 我这里用的 Comm ...
- gRPC的简单Go例子
gRPC是一个高性能.通用的开源RPC框架,其由Google主要面向移动应用开发并基于HTTP/2协议标准而设计,基于ProtoBuf(Protocol Buffers)序列化协议开发,且支持众多开发 ...
- Ubuntu重启网卡的三种方法
一.network利用root帐户# service network restart 或者/etc/init.d/networking restart 二.ifdown/ifup# ifdown et ...
- [CTSC2008]祭祀(构造方案)
前面的话 这道题显然就是最长反链 根据 \(Dilworth\) 定理:最小链覆盖数 = 最长反链长度 然后传递闭包跑匹配即可 \(luogu\)交了一下,\(WA\) 了 \(QAQ\) 本来各种 ...
- Linux VPS主机利用Crontab实现定时重启任务
第一.安装Crontab可执行环境 一般的VPS/服务器是支持的,但是有些可能没有支持就需要我们来给予安装. A - centos系统 #安装Crontab yum install vixie-cro ...
- 远景GIS云上线
没有发布会.没有嘉宾.没有掌声,趁着国庆假期悄悄地将系统部署到服务器上线运行. 远景GIS云(RGIS Cloud)基于自主研发的远景GIS基础平台开发,目前已实现了Shape上传和导出.符号配置.动 ...
- 微服务架构之spring cloud zipkin
Spring Cloud Zipkin是微服务的链路跟踪组件,帮助详细了解一次request&response的总计时,及每个微服务的消耗时间.微服务名称.异常信息等等过程信息. (一) 版本 ...
- 理解ASP.NET 5运行时命令:DNVM, DNX, 和DNU
ASP.NET 5 引入了一个新型的运行时,让我们可以现场交付模式组合式构建应用程序,而不依赖于宿主机上的.NET框架.这种新模式为我们提供了命令行工具(DNVM.DNX.DNU)用于管理我们的.ne ...
- 记录一次json转换的经历
需求:数据库里面的一个字段,存的是json数据,类似{‘name’:“name1”,'items':“[{code:0,name:'name2'}]”},{‘name’:“name3”,'items' ...
- spring boot(2)-@SpringBootApplication详解
pom.xml <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spr ...
