6-16 Topological Sort(25 分)
Write a program to find the topological order in a digraph.
Format of functions:
bool TopSort( LGraph Graph, Vertex TopOrder[] );
where LGraph is defined as the following:
typedef struct AdjVNode *PtrToAdjVNode;
struct AdjVNode{
Vertex AdjV;
PtrToAdjVNode Next;
};
typedef struct Vnode{
PtrToAdjVNode FirstEdge;
} AdjList[MaxVertexNum];
typedef struct GNode *PtrToGNode;
struct GNode{
int Nv;
int Ne;
AdjList G;
};
typedef PtrToGNode LGraph;
The topological order is supposed to be stored in TopOrder[] where TopOrder[i] is the i-th vertex in the resulting sequence. The topological sort cannot be successful if there is a cycle in the graph -- in that case TopSort must return false; otherwise return true.
Notice that the topological order might not be unique, but the judge's input guarantees the uniqueness of the result.
Sample program of judge:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef enum {false, true} bool;
#define MaxVertexNum 10 /* maximum number of vertices */
typedef int Vertex; /* vertices are numbered from 0 to MaxVertexNum-1 */
typedef struct AdjVNode *PtrToAdjVNode;
struct AdjVNode{
Vertex AdjV;
PtrToAdjVNode Next;
};
typedef struct Vnode{
PtrToAdjVNode FirstEdge;
} AdjList[MaxVertexNum];
typedef struct GNode *PtrToGNode;
struct GNode{
int Nv;
int Ne;
AdjList G;
};
typedef PtrToGNode LGraph;
LGraph ReadG(); /* details omitted */
bool TopSort( LGraph Graph, Vertex TopOrder[] );
int main()
{
int i;
Vertex TopOrder[MaxVertexNum];
LGraph G = ReadG();
if ( TopSort(G, TopOrder)==true )
for ( i=0; i<G->Nv; i++ )
printf("%d ", TopOrder[i]);
else
printf("ERROR");
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
/* Your function will be put here */
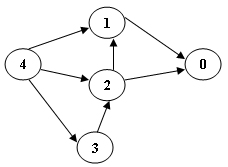
Sample Input 1 (for the graph shown in the figure):
5 7
1 0
4 3
2 1
2 0
3 2
4 1
4 2
Sample Output 1:
4 3 2 1 0
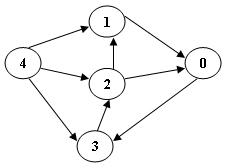
Sample Input 2 (for the graph shown in the figure):
5 8
0 3
1 0
4 3
2 1
2 0
3 2
4 1
4 2
Sample Output 2:
ERROR
bool TopSort( LGraph Graph, Vertex TopOrder[] )
{
int c = ;
int book[Graph -> Nv],h[Graph -> Nv + ],head = ,tail = ;
PtrToAdjVNode t;
for(int i = ;i < Graph -> Nv;i ++)
book[i] = ;
for(int i = ;i < Graph -> Nv;i ++)
{
t = Graph -> G[i].FirstEdge;
while(t)
{
book[t -> AdjV] ++;
t = t -> Next;
}
}
for(int i = ;i < Graph -> Nv;i ++)
{
if(book[i] == )
{
h[tail ++] = i;
}
}
if(head == tail)return false;
while(head < tail)
{
t = Graph -> G[h[head]].FirstEdge;
while(t)
{
if(book[t -> AdjV] <= )return false;
book[t -> AdjV] --;
if(book[t -> AdjV] == )h[tail ++] = t -> AdjV;
t = t -> Next;
}
book[h[head]] = -;
TopOrder[c ++] = h[head ++];
}
if(c != Graph -> Nv)return false;///有回路
return true;
}
6-16 Topological Sort(25 分)的更多相关文章
- PTA 09-排序3 Insertion or Heap Sort (25分)
题目地址 https://pta.patest.cn/pta/test/16/exam/4/question/676 5-14 Insertion or Heap Sort (25分) Accor ...
- PAT 甲级 1146 Topological Order (25 分)(拓扑较简单,保存入度数和出度的节点即可)
1146 Topological Order (25 分) This is a problem given in the Graduate Entrance Exam in 2018: Which ...
- 【PAT甲级】1101 Quick Sort (25 分)
题意: 输入一个正整数N(<=1e5),接着输入一行N个各不相同的正整数.输出可以作为快速排序枢纽点的个数并升序输出这些点的值. trick: 测试点2格式错误原因:当答案为0时,需要换行两次
- A1101 Quick Sort (25 分)
一.技术总结 这里的一个关键就是理解调换位置排序是时,如果是元主,那么它要确保的条件就只有两个一个是,自己的位置不变,还有就是前面的元素不能有比自己大的. 二.参考代码 #include<ios ...
- 09-排序3 Insertion or Heap Sort (25 分)
According to Wikipedia: Insertion sort iterates, consuming one input element each repetition, and gr ...
- 【PAT甲级】1098 Insertion or Heap Sort (25 分)
题意: 输入一个正整数N(<=100),接着输入两行N个数,表示原数组和经过一定次数排序后的数组.判断是经过插入排序还是堆排序并输出再次经过该排序后的数组(数据保证答案唯一). AAAAAcce ...
- PAT甲级——1146 Topological Order (25分)
This is a problem given in the Graduate Entrance Exam in 2018: Which of the following is NOT a topol ...
- 1098 Insertion or Heap Sort (25分)
According to Wikipedia: Insertion sort iterates, consuming one input element each repetition, and gr ...
- PTA 10-排序6 Sort with Swap(0, i) (25分)
题目地址 https://pta.patest.cn/pta/test/16/exam/4/question/678 5-16 Sort with Swap(0, i) (25分) Given a ...
随机推荐
- cocos代码研究(23)Widget子类ScrollView学习笔记
基础理论 一个能够被用户触摸滚动的一个层次型布局容器视图,允许其尺寸大于屏幕显示的物理尺寸,其内部维护有一个布局用于水平的或垂直的存放子节点.继承自 Layout,被 ListView 继承. 代码实 ...
- 商品的spu、sku及其之间的关系
今日来总结一下,电商系统中涉及到商品时必然会遇到的几个概念,SPU.SKU.单品等.彻底搞懂和明白了这几个概念对我们设计商品表是十分必要的前提条件. SPU:标准化产品单元 SPU = Standar ...
- C#反射——简单反射操作类的封装
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.Re ...
- springcloud7---hystrix
目前使用eureka server完成了服务注册和服务发现,ribbon完成了客户端负载均衡.如果服务提供者的响应很慢那么服务消费者会强制等待,一直等到http请求超时,如果服务消费者还是其他的服务提 ...
- Python 操作 SQL 数据库 (ORCAL)
MySQLdb.connect是python 连接MySQL数据库的方法,在Python中 import MySQLdb即可使用,至于connect中的参数很简单:host:MySQL服务器名user ...
- PHP设计模式_注册树模式
通过注册树模式可以更加简单快捷的获取对象,在某个地方实例化了一个对象,可以将这个对象“保存”起来(放入可以全局使用的数组里),用的时候只需要提供 保存对象的时候 的那个标识即可,解决全局共享和交换对象 ...
- 常用php操作redis命令整理(二)哈希类型
HSET将哈希表key中的域field的值设为value;如果field是哈希表中的一个新建域,并且值设置成功,返回1;如果哈希表中域field已经存在且旧值已被新值覆盖,返回0. <?php ...
- Python3.x:os.chdir(改变当前路径方法)介绍
Python3.x:os.chdir(改变当前路径方法)介绍 1,os.chdir() import os os.chdir(r'C:\python36\test_chdir') 说明:chdir() ...
- ISSCC 2017论文导读 Session 14: A 28nm SoC with a 1.2GHz Prediction Sparse Deep-Neural-Network Engine
A 28nm SoC with a 1.2GHz 568nJ/Prediction Sparse Deep-Neural-Network Engine with >0.1 Timing Erro ...
- 简单线性dp
小zc现在有三个字符串,他想知道前两个字符串能不能生成第三个字符串,生成规则如下:第一个串的每个字符都可以往第二个串的任意位置插入(包括首尾位置),但必须保证来源于第一个串中的字符在生成后的串中的相对 ...