《机器学习_01_线性模型_线性回归_正则化(Lasso,Ridge,ElasticNet)》
一.过拟合
建模的目的是让模型学习到数据的一般性规律,但有时候可能会学过头,学到一些噪声数据的特性,虽然模型可以在训练集上取得好的表现,但在测试集上结果往往会变差,这时称模型陷入了过拟合,接下来造一些伪数据进行演示:
import os
os.chdir('../')
from ml_models.linear_model import *
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
#造伪样本
X=np.linspace(0,100,100)
X=np.c_[X,np.ones(100)]
w=np.asarray([3,2])
Y=X.dot(w)
X=X.astype('float')
Y=Y.astype('float')
X[:,0]+=np.random.normal(size=(X[:,0].shape))*3#添加噪声
Y=Y.reshape(100,1)
#拟合数据并可视化
lr=LinearRegression()
lr.fit(X[:,:-1],Y)
lr.plot_fit_boundary(X[:,:-1],Y)
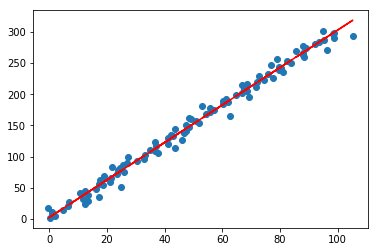
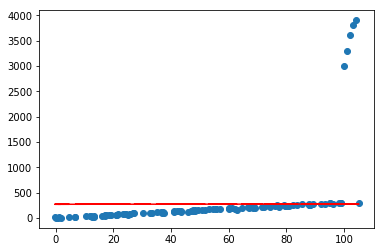
目前看起来效果还是可以的,但如果加入几个异常点,再看看效果呢
X=np.concatenate([X,np.asanyarray([[100,1],[101,1],[102,1],[103,1],[104,1]])])
Y=np.concatenate([Y,np.asanyarray([[3000],[3300],[3600],[3800],[3900]])])
lr=LinearRegression()
lr.fit(X[:,:-1],Y)
lr.plot_fit_boundary(X[:,:-1],Y)
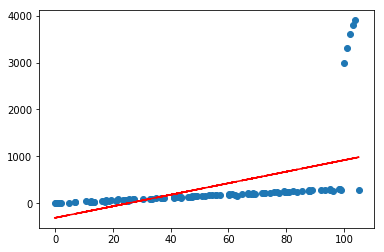
二.正则化
可以看到,仅仅加入了几个很离谱的异常点,就会对预测产生很大的影响,且偏离很远,这在实际情况中是很常见的;通常可以通过对模型参数添加正则化约束来避免这种情况,使其不会太“飘”,做法是在loss函数中为权重\(w\)添加\(L_1\)或者\(L_2\)约束,借用上一节的公式推导,直接推出loss部分:
1.线性回归中添加\(L_1\)约束称为Lasso回归,其损失函数如下:
\]
2.线性回归中添加\(L_2\)约束称为Ridge回归,其损失函数如下:
\]
3.如果不太确定用\(L_1\)好,还是\(L_2\)好,可以用它们的组合,称作ElasticNet,损失函数如下:
\]
可以发现通过调整超参,可以控制\(w\)的大小,如果\(\lambda\)或\(\alpha\)设置很大,\(w\)会被约束的很小,而如果\(\alpha\)或\(\lambda\)设置为0,等价于原始的不带正则项的线性回归;通常可以通过交叉验证,根据验证集上的表现来设置一个合适的超参;接下来在上一节线性回归代码的基础上实现Lasso,Ridge,ElasticNet模型,另外设置两个参数l1_ratio以及l2_ratio,分别用来控制\(L_1\)和\(L_2\)的loss部分的权重
三.代码实现
class LinearRegression(object):
def __init__(self, fit_intercept=True, solver='sgd', if_standard=True, epochs=10, eta=1e-2, batch_size=1,
l1_ratio=None, l2_ratio=None):
"""
:param fit_intercept: 是否训练bias
:param solver:
:param if_standard:
"""
self.w = None
self.fit_intercept = fit_intercept
self.solver = solver
self.if_standard = if_standard
if if_standard:
self.feature_mean = None
self.feature_std = None
self.epochs = epochs
self.eta = eta
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.l1_ratio = l1_ratio
self.l2_ratio = l2_ratio
# 注册sign函数
self.sign_func = np.vectorize(utils.sign)
def init_params(self, n_features):
"""
初始化参数
:return:
"""
self.w = np.random.random(size=(n_features, 1))
def _fit_closed_form_solution(self, x, y):
"""
直接求闭式解
:param x:
:param y:
:return:
"""
if self.l1_ratio is None and self.l2_ratio is None:
self.w = np.linalg.pinv(x).dot(y)
elif self.l1_ratio is None and self.l2_ratio is not None:
self.w = np.linalg.inv(x.T.dot(x) + self.l2_ratio * np.eye(x.shape[1])).dot(x.T).dot(y)
else:
self._fit_sgd(x, y)
def _fit_sgd(self, x, y):
"""
随机梯度下降求解
:param x:
:param y:
:param epochs:
:param eta:
:param batch_size:
:return:
"""
x_y = np.c_[x, y]
# 按batch_size更新w,b
for _ in range(self.epochs):
np.random.shuffle(x_y)
for index in range(x_y.shape[0] // self.batch_size):
batch_x_y = x_y[self.batch_size * index:self.batch_size * (index + 1)]
batch_x = batch_x_y[:, :-1]
batch_y = batch_x_y[:, -1:]
dw = -2 * batch_x.T.dot(batch_y - batch_x.dot(self.w)) / self.batch_size
# 添加l1和l2的部分
dw_reg = np.zeros(shape=(x.shape[1] - 1, 1))
if self.l1_ratio is not None:
dw_reg += self.l1_ratio * self.sign_func(self.w[:-1]) / self.batch_size
if self.l2_ratio is not None:
dw_reg += 2 * self.l2_ratio * self.w[:-1] / self.batch_size
dw_reg = np.concatenate([dw_reg, np.asarray([[0]])], axis=0)
dw += dw_reg
self.w = self.w - self.eta * dw
def fit(self, x, y):
# 是否归一化feature
if self.if_standard:
self.feature_mean = np.mean(x, axis=0)
self.feature_std = np.std(x, axis=0) + 1e-8
x = (x - self.feature_mean) / self.feature_std
# 是否训练bias
if self.fit_intercept:
x = np.c_[x, np.ones_like(y)]
# 初始化参数
self.init_params(x.shape[1])
# 训练模型
if self.solver == 'closed_form':
self._fit_closed_form_solution(x, y)
elif self.solver == 'sgd':
self._fit_sgd(x, y)
def get_params(self):
"""
输出原始的系数
:return: w,b
"""
if self.fit_intercept:
w = self.w[:-1]
b = self.w[-1]
else:
w = self.w
b = 0
if self.if_standard:
w = w / self.feature_std.reshape(-1, 1)
b = b - w.T.dot(self.feature_mean.reshape(-1, 1))
return w.reshape(-1), b
def predict(self, x):
"""
:param x:ndarray格式数据: m x n
:return: m x 1
"""
if self.if_standard:
x = (x - self.feature_mean) / self.feature_std
if self.fit_intercept:
x = np.c_[x, np.ones(shape=x.shape[0])]
return x.dot(self.w)
def plot_fit_boundary(self, x, y):
"""
绘制拟合结果
:param x:
:param y:
:return:
"""
plt.scatter(x[:, 0], y)
plt.plot(x[:, 0], self.predict(x), 'r')
Lasso
lasso=LinearRegression(l1_ratio=100)
lasso.fit(X[:,:-1],Y)
lasso.plot_fit_boundary(X[:,:-1],Y)
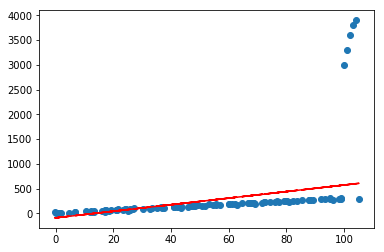
Ridge
ridge=LinearRegression(l2_ratio=10)
ridge.fit(X[:,:-1],Y)
ridge.plot_fit_boundary(X[:,:-1],Y)
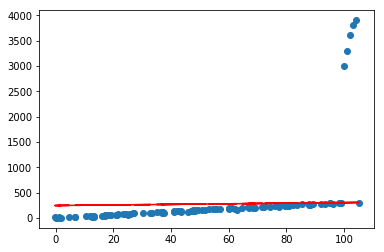
ElasticNet
elastic=LinearRegression(l1_ratio=100,l2_ratio=10)
elastic.fit(X[:,:-1],Y)
elastic.plot_fit_boundary(X[:,:-1],Y)
将sign函数整理到ml_models.utils中
《机器学习_01_线性模型_线性回归_正则化(Lasso,Ridge,ElasticNet)》的更多相关文章
- 简单物联网:外网访问内网路由器下树莓派Flask服务器
最近做一个小东西,大概过程就是想在教室,宿舍控制实验室的一些设备. 已经在树莓上搭了一个轻量的flask服务器,在实验室的路由器下,任何设备都是可以访问的:但是有一些限制条件,比如我想在宿舍控制我种花 ...
- 利用ssh反向代理以及autossh实现从外网连接内网服务器
前言 最近遇到这样一个问题,我在实验室架设了一台服务器,给师弟或者小伙伴练习Linux用,然后平时在实验室这边直接连接是没有问题的,都是内网嘛.但是回到宿舍问题出来了,使用校园网的童鞋还是能连接上,使 ...
- 外网访问内网Docker容器
外网访问内网Docker容器 本地安装了Docker容器,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Docker容器? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Docker容器 ...
- 外网访问内网SpringBoot
外网访问内网SpringBoot 本地安装了SpringBoot,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地SpringBoot? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装Java 1 ...
- 外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB
外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB 本地安装了Elasticsearch,只能在局域网内访问其WEB,怎样从外网也能访问本地Elasticsearch? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Rails
外网访问内网Rails 本地安装了Rails,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Rails? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Rails 默认安装的Rails端口 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Memcached数据库
外网访问内网Memcached数据库 本地安装了Memcached数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Memcached数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网CouchDB数据库
外网访问内网CouchDB数据库 本地安装了CouchDB数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地CouchDB数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Cou ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网DB2数据库
外网访问内网DB2数据库 本地安装了DB2数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地DB2数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动DB2数据库 默认安装的DB2 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库
外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库 本地安装了OpenLDAP数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地OpenLDAP数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动 ...
随机推荐
- 一、搭建SpringBoot2.0.0M4基础Web项目
本次开发环境为: 系统:Linux Mint 18 JDK:1.8 开发工具:IntelliJ IDEA 2017.2.4 1.启动IDEA工具,开始创建一个基础项目.点击Create New Pro ...
- git在用https进行push时候免输账密的方法
先新建一个文件 $ touch ~/.git-credentials $ vim ~/.git-credentials 进去添加内容(github为github.com,码云为gitee.com) h ...
- Apache Rewrite实现URL的跳转和域名跳转
Apache Rewrite实现URL的跳转和域名跳转 Rewirte主要的功能就是实现URL的跳转,它的正则表达式是基于Perl语言.可基 于服务器级的(httpd.conf)和目录级的 (.h ...
- 如何调试 Inno Setup
从命令行运行安装包,并加上 /log=filename
- Golang Map实现(四) map 的赋值和扩容
title: Golang Map 实现 (四) date: 2020-04-28 18:20:30 tags: golang map 操作,是map 实现中较复杂的逻辑.因为当赋值时,为了减少has ...
- Libra教程之:数据结构和存储
文章目录 存储的数据结构 账本历史 账本状态 账户 事件 前面的文章我们知道,libra会把所有的数据都存储在账本中.为了方便业务逻辑和数据的校验,这个存储是以特定的数据结构来实现的,这里我们叫做验证 ...
- spark下dataframe转为rdd格式
dataframe可以实现很多操作,但是存储到本地的时候,只能存 parquest格式 需要存储源格式,需要转换为rdd类型 将dataframe中的每一行都map成有逗号相连的string,就变为了 ...
- SQL语句学习(二)
为一张表添加外键: 这里我们希望再建一张订单的表为t_order,包含order_id,customer_id和price: ) NOT NULL auto_increment PRIMARY KEY ...
- SQL SERVER 性能优化二: 数据库初始值大小及增长方式设置
数据库增长方式主要有两种,按百分比自动增长和按固定大小自动增长,设置初始大小和增长方式需谨慎. 初始大小就是建库的大小,设小了,容易造成磁盘碎片,频繁增长也会影响IO响应.设大了,也不行,设大了,每次 ...
- Java 线程池(ThreadPoolExecutor)原理分析与实际运用
在我们的开发中"池"的概念并不罕见,有数据库连接池.线程池.对象池.常量池等等.下面我们主要针对线程池来一步一步揭开线程池的面纱. 有关java线程技术文章还可以推荐阅读:< ...
