【テンプレート】LCA
LCA目前比较流行的算法主要有tarjian,倍增和树链剖分
1)tarjian
是一种离线算法,需要提前知道所有询问对
算法如下
1.读入所有询问对(u,v),并建好树(建议邻接表)
2.初始化每个节点各属一个并查集,都指向自己
3.对整棵树进行dfs(深度优先搜索)遍历
每处理到一个新节点(u)时看他的另一半(询问对象v)是否visit过,如果visit过了,则这组询问对的lca即v的并查集的根节点,若没有visit过,则继续向下深搜,该节点记为已visit
每当回溯的时候都将子节点的并查集并到父节点的并查集中
这样一遍走下来就完成了tarjian算法。
超详细tarjain:orz
2)树上倍增
f[i,j]表示i的第2^j祖先dfs预处理f[i,j]=f[f[i,j-1],j-1];
对于每一对x,y先将深度调成一样再枚举j逐一往上找,这两个过程都是log的
超详细树上倍增:orz
3)树剖
树剖(树链剖分)是一种在线算法,跑起来非常快,应该是目前LCA算法中最优的
建树后,我们需要把整棵树划为轻重链,
每一个非叶子节点都一定在一条重链上
定义:
重边:父节点与其子树最大(子节点最多)的节点的连边称为重边
轻边:非重边即为轻边
重链:相连的重边称为重链
划分重链后,我们要记一个jump数组表示存每个节点的“跳”的信息
如果这个节点在重链上,则jump[i]为它所属重链的根节点(最顶端)
如果这个节点不在重链上或者它是一条重链的顶端(根节点),那么jump[i]为它的父节点
接下来我们就可以处理询问对了
比如求两个节点a,b的LCA
我们先看他们是否在同一条重链上,如果是,则LCA即为深度较小的节点
如果不是,则我们需要比较jump[a]和jump[b]的深度,jump[a]比较浅则令a=jump[a]反之令b=jump[b]
重复以上过程直到a==b(LCA为这个节点)或a,b在同一条重链上时(LCA为深度浅的节点)
这样就完成了,复杂度虽说评是O(n*logn)但实际上跑起来快得多
超详细树剖:orz
练手题
洛谷 P3379 【模板】最近公共祖先(LCA)
题目描述
如题,给定一棵有根多叉树,请求出指定两个点直接最近的公共祖先。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第一行包含三个正整数N、M、S,分别表示树的结点个数、询问的个数和树根结点的序号。
接下来N-1行每行包含两个正整数x、y,表示x结点和y结点之间有一条直接连接的边(数据保证可以构成树)。
接下来M行每行包含两个正整数a、b,表示询问a结点和b结点的最近公共祖先。
输出格式:
输出包含M行,每行包含一个正整数,依次为每一个询问的结果。
输入输出样例
5 5 4
3 1
2 4
5 1
1 4
2 4
3 2
3 5
1 2
4 5
4
4
1
4
4
说明
时空限制:1000ms,128M
数据规模:
对于30%的数据:N<=10,M<=10
对于70%的数据:N<=10000,M<=10000
对于100%的数据:N<=500000,M<=500000
样例说明:
该树结构如下:
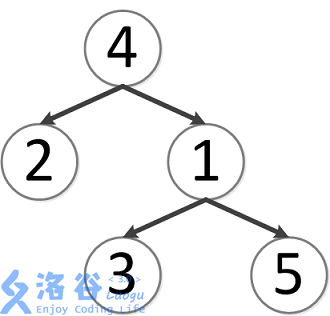
第一次询问:2、4的最近公共祖先,故为4。
第二次询问:3、2的最近公共祖先,故为4。
第三次询问:3、5的最近公共祖先,故为1。
第四次询问:1、2的最近公共祖先,故为4。
第五次询问:4、5的最近公共祖先,故为4。
故输出依次为4、4、1、4、4。
LCA板子!!!
1)tarjan
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std; const int N = ;
const int M = ;
int top,cnt,dad[N],ans[N];
bool used[N]; struct heads {
int head;
}v1[N],v2[N]; struct Edge {
int v,next,num;
}e1[M],e2[M]; void chu()
{
memset(v1,-,sizeof(v1));
memset(v2,-,sizeof(v2));
memset(dad,-,sizeof(dad));
memset(used,,sizeof(used));
} int getdad(int x)
{return dad[x] == - ? x : dad[x] = getdad(dad[x]);} void Unions(int a,int b)
{
int r1=getdad(a);
int r2=getdad(b);
if(r1!=r2)
dad[r2]=r1;
} void add1(int u,int v)
{
e1[top].v=v;
e1[top].next=v1[u].head;
v1[u].head=top++;
} void add2(int u,int v,int i)
{
e2[cnt].num=i;
e2[cnt].v=v;
e2[cnt].next=v2[u].head;
v2[u].head=cnt++;
} void Tarjan(int u)
{
used[u]=true;
for(int i=v1[u].head;i!=-;i=e1[i].next)
{
int v=e1[i].v;
if(used[v])
continue;
Tarjan(v);
Unions(u,v);
}
int Ms;
for(int i=v2[u].head;i!=-;i=e2[i].next)
{
int v=e2[i].v;
Ms=e2[i].num;
if(used[v])///==getdad(v)
ans[Ms]=getdad(v);
}
} int main()
{
int n,m,s,u,v;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s);
chu();
int nn=n;
n--;
while(n--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
add1(u,v),add1(v,u);
}
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
add2(u,v,i),add2(v,u,i);
}
Tarjan(s);
for(int i=;i<=nn;i++)
printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
return ;
}
Tarjan版(无注释...)
2)树上倍增
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
//maybe my English is not very good using namespace std; const int M = 5e5 + ;
int n,m,s;
int num;
int deep[M],h[M];
bool vs[M];
int jumps[M][];
int p; struct A{
int next;
int to;
}t[M<<]; inline int read() //optimize
{
int x=,f=;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<''||ch>'')
{
if(ch=='-') f=-;
ch=getchar();
} while(ch>=''&&ch<='')
{
x=x*+ch-'';
ch=getchar();
} return x*f;
} void ADD(int x,int y) //connect the x and the y
{
num++;
t[num].to=y;
t[num].next=h[x];
h[x]=num;
} void Dfs(int u)
{
for(int i=h[u];i!=-;i=t[i].next)
{
int v=t[i].to; //u's next side
if(deep[v] == ) //if v is not visited
{
deep[v]=deep[u]+; //deep+1
jumps[v][]=u; //u is v's dad
Dfs(v); //continue Dfs
}
}
} void steps()
{
p=int(log(n)/log()+0.001); //find the biggest
for(int i=;i<=p;i++) //the Limit
for(int j=;j<=n;j++)
jumps[j][i]=jumps[jumps[j][i-]][i-];
//the j jump 2^i can get to the (first jump 2^(i-1),then jump 2^i-1 can get to)
//eh...I will speak in Chinese.
//because 倍增 is use 次方的形式 increase
} int LCA(int a,int b)
{
//We let the b's deep is small
if(deep[a]<deep[b]) swap(a,b);
for(int i=p;i>=;i--)
{//first let the a jump to the b's deep
if(deep[jumps[a][i]]>=deep[b])
a=jumps[a][i];
}
if(a == b) return b; //if the b is them's LCA , return b
for(int i=p;i>=;i--) //jump together
{
if(jumps[a][i]!=jumps[b][i])
a=jumps[a][i],b=jumps[b][i]; //update
}
return jumps[a][];
} int main()
{
//s is the root
n=read();m=read();s=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) h[i]=-;
int x,y;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
x=read();y=read();
//connect the x and the y
ADD(x,y);
ADD(y,x);
}
deep[s]=; //this is too important !!!
//if you don't think so ,"//" it.
//and then you will know
Dfs(s); //Dfs the root(s)
steps(); //find the steps
int a,b;
while(m--)
{
a=read();b=read();
printf("%d\n",LCA(a,b));
}
return ;
}
树上倍增英文版???
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#define maxn 500500
using namespace std;
///隶属邻接表
struct Edge{ //邻接表的结构体
int from,to;
}edges[*maxn]; //边要乘2,因为是无向图 ;
int first[maxn],next[*maxn]; //同理;
int read(){ //读入优化,可以照着这个模板来写,这个还算写的比较好看。
int re=;
char ch=getchar();
while (ch<'' || ch>'') ch=getchar();
while (ch>='' && ch<=''){
re=re*+ch-'';
ch=getchar();
}
return re;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////
///全局变量
int n,m;
int root;
int height[maxn];
float log2n;
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////
///隶属LCA的全局变量
int f[maxn][];//
int have[maxn]; //have,有没有找过,这都是套路 。
void dfs(int u,int h){ //u代表点的标号,h代表高度。
int v;
height[u]=h;
for(int i=;i<=log2n;i++) {
if(h<=(<<i)) break; //由于i是从小到大计算的,故(1<<i)>=h 时可直接退出。请务必想清楚是<= 还是=。
f[u][i] = f[ f[u][i-] ][i-]; //动规计算。同样也是一切倍增算法的核心。
}
int k=first[u];
while(k!=-){
v=edges[k].to;
if(!have[v]) {
have[v]=;
f[v][]=u; //将要找的下一个点的父节点标为当前处理的节点u。
dfs(v,h+);
}
k=next[k];
}
}
int require_LCA(int a,int b){
int da=height[a],db=height[b];
//第一步,将a,b两点移到同样的高度,只动高度大的那个点而不动高度小的那个点。
if(da!=db) {
if(da<db){ //保证a的高度是大于b的高度的。
swap(a,b);
swap(da,db);
}
int d=da-db;
for(int i=;i<=log2n;i++)
if( (<<i) & d) a=f[a][i]; //这里的位运算可以减少代码量
//考虑到d是一个定值,而(1<<i)在二进制中只有第(i+1)位是1;
//那么d与(1<<i)如果某一位为1,那么表示可以向上移动,
//如果此时不移动,那么i增大了后就无法使height[a]==height[b]了
}
//第二步,找到某个位置i,在这个位置时,f[a][i]!=f[b][i],但再向上移动一步,a,b相同了
//从log2n开始从大到小枚举i,如果超过了a,b的高度,则令i继续减小
//如果没有超过a,b的高度,那么就判断移动了后会不会让a==b,
//是,则i继续减小,否则,令此时的a=f[a][i],b=f[b][i];
if(a==b) return b;
int i=;
for(i=log2n;i>=;i--) {
if(height[ f[a][i] ]<) continue;
if( f[a][i]==f[b][i] ) continue;
else a=f[a][i],b=f[b][i]; //顺便一提,在第二步任何地方没有break;
//我就是因为在这里写了一个break,然后找了我两个小时啊。
}
return f[a][];
}
/////////////////////////////////
///据说从主函数开始阅读是个好习惯。
int main(){
// freopen("in2.txt","r",stdin);
n=read();m=read();root=read();
memset(first,-,sizeof(first));
memset(next,-,sizeof(next));
int s,t;
int dsd=*(n-);
for(int i=;i<=dsd;i+=) {
s=read();t=read(); //读入优化。
edges[i].from=s;
edges[i].to=t;
edges[i+].from=t;
edges[i+].to=s;
next[i]=first[s];
first[s]=i;
next[i+]=first[t];
first[t]=i+;
}
// 以上是邻接表,在此不再赘述。
log2n=log(n)/log()+; //C++计算log是自然对数,我们要用的以2为底的对数,故要除以log(2);
//对无理数加上1或是0.5是个好习惯,可以减小误差;
memset(have,,sizeof(have));
memset(height,,sizeof(height));
memset(f,-,sizeof(f));
have[root]=; //fa[][]和height[]要在dfs理进行计算,不然根本找不到某个非根节点的父亲是谁;
dfs(root,);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=;j<=log2n;j++) {
if(height[i] <=(<<j) ) break;
}
}
for(int i=;i<m;i++) { //应对要求进行求解。
s=read();t=read();
int y=require_LCA(s,t);
printf("%d\n",y);
}
return ;
}
中文版23333
3)树剖
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#define _(ch) ch=read() //便于读入 using namespace std; const int S = ;
bool f[S]; //dfs 标记
int n,m,s;
int fa[S]; //并查集
int num,h[S]; //邻接表
int deep[S]; //深度
int sum[S]; //子结点个数
int dad[S]; //链头元素 struct B{
int to,next;
}t[S<<]; inline int read() //optimize
{
int x=,f=;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<''||ch>'')
{
if(ch=='-') f=-;
ch=getchar();
} while(ch>=''&&ch<='')
{
x=x*+ch-'';
ch=getchar();
} return x*f;
} void ADD(int x,int y) //connect the x and the y
{
num++;
t[num].to=y;
t[num].next=h[x];
h[x]=num;
} inline int Find(int x)
//find the root (重链's top)
{return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = Find(fa[x]);} inline void Unions(int a,int b)
{ //union(搭重链)
/*int f1=Find(a);
int f2=Find(b);
if(f1!=f2)
{
fa[f1]=f2;
}*/
fa[Find(b)]=Find(a);
} inline void dfs(int p)//D is the (结点)
{//calc every D's son D
//每个结点的深度
f[p]=true;
int maxx=; //寻找子节点中拥有子结点个数最多的节点编号
sum[]=-; //0号没有子结点
for(int j=h[p];j;j=t[j].next)
{ //进行遍历
int v=t[j].to;
if(f[v]) continue;
deep[v]=deep[p]+;
dad[v]=p; //p is v's dad
dfs(v); //continue dfs
if(sum[v] > sum[maxx]) maxx=v; //update
sum[p]+=sum[v]+;
// p的子结点数 = p 的以'v'为根的子树的结点数目加上'v'这个点(即+1)
}
if(maxx) Unions(p,maxx); //if updated
//that means find the (重链) succeed
} inline int jump(int p) //find p can jump to
{
int top=Find(p); //(重链)'s top
if(top == p) return dad[p];
// 如果p所处于的链的链头就是自己,也就是说,已经位于链的top处,所以只能够跳到他的父结点的位置,
// 所以直接return it's dad,即跳一步到达父结点处
// 说白了就是说,一定要跳!!!
return top; //其余情况就返回链头就好(就是当前结点跳到了链头位置)
} inline int Lca(int a,int b) //Lca
{
while(a!=b) //当两点不相等的时候就开始跳
{
if(Find(a)==Find(b)) //如果它们位于同一条重链上
return deep[a]<deep[b] ? a:b; //直接返回深度较浅的那个点
int ja=jump(a),jb=jump(b);
if(deep[ja] > deep[jb]) //如果a跳了之后没有到达b跳了之后的深度
a=ja; //就选取深度较深的点跳
else
b=jb;
}
return a;
} int main()
{
_(n),_(m),_(s);
int x,y;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
_(x),_(y);
ADD(x,y),ADD(y,x);
fa[i]=i; //顺便初始化一下并查集
}
fa[n]=n; //有一个没有进行初始化的并查集,进行初始化
deep[s]=; //根结点的深度设置为1,非常重要!!!!
dfs(s); //寻找子节点个数,位于哪一条重链上
while(m--)
{
_(x),_(y);
printf("%d\n",Lca(x,y));
}
return ;
}
混杂版(才不是英语不好!)
【テンプレート】LCA的更多相关文章
- 【BZOJ3626】LCA(树链剖分,Link-Cut Tree)
[BZOJ3626]LCA(树链剖分,Link-Cut Tree) 题面 Description 给出一个n个节点的有根树(编号为0到n-1,根节点为0).一个点的深度定义为这个节点到根的距离+1. ...
- 【&】位与运算符【|】位或运算符之权限控制算法
[&]位与运算符: 按位与运算符"&"是双目运算符. 其功能是参与运算的两数各对应的二进位相与.只有对应的两个二进位均为1时,结果位才为1 ,否则为0.参与运算的数 ...
- 存储过程 分页【NOT IN】和【>】效率大PK 千万级别数据测试结果
use TTgoif exists (select * from sysobjects where name='Tonge')drop table Tongecreate table Tonge( I ...
- 普通方式 分页【NOT IN】和【>】效率大PK 千万级别数据测试结果
首现创建一张表,然后插入1000+万条数据,接下来进行测试. use TTgoif exists (select * from sysobjects where name='Tonge')drop t ...
- java byte【】数组与文件读写(增加新功能)
今天在测试直接写的文章: java byte[]数组与文件读写 时,想调用FileHelper类对字节数组以追加的方式写文件,结果无论怎样竟然数据录入不全,重新看了下文件的追加模式,提供了两种方式: ...
- Spring 当 @PathVariable 遇上 【. # /】等特殊字符
@PathVariable注解应该不是新鲜东西了Spring3.0就开始有了 URL中通过加占位符把参数传向后台 举个栗子,如下比较要说的内容比较简单就大概齐的写一下 画面侧 $.ajax({ typ ...
- 【php正则】php正则匹配UTF-8格式的中文汉字 和 【,】【,】【。】等符号
1.php正则匹配UTF-8格式的中文汉字 和 [,][,][.]等符号 if (preg_match_all("/([\x{4e00}-\x{9fa5}]+((,)?)+((,)?)+(( ...
- 公式中表达单个双引号【"】和空值【""】的方法及说明
http://club.excelhome.net/thread-661904-1-1.html 有人问为什么不用三个双引号"""来表示单个双引号["]呢,如果 ...
- ubuntu fcitx google 输入法打不出中括号【】
编辑/usr/share/fcitx/data/punc.mb.zh_CN, 将 [ · ] 「 」 这部分改成自己习惯的: [ [ ] ] 保存后,重启一下fcitx就OK了.
随机推荐
- servlet过滤器Filter使用之DelegatingFilterProxy类
正常情况下,我们需要添加一个过滤器,需要实现javax.servlet.Filter接口,再在web.xml中配置filter,如下: package cc.eabour.webapp.securit ...
- 查询SQL Server数据库所有表字段备注
SELECT 表名 = case when a.colorder=1 then d.name else '' end, 表说明 = case when a.colorder=1 then isnull ...
- react 样式的写法之一 ---》styled-components的基本使用
[react]---styled-components的基本使用---[WangQi] 一.官网地址 https://www.styled-components.com/ 二.styled-com ...
- HIbernate入门3
HIbernate的一对多操作: 1. 创建实体类:一个Customer类(客户类)和一个LinkMan类(联系人),两者的关系为:一个客户中可能有多个联系人(关于一对多的实体类之间的关联,不做详细介 ...
- Django forms组件的校验
引入: from django import forms 使用方法:定义规则,例: class UserForm(forms.Form): name=forms.CharField(max_lengt ...
- QT中使用Event Filter监听button事件,Release后button不见
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/zhenyu5211314/article/details/27201043 问题RT,在程序中我使用 ...
- nodejs、npm、 typescript、angular-cli安装
一.node.js环境安装 1.从Node.js官网下载对应平台的安装程序,进行安装,在Windows上安装时务必选择全部组件,包括勾选Add to Path. 2.安装完成后,打开window命令行 ...
- 计算机体系结构——流水线技术(Pipelining)
本文导读: 一.并行技术 .并行技术分类 .新技术的设计与实现 .指令周期 二.流水线技术 .什么是流水线 .指令重叠方式 .流水工作设计 .流水线的描述方法(时空图) .流水线特点 三.流水线的分类 ...
- C#学习——控件
Windows应用程序控件的基类是位于System.Windows.Forms命名空间的Control类. Control类定义了控件类的共同属性.方法和事件,其他的控件类都直接或间接到派生自这个类. ...
- 【学习总结】SQL学习总结
参考链接: 菜鸟教程: 一.认识sql 二.sql语法 三.sql高级教程 四.sql函数 一.认识SQL SQL是什么? SQL 是用于访问和处理数据库的标准的计算机语言. SQL,指结构化查询语言 ...
