MyBatis框架原理4:插件
插件的定义和作用
首先引用MyBatis文档对插件(plugins)的定义:
MyBatis 允许你在已映射语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截调用。默认情况下,MyBatis 允许使用插件来拦截的方法调用包括:
- Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed)
- ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)
- ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)
- StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
这些类中方法的细节可以通过查看每个方法的签名来发现,或者直接查看 MyBatis 发行包中的源代码。 如果你想做的不仅仅是监控方法的调用,那么你最好相当了解要重写的方法的行为。 因为如果在试图修改或重写已有方法的行为的时候,你很可能在破坏 MyBatis 的核心模块。 这些都是更低层的类和方法,所以使用插件的时候要特别当心。
Mybatis插件所拦截的4个对象正是在之前的文章MyBatis框架原理2:SqlSession运行过程中介绍的4个实现核心功能的接口。那么插件拦截这4个接口能做什么呢?根据之前文章对4个接口的介绍,可以猜测到:
- Executor是SqlSession整个执行过程的总指挥,同时还对缓存进行操作,通过插件可以使用自定义的缓存,比如mybatis-enhanced-cache插件。
- StatementHandler负责SQL的编译和执行,通过插件可以改写SQL语句。
- ParameterHandler负责SQL的参数设置,通过插件可以改变参数设置。
- ResultSetHandler负责结果集映射和存储过程输出参数的组装,通过插件可以对结果集映射规则改写。
插件的原理
在理解插件原理之前,得先搞清楚以下三个概念:
动态代理
代理模式是一种给真实对象提供一个代理对象,并由代理对象控制对真实对象的引用的一种设计模式,动态代理是在程序运行时动态生成代理类的模式,JDK动态代理对象是由java提供的一个Proxy类和InvocationHandler接口以及一个真实对象的接口生成的。通常InvocationHandler的实现类持有一个真实对象字段和定义一个invoke方法,通过Proxy类的newProxyInstance方法就可以生成这个真实对象的代理对象,通过代理对象调度方法实际就是调用InvocationHandler实现类的invoke方法,在invoke方法中可以通过反射实现调用真实对象的方法。拦截器(Interceptor)
动态代理对象可以对真实对象方法引用,是因为InvocationHandler实现类持有了一个真实对象的字段,通过反射就可以实现这个功能。如果InvocationHandler实现类再持有一个Interceptor接口的实现类,Interceptor接口定义了一个入参为真实对象的intercept方法,Interceptor接口的实现类通过重写intercept方法可以对真实对象的方法引用或者实现增强功能等等,也就是当我们再次使用这个动态代理对象调度方法时,可以根据需求对真实对象的方法做出改变。从这个Interceptor接口实现类的功能上来看,可以叫做真实对象方法的拦截器。于是我们再想一下,如果前面讲到MyBatis的4个核心功能接口的实现类(比如PreparedStatementHandler)是一个真实对象,我们通过JDK动态代理技术生成一个代理对象,并且生成代理类所需的InvocationHandler实现类同时还持有了一个Interceptor接口实现类,通过使用代理对象调度方法,我们就可以根据需求对PreparedStatementHandler的功能进行增强。
实际上MyBatis确实提供了这样一个Interceptor接口和intercept方法,也提供了这样的一个InvocationHandler接口的实现类,类名叫Plugin,它们都位于MyBatis的org.apache.ibatis.plugin包下。等等,那么MyBatis的插件不就是拦截器吗?拦截器的原理都讲完了,等下还怎么讲什么插件原理?

责任链模式
我们通过JDK动态代理技术生成一个代理对象,代理的真实对象是个StatementHandler,并且持有StatementHandler的拦截器(插件)。如果我们把这个代理对象视为一个target对象,再利用动态代理生成一个代理类,并且持有对这个target对象的拦截器(插件),如果再把新生成的代理视为一个新的target类,同样持有对新target类的拦截器(插件),那么我们就得到了一个像是被包裹了三层拦截器(插件)的StatementHandler的代理对象:
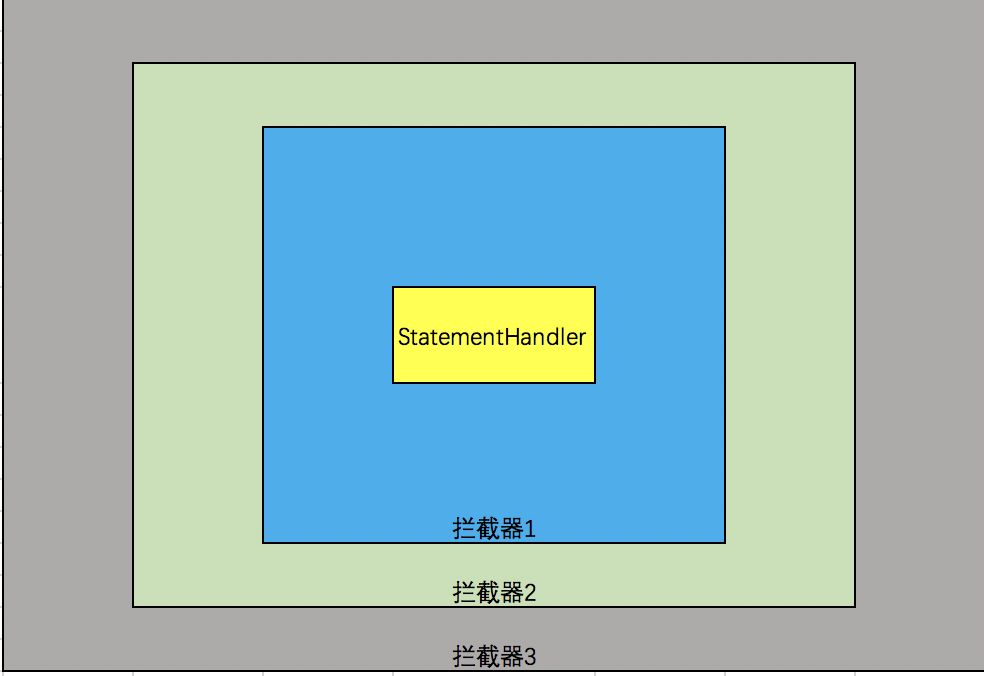
当MyBatis每一次SqlSession会话需要引用到StatementHandler的方法时,如过符合上图中拦截器3的拦截逻辑,则按拦截器3的定义的方法执行;如果不符合拦截逻辑,则将执行责任交给拦截器2处理,以此类推,这样的模式叫做责任链模式。MyBatis全局配置文件里可以配置多个插件,多个插件的运行就是按照这样的责任链模式执行的。
通过对以上三点的理解,我们已经对MyBatis插件原理已经有了初步认识,下面就通过源码看看MyBatis插件是如何运行起来的。
插件的运行过程
插件的接口
MyBatis提供了一个Interceptor接口,插件必须实现这个接口,接口定义了3个方法如下:public interface Interceptor {
// 执行插件实现的方法,Invocation对象持有真实对象,可通过反射调用真实对象的方法
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
// 设置插件拦截的对象target,通常调用Pulgin类的wrap方法生成一个代理类
Object plugin(Object target);
// 根据配置文件初始化插件
void setProperties(Properties properties); }插件的初始化
在MyBatis初始化时XMLConfigBuilderder的pluginElement方法对插件配置文件解析:private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 通过反射生成插件的实例
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance();
// 调用插件配置参数
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
// 将插件实例保存到Configuration对象中
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
}
}
}
Configuration对象最终将解析出的插件配置保存在持有InterceptorChain对象中,InterceptorChain对象又是通过一个ArrayList来保存所有插件,可见在MyBatis初始化的时候插件配置就已经加载好了,运行时就会根据插件编写的规则执行拦截逻辑。
``` java
public class InterceptorChain {
// 通过集合来保存插件
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<Interceptor>();
// 通过责任链模式调用插件plugin方法生成代理对象
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
// Configuration对象调用的添加插件的方法
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
}
}
```
插件的运行
如果我们需要拦截MyBatis的Executor接口,Configuration在初始化Executor时就会通过责任链模式将初始化的Executor作为真实对象,调用InterceptorChain的pluginAll放法生成代理对象:public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
// 根据配置文件生成相应Executor
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 调用InterceptorChain的pluginAll放法生成代理对象
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}InterceptorChain的 pluginAll方法调用插件的plugin方法,plugin方法可以调用MyBatis提供的工具类Plugin类来生成代理对象,Plugin类实现了InvocationHandler,在Plugin类中定义invoke方法来实现拦截逻辑和执行插件方法:
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler { // target为需要拦截的真实对象
private final Object target;
// interceptor为插件
private final Interceptor interceptor;
private final Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap; private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
} public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
// 动态代理生成代理对象并返回
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
} @Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
// 根据拦截逻辑执行插件的方法
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
// 直接调用真是对象的方法
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
...
插件的intercept方法参数为Invocation对象,Invocation对象持有真实对象和一个proceed方法,proceed方法通过反射调用真实对象的方法。于是多个插件生成的责任链模式的代理对象,就可以通过一层一层执行proceed方法来调用真实对象的方法。
插件的开发
自己编写插件必须继承MyBatis的Interceptor接口
public interface Interceptor {
// 执行插件实现的方法,Invocation对象持有真实对象,可通过反射调用真实对象的方法
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
// 设置插件拦截的对象target,通常调用Pulgin类的wrap方法生成一个代理类
Object plugin(Object target);
// 根据配置文件初始化插件
void setProperties(Properties properties); }
使用@Intercepts和@Signature注解
@Intercepts({@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "prepare", args = {Connection.class ,Integet.class})})
public class MyPlugin implements Interceptor {...}用@Intercepts注解申明是一个插件,@Signature注解申明拦截的对象,方法和参数。上面的写法表明了拦截了StatementHandler对象的prepare方法,参数是一个Connection对象和一个Integet。
编写拦截方法
MyBatis提供了一个Invocation工具类,通常我们将需要拦截的真实对象,方法及参数封装在里面作为一个参数传给插件的intercept方法,在插件intercept方法里可以编写拦截逻辑和执行拦截方法,方法参数invocation可以通过反射调用被代理对象的方法:@Intercepts({@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "prepare", args = {Connection.class ,Integet.class})})
public class MyPlugin implements Interceptor {
@override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// do something ...
// 调用被代理对象的方法
invocation.proceed();
// do something ...
@override
调用Plugin工具类生成代理对象
public Object plugin(Object target){
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
... }生成代理对象
MyBatis还提供了一个Plugin工具类,其中wrap方法用于生成代理类,invoke方法验证拦截类型和方法,并选择是否按拦截器的方法,代码如下:public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler { private final Object target; // 真实对象
private final Interceptor interceptor; // 拦截器(插件)
private final Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap; // Map保存签名的类型,方法和参数信息 private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
} public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// getSignatureMap方法通过反射获取插件里@Intercepts和@Signature注解声明的拦截类型,方法和参数信息
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
从signatureMap中获取拦截对象的类型
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
// 生成代理对象,如果target的类型不是插件里注解声明的类型则直接返回target不作拦截。
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
} @Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 验证代理对象调用的方法是否为插件里申明拦截的方法
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
// 如果是声明拦截的方法,则调用插件的intercept方法执行拦截处理
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
// 如果不是声明拦截的方法,则直接调用真实对象的方法
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
...
总结
MyBatis插件运行依靠Java动态代理技术实现,虽然原理很简单,但是编写插件涉及到修改MyBatis框架底层的接口,需要十分谨慎,做为初学者,最好使用现成的插件。
MyBatis框架原理4:插件的更多相关文章
- Mybatis的分页插件PageHelper
Mybatis的分页插件PageHelper 项目地址:http://git.oschina.net/free/Mybatis_PageHelper 文档地址:http://git.oschina. ...
- Mybatis 的分页插件PageHelper-4.1.1的使用
Mybatis 的分页插件 PageHelper 项目地址:http://git.oschina.net/free/Mybatis_PageHelper 文档地址:http://git.oschin ...
- Eclipse 安装mybatis的编辑插件
1.MyEditor安装的方式 Eclipse 安装mybatis的编辑插件有以下4种方式,您可以使用下列方法之一来安装MyBatis的编辑器: Eclipse 3.7的(市场客户机安装):此图像拖放 ...
- Mybatis 数据库物理分页插件 PageHelper
以前使用ibatis/mybatis,都是自己手写sql语句进行物理分页,虽然稍微有点麻烦,但是都习惯了.最近试用了下mybatis的分页插件 PageHelper,感觉还不错吧.记录下其使用方法. ...
- idea + mybatis generator + maven 插件使用
idea + mybatis generator + maven 插件使用 采用的是 generator 的 maven 插件的方式 ~ 1 pom.xml mybatis其它配置一样,下面是配置my ...
- SpringBoot集成MyBatis的分页插件 PageHelper
首先说说MyBatis框架的PageHelper插件吧,它是一个非常好用的分页插件,通常我们的项目中如果集成了MyBatis的话,几乎都会用到它,因为分页的业务逻辑说复杂也不复杂,但是有插件我们何乐而 ...
- Mybatis之分页插件pagehelper的简单使用
最近从家里回来之后一直在想着减肥的事情,一个月都没更新博客了,今天下午没睡午觉就想着把mybatis的分页插件了解一下,由于上个月重新恢复了系统,之前创建的项目都没了,又重新创建了一个项目. 一.创建 ...
- (转)mybatis数据库物理分页插件PageHelper
以前使用ibatis/mybatis,都是自己手写sql语句进行物理分页,虽然稍微有点麻烦,但是都习惯了.最近试用了下mybatis的分页插件 PageHelper,感觉还不错吧.记录下其使用方法. ...
- mybatis plugin作为一款优秀的mybatis跳转插件
阅读目录: 1. 简介2. 下载mybatis plugin插件3. 安装mybatis plugin插件4. 启动并验证5.说明1. 简介 mybatis plugin作为一款优秀的mybatis跳 ...
随机推荐
- [易学易懂系列|rustlang语言|零基础|快速入门|(18)|use关键词]
[易学易懂系列|rustlang语言|零基础|快速入门|(18)|use关键词] 实用知识 use关键词 我们今天来讲讲use关键词. 1.简单来说,use是给其他方法或资源定义一个别名,然后调用者, ...
- poj1015 Jury Compromise[背包]
每一件物品有两个属性.朴素思想是把这两种属性都设计到状态里,但空间爆炸.又因为这两个属性相互间存在制约关系(差的绝对值最小),不妨把答案设计入状态中,设$f[i][j]$选$i$个人,两者之差$j$. ...
- IC SPEC相关数据
---恢复内容开始--- 静态电流:静态电流是指没有信号输入时的电流,也就是器件本身在不受外部因素影响下的本身消耗电流. 纹波电压的害处: 1.容易在用设备中产生不期望的谐波,而谐波会产生较多的危害: ...
- 使用Vue自定义组件时,报did you register the component correctly? For recursive components, make sure to provide the "name" option.(未注册组件)的原因之一
错误信息: [Vue warn]: Unknown custom element: <list> - did you register the component correctly? F ...
- Ubuntu caffe 测试matlab接口
这是17年8月份新增的: make matcaffe error 255解决:在Makefile里面,大约第410行那一句话CXXFLAGS += -MMD -MP下面添加CXXFLAGS += -s ...
- dlerror和dlclose用法
dlclose() 1. 包含头文件 #include<dlfcn.h> 2. 函数定义 int dlclose(void *handle) dlclose用于关闭指定句柄的动态链接库, ...
- 【51nod1792】Jabby's segment tree
题目 线段树是一种经典的数据结构,一颗[1,n]的线段树他的根是[1,n],当一个线段树的结点是[l,r]时,设mid=(l+r)>>1,则这个结点的左儿子右儿子分别是[l,mid],[m ...
- Python在VSCode环境抓取TuShare数据存入MongoDB环境搭建
本文出自:https://www.cnblogs.com/2186009311CFF/p/11573094.html 总览 此文分为5个部分 第一:Anaconda(下载和安装) 第二:VSCode( ...
- C# checkedlistbox 控件 有bug
加入集合 private void Form2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { DataTable dt = new DataTable(); dt.Column ...
- the nearest point/vertex point of linestring
引用https://github.com/Toblerity/Shapely/issues/190 snorfalorpagus commented on 18 Oct 2014 The point ...
