Spring源码分析 手写简单IOC容器
Spring的两大特性就是IOC和AOP。
IOC Container,控制反转容器,通过读取配置文件或注解,将对象封装成Bean存入IOC容器待用,程序需要时再从容器中取,实现控制权由程序员向程序的转变。
一、代码结构
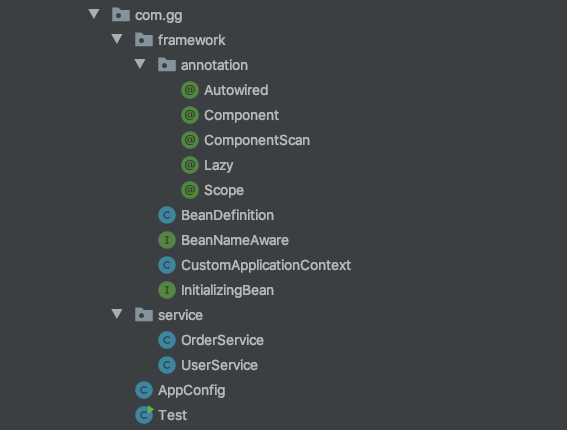
二、注解扫描
1、新建OrderService、UserService、Test类用于模拟实际开发
@Component("orderService")
@Scope("prototype")
public class OrderService implements BeanNameAware {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
public void test() {
System.out.println(userService);
}
public void setBeanName(String name) {
this.beanName = beanName;
}
}
@Component("userService")
public class UserService {
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//对应AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
//扫描 (判断是否存在Component) + 实例化(Bean的生命周期:1、实例化 2、依赖注入)
CustomApplicationContext customApplicationContext = new CustomApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Object userService1 = customApplicationContext.getBean("orderService");
System.out.println(userService);
System.out.println(userService1);
}
}
2、新建注解Component、ComponentScan、Autowired、Scope
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Component { // 用于将类注册成Bean
String value() default "";
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface ComponentScan { //用于配置类扫描的包
String value() default "";
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface Autowired { //属性注入
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Scope { //bean的范围
String value() default "singleton";
}
3、定义CustomApplicationContext实现注解扫描
- 对应Spring的AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,通过传入配置文件对象,读取ComponentScan的Value进行包扫描,扫描后获取带@Component注解的类
public class CustomApplicationContext {
private Class configClass;
public CustomApplicationContext(Class configClass) {
this.configClass = configClass;
//扫描(判断类上是否存在Component)(class文件) --> 形成beanDefinition
List<Class> classList = scan(configClass);
}
private List<Class> scan(Class configClass) {
List<Class> list = new ArrayList<Class>();
//存在注解,通过value获取要扫描包路径
if (configClass.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class)){
ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan)configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = componentScan.value();
path = path.replace(".","/"); //包转化为包路径(com.gg.service)
//扫描path路径下到类
ClassLoader classLoader = CustomApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
// 利用类加载器,根据包路径获取URL/target/classes/com/gg/service
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
File file = new File(resource.getFile());
if (file.isDirectory()) {
for (File f: file.listFiles()){
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath(); //类的完整路径
absolutePath = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.indexOf("com"),absolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
absolutePath = absolutePath.replace("/",".");
//com.gg.service.userService
Class clazz = null;
try {
clazz = classLoader.loadClass(absolutePath);
// 存在注解,将类加入数组
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
list.add(clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
4、将扫描获得的类封装成beanDefinition
- 扫描得到的类,将beanName、类型、类的范围封装成beanDefinition
- getBean时不用重新扫描,直接冲beanDefinitionMap获取
private Map<String,BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>();
public CustomApplicationContext(Class configClass) {
this.configClass = configClass;
List<Class> classList = scan(configClass); //扫描得到class
for (Class clazz: classList){
Component component = (Component) clazz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanName = component.value();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)){
Scope scope = (Scope) clazz.getAnnotation(Scope.class);
beanDefinition.setScope(scope.value());
}else{
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");//默认为单例
}
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(clazz);
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName,beanDefinition);
}
public class BeanDefinition { //bean的定义
private String scope;
private Class beanClass;
public String getScope() {
return scope;
}
public void setScope(String scope) {
this.scope = scope;
}
public Class getBeanClass() {
return beanClass;
}
public void setBeanClass(Class beanClass) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
}
}
- 至此,我们通过新建CustomApplicationContext,将添加注解的类加入到beanDefinitionMap。
三、实例化Bean
1、单例类先实例化,存入单例池
- 从beanDefinitionMap取出BeanDefinition,对单例类调用createBean()实例化,添加到单例池
private Map<String,Object> singletonPool = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>();
public CustomApplicationContext(Class configClass) {
this.configClass = configClass;
//扫描将注解的类存入beanDefinitionMap
List<Class> classList = scan(configClass);
for (Class clazz: classList){
Component component = (Component) clazz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanName = component.value();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)){
Scope scope = (Scope) clazz.getAnnotation(Scope.class);
beanDefinition.setScope(scope.value());
}else{
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(clazz);
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName,beanDefinition);
}
//将单例类添加到单例池singletonPool
for (String beanName : beanDefinitionMap.keySet()){
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton")){
//实例化bean
Object bean = createBean(beanName,beanDefinition);
singletonPool.put(beanName,bean);
}
}
}
private Object createBean(String beanName,BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
//实例化、填充属性、Aware、初始化
Class beanClass = beanDefinition.getBeanClass();
try {
// 从beanDefinition中获取类型,并实例化
Object bean = beanClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
//属性填充
Field[] fields = beanClass.getDeclaredFields(); //DeclaredFields 所有属性
for(Field field: fields){
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)){
Object annotationField = getBean(field.getName());
field.setAccessible(true); //反射产生对象要打开权限
field.set(bean,annotationField);
}
}
// Aware
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware){
((BeanNameAware)bean).setBeanName(beanName); //实现该端口就调用此方法
}
// 初始化
if (bean instanceof InitializingBean){
((InitializingBean)bean).afterPropertiesSet(); //实现该端口就调用此方法
}
return bean;
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
- 新建BeanNameAware、InitializingBean接口,实例类时,通过判断是否实现该接口,在实例初始化时
public interface BeanNameAware {
public void setBeanName(String name);
}
public interface InitializingBean {
public void afterPropertiesSet();
}
- 通过调用createBean()实例化beanDefinition中的类,单例在启动时实例,原型在调用getBean()再实例
2、getBean()
public Object getBean(String beanName){
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("prototype")){
return createBean(beanName,beanDefinition);
}else{
Object bean = singletonPool.get(beanName);
if (bean == null){
Object newBean = createBean(beanName,beanDefinition);
singletonPool.put(beanName,newBean);
return newBean;
}
return bean;
}
}
Spring源码分析 手写简单IOC容器的更多相关文章
- Spring源码分析之-加载IOC容器
本文接上一篇文章 SpringIOC 源码,控制反转前的处理(https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9RbVP2ZQVx9-vKngqndW1w) 继续进行下面的分析 首先贴出 Spr ...
- 源码分析 | 手写mybait-spring核心功能(干货好文一次学会工厂bean、类代理、bean注册的使用)
作者:小傅哥 博客:https://bugstack.cn - 汇总系列原创专题文章 沉淀.分享.成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获! 一.前言介绍 一个知识点的学习过程基本分为:运行helloworld ...
- 面试必会之ArrayList源码分析&手写ArrayList
简介 ArrayList是我们开发中非常常用的数据存储容器之一,其底层是数组实现的,我们可以在集合中存储任意类型的数据,ArrayList是线程不安全的,非常适合用于对元素进行查找,效率非常高. 线程 ...
- spring源码分析之玩转ioc:bean初始化和依赖注入(一)
最近赶项目,天天加班到十一二点,终于把文档和代码都整完了,接上继续整. 上一篇聊了beanProcess的注册以及对bean的自定义修改和添加,也标志着创建bean的准备工作都做好了,接下来就是开大招 ...
- Spring源码 20 手写模拟源码
参考源 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1tR4y1F75R?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click https://ww ...
- Spring源码分析(十九)容器的功能扩展概览
摘要: 本文结合<Spring源码深度解析>来分析Spring 5.0.6版本的源代码.若有描述错误之处,欢迎指正. 经过前面几章的分析,相信大家已经对 Spring 中的容器功能有了简单 ...
- 《四 spring源码》手写springmvc
手写SpringMVC思路 1.web.xml加载 为了读取web.xml中的配置,我们用到ServletConfig这个类,它代表当前Servlet在web.xml中的配置信息.通过web.xml ...
- 《四 spring源码》手写springioc框架
手写SpringIOCXML版本 /** * 手写Spring专题 XML方式注入bean * * * */ public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext { ...
- spring源码分析系列3:BeanFactory核心容器的研究
目录 @(spring源码分析系列3:核心容器的研究) 在讲容器之前,再明确一下知识点. BeanDefinition是Bean在容器的描述.BeanDefinition与Bean不是一个东西. Be ...
随机推荐
- PHP入门之数组
前言 之前几篇文章分别介绍了PHP的运算符,流程控制,函数.有兴趣的可以去看看. PHP入门之类型与运算符 PHP入门之流程控制 PHP入门之函数 接下来简单介绍一下数组. 数组初探 为什么要引进数组 ...
- Java高级篇反射和注解
反射是什么? 反射的作用?能带来什么好处? 反射的使用? 注解的使用? 注解和反射配合实战...
- 2020-06-25:B+树和B树有什么区别?
福哥答案2020-06-25: B树:1.叶子节点和非叶子节点都存数据.2.数据无链指针.B+树:1.只有叶子节点存数据.2.数据有链指针.B树优势:1.靠近根节点的数据,访问速度快.B+树优势:1. ...
- Remix+Geth 实现智能合约部署和调用详解
Remix编写智能合约 编写代码 在线调试 实现部署 调用接口 Geth实现私有链部署合约和调用接口 部署合约 调用合约 获得合约实例 通过实例调用合约接口 Remix编写智能合约 编写代码 Remi ...
- 搭建 WordPress 博客教程
搭建 WordPress 博客教程(超详细) 在 2018年7月29日 上张贴 由 suncent一条评论 本文转自:静候那一米阳光 链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/5675 ...
- golang 字符型
目录 前言 1. 基本 介绍 2. 声明 3. 使用细节 4. 字符类型的本质 跳转 前言 不做文字的搬运工,多做灵感性记录 这是平时学习总结的地方,用做知识库 平时看到其他文章的相关知识,也会增加到 ...
- 基础类库积累--ExeclHelper类
前言: 相信大家都玩过NPOI这个第三方组件,我就分享一下我平时使用的工具类,如果有不好的地方,请赐教! NPOI是什么? NPOI是一个开源的C#读写Excel.WORD等微软OLE2组件文档的项目 ...
- day33:进程II
目录 1.锁:Lock 2.信号量:Semaphone 3.事件:Event 4.进程队列:Queue 5.生产者和消费者模型 6.JoinableQueue 锁:Lock 1.锁的基本概念 上锁和解 ...
- 免费API接口记录
用来记录一些无次数限制的免费API接口,主要是聚合数据上和API Store上的一些,还有一些其他的. 手机号码归属地API接口: https://www.juhe.cn/docs/api/id/11 ...
- 第4章 DDL数据定义
第4章 DDL数据定义 4.1 创建数据库 1)创建一个数据库,数据库在HDFS上的默认存储路径是/user/hive/warehouse/*.db. hive (default)> creat ...
