Ordering Cows
题意描述
好像找不到链接(找到了请联系作者谢谢),所以题目描述会十分详细:
Problem 1: Ordering Cows [Bruce Merry, South African Computer Olympiad, 2003]
Farmer John has noticed that when his N (1 <= N <= 1,500) cows line up to be milked, certain cows always line up ahead of certain other cows. He has made a list of L (1 <= L <= 10,000) pairs of cows for which he has noticed this. He wants to send this list to his friend, Farmer Bob. Unfortunately, the inter-farm cowmunication network is very slow.
FJ has realized that he can compress the list by removing redundant information. The information he has is all of the form "cow A lines up before cow B". Information is redundant if it can be deduced from
other information on the list. For example, given "Alice is before Betty", "Betty is before Carol" and "Alice is before Carol" the last statement is redundant. Of course, the cows are numbered with unique serial numbers in the range 1..N; only a few of them have names (and those are not used here).Help Farmer John by finding the smallest subset of his list from which the rest of the list can be deduced. Happily, the answer is guaranteed to be unique, and the original list contains no contradictions such as "Alice before Betty" and "Betty before Alice".
PROBLEM NAME: order
INPUT FORMAT:
Line 1: Two space-separated integers: N and L.
Lines 2..L+1: Two integers X and Y (1 <= X,Y <= N), indicating that cow X lines up before cow Y. No fact is duplicated.
SAMPLE INPUT (file order.in):
5 6
3 5
4 2
5 2
2 1
3 1
4 1OUTPUT FORMAT:
Line 1: A single line with the number of facts that Farmer John will send to Farmer Bob.
Lines 2..U+1: The facts from the input file that Farmer John will transmit. These must be lists in the same format as the entries in the input file. They must be sorted numerically on the first entry in the line, with ties being broken by the second entry on the line.
SAMPLE OUTPUT (file order.out):
4
2 1
3 5
4 2
5 2OUTPUT DETAILS:
The facts "cow 3 before cow 1" and "cow 4 before cow 1" can be deduced from the 4 facts listed in the output. However, none of the output facts can be deduced from the others.
给你关于 \(N\) 个数的 \(L\) 对大小关系,其中关系 x y 表示 x>y。
如果有关系 x y 与关系 y z 那么显然关系 x z 是不必要的。
求出这 \(L\) 对关系中的最少必要关系。(即通过省下的这些关系可以推出被删去的关系)
写出其数量并按照以数字一为主关键字,以数字二为次关键字的顺序从小到大输出。
算法分析
类似传递闭包,但是这里要求你排除冗余的关系。
那么显然,如果我们可以确定一个顺序,保证后面的关系不会影响前面的关系。
那么只需要从前往后扫一遍,遇到多余的关系排除即可。(因为只有前面的关系可能影响后面的关系)
排除的方法之后再说。
确定方法的关系:
- 将每个关系当做有向边建图,易证这是个 DAG 图。
- 将此图拓扑排序,按照拓扑排序的顺序给各个节点从小到大赋值。
- 按照每个关系的数字一拓扑值从大到小为主关键字,数字二拓扑值从小到大为次关键字排序。
- 所得即上面所说的遍历顺序。
解释一下,我们给每个节点赋予一个 ”贡献值“,表示其对其它节点的影响力。
那么显然影响大的边要先考虑(这也符合上面的顺序)。
易得,拓扑值大的节点影响力也大,所以以其从大到小为主关键字。
但是,当从同一个点出发考虑关系时,就应当优先考虑拓扑值小的,理由如下:
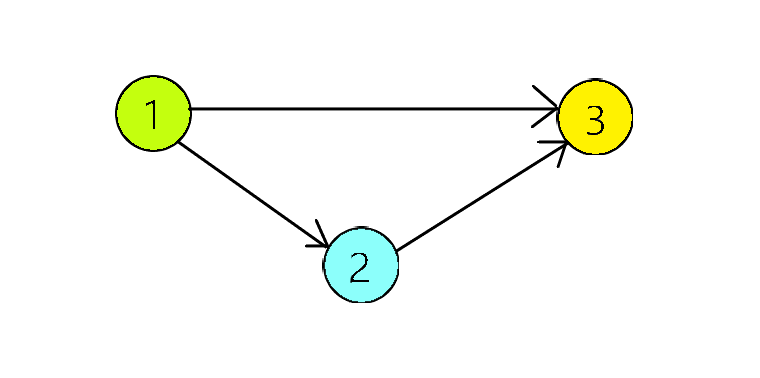
那么显然只有按照以从小到大为次关键字,才能将关系 1 3 排除。
然后就按照这个顺序往后排查即可,具体方法为状压 DP。
但是由于节点数量很多,所以要用到 C++ STL 的 bitset。
假设有关系 \(x\to y\),如果 \(bits(x,y)\) 这个关系为多余关系。
否则 \(bits(x)|=bits(y)\)。
代码实现
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<bitset>
#include<queue>
#define N 1510
#define M 10010
using namespace std;
int n,m,head[N],cnt=0;
int ru[N],Topo[N],tot=0;
struct Edge{
int nxt,to,frm;
}ed[M];
struct Ans{
int u,v;
}ans[M];
bitset<N>bits[N];
queue<int>q;
int read(){
int x=0,f=1;char c=getchar();
while(c<'0' || c>'9') f=(c=='-')?-1:1,c=getchar();
while(c>='0' && c<='9') x=x*10+c-48,c=getchar();
return x*f;
}
void add(int u,int v){
ed[++cnt].nxt=head[u];
ed[cnt].frm=u;
ed[cnt].to=v;
head[u]=cnt;
return;
}
void topo(){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(!ru[i]) q.push(i);
while(!q.empty()){
int u=q.front();q.pop();
Topo[u]=++tot;
for(int i=head[u];i;i=ed[i].nxt)
if(!--ru[ed[i].to]) q.push(ed[i].to);
}
return;
}
bool cmp(Edge a,Edge b){
if(a.frm!=b.frm)
return Topo[a.frm]>Topo[b.frm];
return Topo[a.to]<Topo[b.to];
}
bool cnp(Ans a,Ans b){
if(a.u!=b.u) return a.u<b.u;
return a.v<b.v;
}
int main(){
//freopen("order.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("order.out","w",stdout);
memset(ru,0,sizeof(ru));
n=read(),m=read();
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int u=read(),v=read();
add(u,v);++ru[v];
}
topo();//简简单单的拓扑排序。
sort(ed+1,ed+m+1,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
bits[i][i]=true;//预处理。
tot=0;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int u=ed[i].frm,v=ed[i].to;
if(bits[u][v]) continue;
bits[u]=bits[u]|bits[v];//DP。
ans[++tot]=(Ans){u,v};
}
sort(ans+1,ans+tot+1,cnp);
printf("%d\n",tot);
for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++)
printf("%d %d\n",ans[i].u,ans[i].v);
//fclose(stdin);fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
完结撒花。
Ordering Cows的更多相关文章
- DP百题练(二)
目录 DP百题练(二) 区间 DP NOI1995 石子合并 IOI1998 Polygon CH5302 金字塔 USACO06FEB Treats for the Cows G/S LG1043 ...
- [poj2182] Lost Cows (线段树)
线段树 Description N (2 <= N <= 8,000) cows have unique brands in the range 1..N. In a spectacula ...
- Lost Cows
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 9669 Accepted: 6228 Description N (2 ...
- Lost Cows(线段树 POJ2182)
Lost Cows Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 10354 Accepted: 6631 Descriptio ...
- POJ 2182 Lost Cows
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 10996 Accepted: 7059 Description N (2 ...
- HDU-2711 Lost Cows
Lost Cows Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Total ...
- Lost Cows(BIT poj2182)
Lost Cows Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 10609 Accepted: 6797 Descri ...
- POJ 2182 Lost Cows(牛排序,线段树)
Language: Default Lost Cows Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 9207 Acce ...
- poj 2182 Lost Cows(段树精英赛的冠军)
主题链接:http://poj.org/problem? id=2182 Lost Cows Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submi ...
随机推荐
- 再玩树莓派(二)Jexus&.NetCore
接上一篇,操作系统弄好之后,轮到开发运行环境的搭建. 先说说目标,也就是我到底想搞什么飞机.先说说小目标吧. 现有一个手机App客户端,以答题小游戏作为其内容(例如:口算题,24点,科学百科等) 树莓 ...
- Web开发初探之JavaScript 快速入门
本文改编和学习自 A JavaScript Primer For Meteor 和 MDN Web教程 前文 Web开发初探 概述 本文以介绍 JavaScript 为主,初学者掌握本文的内容后,将能 ...
- 04 ArcPython实战篇二
1.删除Default.gdb中的所有要素类.表.栅格 2.空间随机抽取若干数 3.地震目录自动空间化 参考:esrichina易智瑞中国公开课
- spring-boot-route(十一)数据库配置信息加密
Spring Boot最大的特点就是自动配置了,大大的减少了传统Spring框架的繁琐配置,通过几行简单的配置就可以完成其他组件的接入.比如你想要连接mysql数据库,只需要的配置文件里面加入mysq ...
- dockerfile-maven-plugin极简教程
目录 一.简介 二.概述 三.将spring-boot-app打包成docker镜像 创建示例应用 修改pom文件 增加Dockerfile文件 使用Maven打包应用 运行应用镜像 四.分析mvn ...
- 编程体系结构(08):Spring.Mvc.Boot框架
本文源码:GitHub·点这里 || GitEE·点这里 一.Spring框架 1.框架概述 Spring是一个开源框架,框架的主要优势之一就是其分层架构,分层架构允许使用者选择使用哪一个组件,同时为 ...
- JS关闭chorme页面
百度到的很多答案都失效了,这是收集一位博主的(https://www.jianshu.com/p/9dc2752194b8),目前可以使用. 代价是打开一个空白页面,能实现无提示关闭当前页面.不需要是 ...
- python面试题-django相关
1.中间件 中间件一般做认证或批量请求处理,django中的中间件,其实是一个类,在请求和结束后,django会根据自己的规则在合适的时机执行中间件中相应的方法, 如请求过来 执行process_re ...
- linux(centos8):用cut显示文本内容的指定列
一,cut命令的用途 从一个文本文件或者文本流中提取文本列 分别用: 字节.字符.字段 作为单位进行提取 说明:刘宏缔的架构森林是一个专注架构的博客,地址:https://www.cnblogs.co ...
- Linux系统及第三方应用官方文档
通过在线文档获取帮助 http://www.github.com https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/ http://httpd.apache.org htt ...
