Go Programming Language
【Go Programming Language】
1、go run %filename 可以直接编译并运行一个文件,期间不会产生临时文件。例如 main.go。
go run main.go
2、Package
Go code is organized into packages, which are similar to libraries or modules in other languages. A package consists of one or more .go source files in a single directory that define what the package does.
The Go standard library has over 100 packages for common tasks like input and output, sorting, and text manipulation.
Package main is speci al. It defines a standalone executable program, not a library. Within package main the func tion main is also special—it’s where execution of the program begins.
package main
import "fmt"
func main(){
fmt.Printf("hello, world\n")
}
A prog ram will not compile if there are missing imports or if there are unnecessary ones. This strict requirement prevents references to unused packages from accumulating as programs evolve.
3、Go does not require semicolons at the end s of statements or declarat ions, except where two or more app ear on the same line.
In effect, newlines following certain tokens are converted into semicolons, so where newlines following certain tokens are converted into semicolons.
token后面跟着换行符会被转换为 semicolon。
4、Go takes a strong stance on code formatting . The gofmt tool rewrites code into the standard format, and the go tool’s fmt subcommand applies gofmt to all the files in the specified package, or the ones in the current directory by default.
goimports, addition ally manages the insertion and removal of import declarations as needed. It is not part of the standard distribution but you can obtain it with this command:
$ go get golang.org/x/tools/cmd/goimports
5、os.Args
The os package provides functions and other values for dealing with the operating system in a platform-independent fashion.
os.Args 可以获取命令行参数。
os.Args is a slice of strings. a slice as a dynamically sized sequence s of array elements where individual elements can be accessed as s[i] and a contiguous subsequence as s[m:n]. The number of elements is given by len(s). As in most other programming languages, all indexing in Go uses half-open intervals that include the first index but exclude the last, because it simplifies logic. For example, the slice s[m:n], where 0 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ len(s), contains n-m elements.
If m or n is omitted, it defaults to 0 or len(s) respectively, so we can abbreviate the desired slice as os.Args[1:].
6、echo1 示例
package main import (
"fmt"
"os"
) func main(){
var s, sep string
for i:=; i<len(os.Args); i++{
s += sep+os.Args[i]
sep = ""
}
fmt.Println(s)
}
注意点:
1)一个 import 可以导入多个 package。
2)变量类型旋转在变量定义后。
3)for 语句没有 ()。
4)The := symbol is part of a short variable declaration, a statement that declares one or more variables and gives them appropriate types based on the initializer values;
:= 定义并且赋予初始值。
7、Go 中只有 i++,没有++i。
8、for循环语法。没有(),以及必须有{}。

可以没有 initialization、post,如下:

下面是无穷循环:

9、echo2示例
package main import (
"fmt"
"os"
) func main(){
s,sep:="",""
for _,arg:=range os.Args[:]{
s+=sep+arg
sep=""
}
fmt.Println(s)
}
1)range produces a pair of values: the index and the value of the element at that index.
2)blank identifier, whose name is _(an underscore).The blank identifier may be used whenever syntax requires a variable name but program logic does not..
3)several ways to declare a string variable:

4)上述代码中字符串累加非常的低效,可以使用 strings.Join()方法来优化。
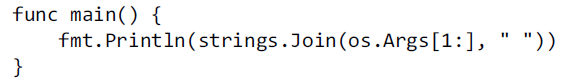
10、dup1示例
package main import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
) func main(){
counts := make(map[string]int)
input:=bufio.NewScanner(ois.Stdin)
for input.Scan(){
counts[input.Text()]++
} for line,n:=range counts{
if n> {
fmt.Printf("%d\t%s\n", n, line)
}
}
}
1)map[string]int,代表key是string类型,value是int类型。加上make() 用于创建一个此类型的map。
2)The order of map iteration is not specified, but in practice it is random. This design is intentional, since it prevents programs from relying on any particular ordering where none is guaranteed.
3)The Scan functino returns true if there is a line and false when there is no more input.
11、dup2 示例
package main import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
) func main(){
counts :=make(map[string]int)
files:=os.Args[:]
if len(files)=={
countLines(os.Stdin, counts)
}else{
for _,arg:=range files{
f,err:=os.Open(arg)
if err!=nil{
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "dup2:%v\n", err)
continue
}
countLines(f, counts)
f.Close()
}
}
for line, n:=range counts{
if n>{
fmt.Printf("%d\t%s\n", n, line)
}
}
} func countLines(f *of.File, counts map[string]int){
input:=bufio.NewScanner(f)
for input.Scan(){
counts[input.Text()]++
}
}
1)函数调用可以放置函数定义前。本例中 countLines()函数,比C++强。
2)fmt.Fprintf()函数类似于C++中的fprint。
12、lissajous 示例
package main import(
"image"
"image/color"
"image/gif"
"io"
"math"
"math/rand"
"os"
) var palette = []color.Color{color.White, color.Black} const (
whiteIndex =
blackIndex =
) func main(){
const(
cycles =
res = 0.001
size =
nframes =
delay =
) freq:=rand.Float64()*3.0
anim:=gif.GIF{LoopCount:nframes}
phase:=0.0
for i:=;i<nframes;i++{
rect:=image.Rect(,,*size+,*size+)
img:=image.NewPaletted(rect,palette)
for t:=;t<cycles**math.Pi;t+=res{
x:=math.Sin(t)
y:=math.Sin(t*freq+phase)
img.SetColorIndex(size+int(x*size+0.5),size+int(y*size+0.5),
blackIndex)
}
phase+=0.1
anim.Delay = append(anim.Delay, delay)
anim.Image = append(anim.Image, img);
}
}
1)import "image/gif",通过 gif 就能直接引用。
2)const (),the valu of const must be a number, string or boolean.
13、fetch示例
package main import(
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"os"
) func main(){
for _, url:=range os.Args[:]{
resp, err := http.Get(url)
if err!=nil{
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "fetch:%v\n", err)
os.Exit()
} b,err:=ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
resp.Body.Close()
if err!=nil{
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "fetch:reading %s:%v\n", url, err)
os.Exit()
}
fmt.Printf("%s", b)
}
}
1)net/http,其中的 http.Get() 方法可以用于发起一个Http请求,并返回内容。
14、fetch all 示例
package main import (
"fmt"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"os"
"time"
) func main(){
start :=time.Now()
ch:=make(chan string)
for _,url :=range os.Args[:]{
go fetch(url, ch) // start a goroutine
} for range os.Args[:]{
fmt.Println(<-ch) // receive from channel ch
} fmt.Printf("%.2fs elapsed\n", time.Since(start).Seconds())
} func fetch(url string, ch chan<- string){
start:=time.Now()
resp, err:=http.Get(url)
if err!=nil{
ch<-fmt.Sprint(err) // send to channel ch
return
} nbytes, err:=io.Copy(ioutil.Discard, resp.Body)
resp.Body.Close()
if err!=nil{
ch<-fmt.Sprintf("while reading %s:%v", url, err)
return
}
secs:=time.Since(start).Seconds()
ch<-fmt.Sprintf("%.2fs %7d %s", secs, nbytes, url)
}
1)A goroutine is a concurrent function execution. A channel is a communication mechanism that allows one goroutine to pass values of a specified typ e to another goroutine. The function main runs in a goroutine and the go st atement cre ates addition al goroutines.
2)通过 ch:=make(chan string) 创建一个channel,通过 ch <- str 向 ch中写入内容,通过 <-ch 从ch中读取内容
3)通过 go func(),创建一个新 goroutine
15、server1示例,使用内置的http package,创建一个 http服务器。
package main import(
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
) func main(){
http.HandleFunc("/", handle)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndserve("localhost:8000", nil))
} func handler(w httpResponseWritter, r *http.Request){
fmt.Fprintf(w, "URL.Path = %q\n", r.URL.Path)
}
1)http.ListenAndServer(port) 开启Http服务,http.HandleFunc(path, func)设置路由。
2)http.Request 代表一个请求。
16、server2 示例,通过请求 /count 路径,获得 / 路径的调用次数。
package main import(
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"sync"
) var mu sync.Mutex
var count int func main(){
http.HandleFunc("/", handler)
http.HandleFunc("/count", counter)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8000", nil))
} func handler(w http.ResponseWritter, r *http.Request){
mu.Lock()
count++
mu.Unlock()
fmt.Fprintf(w, "URL.Path = %q\n", r.URL.Path)
} func counter(w http.ResponseWritter, r *http.Request){
mu.Lock()
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Count %d\n", count)
mu.Unlock()
}
1)import "sync", var mu sync.Mutex 用于定义一个互斥锁。
2)A handler pattern that ends with a slash matches any URL that has the pattern as a prefix.
17、server3 示例,用于解析 http 请求 Header & FormData。
func handler(w http.ResponseWritter, r *http.Request){
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s %s %s\n", r.Method, r.URL, r.Proto)
for k,v:=range r.Header{
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Header[%q] = %q\n", k,v)
}
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Host = %q\n", r.Host)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "RemoteAddr=%q\n", r.RemoteAddr)
if err:=r.ParseForm(); err!=nil{
log.Printf(err)
}
for k,v:=range r.Form{
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Form[%q] = %q\n", k, v)
}
}
1)使用 http.Request.Form 前需要先调用和 http.Request.ParseForm。
2)在前例中,range 用于获取 [index,value],而本例中 range 用于获取 [key,value]。
3)if 的条件中可以使用多条语句。下述写法,将 err 的 scope 限制在了 if 语句内。
if err:=r.ParseForm(); err!=nil{
log.Printf(err)
}
4)
18、Named Types

19、Point ers are explicitly visible. The & operator yields the address of a variable, and the operator retrieves the variable that the * pointer refers to, but there is no point er arithmetic.
20、If an entity is declare d within a function, it is local to that function. If declared outside of a function, however, it is visible in all files of the package to which it belongs.
函数外定义的变量,事个package中所有的file都可以访问。
package-level entity is visible not only throughout the source file that contains its declaration, but throughout all the files of the package.
21、The case of the first letter of a name determines its visibility across package boundaries.
If the name begins with an upper-case letter, it is exported, which means that it is visible and accessible outside of its own package and may be refer red to by other par ts of the program, as wit h Printf in the fmt package.
如果变量以大写字母开头,则它可以被包外代码引用。
Package names themselves are always in lower case. 包名永远是小写。
22、variables. Either the type or the = expression part may be omitted, but not both.

Omitt ing the typ e allows decl arat ion of multiple var iables of different types:
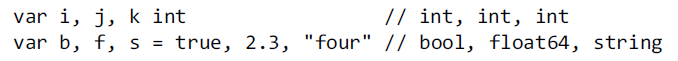
23、in Go there is no such thing as an uninitialize d variable.
24、一个函数可以返回多个返回值。

25、short variable declaration.
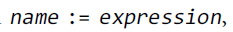
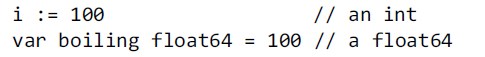
multiple variables may be declared and initialized in the same short variable declaration。
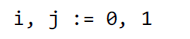
短变量声明的左边必须包含至少一个新变量,下左图是ok的,而下右图则会编译错误。


:= 只对同一语法块中的变量起 assignment 作用,语法块以外的同名变量会被 ignored。
26、Pointer
Not every value has an address, but every variable does.

It is perfectly safe for a function to return the address of a local variable !!! Each call of f returns a distinct value.
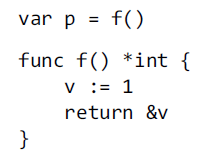
27、flag package 示例
package main import(
"flag"
"fmt"
"strings"
) var n = flag.Bool("n", false, "omit trailing newline")
var sep = flag.String("s", "", "separator") func main(){
flag.Parse()
fmt.Print(strings.Join(flag.Args(), *sep))
if !*n {
fmt.Println()
}
}
1)flag.Parse() 必须最先调用,默认带有 -h -help的解释。
28、new Function()
The expression new(T) creates an unnamed variable of type T, initializes it to the zero value of T, and returns its address, which is a value of type *T.

A variable created with new is no different from an ordinary local variable whose address is taken, Thus new is only a syntactic convenience, not a fundamental notion.
The two newInt functions below have identical behaviors.

29、Lifetime of Variables
The lifetime of a package-level variable is the entire execution of the program.
By contrast, local variables have dynamic lifetimes: a new instance is create d each time the declaration statement is executed, and the variable lives on until it becomes unreachable, at which point its storage may be rec ycled.
A compiler may choose to allocate local variables on the heap or on the stack but, perhaps surprisingly, this choice is not determined by whether var or new was used to declare the variable.
变量分配在堆上还是栈上,由编译器决定, var、new无法对此产生影响。

30、Tuple Assignment
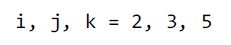
31、Type Declarations

可以为自定义类型添加Method。
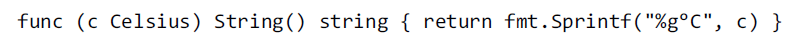
Many types declare a String method of this form because it controls how values of the type appear when printed as a string by the fmt package.
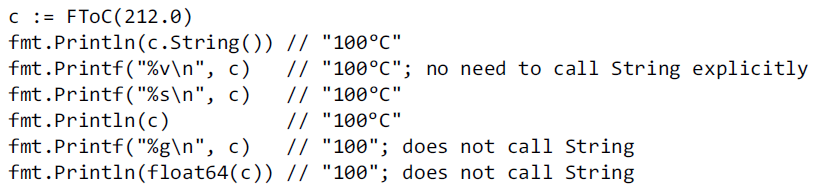
32、Packages and Files
Extensive doc comments are often placed in a file of their own, conventionally called go.doc.
use the golang.org/x/tools/cmd/goimports tool, which automatically inserts and removes packages from the import declaration as necessary ; most editors can be configured to run goimports each time you save a file. Like the gofmt to ol, it also pretty-prints Go source files in the canonical format.
33、Package Initialization
Any file may contain any number of functions whose declaration is just:

init functions are automatically executed when the program starts, in the order in which they are declared.
一个文件可以包含多个 init() 函数,在执行main()前,会按照声明的顺序依次调用。
34、不同的 lexical block 可以定义同名变量。 Inner lexical 优先级高于 Outer Lexical。

35、if scope

The second if statement is nested within the first, so variables declared within the first statement's initializer are visible within the second.
if 中的变量作用范围限定在 if语句中,所以以下代码中对 f 的引用会引起编译错误。

为了解决上述问题,可以像下面这样写代码(但不推荐):

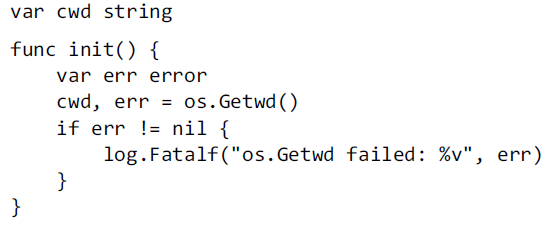
36、short variable declaration 要点
下述代码中, 函数内会新创建一个 local cwd,导致 global cwd 未被初始化。

一种解决方法是,使用 assignment,而不是使用 short variable declaration:
37、
38、
39、
40、
Go Programming Language的更多相关文章
- iOS Swift-元组tuples(The Swift Programming Language)
iOS Swift-元组tuples(The Swift Programming Language) 什么是元组? 元组(tuples)是把多个值组合成一个复合值,元组内的值可以使任意类型,并不要求是 ...
- iOS Swift-控制流(The Swift Programming Language)
iOS Swift-控制流(The Swift Programming Language) for-in 在Swift中for循环我们可以省略传统oc笨拙的条件和循环变量的括号,但是语句体的大括号使我 ...
- iOS Swift-简单值(The Swift Programming Language)
iOS Swift-简单值(The Swift Programming Language) 常量的声明:let 在不指定类型的情况下声明的类型和所初始化的类型相同. //没有指定类型,但是初始化的值为 ...
- Java Programming Language Enhancements
引用:Java Programming Language Enhancements Java Programming Language Enhancements Enhancements in Jav ...
- The Swift Programming Language 英文原版官方文档下载
The Swift Programming Language 英文原版官方文档下载 今天Apple公司发布了新的编程语言Swift(雨燕)将逐步代替Objective-C语言,大家肯定想学习这个语言, ...
- The Swift Programming Language 中文翻译版(个人翻新随时跟新)
The Swift Programming Language --lkvt 本人在2014年6月3日(北京时间)凌晨起来通过网络观看2014年WWDC 苹果公司的发布会有iOS8以及OS X 10.1 ...
- [iOS翻译]《The Swift Programming Language》系列:Welcome to Swift-01
注:CocoaChina翻译小组已着手此书及相关资料的翻译,楼主也加入了,多人协作后的完整译本将很快让大家看到. 翻译群:291864979,想加入的同学请进此群哦.(本系列不再更新,但协作翻译的进度 ...
- Questions that are independent of programming language. These questions are typically more abstract than other categories.
Questions that are independent of programming language. These questions are typically more abstract ...
- What is the Best Programming Language to Learn in 2014?
It’s been a year since I revealed the best languages to learn in 2013. Once again, I’ve examined the ...
- C: Answers to “The C programming language, Edition 2”
<The C programming language> Edition 2的习题答案地址: http://users.powernet.co.uk/eton/kandr2/index.h ...
随机推荐
- ESP8266 LUA脚本语言开发: 准备工作-LUA开发说明
前言 开发Lua需要使用这个软件 注:该软件需要按照JDK 即 JAVA虚拟机,如果没有安装过JDK,请先看JDK安装教程安装JDK USB线连接开发板接入电脑 选择自己的串口号 波特率115200 ...
- read articles list
done 如何通俗易懂地解释卷积: https://www.zhihu.com/question/22298352/answer/637156871 如何通俗易懂地理解卷积神经网路: http://w ...
- [LeetCode] 39. Combination Sum 组合之和
Given a set of candidate numbers (candidates) (without duplicates) and a target number (target), fin ...
- 推荐一款年轻人交友软件get
推荐一款年轻人交友软件get 1 介绍 Get是一款认识新朋友的年轻人交友软件.接唱,发现有趣的声音,找到你的音缘.限时聊天,加入给你分配一个3分钟的对象,你们能不能碰撞出一点火花呢?推荐好友,扩列处 ...
- 第24课 std::thread线程类及传参问题
一. std::thread类 (一)thread类摘要及分析 class thread { // class for observing and managing threads public: c ...
- 好用的低延迟vps
ZeptoVM是一个俄罗斯的云提供商, 由于提供了黑龙江北边的机房, 所以延迟比较低 注意一定要选Khabarovsk节点, 这个节点延迟很低, 我在上海延迟大约有70ms 缺点就是比较贵, 按照年付 ...
- PowerShell的异常处理办法
$ErrorActionPreference = 'Stop' Try{ # C:\xxx 不存在 Copy-Item C:\xxx -ErrorAction Stop } Catch ...
- mybatis解决字段名和实体属性不相同
两种方法: 1.在xml文件里面使用别名 2.使用resultMap标签
- MongoDB学习笔记(六)
初识 MongoDB 中的索引 索引就像图书的目录一样,可以让我们快速定位到需要的内容,关系型数据库中有索引,NoSQL 中当然也有,本文我们就先来简单介绍下 MongoDB 中的索引. 索引创建 默 ...
- 图解微信小程序---实现行的删除和增加操作
图解微信小程序之实现行的删除和增加操作 代码笔记部分 第一步:在项目的app.json中创建一个新的页面(页面名称英文,可自定义) 第二步:在创建的新页面中编写页面(注意bindtap属性值,因为是我 ...
