Faster-RCNN用于场景文字检测训练测试过程记录(转)
[训练测试过程记录]Faster-RCNN用于场景文字检测
原创
2017年11月06日 20:09:00
<ul class="article_tags clearfix csdn-tracking-statistics tracking-click" data-mod="popu_377" style="display: none;">
<li class="tit">标签:</li>
<!-- [endarticletags]-->
</ul>
<ul class="right_bar">
<li><button class="btn-noborder"><i class="icon iconfont icon-read"></i><span class="txt">609</span></button></li>
<li class="edit" style="display: none;">
<a class="btn-noborder" href="https://mp.csdn.net/postedit/78457624">
<i class="icon iconfont icon-bianji"></i><span class="txt">编辑</span>
</a>
</li>
<li class="del" style="display: none;">
<a class="btn-noborder" onclick="javascript:deleteArticle(fileName);return false;">
<i class="icon iconfont icon-shanchu"></i><span class="txt">删除</span>
</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div id="article_content" class="article_content csdn-tracking-statistics tracking-click" data-mod="popu_519" data-dsm="post" style="overflow: hidden;">
<div class="htmledit_views">
写在前面:github上面的Text-Detection-with-FRCN项目是基于py-faster-rcnn项目在场景文字识别领域的扩展。
和py-faster-rcnn相比,该项目的主要改动为:将检测类别换成了背景和文字,并且更改了数据集。
对于初学者而言,要实现一个自己的baseline,第一步可以尝试训练别人已经实现了的网络,看看整个的运行流程是怎么样的。那么,接下来,我就记录一下我自己在训练和测试过程中遇到的问题。大家在参考的时候可以参照Text-Detection-with-FRCN项目中的README.md文件。
一.编译部分
在编译caffe的时候,可能会遇到一些问题,这里,我来介绍一下我遇到的问题。
1.Makefile.config.example文件修改问题
切换到caffe目录:cd $Text-Detection-with-FRCN/py-faster-rcnn/caffe-fast-rcnn
修改Makefile.config.example文件:
(1)去掉USE_CUDNN := 1的注释
# cuDNN acceleration switch (uncomment to build with cuDNN).
USE_CUDNN := 1
(2)去掉WITH_PYTHON_LAYER := 1的注释
# Uncomment to support layers written in Python (will link against Python libs)
WITH_PYTHON_LAYER := 1
2.CUDNN版本问题
在上一步中,修改了Makefile.config.example问题,再执行如下指令:
cp Makefile.config.example Makefile.config
make -16 && make pycaffe
在make的过程中,可能出现由于CUDNN版本问题导致的错误:
- In file included from ./include/caffe/util/device_alternate.hpp:40:0,
- from ./include/caffe/common.hpp:19,
- from src/caffe/common.cpp:7:
- ./include/caffe/util/cudnn.hpp: In function ‘void caffe::cudnn::createPoolingDesc(cudnnPoolingStruct**, caffe::PoolingParameter_PoolMethod, cudnnPoolingMode_t*, int, int, int, int, int, int)’:
- ./include/caffe/util/cudnn.hpp:127:41: error: too few arguments to function ‘cudnnStatus_t cudnnSetPooling2dDescriptor(cudnnPoolingDescriptor_t, cudnnPoolingMode_t, cudnnNanPropagation_t, int, int, int, int, int, int)’
- pad_h, pad_w, stride_h, stride_w));
- ^
- ./include/caffe/util/cudnn.hpp:15:28: note: in definition of macro ‘CUDNN_CHECK’
- cudnnStatus_t status = condition; \
- ^
- In file included from ./include/caffe/util/cudnn.hpp:5:0,
- from ./include/caffe/util/device_alternate.hpp:40,
- from ./include/caffe/common.hpp:19,
- from src/caffe/common.cpp:7:
- /usr/local/cuda-7.5//include/cudnn.h:803:27: note: declared here
- cudnnStatus_t CUDNNWINAPI cudnnSetPooling2dDescriptor(
- ^
- make: *** [.build_release/src/caffe/common.o] Error 1
In file included from ./include/caffe/util/device_alternate.hpp:40:0,
from ./include/caffe/common.hpp:19,
from src/caffe/common.cpp:7:
./include/caffe/util/cudnn.hpp: In function ‘void caffe::cudnn::createPoolingDesc(cudnnPoolingStruct**, caffe::PoolingParameter_PoolMethod, cudnnPoolingMode_t*, int, int, int, int, int, int)’:
./include/caffe/util/cudnn.hpp:127:41: error: too few arguments to function ‘cudnnStatus_t cudnnSetPooling2dDescriptor(cudnnPoolingDescriptor_t, cudnnPoolingMode_t, cudnnNanPropagation_t, int, int, int, int, int, int)’
pad_h, pad_w, stride_h, stride_w));
^
./include/caffe/util/cudnn.hpp:15:28: note: in definition of macro ‘CUDNN_CHECK’
cudnnStatus_t status = condition; \
^
In file included from ./include/caffe/util/cudnn.hpp:5:0,
from ./include/caffe/util/device_alternate.hpp:40,
from ./include/caffe/common.hpp:19,
from src/caffe/common.cpp:7:
/usr/local/cuda-7.5//include/cudnn.h:803:27: note: declared here
cudnnStatus_t CUDNNWINAPI cudnnSetPooling2dDescriptor(
^
make: *** [.build_release/src/caffe/common.o] Error 1
这是由于当前版本的caffe的cudnn实现与系统所安装的cudnn的版本不一致引起的。
解决办法:
下载最新版的caffe
1)将./include/caffe/util/cudnn.hpp换成最新版的caffe里的cudnn.hpp;
2)将./include/caffe/layers里面,所有以cudnn开头的文件,都换成最新版的caffe里面相应的同名文件;
3)将./src/caffe/layers里面,所有以cudnn开头的文件,都换成最新版的caffe里面相应的同名文件。
tips:其他部分的以cudnn开头的文件,就不要动了。
二.准备数据集
在Text-Detection-with-FRCN项目的readme中,给出了coco-text数据集的制作方式。下面,就来具体说明。
1.下载数据集
切换目录:cd $Text-Detection-with-FRCN/datasets/script
原指令为:./fetch_dataset.sh coco-text,可能会出现-bash: ./fetch_dataset.sh: Permission denied的错误。
可先运行:chmod +x ./fetch_dataset.sh
再运行: ./fetch_dataset.sh coco-text
下载到的数据集包括:train2014.zip文件和COCO_Text.json,下面,需要将数据进行格式化,与原py-faster-rcnn中的pascal_voc的数据格式进行统一。
2.数据格式化
(1)pascal_voc数据集的格式为:
--Annotations
--*.xml
--JPEGImages
--*.jpg
--ImageSets
--Main
......
图像文件夹(JPEGImages):例如2008_000200.jpg
标记文件夹(Annotations):例如2008_000200.xml:
<annotation>
<folder>VOC2012</folder>
<filename>2008_000200.jpg</filename>
<source>
<database>TheVOC2008
Database</database>
<annotation>PASCALVOC2008</annotation>
<image>flickr</image>
</source>
<size>
<width>500</width>
<height>375</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented>
<object>
<name>person</name>
<bndbox>
<xmin>119</xmin>
<ymin>76</ymin>
<xmax>184</xmax>
<ymax>311</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
......
区分训练样本与测试样本(ImageSets):
以test.txt为例:
2008_000001
2008_000004
2008_000005
2008_000006
(2)coco-text的格式为:
图片集:Train2014.zip:COCO_train2014_000000378466.jpg
文件标记:
COCO_Text.json
{"imgs":
{"378466":{"width": 612, "file_name":"COCO_train2014_000000378466.jpg",
"set":"train", "id": 378466, "height": 612},
"370250":{"width": 427, "file_name":"COCO_train2014_000000370250.jpg",
"set": "test","id": 370250, "height": 640},
"36606":{"width": 640, "file_name":"COCO_train2014_000000036606.jpg",
"set": "val","id": 36606, "height": 480}
(3)将coco-text的数据集格式转换为pascal_voc的格式
切换目录:cd $Text-Detection-with-FRCN/datasets/script
运行指令:./format_annotation.py --dataset coco-text
在format_annotation.py中:
1.format_coco_text函数,是利用coco-text.json中的信息,生成类似于pascal_voc的ImageSets文件夹中的信息。
2.os.system('./ann2voc2007.sh ' + args.dataset),是调用相同文件夹下面的ann2voc2007.m文件,来生成类似于pascal_voc的Annotations文件夹中的信息。
如果不想花时间安装matlib,可以将ann2voc2007.m改写为python文件,效果是一样的。
改写后的代码如下:(具体原理可参考:利用python生成xml文件)
- #coding:utf-8
- from PIL import Image
- from xml.dom.minidom import Document
- import os
- def main():
- imgpath = 'JPEGImages/'
- txtpath = 'images.annotations'
- xmlpath_new = 'Annotations/'
- coco = {}
- # 得到图像的标注信息
- file_object = open(txtpath,'rU')
- try:
- for line in file_object:
- line = line.rstrip('\n')
- strs = line.split(' ')
- print strs[0]
- foldername = 'VOC2007'
- # 用xml替换jpg,得到同名文件
- xmlname = strs[0].replace('.jpg','.xml')
- info = Image.open(imgpath + strs[0])
- # read image size
- (width,height) = info.size
- strs[2] = max(int(strs[2]), 1)
- strs[3] = max(int(strs[3]), 1)
- strs[4] = min(int(strs[4]), width);
- strs[5] = min(int(strs[5]), height);
- # 过滤异常
- if strs[2] >= strs[4] or strs[3] >= strs[5] or strs[2] <=0 or strs[3] <= 0 or strs[4] > width or strs[5] > height:
- continue
- if os.path.exists(imgpath + strs[0]):
- if xmlname in coco:
- Createnode = coco[xmlname]
- object_node = Createnode.createElement('object')
- Root = Createnode.getElementsByTagName('annotation')[0]
- Root.appendChild(object_node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('name')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(strs[1]))
- object_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('pose')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('Unspecified'))
- object_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('truncated')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('0'))
- object_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('difficult')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('0'))
- object_node.appendChild(node)
- bndbox_node=Createnode.createElement('bndbox')
- object_node.appendChild(bndbox_node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('xmin')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[2])))
- bndbox_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('ymin')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[3])))
- bndbox_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('xmax')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[4])))
- bndbox_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('ymax')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[5])))
- bndbox_node.appendChild(node)
- else:
- Createnode=Document() #创建DOM文档对象
- Root=Createnode.createElement('annotation') #创建根元素
- Createnode.appendChild(Root)
- # folder
- folder=Createnode.createElement('folder')
- folder.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(foldername))
- Root.appendChild(folder)
- # filename
- filename = Createnode.createElement('filename')
- filename.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(strs[0]))
- Root.appendChild(filename)
- # source
- source_node = Createnode.createElement('source')
- Root.appendChild(source_node)
- node = Createnode.createElement('database')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('MS COCO-Text'))
- source_node.appendChild(node)
- node = Createnode.createElement('annotation')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('MS COCO-Text 2014'))
- source_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('image')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('NULL'))
- source_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('flickrid');
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('NULL'));
- source_node.appendChild(node);
- # owner
- owner_node=Createnode.createElement('owner')
- Root.appendChild(owner_node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('flickrid')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('NULL'))
- owner_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('name')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('ligen'))
- owner_node.appendChild(node)
- # size
- size_node=Createnode.createElement('size')
- Root.appendChild(size_node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('width')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(width)))
- size_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('height');
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(height)))
- size_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('depth')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('3'))
- size_node.appendChild(node)
- # segmented
- node=Createnode.createElement('segmented')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('0'))
- Root.appendChild(node)
- # object
- object_node=Createnode.createElement('object')
- Root.appendChild(object_node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('name')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(strs[1]))
- object_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('pose')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('Unspecified'))
- object_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('truncated')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('0'))
- object_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('difficult')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('0'))
- object_node.appendChild(node)
- bndbox_node=Createnode.createElement('bndbox')
- object_node.appendChild(bndbox_node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('xmin')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[2])))
- bndbox_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('ymin')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[3])))
- bndbox_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('xmax')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[4])))
- bndbox_node.appendChild(node)
- node=Createnode.createElement('ymax')
- node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[5])))
- bndbox_node.appendChild(node)
- coco[xmlname] = Createnode
- finally:
- file_object.close()
- print 'begin load xml...'
- for key in coco:
- print key
- f = open(xmlpath_new + key,'w')
- f.write(coco[key].toprettyxml(indent = '\t'))
- f.close()
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- main()
#coding:utf-8
from PIL import Image
from xml.dom.minidom import Document
import os def main():
imgpath = 'JPEGImages/'
txtpath = 'images.annotations'
xmlpath_new = 'Annotations/'
coco = {}# 得到图像的标注信息
file_object = open(txtpath,'rU')
try:
for line in file_object:
line = line.rstrip('\n')
strs = line.split(' ')
print strs[0]
foldername = 'VOC2007' # 用xml替换jpg,得到同名文件
xmlname = strs[0].replace('.jpg','.xml')
info = Image.open(imgpath + strs[0])
# read image size
(width,height) = info.size
strs[2] = max(int(strs[2]), 1)
strs[3] = max(int(strs[3]), 1)
strs[4] = min(int(strs[4]), width);
strs[5] = min(int(strs[5]), height); # 过滤异常
if strs[2] >= strs[4] or strs[3] >= strs[5] or strs[2] <=0 or strs[3] <= 0 or strs[4] > width or strs[5] > height:
continue if os.path.exists(imgpath + strs[0]):
if xmlname in coco:
Createnode = coco[xmlname]
object_node = Createnode.createElement('object') Root = Createnode.getElementsByTagName('annotation')[0]
Root.appendChild(object_node) node=Createnode.createElement('name')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(strs[1]))
object_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('pose')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('Unspecified'))
object_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('truncated')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('0'))
object_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('difficult')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('0'))
object_node.appendChild(node) bndbox_node=Createnode.createElement('bndbox')
object_node.appendChild(bndbox_node) node=Createnode.createElement('xmin')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[2])))
bndbox_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('ymin')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[3])))
bndbox_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('xmax')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[4])))
bndbox_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('ymax')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[5])))
bndbox_node.appendChild(node)
else:
Createnode=Document() #创建DOM文档对象 Root=Createnode.createElement('annotation') #创建根元素
Createnode.appendChild(Root) # folder
folder=Createnode.createElement('folder')
folder.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(foldername))
Root.appendChild(folder) # filename
filename = Createnode.createElement('filename')
filename.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(strs[0]))
Root.appendChild(filename) # source
source_node = Createnode.createElement('source')
Root.appendChild(source_node) node = Createnode.createElement('database')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('MS COCO-Text'))
source_node.appendChild(node) node = Createnode.createElement('annotation')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('MS COCO-Text 2014'))
source_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('image')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('NULL'))
source_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('flickrid');
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('NULL'));
source_node.appendChild(node); # owner
owner_node=Createnode.createElement('owner')
Root.appendChild(owner_node) node=Createnode.createElement('flickrid')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('NULL'))
owner_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('name')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('ligen'))
owner_node.appendChild(node) # size
size_node=Createnode.createElement('size')
Root.appendChild(size_node) node=Createnode.createElement('width')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(width)))
size_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('height');
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(height)))
size_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('depth')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('3'))
size_node.appendChild(node) # segmented
node=Createnode.createElement('segmented')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('0'))
Root.appendChild(node) # object
object_node=Createnode.createElement('object')
Root.appendChild(object_node) node=Createnode.createElement('name')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(strs[1]))
object_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('pose')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('Unspecified'))
object_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('truncated')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('0'))
object_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('difficult')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode('0'))
object_node.appendChild(node) bndbox_node=Createnode.createElement('bndbox')
object_node.appendChild(bndbox_node) node=Createnode.createElement('xmin')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[2])))
bndbox_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('ymin')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[3])))
bndbox_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('xmax')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[4])))
bndbox_node.appendChild(node) node=Createnode.createElement('ymax')
node.appendChild(Createnode.createTextNode(str(strs[5])))
bndbox_node.appendChild(node) coco[xmlname] = Createnode finally:
file_object.close()
print 'begin load xml...'
for key in coco:
print key
f = open(xmlpath_new + key,'w')
f.write(coco[key].toprettyxml(indent = '\t'))
f.close()
if name == "main":
main()
最后,再运行rm_headline.sh。就得到我们所需要的数据集。
我得到的文件目录如下:
在Annotations的目录下,
在JPEGImages的目录下,
在ImageSets的目录下,
以train.txt为例,包含的内容为:
COCO_train2014_000000351622
COCO_train2014_000000058397
COCO_train2014_000000282380
COCO_train2014_000000223830
......
均为文件名
3.创建软链接
软链接就是:ln -s 源文件 目标文件
在代码中给出的数据集的目录为:train_data
因此,需要将上面得到的coco-text的目录链接到train_data上。
在github的readme中,给出的软链接操作为:
# link your data folder to train_data
cd $Text-Detection-with-FRCN/datasets/
ln -s train_data coco-text # $YOUR_DATA
但是在我实际操作的时候,是需要:
ln -s coco-text train_data 的。
三.下载预训练模型
首先,下载在imagenet上面预先训练好的模型。
# finetune on this model, you can also use one model you train before
cd $Text-Detection-with-FRCN/py-faster-rcnn
./data/scripts/fetch_imagenet_models.sh
# download it takes long!
可能由于这个项目clone “py-faster-rcnn” 的时间比较早,这里面/data/scripts文件夹下面,fetch_imagenet_models.sh中的下载url已经不能用了。该文件夹下面的其他.sh文件中的url应该也都失效了。
新的py-faster-rcnn中已经对此做了更正。fetch_imagenet_models.sh中的url可改为:
- ......
- 6 FILE=imagenet_models.tgz
- 7 URL=https://dl.dropbox.com/s/gstw7122padlf0l/imagenet_models.tgz?dl=0
- 8 CHECKSUM=ed34ca912d6782edfb673a8c3a0bda6d
- .....
......
6 FILE=imagenet_models.tgz
7 URL=https://dl.dropbox.com/s/gstw7122padlf0l/imagenet_models.tgz?dl=0
8 CHECKSUM=ed34ca912d6782edfb673a8c3a0bda6d
.....
具体更改位置为第8行。
注意:下载需要翻墙。
三.开始训练
切换目录:
cd $Text-Detection-with-FRCN/py-faster-rcnn/
运行指令:
./experiments/scripts/faster_rcnn_end2end.sh 0 VGG16 pascal_voc
需要注意的是:在运行指令的时候,需要切换到指定的目录。
运行的时候,可能会保错:
1)TypeError: 'numpy.float64' object cannot be interpreted as an index
2)TypeError: slice indices must be integers or None or have an index method
这两个问题的出现,都是由于Numpy的版本问题。在numpy 1.12.0中,不支持float index。类似于x[1.0, 3.0],会被看作无效。
解决这个问题,有如下可能的解决办法:
1.对numpy进行降级
sudo pip install -U
numpy==1.11.0
但是这种做法,可能会引入新的错误:
ImportError: numpy.core.multiarray failed to import
解决这个问题是要升级numpy ,于是又升回去:pip install -U numpy
所以,只能逐个将float类型转换为int类型
2.目前发现的几处需要进行修改的地方:
1.添加astype(np.int)
lib/roi_data_layer/minibatch.py line 26:将fg_rois_per_image = np.round(cfg.TRAIN.FG_FRACTION * rois_per_image)
改为:fg_rois_per_image = np.round(cfg.TRAIN.FG_FRACTION * rois_per_image).astype(np.int)
同理,其他需要在末尾添加.astype(np.int) 的地方:
lib/datasets/ds_utils.py line 12 : hashes = np.round(boxes * scale).dot(v)
lib/fast_rcnn/test.py line 129 : hashes = np.round(blobs['rois'] * cfg.DEDUP_BOXES).dot(v)
lib/rpn/proposal_target_layer.py line 60 : fg_rois_per_image = np.round(cfg.TRAIN.FG_FRACTION * rois_per_image)
2.强制转化为int类型
lib/roi_data_layer/minibatch.py line173:将cls = clss[ind] 改为:cls = int(clss[ind])
lib/rpn/proposal_target_layer.py line 124:将cls = clss[ind] 改为:cls = int(clss[ind])
四.训练模型
当解决了上面所有的问题,我们就可以开始训练了。
具体训练过程:
1.创建输入层
layer_factory.hpp:77 Creatinglayer input-data
net.cpp:106 CreatingLayer input-data
net.cpp:411 input-data-> data
net.cpp:411 input-data-> im_info
net.cpp:411 input-data-> gt_boxes
net.cpp:150 Settingup input-data
net.cpp:157 Topshape: 1 3 600 1000 (1800000)
net.cpp:157 Topshape: 1 3 (3)
net.cpp:157 Topshape: 1 4 (4)
net.cpp:165 Memoryrequired for data: 7200028
............
2.创建卷积层
layer_factory.hpp:77 Creatinglayer conv1_1
net.cpp:106 CreatingLayer conv1_1
net.cpp:454 conv1_1<- data_input-data_0_split_0
net.cpp:411 conv1_1-> conv1_1
net.cpp:150 Settingup conv1_1
net.cpp:157 Topshape: 1 64 600 1000 (38400000)
net.cpp:165 Memoryrequired for data: 175200084
............
3.创建激活层
layer_factory.hpp:77 Creatinglayer relu1_1
net.cpp:106 CreatingLayer relu1_1
net.cpp:454 relu1_1<- conv1_1
net.cpp:397 relu1_1-> conv1_1 (in-place)
net.cpp:150 Settingup relu1_1
net.cpp:157 Topshape: 1 64 600 1000 (38400000)
net.cpp:165 Memoryrequired for data: 328800084
............
判断是否需要反向计算(back forward)
部分需要反向计算:
net.cpp:226 loss_bboxneeds backward computation.
loss_clsneeds backward computation.
bbox_predneeds backward computation.
cls_scoreneeds backward computation.
fc7_drop7_0_splitneeds backward computation.
............
部分不需要反向计算:
net.cpp:228pool2does not need backward computation.
relu2_2does not need backward computation.
conv2_2does not need backward computation.
relu2_1does not need backward computation.
conv2_1does not need backward computation.
input-datadoes not need backward computation.
............
整个网络初始化完毕:
net.cpp:270 Thisnetwork produces output loss_bbox
Thisnetwork produces output loss_cls
Thisnetwork produces output rpn_cls_loss
Thisnetwork produces output rpn_loss_bbox
Networkinitialization done.
solver.cpp:60 Solverscaffolding done.
开始迭代,输出结果:
solver.cpp:229 Iteration0, loss = 1.98441
solver.cpp:245:
Trainnet output #0: loss_bbox = 0.00188451 (* 1 = 0.00188451 loss)
Trainnet output #1: loss_cls = 0.484446 (* 1 = 0.484446 loss)
Trainnet output #2: rpn_cls_loss = 0.766564 (* 1 = 0.766564 loss)
Trainnet output #3: rpn_loss_bbox = 0.484638 (* 1 = 0.484638 loss)
sgd_solver.cpp:106:Iteration0, lr = 0.001
solver.cpp:229 Iteration20, loss = 1.58353
solver.cpp:245:
Trainnet output #0: loss_bbox = 0.00184912 (* 1 = 0.00184912 loss)
Trainnet output #1: loss_cls = 0.213403 (* 1 = 0.213403 loss)
Trainnet output #2: rpn_cls_loss = 0.444577 (* 1 = 0.444577 loss)
Trainnet output #3: rpn_loss_bbox = 0.818097 (* 1 = 0.818097 loss)
sgd_solver.cpp:106:Iteration20, lr = 0.001
.......
solver.cpp:229 Iteration69980, loss =0.374131
solver.cpp:245:
Trainnet output #0: loss_bbox =0.00462239 (* 1 =0.00462239
loss)
Trainnet output #1: loss_cls =0.00527413 (* 1 =0.00527413 loss)
Trainnet output #2: rpn_cls_loss =0.0607663 (* 1 =0.0607663
loss)
Trainnet output #3: rpn_loss_bbox =0.139714 (* 1 =0.139714
loss)
sgd_solver.cpp:106:Iteration69980, lr = 0.001
real 681m44.284s
user 565m0.152s
sys 115m29.578s
生成的模型
保存在:
/Text-Detection-with-FRCN/py-faster-rcnn/output/faster_rcnn_end2end/voc_2007_trainval文件夹中。
vgg16_faster_rcnn_iter_*.caffemodel中,其中*为迭代次数
每迭代10000次,生成一个模型。迭代了70000次,共生成了7个模型。
五.测试模型
实际上,在./experiments/scripts/faster_rcnn_end2end.sh 中,训练完毕后会对模型进行测试。
那么,怎样单独执行测试呢?
切换目录:
cd $Text-Detection-with-FRCN/py-faster-rcnn/
运行指令:
tools/test_net.py --gpu 0
--def models/coco_text/VGG16/faster_rcnn_end2end/test.prototxt \
--netoutput/faster_rcnn_end2end/voc_2007_trainval/vgg16_faster_rcnn_iter_70000.caffemodel\
--imdb voc_2007_test\
--cfg experiments/cfgs/faster_rcnn_end2end.yml \
1.运行可能出现的错误:
File "/Text-Detection-with-FRCN/py-faster-rcnn/tools/../lib/datasets/voc_eval.py", line 23, in parse_rec
obj_struct['bbox'] = [int(bbox.find('xmin').text),
ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: '391.0'
解决方案:改为:
obj_struct['bbox'] = [int(float(bbox.find('xmin').text)),
int(float(bbox.find('ymin').text)),
int(float(bbox.find('xmax').text)),
int(float(bbox.find('ymax').text))]
2.测试运行结果:
对于vgg16_faster_rcnn_iter_70000.caffemodel:
AP for text = 0.3422
Mean AP = 0.3422
~~~~~~~~
Results:
0.342
0.342
~~~~~~~~
对于github中已经训练好的vgg16_faster_rcnn_fine_tune_on_coco.caffemodel:
AP for text = 0.1013
Mean AP = 0.1013
~~~~~~~~
Results:
0.101
0.101
~~~~~~~~
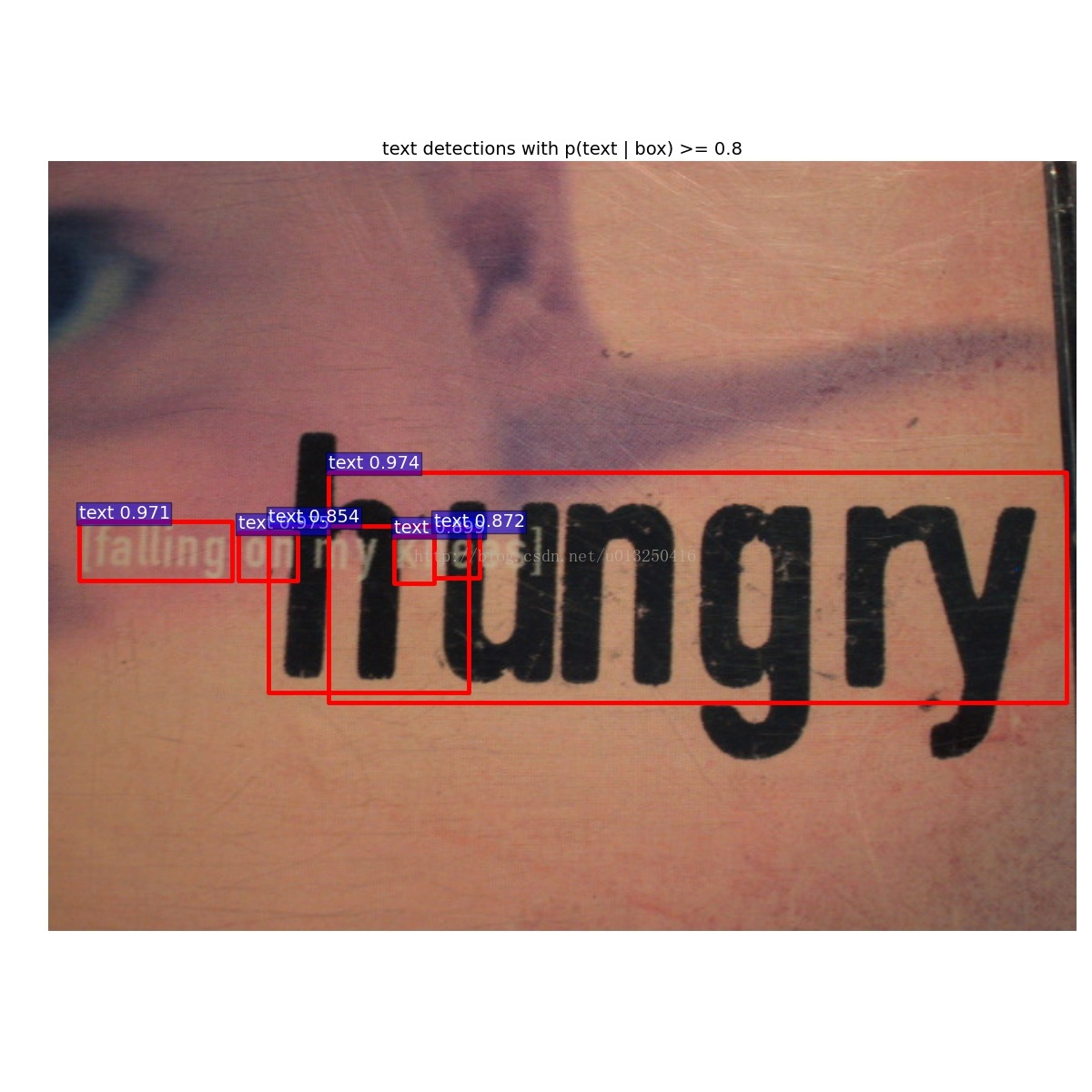
3.运行demo
在/Text-Detection-with-FRCN/script目录下,有text_detect_demo.sh文件:
./py-faster-rcnn/tools/text_detect_demo.py \
--gpu 0 \
--net models/deploy.prototxt \
--model models/vgg16_faster_rcnn_fine_tune_on_coco.caffemodel \
--dataset datasets/test
通过修改其中的model,来指定模型。
运行demo得到的结果:
左边:vgg16_faster_rcnn_iter_70000.caffemodel的测试结果,右边:github中已经训练好的vgg16_faster_rcnn_fine_tune_on_coco.caffemodel的测试结果。
Faster-RCNN用于场景文字检测训练测试过程记录(转)的更多相关文章
- faster r-cnn 在CPU配置下训练自己的数据
因为没有GPU,所以在CPU下训练自己的数据,中间遇到了各种各样的坑,还好没有放弃,特以此文记录此过程. 1.在CPU下配置faster r-cnn,参考博客:http://blog.csdn.net ...
- Faster R-CNN:详解目标检测的实现过程
本文详细解释了 Faster R-CNN 的网络架构和工作流,一步步带领读者理解目标检测的工作原理,作者本人也提供了 Luminoth 实现,供大家参考. Luminoth 实现:https:// ...
- 深度学习笔记之目标检测算法系列(包括RCNN、Fast RCNN、Faster RCNN和SSD)
不多说,直接上干货! 本文一系列目标检测算法:RCNN, Fast RCNN, Faster RCNN代表当下目标检测的前沿水平,在github都给出了基于Caffe的源码. • RCNN RCN ...
- [目标检测] 从 R-CNN 到 Faster R-CNN
R-CNN 创新点 经典的目标检测算法使用滑动窗法依次判断所有可能的区域,提取人工设定的特征(HOG,SIFT).本文则预先提取一系列较可能是物体的候选区域,之后仅在这些候选区域上用深度网络提取特征, ...
- 目标检测算法的总结(R-CNN、Fast R-CNN、Faster R-CNN、YOLO、SSD、FNP、ALEXnet、RetianNet、VGG Net-16)
目标检测解决的是计算机视觉任务的基本问题:即What objects are where?图像中有什么目标,在哪里?这意味着,我们不仅要用算法判断图片中是不是要检测的目标, 还要在图片中标记出它的位置 ...
- py-faster R-CNN 用于训练自己的数据(1)
官方给出的faster R-CNN的源码python版:https://github.com/rbgirshick/py-faster-rcnn 先来分析一下 整个文件,根目录下的文件 caffe-f ...
- 实战 | 源码入门之Faster RCNN
前言 学习深度学习和计算机视觉,特别是目标检测方向的学习者,一定听说过Faster Rcnn:在目标检测领域,Faster Rcnn表现出了极强的生命力,被大量的学习者学习,研究和工程应用.网上有很多 ...
- 【OCR技术系列之五】自然场景文本检测技术综述(CTPN, SegLink, EAST)
文字识别分为两个具体步骤:文字的检测和文字的识别,两者缺一不可,尤其是文字检测,是识别的前提条件,若文字都找不到,那何谈文字识别.今天我们首先来谈一下当今流行的文字检测技术有哪些. 文本检测不是一件简 ...
- 中文版 Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks
Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks 摘要 最先进的目标检测网络依靠区域提出算法 ...
随机推荐
- 高性能Java代码的规范
代码优化的目标是 减小代码的体积 提高代码运行的效率 代码优化细节 1.尽量指定类.方法的final修饰符 带有final修饰符的类是不可派生的.在Java核心API中,有许多应用final的例子,例 ...
- LeetCode 150. 逆波兰表达式求值(Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation) 24
150. 逆波兰表达式求值 150. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation 题目描述 根据逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值. 有效的运算符包括 +, -, *, /.每个运算对象 ...
- 【LeetCode】整数反转【不能借助辅助空间,需要处理溢出】
给出一个 32 位的有符号整数,你需要将这个整数中每位上的数字进行反转. 示例 1: 输入: 123 输出: 321 示例 2: 输入: -123 输出: -321 示例 3: 输入: 120 输出: ...
- 数组转JSON对象
代码: function arrayToJson(arr){ var js={}; for(var i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ js[arr[i].name]=arr[i].v ...
- python学习-64 面向对象三大特性----继承1
面向对象三大特性 1.三大特性? 继承,多态,封装 2.什么是继承? 类的继承和现实生活中的父与子,继承关系是一样的,父类为基类. python中的类继承分为:单继承和多继承 3.举例说明 class ...
- kafka服务端实验记录
kafka单机实验: 环境准备: 1.下载kafka,zookeeper,并解压 wget http://mirror.bit.edu.cn/apache/kafka/2.3.0/kafka_2.11 ...
- nginx配置http静态站点服务器
1. 系统环境Windows 10 2. 设置静态站点目录,注意不要出现中文(这里踩了很多坑,可以查看错误日志error.log, “No mapping for the Unicode char ...
- springboot笔记07——整合MyBatis
前言 Springboot 整合 MyBatis 有两种方式,分别是:"全注解版" 和 "注解.xml混合版". 创建项目 创建Springboot项目,选择依 ...
- 【洛谷 P3193】 [HNOI2008]GT考试(KMP,dp,矩阵乘法)
题目链接 \(f[i][j]\)表示准考证号到第\(i\)位,不吉利数字匹配到第\(j\)位的方案数. 答案显然是\(\sum_{i=0}^{m-1}f[n][i]\) \(f[i][j]=\sum_ ...
- c#读写apk的 comment
写入: ZipFile zipFile = new ZipFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\2.apk"); zipFile.Beg ...