shell 学习笔记1-什么是shell,shell变量
一、介绍
1、什么是shell
Shell 既是一种命令语言,又是一种程序设计语言,他在操作系统得最外层,负责直接与用户对话,把用户得输入解释个OS,并处理各类操作系统得输出结果,输出到屏幕返回个i用户,这种对话方式可以是交互方式(键盘输入命令,可以立即得到shell得回应),或非交互式(执行脚本程序)得方式
图示如下:
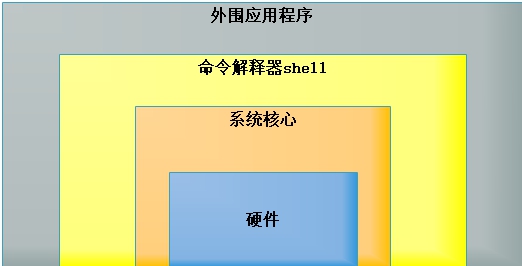
2、什么是shell脚本
其实就是通过一个程序文件执行的程序,可以由一系列命令及命令语句组成,这些命令、变量和流程控制语句等有机得综合形成一个功能强大得shell脚本,类似dos系统下得批处理文件批处理示例如下:(备份网站数据库脚本)
@echo off
set date=%date:~,%-%date::~,%-%date:~,%
mysqldump -uroot -poldboy -A -B >D:\bak\"%date%.sql"
rar.exe a -k -r -s -ml D:\bak\"%date%".sql.rar D:\bak\"%date%".sql
del D:\bak\*.sql
rar.exe a -k -r -s -ml d:\bak\"%date%" htdocs.rar D:\work\PHPnow\htdocs
3、shell在工作中位置

4、shell的种类
shell 脚本语言是弱类型语言,较为通用shell 有标准的Bourne shell (sh)和C shell(csh),其中Bourne shell(sh)已经被bash shell 取代
bourne shell(sh,ksh,an bash)
bourene shell(sh)
bourne again shell (bash)
POSIX shell (sh)
c shell
c shell (csh)
TENEX/TOPS C shell (tcsh)
查看系统得shell
[root@web1 ~]# cat /etc/shells
/bin/sh
/bin/bash
/sbin/nologin
/usr/bin/sh
/usr/bin/bash
/usr/sbin/nologin
/bin/tcsh
/bin/csh
用的最多得莫属bash了,bash是bourne again shell的缩写,bash是 bourne shell(sh)发展来的,但又不完全相同,它包含了csh和ksh的特色,但大多数脚本都可以不加修改的在bash上运行,是bourne shell的扩展,增加了一些特性,命令补全,命令编辑和命令历史等
5、其他常用脚本语言种类
php
perl
python
js
6、第一个shell脚本
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello World !" [root@web1 bash-test]# chmod +x .sh #<---添加运行权限
[root@web1 bash-test]# .sh #<---这样运行不了,因为运行其它二进制的程序也一样,直接写 1.sh,linux 系统会去 PATH 里寻找有没有叫 1.sh 的,而只有 /bin, /sbin, /usr/bin,/usr/sbin 等在 PATH 里,你的当前目录通常不在 PATH 里,所以写成 1.sh 是会找不到命令的,要用 ./test.sh 告诉系统说,就在当前目录找。
[root@web1 bash-test]# ./.sh
hello world!
[root@web1 bash-test]# bash .sh #<---这是另一种方式,指定解释器直接运行
hello world!
[root@web1 bash-test]#
二、shell变量
1、变量
命名的内存空间(可以理解为盒子)
Shell支持自定义变量。
变量是暂时存储数据的地方及数据标记,所存储的数据存在内存空间中
常见的变量类型为整数,字符串,小数等属于弱类型语言有别于其他强类型语言比如java/c,可以使用declare显示定义变量的类型
2、变量类型
环境变量(全局变量):可以是自定义环境变量和bash内置的环境变量
普通变量(局部变量):在创建时shell函数或shell脚本种使用
有三个命令可以显示变量的值set(set -o 输出所有变量)、env(只显示全局变量)和declare(输出所有变量、函数、整数和已经导出的变量)
[root@web1 bash-test]# env |tail
HISTCONTROL=ignoredups
SHLVL=
HOME=/root
LOGNAME=root
QTLIB=/usr/lib64/qt-3.3/lib
SSH_CONNECTION=192.168.216.1 192.168.216.51
LESSOPEN=||/usr/bin/lesspipe.sh %s
XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/
_=/usr/bin/env
OLDPWD=/root
[root@web1 bash-test]# set -o |tail
notify off
nounset off
onecmd off
physical off
pipefail off
posix off
privileged off
verbose off
vi off
xtrace off
[root@web1 bash-test]# declare |tail
{
local quoted=${//\'/\'\\\'\'};
printf "'%s'" "$quoted"
}
quote_readline ()
{
local quoted;
_quote_readline_by_ref "$1" ret;
printf %s "$ret"
}
[root@web1 bash-test]#
3、定义自定义环境变量
1)设置环境变量
使用export和declare命令格式的三种方法
1、export 变量名 =value
2、变量名 =value;export 变量名
3、declare -x 变量名 =value
定义环境变量并赋值的方法:
[root@web1 bash-test]# export NAME=abc
[root@web1 bash-test]# declare -x NAME=abc
[root@web1 bash-test]# NAME=abc ;export NAME
自定义全局环境变量的方法:
vim /etc/profile #<---编辑profile文件
export zxg='zhangxingeng' #<---插入一行定义的变量 [root@web1 bash-test]# cat /etc/profile |grep zxg #<---确认
export zxg='zhangxingeng'
[root@web1 bash-test]# source /etc/profile #<---使其生效
[root@web1 bash-test]# echo $zxg #<---查看结果
zhangxingeng
[root@web1 bash-test]# env |grep zxg
zxg=zhangxingeng
[root@web1 bash-test]#
常用的环境变量永久生效的常规设置文件
用户环境变量
[root@web1 bash-test]# ls /root/.bashrc #<---推荐
/root/.bashrc
[root@web1 bash-test]# ls /root/.bash_profile
/root/.bash_profile
[root@web1 bash-test]#
全局环境变量
[root@web1 bash-test]# ll /etc/profile
[root@web1 bash-test]# ll /etc/bashrc #<---推荐
[root@web1 bash-test]# ll /etc/profile.d/
2)查看与取消环境变量
4、定义普通变量
定义变量时,变量名不加美元符号($),如:
variableName="value"
注意,变量名和等号之间不能有空格,这可能和你熟悉的所有编程语言都不一样。同时,变量名的命名须遵循如下规则:
首个字符必须为字母(a-z,A-Z)。
中间不能有空格,可以使用下划线(_)。
不能使用标点符号。
不能使用bash里的关键字(可用help命令查看保留关键字)。
例如:
[root@web1 bash-test]# web1=web1.zxg.com
1)、三种方式定义普通变量
[root@web1 bash-test]# a=
[root@web1 bash-test]# b=''
[root@web1 bash-test]# c=""
[root@web1 bash-test]# echo "a=$a"
a=
[root@web1 bash-test]# echo "b=$b"
b=
[root@web1 bash-test]# echo "c=${c}" <---$变量名表示输出变量,可以用$c或者${c}两种用法
c=
[root@web1 bash-test]#
2)、测试
[root@web1 ~]# a=
[root@web1 ~]# b=''
[root@web1 ~]# c=""
[root@web1 ~]# a=-$a
[root@web1 ~]# b='111-$a'
[root@web1 ~]# c="111-$a"
[root@web1 ~]# echo "a=$a"
a=-
[root@web1 ~]# echo "c=${c}"
c=--
[root@web1 ~]# echo "b=$b"
b=-$a
[root@web1 ~]#
3)三种方式总结
不加引号,当内容为简单连续的数字、字符串、路径名时,可以使用,值里面有变量会被解释后再输出
加单引号,输出变量内容时,单引号里面是啥就输出啥即使是变量或命令(命令需要反引起来),这种比较适合显示纯字符串的请看
加双引号,输出变量内容时引号里的变量及命令会经过解析后再输出内容,这种就比较适合字符串中附带有变量及命令且向将其解析后再输出的变量定义
4)把一个命令结果作为变量的内容赋值的两种方法
变量名=`ls` <---反引号引起来,缺点容易和单引号弄混
变量名=$(ls) <---可以使用这种方法
示例1
[root@web1 ~]# hh=`ls`
[root@web1 ~]# echo $hh
anaconda-ks.cfg bash-test Desktop Downloads google-chrome-stable_current_x86_64.rpm initial-setup-ks.cfg original-ks.cfg
[root@web1 ~]# hh1=$(ls)
[root@web1 ~]# echo $hh1
anaconda-ks.cfg bash-test Desktop Downloads google-chrome-stable_current_x86_64.rpm initial-setup-ks.cfg original-ks.cfg
[root@web1 ~]#
示例2 按天打包网站站点目录程序,生成不同的文件名
[root@web1 scripts]# CMD=$(date +%F) #<---将当前日志(格式为2019-07-03)赋值给CMD变量
[root@web1 scripts]# echo $CMD #<---输出变量的值
--
[root@web1 scripts]# CMD=$(date +%F).tar.gz #<--- 直接输出时间命令的结果
[root@web1 scripts]# CMD=$(date +%F)
[root@web1 scripts]# echo $(date +%F).tar.gz
--.tar.gz
[root@web1 scripts]# tar zcf etc_$(date +%F).tar.gz /etc #<---将时间作为压缩包打包
tar: Removing leading `/' from member names
[root@web1 scripts]# ll #<---打包结果
total
-rw-r--r-- root root Jul : etc_2019--.tar.gz
[root@web1 scripts]# H=$(uname -n) #<---将或者主机名并赋值给H
[root@web1 scripts]# echo $H
web1
[root@web1 scripts]# tar zcf $H.tar.gz /etc/services #<---以主机名打包
tar: Removing leading `/' from member names
[root@web1 scripts]# ll #<---打包结果
total
-rw-r--r-- root root Jul : etc_2019--.tar.gz
-rw-r--r-- root root Jul : web1.tar.gz
[root@web1 scripts]#
5)局部(普通)变量定义及赋值的小结
若变量内容为连续数字、字符串的赋值时,变量内容两边可以不加引号,例如a=111
变量的内容很多时,如果有空格且希望解析内容中变量,请加双引号
如果需要原样输出,请加单引号
使用命令行可以使用反引号括起来或者用$()括起来,推荐后者
输出可以用echo或者更复杂的printf 方法为,echo $变量的方式
$a和${a}效果一样
当变量后面连接其他字符的时候必须给变量加上大括号${a}_bc
再grep和sed中关于引号是和shell相符的
不加引号、单引号、双引号再awk调用shell中的变量中效果相反,所以再awk调用shell变量时,可以先echo出加符号输出变量,然后再通过管道给awk
6)变量名定义小结
变量名只能为字母、数字、或下划线,只能以字母或者下划线开头
变量名的定义要有一定的规范,并且要见名知意
首字母大写、单词间用_、驼峰语法、单词全大写
5、使用变量
使用一个定义过的变量,只要在变量名前面加美元符号($)即可,如:
[root@web1 bash-test]# name=zxg #<===设置变量
[root@web1 bash-test]# echo $name #<===打印变量
zxg
[root@web1 bash-test]# echo $web1
web1.zxg.com
[root@web1 bash-test]#
变量名外面的花括号是可选的,加不加都行,加花括号是为了帮助解释器识别变量的边界,比如下面这种情况:
[root@web1 bash-test]# vim .sh #!/bin/bash
for i in abc;do
echo "i am ${i}" #<---变量加花括号
done [root@web1 bash-test]# chmod +x .sh
[root@web1 bash-test]# ./.sh
i am abc
把阔号去掉改一下参数,写成echo "I am $i111",解释器就会把$i111当成一个变量(其值为空),代码执行结果不能输出正确的变量值了
[root@web1 bash-test]# vim 2.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in abc;do
echo "i am $i111" #<---不加花括号的变量
done
[root@web1 bash-test]# ./.sh
i am
推荐给所有变量添加上花括号,培养良好编程习惯
6、重新定义变量
已经被定义的变量可以重新定义,如下:
[root@web1 bash-test]# echo $name
zxg
[root@web1 bash-test]# name=zhangxingeng #<---直接重新定义即可
[root@web1 bash-test]# echo $name
zhangxingeng
7、只读变量
使用readonly命令可以将变量定义为只读变量,只读变量的值不能被改变
[root@web1 bash-test]# vim .sh #!/bin/bash
aaaa=""
readonly aaaa
aaaa=""
echo $aaaa [root@web1 bash-test]# chmod +x .sh
[root@web1 bash-test]# ./.sh
./.sh: line : aaaa: readonly variable #<---可以看到readonly variable [root@web1 bash-test]#
8、删除变量
使用unset命令可以删除变量,请看如下脚本:
[root@web1 bash-test]# cat .sh
#!/bin/bash
myname=web1
unset myname #<---unset命令
echo $myname [root@web1 bash-test]# chmod +x .sh
[root@web1 bash-test]# ./.sh
#<---已经删除变量
转载请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangxingeng/p/11064571.html
shell 学习笔记1-什么是shell,shell变量的更多相关文章
- UNIX shell 学习笔记 一 : 几个shell的规则语法对比
1. 查看系统有哪些可用的shell cat /etc/shell 2. 每种shell都有一个特殊内置变量来存上一条命令的退出状态,例: C/TC shell $status % cp fx fy ...
- SHELL学习笔记----IF条件判断,判断条件
SHELL学习笔记----IF条件判断,判断条件 前言: 无论什么编程语言都离不开条件判断.SHELL也不例外. if list then do something here ...
- C / C++算法学习笔记(8)-SHELL排序
原始地址:C / C++算法学习笔记(8)-SHELL排序 基本思想 先取一个小于n的整数d1作为第一个增量(gap),把文件的全部记录分成d1个组.所有距离为dl的倍数的记录放在同一个组中.先在各组 ...
- shell学习笔记
shell学习笔记 .查看/etc/shells,看看有几个可用的Shell . 曾经用过的命令存在.bash_history中,但是~/.bash_history记录的是前一次登录前记录的所有指令, ...
- [转帖][Bash Shell] Shell学习笔记
[Bash Shell] Shell学习笔记 http://www.cnblogs.com/maybe2030/p/5022595.html 阅读目录 编译型语言 解释型语言 5.1 作为可执行程序 ...
- shell学习笔记汇总
1.shell脚本中函数使用 函数定义在前,调用在后,顺序反了就没有效果了.函数调用为:函数名 参数列表 函数内部通过以下变量访问函数的参数:shell脚本函数中: $0: 这个脚本的名字 $n: 这 ...
- shell 学习笔记2-shell-test
一.字符串测试表达式 前面一篇介绍:什么是shell,shell变量请参考: shell 学习笔记1-什么是shell,shell变量 1.字符串测试表达式参数 字符串需要用""引 ...
- SHELL学习笔记三
SHELL学习笔记一 SHELL学习笔记二 SHELL学习笔记三 for 命令 读取列表中的复杂值 从变量读取列表 从命令读取值 更改字段分隔符 用通配符读取目录 which 使用多个测试命令 unt ...
- MongoDB学习笔记:文档Crud Shell
MongoDB学习笔记:文档Crud Shell 文档插入 一.插入语法 db.collection.insertOne() 将单个文档插入到集合中.db.collection.insertMan ...
- Fortran学习笔记:01 基本格式与变量声明
Fortran学习笔记目录 01 基本格式与变量声明 格式 固定格式(Fixed Format):Fortran77 程序需要满足一种特定的格式要求,具体形式参考教材 自由格式(Free Format ...
随机推荐
- PHP 自动加载类
类的自动加载 (Autoloading Classes) 在编写面向对象(OOP) 程序时,很多开发者为每个类新建一个 PHP 文件. 这会带来一个烦恼:每个脚本的开头,都需要包含(include)一 ...
- leetcode 576. Out of Boundary Paths 、688. Knight Probability in Chessboard
576. Out of Boundary Paths 给你一个棋盘,并放一个东西在一个起始位置,上.下.左.右移动,移动n次,一共有多少种可能移出这个棋盘 https://www.cnblogs.co ...
- Flutter 目录结构介绍、入口、自定义 Widget、MaterialApp 组件、Scaffold 组件
Flutter 目录结构介绍 文件夹 作用 android android 平台相关代码 ios ios 平台相关代码 lib flutter 相关代码,我们主要编写的代 码就在这个文件夹 test ...
- 时序数据库技术体系 – 初识InfluxDB(原理)
原贴地址:http://hbasefly.com/2017/12/08/influxdb-1/?qytefg=c4ft23 在上篇文章<时序数据库体系技术 – 时序数据存储模型设计>中笔者 ...
- ES6深入浅出-8 新版的类(下集)-2.全部语法
解答提问 两边都没有构造函数的情况 父类没有构造函数,子类有构造函数的情况 下面用到的了this.body这个属性,所以super()必须要放在这行代码的上面. 在调用this之前必须调用super( ...
- Spring MVC入门的实例
作为Spring MVC入门,以XML配置的方式为例.首先需要配置Web工程的web.xml文件. 代码清单14-1:web.xml配置Spring MVC <?xml version=&q ...
- js 次方 开方 对数
次方 ,用Math.pow(值,次方数) 如: Math.pow(3,2); 3的平方 Math.Pow(2,3); 2的立方 开方Math.sqrt(值) 如: Math.sqrt(9); ...
- android基础---->数据保存到文件
Android使用与其他平台类似的基于磁盘的文件系统(disk-based file systems).这篇博客将描述如何在Android文件系统上使用File的读写APIs对Andorid的file ...
- JavaScript控制浏览器全屏及各种浏览器全屏模式的方法、属性和事件
实现全屏 个人版:function isFullScreen() { var fullscreenElement = document.fullscreenElement || document.we ...
- 关于TV工厂菜单参数的具体说明
1.ADC Adjust 此项是针对YPbPr.VGA端口进行处理的,在三路R/G/B或者YPb/Pr信号输入到芯片时候,由于存在硬件上的偏差,导致信号和标准信号存在偏差,需要对信号进行ADC校正.光 ...
