Golang爬虫:使用正则表达式解析HTML
之前所写的爬虫都是基于Python,而用Go语言实现的爬虫具有更高的性能。
第一个爬虫
使用http库,发起http请求
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
)
func fetch(url string) string {
client := &http.Client{} // 创建http客户端对象
// 创建一个请求,使用get方法
req, _ := http.NewRequest("GET", url, nil)
// 设置请求头内容
req.Header.Set("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64)")
resp, err := client.Do(req) // 发起请求
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return ""
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return ""
}
return string(body)
}
func main() {
url := "https://www.cnblogs.com/N3ptune"
res := fetch(url)
fmt.Println(res)
}
运行这段代码,可以看到终端打印除了网页代码,这是服务端回应的内容
对上述几个函数作一个特别说明
http.NewRequest
$ go doc http.NewRequest
package http // import "net/http"
func NewRequest(method, url string, body io.Reader) (*Request, error)
NewRequest wraps NewRequestWithContext using context.Background.
该函数是构建请求的第一步
req.Header即Request Header,所谓请求头。req.Header.Set是设置请求头,可以用来应对一些反爬虫机制,如上是设置了User-Agent。
User-Agent 即用户代理,简称“UA”,它是一个特殊字符串头。网站服务器通过识别 “UA”来确定用户所使用的操作系统版本、CPU 类型、浏览器版本等信息。
http.Do
用于发送HTTP请求,同时会返回响应内容
$ go doc http.Do
package http // import "net/http"
func (c *Client) Do(req *Request) (*Response, error)
Do sends an HTTP request and returns an HTTP response, following policy
(such as redirects, cookies, auth) as configured on the client.
Body是响应的正文,不用时要关闭
ioutil.ReadAll
上述代码中用于读取响应中的正文内容,返回一个字节切片
$ go doc io.ReadAll
package io // import "io"
func ReadAll(r Reader) ([]byte, error)
ReadAll reads from r until an error or EOF and returns the data it read. A
successful call returns err == nil, not err == EOF. Because ReadAll is
defined to read from src until EOF, it does not treat an EOF from Read as an
error to be reported.
因为是字节类型的切片,所以要转成string
如下是main函数
func main() {
url := "https://www.cnblogs.com/N3ptune"
res := fetch(url)
fmt.Println(res)
}
解析页面
这里先使用正则表达式 目标URL:GORM 指南

目标是爬取到左侧每个条目的链接
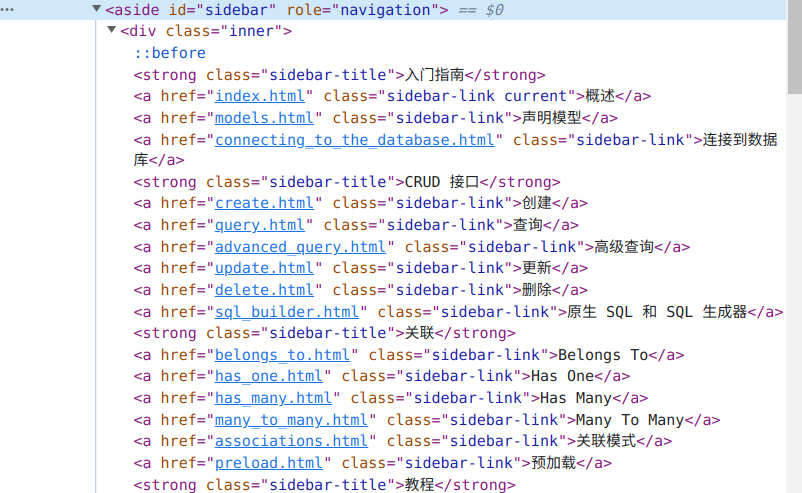
查看网页源码就可以找到链接,显然这些链接都是用固定格式的,可以轻易使用正则表达式匹配。
func parse(html string) {
// 替换换行
html = strings.Replace(html, "\n", "", -1)
// 边栏内容块 正则
reSidebar := regexp.MustCompile(`<aside id="sidebar" role="navigation">(.*?)</aside>`)
sidebar := reSidebar.FindString(html)
// 链接 正则
reLink := regexp.MustCompile(`href="(.*?)"`)
// 找到所有链接
links := reLink.FindAllString(sidebar, -1)
baseURL := "https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/"
// 遍历链接
for _, v := range links {
s := v[6 : len(v)-1]
url := baseURL + s
fmt.Printf("URL: %v\n", url)
}
}
上面这个函数用于解析HTML文档,构造正则表达式进行匹配。
应用正则表达式要使用regexp模块
MustCompile
$ go doc regexp.MustCompile
package regexp // import "regexp"
func MustCompile(str string) *Regexp
MustCompile is like Compile but panics if the expression cannot be parsed.
It simplifies safe initialization of global variables holding compiled
regular expressions.
该函数的作用是解析正则表达式,因此它的参数是一个正则表达式字符串
FindString
$ go doc regexp.FindString
package regexp // import "regexp"
func (re *Regexp) FindString(s string) string
FindString returns a string holding the text of the leftmost match in s of
the regular expression. If there is no match, the return value is an empty
string, but it will also be empty if the regular expression successfully
matches an empty string. Use FindStringIndex or FindStringSubmatch if it is
necessary to distinguish these cases.
使用FindString函数可以按照正则规则匹配字符串,只返回一个字符串,该字符串包含最左边的匹配文本。
FindAllString 则返回多个字符串
$ go doc regexp.FindAllString
package regexp // import "regexp"
func (re *Regexp) FindAllString(s string, n int) []string
FindAllString is the 'All' version of FindString; it returns a slice of all
successive matches of the expression, as defined by the 'All' description in
the package comment. A return value of nil indicates no match.
首先使用正则表达式匹配边栏的内容块,找到内容块所在的标签,然后将其作为匹配规则,传入FindString函数。然后再构造另一个正则表达式,传入FindAllString函数来匹配链接,返回字符串切片。
对其进行遍历,即可得到链接
main函数
func main() {
url := "https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/index.html"
res := fetch(url)
parse(res)
}
运行结果
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/index.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/models.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/connecting_to_the_database.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/create.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/query.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/advanced_query.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/update.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/delete.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/sql_builder.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/belongs_to.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/has_one.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/has_many.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/many_to_many.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/associations.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/preload.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/context.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/error_handling.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/method_chaining.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/session.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/hooks.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/transactions.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/migration.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/logger.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/generic_interface.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/performance.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/data_types.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/scopes.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/conventions.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/settings.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/dbresolver.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/sharding.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/serializer.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/prometheus.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/hints.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/indexes.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/constraints.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/composite_primary_key.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/security.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/gorm_config.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/write_plugins.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/write_driver.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/changelog.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs//community.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs//contribute.html
URL: https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs//contribute.html#Translate-this-site
进一步解析
下面对每个URL对应的页面再进行解析,获取到每个页面的标题
func getTitle(body string) {
// 替换换行
body = strings.Replace(body, "\n", "", -1)
// 页面内容
reContent := regexp.MustCompile(`<div class="article">(.*?)</div>`)
// 找到页面内容
content := reContent.FindString(body)
// 标题
reTitle := regexp.MustCompile(`<h1 class="article-title" itemprop="name">(.*?)</h1>`)
// 找到页面内容
title := reTitle.FindString(content)
if len(title) < 47 {
return
}
title = title[42 : len(title)-5]
fmt.Printf("title: %v\n", title)
}
访问目标URL,得到HTML文本,使用正则表达式,只要构造出标签的匹配规则即可。
用一个专门的goroutine去做这件事
运行结果
title: GORM 指南
title: 模型定义
title: 连接到数据库
title: 创建
title: 查询
title: 高级查询
title: 更新
title: 删除
title: SQL 构建器
title: Belongs To
title: Has One
title: Has Many
title: Many To Many
title: 实体关联
title: 预加载
title: Context
title: 处理错误
title: 链式方法
title: 会话
title: Hook
title: 事务
title: 迁移
title: Logger
title: 常规数据库接口 sql.DB
title: 性能
title: 自定义数据类型
title: Scopes
title: 约定
title: 设置
title: DBResolver
title: Sharding
title: Serializer
title: Prometheus
title: Hints
title: 数据库索引
title: 约束
目前的完整代码
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"regexp"
"strings"
)
func fetch(url string) string {
client := &http.Client{} // 创建http客户端
// 创建一个请求
req, _ := http.NewRequest("GET", url, nil)
// 设置请求头内容
req.Header.Set("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64)")
resp, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return ""
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return ""
}
return string(body)
}
func parse(html string) {
// 替换空格
html = strings.Replace(html, "\n", "", -1)
// 边栏内容块正侧
reSidebar := regexp.MustCompile(`<aside id="sidebar" role="navigation">(.*?)</aside>`)
// 找到所有链接
sidebar := reSidebar.FindString(html)
// 链接正则
reLink := regexp.MustCompile(`href="(.*?)"`)
// 找到所有链接
links := reLink.FindAllString(sidebar, -1)
baseURL := "https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/"
// 遍历链接
for _, v := range links {
s := v[6 : len(v)-1]
url := baseURL + s
body := fetch(url)
go getTitle(body)
}
}
func getTitle(body string) {
// 替换掉空格
body = strings.Replace(body, "\n", "", -1)
// 页面内容
reContent := regexp.MustCompile(`<div class="article">(.*?)</div>`)
// 找到页面内容
content := reContent.FindString(body)
// 标题
reTitle := regexp.MustCompile(`<h1 class="article-title" itemprop="name">(.*?)</h1>`)
// 找到页面内容
title := reTitle.FindString(content)
if len(title) < 47 {
return
}
title = title[42 : len(title)-5]
fmt.Printf("title: %v\n", title)
}
func main() {
url := "https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/index.html"
res := fetch(url)
parse(res)
}
后续还会考虑将数据保存到本地
Golang爬虫:使用正则表达式解析HTML的更多相关文章
- Python爬虫 | re正则表达式解析html页面
正则表达式(Regular Expression)是一种文本模式,包括普通字符(例如,a 到 z 之间的字母)和特殊字符(称为"元字符"). 正则表达式通常被用来匹配.检索.替换和 ...
- 基础知识 - Golang 中的正则表达式
------------------------------------------------------------ Golang中的正则表达式 ------------------------- ...
- python 3.x 爬虫基础---正则表达式
python 3.x 爬虫基础 python 3.x 爬虫基础---http headers详解 python 3.x 爬虫基础---Urllib详解 python 3.x 爬虫基础---Requer ...
- Golang - 爬虫案例实践
目录 Golang - 爬虫案例实践 1. 爬虫步骤 2. 正则表达式 3. 并发爬取美图 Golang - 爬虫案例实践 1. 爬虫步骤 明确目标(确定在哪个网址搜索) 爬(爬下数据) 取(去掉没用 ...
- python爬虫---爬虫的数据解析的流程和解析数据的几种方式
python爬虫---爬虫的数据解析的流程和解析数据的几种方式 一丶爬虫数据解析 概念:将一整张页面中的局部数据进行提取/解析 作用:用来实现聚焦爬虫的吧 实现方式: 正则 (针对字符串) bs4 x ...
- java对身份证验证及正则表达式解析
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhongshengzhen/ java对身份证验证及正则表达式解析 package service; import java.text.Par ...
- 用正则表达式解析XML
import java.util.regex.*; import java.util.*; /** * * <p>Title: Document</p> * * <p&g ...
- Golang爬虫示例包系列教程(一):pedaily.com投资界爬虫
Golang爬虫示例包 文件结构 自己用Golang原生包封装了一个爬虫库,源码见go get -u -v github.com/hunterhug/go_tool/spider ---- data ...
- golang reflect包使用解析
golang reflect包使用解析 参考 Go反射编码 2个重要的类型 Type Value 其中Type是interface类型,Value是struct类型,意识到这一点很重要 Type和Va ...
- 笔记-爬虫-js代码解析
笔记-爬虫-js代码解析 1. js代码解析 1.1. 前言 在爬取网站时经常会有js生成关键信息,而且js代码是混淆过的. 以瓜子二手车为例,直接请求https://www.guaz ...
随机推荐
- uc 小游戏接入经验
使用引擎,egret 相关资料: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42276579/article/details/107379544 https://minigame.uc ...
- idea乱码
第一步:修改intellij idea配置文件: 找到intellij idea安装目录,bin文件夹下面idea64.exe.vmoptions和idea.exe.vmoptions这两个文件,分别 ...
- idea项目编译时报错:程序包XXX不存在
问题如下: 解决方法: 点击File-->点击settings-->点击maven-->点击Runner-->勾选Delegate IDE build/run action t ...
- docker&docker-compose安装
一.docker安装 1.通过 uname -r 命令查看当前的内核版本,Docker 要求 CentOS 系统的内核版本高于 3.10 uname -r 2.查看系统是否安装过docker yum ...
- 使用JAX构建强化学习agent并借助TensorFlowLite将其部署到Android应用中
在之前发布文章<一个新 TensorFlow Lite 示例应用:棋盘游戏>中,展示了如何使用 TensorFlow 和 TensorFlow Agents 来训练强化学习 (RL) ag ...
- k8s基本操作
注意:k8s的很多操作需要指定命名空间,如果不指定,默认default的命名空间,很多东西就查不出来了 kubectl get cs # 查看集群状态kubectl get nodes # 查看集群节 ...
- 2021SWPUCTF-WEB(一)
gift_F12 给了一个网站,题目提示是F12,就F12找一下 WLLMCTF{We1c0me_t0_WLLMCTF_Th1s_1s_th3_G1ft} jicao 一个代码,逻辑很简单 大 ...
- DASCTF NOV X联合出题人-PWN
太忙了,下午4点才开始做,,剩下的以后补上 签个到 逻辑很简单两个功能的堆,一个就是申请heap.还有一个是检验如果校验通过就会得到flag 申请模块 中间0x886是个很恶心的东西,需要我们绕过 ...
- mysql 以自增id等于某个random()函数算出的值为条件查出两条数据
SELECT id FROM users WHERE id = FLOOR( rand() * ( (SELECT max(id) FROM users) - (SELECT min(id) FROM ...
- 【picoCTF】GET aHEADwrite up
打开链接,页面如下: 这道题我试了两种解法,大家都可以看看哦! 一.burpsuit拦截 1.点击bule,打开burpsuit拦截(记得打开intercept哦) 2.将 POST 请求更改为 HE ...
