spring boot 自动装配的原理
参考: https://blog.csdn.net/Dongguabai/article/details/80865599。如有侵权,请联系本人删除!
入口:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer; @SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class SpringCloundEurekaServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCloundEurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
这里有个很重要的注解:@SpringBootApplication。这是一个组合注解,点击进入可以看到详情如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //作用于类上面
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //作用域运行时
@Documented //doc文档
@Inherited //被继承
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
......
}
上面的组合注解也太多特别的,前面4个注解,就是4个元注解而已。主要关注其中的两个标红的注解。
先分析@SpringBootConfiguration,这也是一个组合注解,点击进去看到详情如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration { }
从上面可以看出,也就是组合了@Configuration,标志是配置类而已。
再看看@EnableAutoConfiguration,点击进入看到详情是:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration"; /**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; /**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
String[] excludeName() default {}; }
其中,@AutoConfigurationPackage,这个注解组合情况如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage { }
AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class 这个类很关键。在我以前的博客Spring的@Enable*注解的工作原理,也写到,关于@Enablexxx 注解的三种实现,其中一种就是用到了这个类似于Registrar.class的
类。该类重写了两个方法,如下:
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, //spring初始化的时候,这个BeandEfinitions用得非常多
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
register(registry, new PackageImport(metadata).getPackageName());
}
@Override
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new PackageImport(metadata));
}
}
单纯从代码还看不出什么,debug的时候,可以看到这个metadata 就是一个我们的启动类,截图如下:
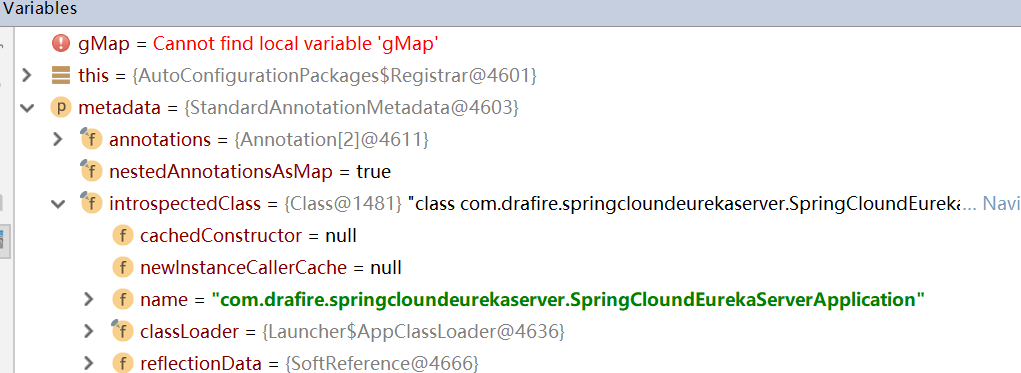
也就是说,这个注解的作用,就是扫描com.drafire.springcloundeurekaserver.SpringCloundEurekaServerApplication 启动类所在的包以及子包,并注入到spring容器中
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
下面再看下:AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class,源码如下:
、public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector
implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware, ResourceLoaderAware,
BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered { private static final AutoConfigurationEntry EMPTY_ENTRY = new AutoConfigurationEntry(); private static final String[] NO_IMPORTS = {}; private static final Log logger = LogFactory
.getLog(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class); private static final String PROPERTY_NAME_AUTOCONFIGURE_EXCLUDE = "spring.autoconfigure.exclude"; private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory; private Environment environment; private ClassLoader beanClassLoader; private ResourceLoader resourceLoader; @Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(
autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
} /**
* Return the {@link AutoConfigurationEntry} based on the {@link AnnotationMetadata}
* of the importing {@link Configuration @Configuration} class.
* @param autoConfigurationMetadata the auto-configuration metadata
* @param annotationMetadata the annotation metadata of the configuration class
* @return the auto-configurations that should be imported
*/
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,
attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
.........
}
这里有个非常重要的重写方法:selectImports,其实这个也是@Enablexxx的三种实现方法之一,具体参考我以前的博客Spring的@Enable*注解的工作原理。
一步一步跟踪,可以看到,最终是调用 getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,attributes),跟踪进入可以看到,源代码如下:
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(
getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations,
"No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryClassName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
int var10 = var9.length;
for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) {
String factoryName = var9[var11];
result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var13) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13);
}
}
}
从上面明显可以看出,classLoader最终是从 META-INF/spring.factories 中循环读取各种配置,并注入到spring 容器中。META-INF/spring.factories 在 spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.19.RELEASE.jar(各个版本号不一样)。看看spring.factories的详细内容,如下:
# Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.AutoConfigurationReportLoggingInitializer # Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer # Auto Configuration Import Listeners
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener # Auto Configuration Import Filters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition # Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.jest.JestAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceResolverAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceDelegatingViewResolverAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.SitePreferenceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.reactor.ReactorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.FallbackWebSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.OAuth2AutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.SocialWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.FacebookAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.LinkedInAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.TwitterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration # Failure analyzers
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBeanCreationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.HikariDriverConfigurationFailureAnalyzer # Template availability providers
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.template.TemplateAvailabilityProvider=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.JspTemplateAvailabilityProvider
上面不仅仅是字符串,其实都是各个配置类的链接来的,可以按住ctrl+鼠标左键进入查看该配置类的详情。
这里面的配置类,包含很多,如果redis、rabbitmq、webmvc、OnClassCondition 等。通过这个配置,自动导入很多配置并生效。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
回顾整体流程,Springboot的启动,主要创建了配置环境(environment)、事件监听(listeners)、应用上下文(applicationContext),并基于以上条件,
在容器中开始实例化我们需要的Bean,至此,通过SpringBoot启动的程序已经构造完成
而自动注入,则是通过Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)注解,通过一系列的操作,包括loadClassName、loadFactoryNames,将META-INF/spring.factories 的类信息,加载到容器(一个ConcurrentHashMap,以BeanDefineTion的封装形式)里面
spring boot 自动装配的原理的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot系列(二):Spring Boot自动装配原理解析
一.Spring Boot整合第三方组件(Redis为例) 1.加依赖 <!--redis--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springf ...
- Spring Boot 自动装配原理
Spring Boot 自动装配原理 Spring Boot 在启动之前还有一系列的准备工作,比如:推断 web 应用类型,设置初始化器,设置监听器,启动各种监听器,准备环境,创建 applicati ...
- Spring Boot 自动装配(二)
目录 目录 前言 1.起源 2.Spring Boot 自动装配实现 2.1.@EnableAutoConfiguration 实现 2.1.1. 获取默认包扫描路径 2.1.2.获取自动装配的组件 ...
- Spring Boot自动装配
前言 一些朋友问我怎么读源码,这篇文章结合我看源码时候一些思路给大家聊聊,我主要从这三个方向出发: 确定目标,这个目标要是一个具体,不要一上来我要看懂Spring,这是不可能的,目标要这么来定,比如看 ...
- Spring Boot自动装配原理源码分析
1.环境准备 使用IDEA Spring Initializr快速创建一个Spring Boot项目 添加一个Controller类 @RestController public class Hell ...
- Spring Boot 自动装配流程
Spring Boot 自动装配流程 本文以 mybatis-spring-boot-starter 为例简单分析 Spring Boot 的自动装配流程. Spring Boot 发现自动配置类 这 ...
- Spring Boot 自动配置的原理、核心注解以及利用自动配置实现了自定义 Starter 组件
本章内容 自定义属性快速入门 外化配置 自动配置 自定义创建 Starter 组件 摘录:读书是读完这些文字还要好好用心去想想,写书也一样,做任何事也一样 图 2 第二章目录结构图 第 2 章 Spr ...
- 深度剖析Spring Boot自动装配机制实现原理
在前面的分析中,Spring Framework一直在致力于解决一个问题,就是如何让bean的管理变得更简单,如何让开发者尽可能的少关注一些基础化的bean的配置,从而实现自动装配.所以,所谓的自动装 ...
- 从源码中理解Spring Boot自动装配原理
个人博客:槿苏的知识铺 一.什么是自动装配 SpringBoot 定义了一套接口规范,这套规范规定:SpringBoot在启动时会扫描外部引用jar包中的META-INF/spring.factori ...
随机推荐
- FPGA+x86构建高性能国产网络测试仪竞技之道
众所周知,以太网已经深入我们的生活无处不在,企业.校园.大数据中心和家庭等都离不开网络,否则我们的生活将受到严重的影响. 以太网的接口速率也是迅速发展:10M.100M.GE.10GE.40GE.10 ...
- ASP.NET Core 6框架揭秘实例演示[13]:日志的基本编程模式[上篇]
<诊断跟踪的几种基本编程方式>介绍了四种常用的诊断日志框架.其实除了微软提供的这些日志框架,还有很多第三方日志框架可供我们选择,比如Log4Net.NLog和Serilog 等.虽然这些框 ...
- 华为服务器设置iBMC管理网口IP地址,开启Monitor图文教程
设置iBMC管理网口IP地址 默认用户名:root 默认密码:Huawei12#$ 操作步骤 服务器重启时,当出现如下界面时,重复按"Delete". 在启动过程出现输入密码对话框 ...
- C#内联函数 特性 MethodImplOptions.AggressiveInlining)
[MethodImpl(MethodImplOptions.AggressiveInlining)] 内联函数 Impl:implement的缩写 内联函数 在计算机科学中,内联函数(有时称作在线函数 ...
- JVM学习笔记(详细)
目录 01 JVM与Java体系结构 简介 JVM整体架构,HotSpot java代码执行流程 JVM架构模型 JVM生命周期 JVM发展历程 02 类加载子系统 JVM细节版架构 类加载器的作用 ...
- 哈工大 计算机网络 实验四 利用 Wireshark 进行协议分析
计算机网络实验代码与文件可见github:计算机网络实验整理 实验名称 利用 Wireshark 进行协议分析 实验目的: 本次实验的主要目的. 熟悉并掌握Wireshark的基本操作,了解网络协议实 ...
- 2020.10.20 利用POST请求模拟登录知乎
前两天学习了Python的requests模块的相关内容,对于用GET和PSOT请求访问网页以抓取需要的内容有了初步的了解,想要再从一些复杂的网站积累些经验.最开始我采用最简单的get(url)方法想 ...
- shell 和python 实现ftp文件上传或者下载
一.shell脚本 #####从ftp服务器上的/home/data 到 本地的/home/databackup#####!/bin/bashftp -n<<!open 172.168.1 ...
- tp5 终端命令总结
D:\PHP\phpstudy_pro\WWW\1906A\tp5>php think build --module examTest Successed D:\PHP\phpstudy_pro ...
- largebin attack
largebin attack 由这个名字就可以看出是对 largebin 进行的操作,需要的条件是存在 UAF 或者可以构造出 UAF.实现的功能是: 1.任意地址写入一个大数字 2.实现任意地址分 ...
