css包含块containing block
《css权威指南》P167:
The Containing Block
Every element is laid out with respect to its containing block; in a very real way, the containing block is the "layout context" for an element. CSS2.1 defines a series of rules for determining an element's containing block. I'll cover only those rules that pertain to the concepts covered in this chapter and leave the rest for future chapters.
每个元素都相对于其包含块摆放,可以这么说,包含块就是一个元素的“布局上下文”。css2.1定义了一系列规则来确定元素的包含块,这里介绍的只是其中部分规则。
For an element in the normal, Western-style flow of text, the containing block is formed by the content edge of the nearest block-level, table cell, or inline-block ancestor box. Consider the following markup:
对于正常的西方语言文本流中的一个元素,包含块由最近的块级祖先框,表单元格或行内块inline-block祖先框的内容边界(content edge)构成。
<body> <div> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> </div> </body>
In this very simple markup, the containing block for the p element is the div element, as that is the closest ancestor element that is block-level, a table cell, or inline-block (in this case, it's a block box). Similarly, the div's containing block is the body. Thus, the layout of the p is dependent on the layout of the div, which is in turn dependent on the layout of the body.
p元素的包含块是div,因为作为块级元素、表单元格或行内块元素,这是最近的祖先元素(本例中是一个块元素框)。类似第,div的包含块是body。因此,p的布局依赖于div的布局,div的布局则依赖body布局。
You don't need to worry about inline elements since the way they are laid out doesn't depend directly on containing blocks. We'll talk about them later in the chapter.
不必担心inline element,因为他们的摆放方式并不直接依赖于包含块。
-------------------------
w3c定义:
http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS2/visudet.html#containing-block-details
10.1 Definition of "containing block"
The position and size of an element's box(es) are sometimes calculated relative to a certain rectangle, called the containing block of the element. The containing block of an element is defined as follows:
- The containing block in which the root element lives is a rectangle called the initial containing block. For continuous media, it has the dimensions of the viewport and is anchored at the canvas origin; it is the page area for paged media. The 'direction' property of the initial containing block is the same as for the root element.
- For other elements, if the element's position is 'relative' or 'static', the containing block is formed by the content edge of the nearest block container ancestor box.
- If the element has 'position: fixed', the containing block is established by the viewport in the case of continuous media or the page area in the case of paged media.
- If the element has 'position: absolute', the containing block is established by the nearest ancestor with a 'position' of 'absolute', 'relative' or 'fixed', in the following way:
- In the case that the ancestor is an inline element, the containing block is the bounding box around the padding boxes of the first and the last inline boxes generated for that element. In CSS 2.1, if the inline element is split across multiple lines, the containing block is undefined.
- Otherwise, the containing block is formed by the padding edge of the ancestor.
If there is no such ancestor, the containing block is the initial containing block.
In paged media, an absolutely positioned element is positioned relative to its containing block ignoring any page breaks (as if the document were continuous). The element may subsequently be broken over several pages.
For absolutely positioned content that resolves to a position on a page other than the page being laid out (the current page), or resolves to a position on the current page which has already been rendered for printing, printers may place the content
- on another location on the current page,
- on a subsequent page, or
- may omit it.
Note that a block-level element that is split over several pages may have a different width on each page and that there may be device-specific limits.
With no positioning, the containing blocks (C.B.) in the following document:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN">
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Illustration of containing blocks</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY id="body">
<DIV id="div1">
<P id="p1">This is text in the first paragraph...</P>
<P id="p2">This is text <EM id="em1"> in the
<STRONG id="strong1">second</STRONG> paragraph.</EM></P>
</DIV>
</BODY>
</HTML>
are established as follows:
| For box generated by | C.B. is established by |
|---|---|
| html | initial C.B. (UA-dependent) |
| body | html |
| div1 | body |
| p1 | div1 |
| p2 | div1 |
| em1 | p2 |
| strong1 | p2 |
If we position "div1":
#div1 { position: absolute; left: 50px; top: 50px }
its containing block is no longer "body"; it becomes the initial containing block (since there are no other positioned ancestor boxes). 确实,我们定义div1为absolute,包含块不再是body。。
If we position "em1" as well:
#div1 { position: absolute; left: 50px; top: 50px }
#em1 { position: absolute; left: 100px; top: 100px }
the table of containing blocks becomes:
| For box generated by | C.B. is established by |
|---|---|
| html | initial C.B. (UA-dependent) |
| body | html |
| div1 | initial C.B. |
| p1 | div1 |
| p2 | div1 |
| em1 | div1 |
| strong1 | em1 |
By positioning "em1", its containing block becomes the nearest positioned ancestor box (i.e., that generated by "div1").
完。
在http://www.w3help.org/zh-cn/kb/008/ 也详细说了这个概念;
包含块判定及其范围
由上面内容可知,元素框的定位和尺寸与其包含块有关,而元素会为它的子孙元素创建包含块。
那么,是不是说,元素的包含块就是它的父元素呢?包含块的区域是不是父元素的内容区域呢? 答案是否定的。此节中,将给出各类元素包含块的判断以及包含块的区域范围。 如果不存在符合判断标准的祖先元素,那么元素的包含块就是初始包含块。
包含块判定总流程图如下:
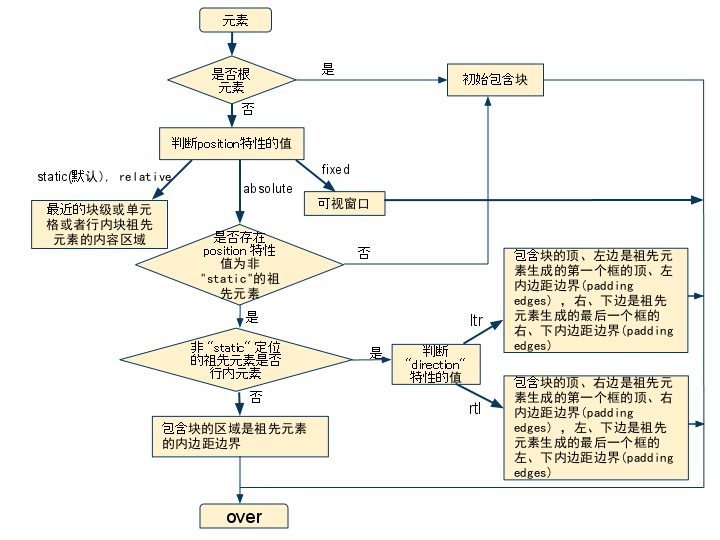
根元素
根元素,就是处于文档树最顶端的元素,它没有父节点。
根元素存在的包含块,被叫做初始包含块 (initial containing block)。具体,跟用户端有关。
- 在 (X)HTML 中,根元素是 html 元 素(尽管有的浏览器会不正确地使用 body 元素)。
- 而初始包含块的 direction 属性与根元素相同。
静态定位元素和相对定位元素
如果该元素的定位(position)为 "relative" (相对定位)或者 "static"(静态定位),它的包含块由它最近的块级、单元格(table cell)或者行内块(inline-block)祖先元素的 内容框1创建。
元素如果未声明 'position' 特性,那么就会采用 'position' 的默认值 "static"。
<table id="table1">
<tr>
<td id="td1">
<div id="div1" style="padding:20px;border:1px solid red;">
<span>
<strong id=”greed” style="position:relative;">greed is</strong>
good 999999
</span>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
包含块关系表:
| 元素 | 包含块 |
|---|---|
| table1 | body |
| td1 | table1 |
| div1 | td1 |
| greed | div1 |
SPAN 元素中包含的文本在 div1 中的位置可以看出,div1 创建的包含块的区域是它的内容边界,也就是内边界。
固定定位元素
如果元素是固定定位 ("position:fixed") 元素,那么它的包含块是当前可视窗口2。
绝对定位元素
总的来说,绝对定位("position: absolute")元素的包含块由离它最近的 'position' 属性为 'absolute'、'relative' 或者 'fixed' 的祖先元素创建。(只要不是static)
如果其祖先元素是行内元素,则包含块取决于其祖先元素的 'direction' 特性
1). 如果 'direction' 是 'ltr',包含块的顶、左边是祖先元素生成的第一个框的顶、左内边距边界(padding edges) ,右、下边是祖先元素生成的最后一个框的右、下内边距边界(padding edges)
css包含块containing block的更多相关文章
- CSS包含块containing block详解
“包含块(containing block)”,W3c中一个很重要的概念,今天带大家一起来好好研究下. 初步理解 在 CSS2.1 中,很多框的定位和尺寸的计算,都取决于一个矩形的边界,这个矩形,被称 ...
- css中margin重叠和一些相关概念(包含块containing block、块级格式化上下文BFC、不可替换元素 non-replaced element、匿名盒Anonymous boxes )
平时在工作中,总是有一些元素之间的边距与设定的边距好像不一致的情况,一直没明白为什么,最近仔细研究了一下,发现里面有学问:垂直元素之间的margin有有互相重叠的情况:新建一个BFC后,会阻止元素与外 ...
- 包含块( Containing block ) 转自W3CHelp
包含块简介 在 CSS2.1 中,很多框的定位和尺寸的计算,都取决于一个矩形的边界,这个矩形,被称作是包含块( containing block ). 一般来说,(元素)生成的框会扮演它子孙元素包含块 ...
- CSS学习笔记——包含块 containing block
以下内容翻译自CSS 2.1官方文档.网址:https://www.w3.org/TR/CSS2/visudet.html#strut 有时,一个元素的盒子的位置和尺寸根据一个确定的矩形计算,这个确定 ...
- (转自MDN)CSS基础一定要看的包含块(containing block)
之前在写<个人常用的水平居中方法>这篇文章的时候,百分比问题涉及到了包含块(containing block)这个概念. 今天刷面试题的时候,又看到了containing block这个词 ...
- CSS中包含块原理解析
CSS包含块原理解析 确定CSS中的包含块也确定就是元素的父元素.关键是:看元素是如何定位的.确定包含块很重要,比如设置百分比.另外也可以进行样式的继承等等. 分两个情况: 相对定位和静态定位 静态定 ...
- CSS2.1SPEC:视觉格式化模型之包含块
原汁原味的才是最有味道的,在阅读CSS标准时对这一点的体会更加深刻了,阅读文档后的一大感觉就是很多看上去理所应当的样式表现也都有了对应的支持机制.本文首先从包含块写起,一方面总结标准中相应的阐述,并且 ...
- 转: Firefox 浏览器对 TABLE 中绝对定位元素包含块的判定有错误
标准参考 元素的包含块 W3C CSS2.1 规范中规定,绝对定位元素的包含块(containing block),由离它最近的 position 特性值是 "absolute". ...
- 由position属性引申的关于css的进阶讨论(包含块、BFC、margin collapse)
写这篇文章的起因是源于这篇文章:谈谈面试与面试题 中关于position的讨论,文中一开始就说的这句话: 面试的时候问个css的position属性能刷掉一半的人这是啥情况…… 其实这问题我本来打算的 ...
随机推荐
- 【codevs】2776寻找代表元
题目描述 Description 广州二中苏元实验学校一共有n个社团,分别用1到n编号.广州二中苏元实验学校一共有m个人,分别用1到m编号.每个人可以参加一个或多个社团,也可以不参加任何社团.每个社团 ...
- Python核心编程读笔 5: python的序列
第六章 序列:字符串.列表.元组 一.序列 (1)序列类型操作符 seq[ind] 获得下标为 ind 的元素 seq[ind1:ind2] 切片操作 seq * expr 序列重复 expr 次 s ...
- EassyMock实践 自定义参数匹配器
虽然easymock中提供了大量的方法来进行参数匹配,但是对于一些特殊场合比如参数是复杂对象而又不能简单的通过equals()方法来比较,这些现有的参数匹配器就无能为力了.easymock为此提供了I ...
- Linux学习之sed命令详解
概述 sed是stream editor的简称,也就是流编辑器.它一次处理一行内容,处理时,把当前处理的行存储在临时缓冲区中,称为“模式空间”(pattern space),接着用sed命令处理缓冲区 ...
- C#时间日期操作
一.C# 日期格式 DateTime dt = DateTime.Now; dt.ToString();//2005-11-5 13:21:25 dt.ToFileTime().ToString() ...
- PHP利用递归法获取多级类别的树状数组
数据结构:category(id, pid, name),对应:信息ID,父项ID,类别名 测试数据: $aryCate = array( array('id' => 1, 'pid' => ...
- codeforces 645C . Enduring Exodus 三分
题目链接 我们将所有为0的位置的下标存起来. 然后我们枚举左端点i, 那么i+k就是右端点. 然后我们三分John的位置, 找到下标为i时的最小值. 复杂度 $ O(nlogn) $ #include ...
- 计算机原理学习(2)-- 存储器和I/O设备和总线
前言 前一篇文章介绍了冯诺依曼体系结构的计算机的基本工作原理,其中主要介绍了CPU的结构和工作原理.这一篇主要来介绍存储区,总线,以及IO设备等其他几大组件,来了解整个计算机是如何工作的. 这些东西都 ...
- linux 获取文件系统信息(磁盘信息)
源代码例如以下: #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <s ...
- Ext.Net 使用总结之GridPanel的删除事件
1.关于Ext.net中GridPanel的删除事件 首先是GridPanel,如下: <ext:GridPanel ID="GridPanel1" runat=" ...
