Spring Environment(一)API 介绍
Spring Environment(一)API 使用
Spring 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10198698.html)
Spring 3.1 提供了新的属性管理 API,而且功能非常强大且很完善,对于一些属性配置信息都应该使用新的 API 来管理。位于 org.springframework.core.env 包内。
Spring Environment 属性配置管理系列文章:
一、新的属性管理 API
PropertySource:属性源,key-value 属性对抽象,比如用于配置数据PropertyResolver:属性解析器,用于解析相应 key 的 valueEnvironment:环境,本身是一个 PropertyResolver,但是提供了 Profile 特性,即可以根据环境得到相应数据(即激活不同的 Profile,可以得到不同的属性数据,比如用于多环境场景的配置(正式机、测试机、开发机 DataSource 配置)Profile:剖面,只有激活的剖面的组件/配置才会注册到 Spring 容器,类似于 maven 中 profile
也就是说,新的 API 主要从配置属性、解析属性、不同环境解析不同的属性、激活哪些组件/配置进行注册这几个方面进行了重新设计,使得 API 的目的更加清晰,而且功能更加强大。
@Test
public void test() {
Environment env = new StandardEnvironment();
// 1. 操作系统的环境变量
Map<String, Object> systemEnvironment = ((StandardEnvironment) env).getSystemEnvironment();
Assert.assertNotNull(systemEnvironment);
// 2. JVM 属性配置
Map<String, Object> systemProperties = ((StandardEnvironment) env).getSystemProperties();
Assert.assertNotNull(systemProperties);
// 3. 属性
Assert.assertEquals("UTF-8", env.getProperty("file.encoding"));
Assert.assertTrue(env.containsProperty("file.encoding"));
// 4. 剖面 spring.profiles.default(默认为 default) spring.profiles.active
// 只要有一个返回 true acceptsProfiles 方法就返回 true,!a 为不包含该 profiles
Assert.assertTrue(env.acceptsProfiles("default"));
Assert.assertTrue(env.acceptsProfiles("a", "default"));
Assert.assertFalse(env.acceptsProfiles("a"));
Assert.assertTrue(env.acceptsProfiles("!a", "b"));
}
二、PropertySource
public abstract class PropertySource<T> {
// 给数据源起个名称
protected final String name;
// 数据源,可能为 Map 或 Properties ...
protected final T source;
public boolean containsProperty(String name) {
return (getProperty(name) != null);
}
public abstract Object getProperty(String name);
}
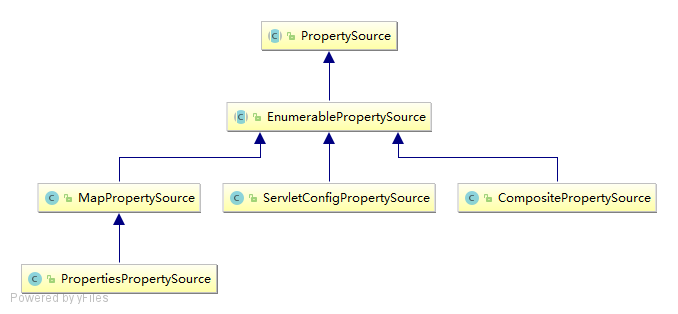
PropertySource 非常类似于 Map,数据源可来自 Map、Properties、Resource 等。PropertySource 接口有两个特殊的子类:StubPropertySource 用于占位用,ComparisonPropertySource 用于集合排序,不允许获取属性值。
2.1 PropertySource 实现类
MapPropertySource 的属性来自于一个 Map,而 ResourcePropertySource 的属性来自于一个 properties 文件,另外还有如 PropertiesPropertySource,其属性来自 Properties,ServletContextPropertySource 的属性来自 ServletContext 上下文初始化参数等等,大家可以查找 PropertySource 的继承层次查找相应实现。
@Test
public void PropertySourceTest() throws IOException {
PropertySource mapPropertySource = new MapPropertySource("map",
Collections.singletonMap("key", "source1"));
Assert.assertEquals("value1", mapPropertySource.getProperty("key"));
ResourcePropertySource resourcePropertySource = new ResourcePropertySource(
"resource", "classpath:resources.properties");
Assert.assertEquals("value2", resourcePropertySource.getProperty("key"));
}
2.2 CompositePropertySource
CompositePropertySource 提供了组合 PropertySource 的功能,查找顺序就是注册顺序。
@Test
public void CompositePropertySourceTest() throws IOException {
PropertySource propertySource1 = new MapPropertySource("source1",
Collections.singletonMap("key", "value1"));
PropertySource propertySource2 = new MapPropertySource("source2",
Collections.singletonMap("key", "value2"));
CompositePropertySource compositePropertySource = new CompositePropertySource("composite");
compositePropertySource.addPropertySource(propertySource1);
compositePropertySource.addPropertySource(propertySource2);
Assert.assertEquals("value1", compositePropertySource.getProperty("key"));
}
2.3 PropertySources
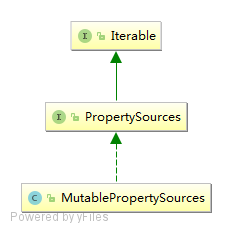
另外还有一个 PropertySources,从名字可以看出其包含多个 PropertySource。默认提供了一个 MutablePropertySources 实现,可以调用 addFirst 添加到列表的开头,addLast 添加到末尾,另外可以通过 addBefore(propertySourceName, propertySource) 或 addAfter(propertySourceName, propertySource) 添加到某个 propertySource 前面/后面;最后大家可以通过 iterator 迭代它,然后按照顺序获取属性。
注意:PropertySource 的顺序非常重要,因为 Spring 只要读到属性值就返回。
@Test
public void PropertySourcesTest() throws IOException {
PropertySource propertySource1 = new MapPropertySource("source1",
Collections.singletonMap("key", "value1"));
PropertySource propertySource2 = new MapPropertySource("source2",
Collections.singletonMap("key", "value2"));
MutablePropertySources propertySources = new MutablePropertySources();
propertySources.addFirst(propertySource1);
propertySources.addLast(propertySource2);
Assert.assertEquals("value1", propertySources.get("source1").getProperty("key"));
Assert.assertEquals("value2", propertySources.get("source2").getProperty("key"));
}
到目前我们已经有属性了,接下来需要更好的 API 来解析属性了。
三、PropertyResolver
PropertyResolver 的使用参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10284826.html
四、Environment
Environment 是对 JDK 环境、Servlet 环境、Spring 环境的抽象;每个环境都有自己的配置数据,如 System.getProperties()、System.getenv() 等可以拿到 JDK 环境数据;ServletContext.getInitParameter()可以拿到 Servlet 环境配置数据等等;也就是说 Spring 抽象了一个 Environment 来表示环境配置。
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
String[] getActiveProfiles();
String[] getDefaultProfiles();
// @since 5.1 废弃,改用 Profiles(Profiles.of("dev"))
@Deprecated
boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles);
boolean acceptsProfiles(Profiles profiles);
}
从 API 上可以看出,除了可以解析相应的属性信息外,还提供了剖面相关的 API。目的是:可以根据剖面有选择的进行注册组件/配置。比如对于不同的环境注册不同的组件/配置(正式机、测试机、开发机等的数据源配置)。它的主要几个实现如下所示:
MockEnvironment:模拟的环境,用于测试时使用;StandardEnvironment:标准环境,普通 Java 应用时使用,会自动注册 System.getProperties() 和 System.getenv()到环境;StandardServletEnvironment:标准 Servlet 环境,其继承了 StandardEnvironment,Web 应用时使用,除了 StandardEnvironment 外,会自动注册 ServletConfig(DispatcherServlet)、ServletContext 及 JNDI 实例到环境;
4.1 web.xml 配置 Servlet 属性
<context-param>
<param-name>myConfig</param-name>
<param-value>hello</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>spring</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
使用 StandardServletEnvironment 加载时,默认除了 StandardEnvironment 的两个属性外,还有另外三个属性:servletContextInitParams(ServletContext)、servletConfigInitParams(ServletConfig)、jndiProperties(JNDI)。
4.2 Environment 获取
(1) 注解
@Autowired
Environment env;
(2) ApplicationContext
applicationContext.getEnvironment();
五、Profile
profile 剖面,大体意思是:我们程序可能从某几个剖面来执行应用,比如正式机环境、测试机环境、开发机环境等,每个剖面的配置可能不一样(比如开发机可能使用本地的数据库测试,正式机使用正式机的数据库测试)等;因此呢,就需要根据不同的环境选择不同的配置;如果 maven 中的 profile 的概念。
profile 有两种:
- 默认的:通过 "spring.profiles.default" 属性获取,如果没有配置默认值是 "default"
- 明确激活的:通过 "spring.profiles.active" 获取
查找顺序是:先进性明确激活的匹配,如果没有指定明确激活的(即集合为空)就找默认的;配置属性值从 Environment 读取。
profile 设置方式常见的有三种:
(1) -D 传入系统参数
-Dspring.profiles.active=dev
(2) web 环境
<context-param>
<param-name>spring.profiles.active</param-name>
<param-value>dev</param-value>
</context-param>
(3) xml 配置
通过在 beans 标签上加上 profile 属性,这样当我们激活相应的 profile 时,此 beans 标签下的 bean 就会注册,如下所示:
<beans>
<beans profile="dev">
<bean id="dataSource" class="...">
</bean>
</beans>
<beans profile="test">
<bean id="dataSource" class="...">
</bean>
</beans>
</beans>
启动应用时设置相应的 "spring.profiles.active" 即可。另外,如果想指定一个默认的,可以使用 指定(如果不是 default,可以通过 "spring.profiles.default" 指定)。
(4) 注解配置
Java Config 方式的 Profile,功能等价于 XML 中的 ,使用方式如下:
@Profile("dev")
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:resources.properties", ignoreResourceNotFound = false)
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer() {
return new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
}
}
Spring4 提供了一个新的 @Conditional 注解,请参考 http://jinnianshilongnian.iteye.com/blog/1989379
(5) @ActiveProfiles()
在测试时,有时候不能通过系统启动参数/上下文参数等指定 Profile,此时 Spring 测试框架提供了 @ActiveProfiles() 注解,示例如下:
@ActiveProfiles("test")
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = GenericConfig.class)
public class GenricInjectTest {
}
到此整个 Spring 的属性管理 API 就介绍完了,对于属性管理,核心是 Environment。
参考:
- 《pring3.1新属性管理API:PropertySource、Environment、Profile》:https://jinnianshilongnian.iteye.com/blog/2000183
每天用心记录一点点。内容也许不重要,但习惯很重要!
Spring Environment(一)API 介绍的更多相关文章
- Spring入门篇——第6章 Spring AOP的API介绍
第6章 Spring AOP的API介绍 主要介绍Spring AOP中常用的API. 6-1 Spring AOP API的Pointcut.advice概念及应用 映射方法是sa开头的所有方法 如 ...
- Spring PropertyResolver 占位符解析(一)API 介绍
Spring PropertyResolver 占位符解析(一)API 介绍 Spring 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10198698.html ...
- Spring Boot 2.x 编写 RESTful API (一) RESTful API 介绍 & RestController
用Spring Boot编写RESTful API 学习笔记 RESTful API 介绍 REST 是 Representational State Transfer 的缩写 所有的东西都是资源,所 ...
- Spring Environment(二)源码分析
Spring Environment(二)源码分析 Spring 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10198698.html) Spring Envi ...
- Spring Environment(三)生命周期
Spring Environment(三)生命周期 Spring 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10198698.html) Spring Envi ...
- Spring Data REST API集成Springfox、Swagger
原文: Documenting a Spring Data REST API with Springfox and Swagger 使用Spring Date REST,你可以迅速为Spring Da ...
- MyBatis 强大之处 多环境 多数据源 ResultMap 的设计思想是 缓存算法 跨数据库 spring boot rest api mybaits limit 传参
总结: 1.mybaits配置工2方面: i行为配置,如数据源的实现是否利用池pool的概念(POOLED – This implementation of DataSource pools JDBC ...
- 使用 JSONDoc 记录 Spring Boot RESTful API
这个博文可以分为两部分:第一部分我将编写一个Spring Boot RESTful API,第二部分将介绍如何使用JSONDoc来记录创建的API.做这两个部分最多需要15分钟,因为使用Spring ...
- Spring Cloud Alibaba-MyShop-项目介绍
本节视频 [视频]Spring Cloud Alibaba-MyShop-项目介绍 开发环境 操作系统:Windows 10 Enterprise 开发工具:Intellij IDEA 数据库:MyS ...
随机推荐
- 05_ssm基础(四)之Spring基础二
24.spring配置dbcp并完成CRUD操作 1.准备jar包 2.编辑Product模型 package com.day02.ssm.spring.model; public class Pro ...
- Linux命令_1
文件和目录命令 从P19开始的笔记 目标 查看目录内容 ls 切换目录 cd 创建和删除操作 touch mkdir rm 拷贝和移动文件 cp mv 查看文件内容 cat more grep 其他 ...
- putty加了密钥ssh不能登陆,PuTTY:server refused our key问题的解决(转)
直接上方法:禁用系统的selinux功能,命令#setenforce0,但重启系统,selinux仍然启用.根治方法:更改SElinux的配置文件/etc/selinux/config,修改SELIN ...
- StringBuffer类和String类(原文地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/springcsc/archive/2009/12/03/1616330.html)
StringBuffer类和String一样,也用来代表字符串,只是由于StringBuffer的内部实现方式和String不同,所以StringBuffer在进行字符串处理时,不生成新的对象,在内存 ...
- jumpserver-1.4.0.2
关闭防火墙和selinux IP:192.168.199.115 一. 准备 Python3 和 Python 虚拟环境 yum -y install wget sqlite-devel xz gcc ...
- JavaScript各种继承方式(一):原型链继承(prototype chaining)
一 原理 子类的构造函数的原型对象,是父类的构造函数创建的实例. function Fruit(){ this.name = '水果'; this.nutrition=['维生素','膳食纤维']; ...
- [剑指Offer]6-从尾到头打印链表
典型的后进先出,可以借助栈,也可以使用递归. 考虑到若链表过长递归可能造成函数调用栈溢出,所以使用栈更好. 注意stack无遍历操作,全部用push(),pop(),top()完成. 以下创建列表胡乱 ...
- day 12 内置函数,装饰器,递归函数
内置函数 内置函数:python给咱们提供了一些他认为你会经常用到的函数,68种 内置函数 abs() dict() help() min() setattr() all() di ...
- 13-linux定时任务不起作用到的问题解决办法
基本操作下面这篇: centos定时任务-不起作用- 没指明路径!!! 最大的问题是路径问题,以及权限问题. 用定时任务执行某些脚本是出现一系列问题,一步一步解决. 问题一:定时任务没反应: 查看日志 ...
- python requests的content和text方法的区别(转)
原文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/xie_0723/article/details/51361006 问题: 一直在想requests的content和text属性的区别,从pri ...
