java基础 -IO流笔记
610,文件的基础知识
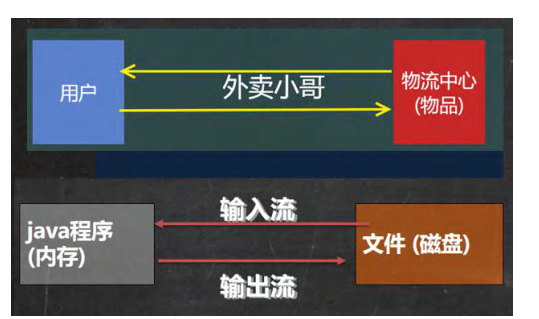
文件流

输入流和输出流都是相对 java程序内存 而言
611,创建文件

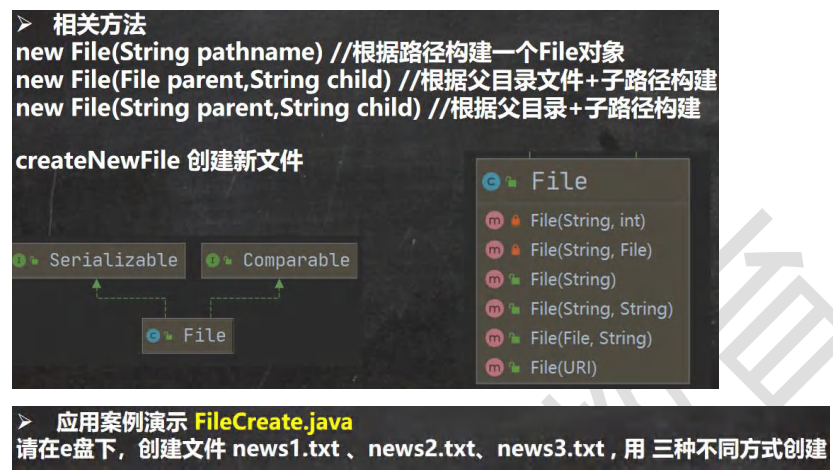
在D盘下创建文件。
package com.hspedu.file; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException; //演示创建文件
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) { } @Test
//方式 1 new File(String pathname)
public void create01() throws IOException {
String filePath = "d:\\news1.txt"; // 路径写 \\,或者, /
File file = new File(filePath);
//只有执行了 createNewFile 方法, 才会真正的, 在磁盘创建该文件
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件1创建成功");
} @Test
//方式 2 new File(File parent,String child) //根据父目录文件+子路径构建
public void create02() throws IOException {
//这里的 file 对象, 在 java 程序中, 只是一个对象
File parentFile = new File("d:\\");
String fileName = "news2.txt";
File file = new File(parentFile, fileName);
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件2创建成功");
} @Test
//方式 3 new File(String parent,String child) //根据父目录+子路径构建
public void create03() throws IOException {
String parentPath = "d:\\";
String fileName = "news3.txt";
File file = new File(parentPath, fileName);
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件3创建成功");
}
}
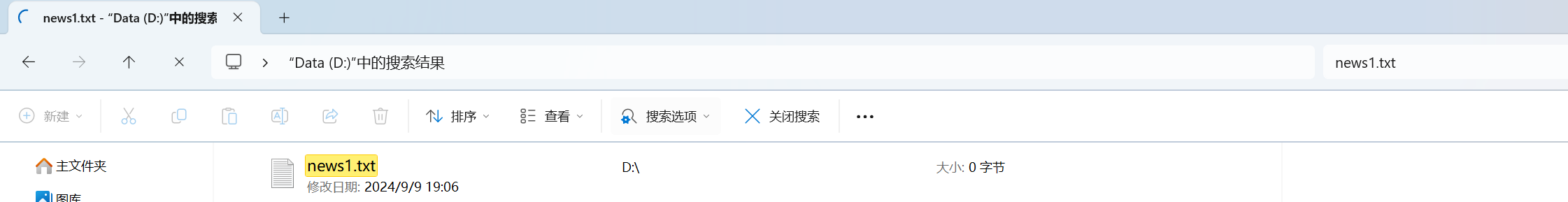
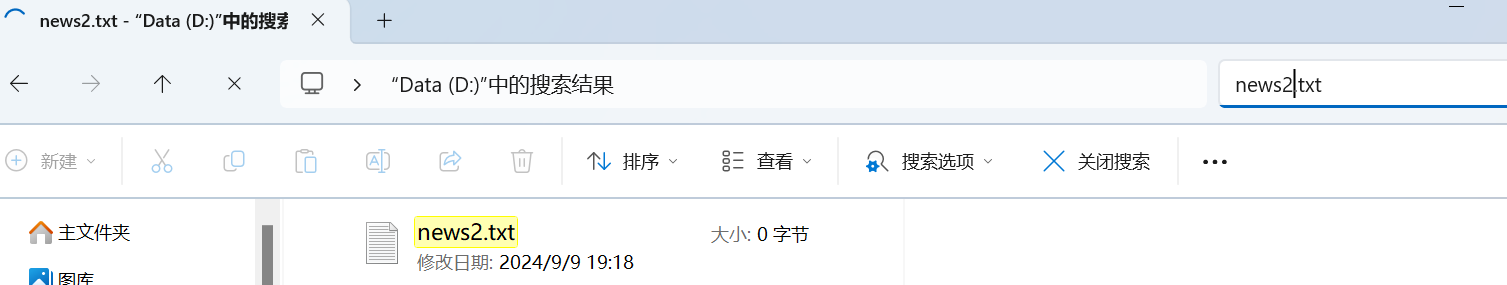
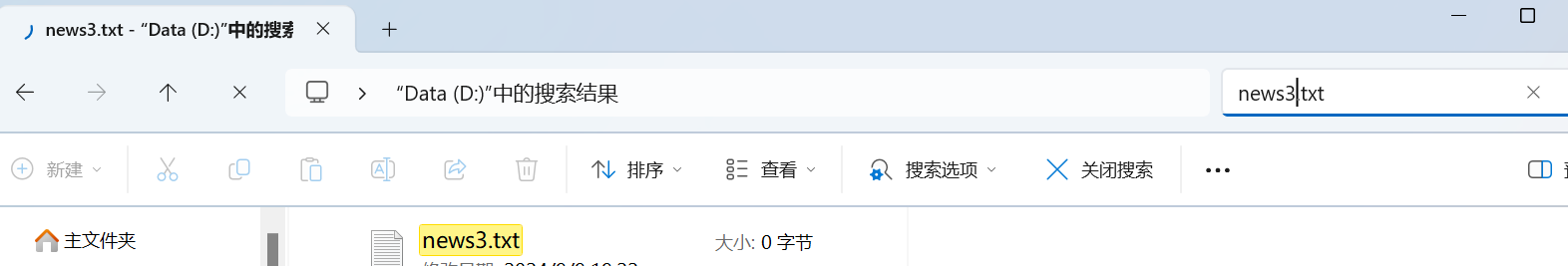
612,获取文件信息
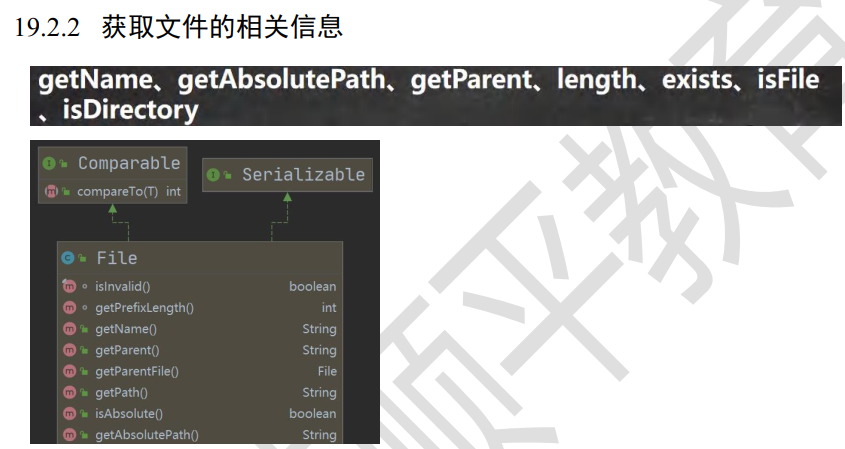

给news1.txt 里写了 hello韩顺平 ,UTF-8编码,一个英文字符占1个字节,一个汉字占3个字节。
package com.hspedu.file; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException; //演示创建文件
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) { } @Test
public void info() {
//先创建文件对象
File file = new File("d:\\news1.txt"); //调用相应的方法, 得到对应信息
//getName、 getAbsolutePath、 getParent、 length、 exists、 isFile、 isDirectory System.out.println("文件名字=" + file.getName());
System.out.println("文件绝对路径=" + file.getAbsoluteFile());
System.out.println("文件父级目录=" + file.getParent());
System.out.println("文件大小(字节)=" + file.length());
System.out.println("文件是否存在=" + file.exists());
System.out.println("是不是一个文件=" + file.isFile());
System.out.println("是不是一个目录=" + file.isDirectory());
} }

613,目录操作

第1个案例代码写出来后,第2个只需把 filePath 改了就行,所以就不写第2个案例代码了。
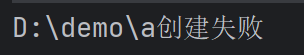
第3个案例,因为D:\\demo\\a 是多级目录,mkdir只能创建一级目录,所以用mkdir 创建失败,
package com.hspedu.file; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException; //演示创建文件
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) { } @Test
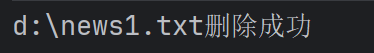
public void m1() {
String filePath = "d:\\news1.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
if (file.exists()) {
//调用delete()方法来删除文件,并通过返回值判断删除操作是否成功。
if(file.delete()) {
System.out.println(filePath + "删除成功");
} else {
System.out.println(filePath + "删除失败");
}
} else {
System.out.println("该文件不存在...");
}
} @Test
public void m2() {
String directoryPath = "D:\\demo\\a";
File file = new File(directoryPath);
if(file.exists()) {
System.out.println(directoryPath + "存在");
} else {
if(file.mkdir()) {
System.out.println(directoryPath + "创建成功");
} else {
System.out.println(directoryPath + "创建失败");
}
}
} }
614,IO流原理和分类
1,原理:

2,流的分类

615,FileInputStream


我们先在D盘创建一个hello.txt文件,里面内容为 hello,world
package com.hspedu.file; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException; //演示 FileInputStream 的使用(字节输入流 文件--> 程序)
public class FileInputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) { } /*
* 演示读取文件...
* 单个字节的读取, 效率比较低
* -> 优化:使用 read(byte[] b),见readFile02函数中
*/
@Test
public void readFile01() throws IOException {
String filePath = "d:\\hello.txt";
int readData = 0; //创建 FileInputStream 对象, 用于读取 文件
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath); //read():从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。 如果没有输入可用, 此方法将阻止。返回值是int类型
//如果返回-1 , 表示读取完毕
while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)readData);//把int转成char显示
} //关闭文件流, 释放资源
fileInputStream.close();
} /*
* 使用 read(byte[] b) 读取文件, 提高效率
*/
@Test
public void readFile02() throws IOException {
String filePath = "d:\\hello.txt"; //字节数组
byte[] buf = new byte[8];//一次读取8个字节 int readLenth = 0;
//创建 FileInputStream 对象, 用于读取 文件
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath); //read(byte[] b):从该输入流读取最多 b.length 字节的数据到字节数组。 此方法将阻塞,直到某些输入可用。
//如果返回-1 , 表示读取完毕
//如果读取正常, 返回实际读取的字节数
while ((readLenth = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, readLenth));//把每个字节数组的返回值转成String显示
} //关闭文件流, 释放资源
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
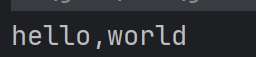
616,FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream 是 字节输出流 OutputStream 的子类

自动创建文件的,没有使用mkdir()
package com.hspedu.file; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import java.io.*; //演示 FileInputStream 的使用(字节输入流 文件--> 程序)
public class FileOutputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) { } /*
* 演示使用 FileOutputStream 将数据写到文件中,
* 如果该文件不存在, 则创建该文件
*/
@Test
public void writeFile() throws IOException {
String filePath = "d:\\a.txt"; //创建 FileOutputStream 对象
//1. new FileOutputStream(filePath) 创建方式, 当写入内容是, 会覆盖原来的内容
//2. new FileOutputStream(filePath, true) 创建方式, 当写入内容是, 是追加到文件后面
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath, true); //从内存写出一个字节到 d:\\a.txt
// fileOutputStream.write('H'); //从内存写出字符串到 d:\\a.txt
//str.getBytes() 可以把 字符串-> 字节数组
String str = " hello,world";
// fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes()); //write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将 len 字节从位于偏移量 off 的指定字节数组写入此文件输出流
String str1 = " hsp";
fileOutputStream.write(str1.getBytes(), 0, str1.length()); fileOutputStream.close();
} }
617,文件拷贝

有的文件太大了,不能一次性读入到内存中去,所以是读取部分数据
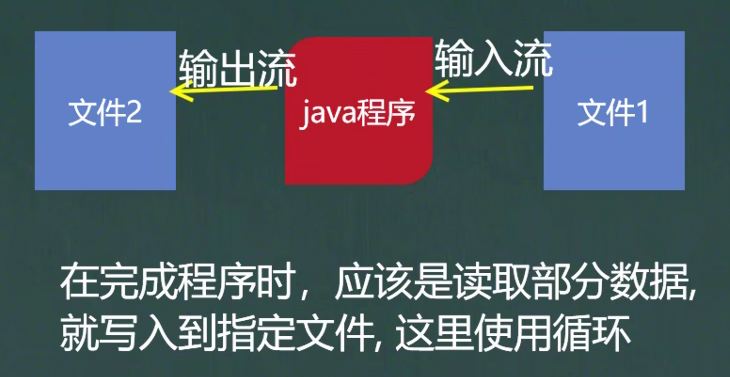
package com.hspedu.file;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.*;
public class FileCopy_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//完成 文件拷贝, 将 d:\图片\4.jpg 拷贝 d:\
//思路分析
//1. 创建文件的输入流 , 将文件读入到程序
//2. 创建文件的输出流, 将读取到的文件数据, 写入到指定的文件
String srcFilePath = "d:\\图片\\4.jpg";
String destFilePath = "d:\\4.jpg";//4.jpg不能忘了
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(srcFilePath);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(destFilePath);
//定义一个字节数组,提高读取效果
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int readLength = 0;
while((readLength = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {
//读取到后, 就写入到文件 通过 fileOutputStream
//即, 一边读, 一边写
fileOutputStream.write(buf, 0, readLength);//一定要使用这个方法
}
System.out.println("拷贝成功");
//关闭输入流和输出流, 释放资源
if (fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
}

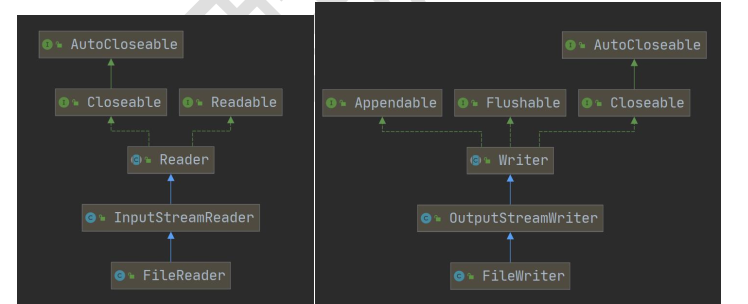
618,文件字符流说明
Reader 和 Writer 是字符流,FileReader 和 FileWriter 是它们的子类

619,FileReader

先在D盘新建一个story.txt,并在里面写内容
package com.hspedu.file;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.*;
public class FileReader_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/*
* 单个字符读取文件
*/
@Test
public void readFile01() throws IOException {
String filePath = "d:\\story.txt";
int data = 0;
//1. 创建 FileReader 对象
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
//循环读取 使用 read, 单个字符读取
while ((data = fileReader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) data);
}
if (fileReader != null) {
fileReader.close();
}
}
/*
* 字符数组读取文件
*/
@Test
public void readFile02() throws IOException {
String filePath = "d:\\story.txt";
int readLength = 0;
char[] buf = new char[8];
//1. 创建 FileReader 对象
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
//循环读取 使用 read(buf), 返回的是实际读取到的字符数
//如果返回-1, 说明到文件结束
while ((readLength = fileReader.read(buf)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, readLength));
}
if (fileReader != null) {
fileReader.close();
}
}
}
620,FileWriter

package com.hspedu.file;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.*;
public class FileWriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "d:\\note.txt";
//创建 FileWriter 对象
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath);//默认是覆盖写入
//write(int):写入单个字符
fileWriter.write('H');
//write(char[]):写入指定数组
char[] chars = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
fileWriter.write(chars);
//write(char[],off,len):写入指定数组的指定部分
fileWriter.write("韩顺平教育".toCharArray(), 0, 3);
//write(string) : 写入整个字符串
fileWriter.write(" 风雨之后, 定见彩虹");
//write(string,off,len):写入字符串的指定部分
fileWriter.write("上海天津", 0, 2);
//在数据量大的情况下, 可以使用循环操作
//对应 FileWriter , 一定要关闭流, 或者 flush 才能真正的把数据写入到文件
fileWriter.close();
}
}
622,处理流设计模式


模拟修饰器设计模式,代码结构如下图:
Reader_ 类:,后面在调用时,利用对象动态绑定机制,绑定到对应的实现子类即可
package com.hspedu.file;
public abstract class Reader_ {//抽象类
public void readFile() {}
public void readString() {}
}
FileReader_ 类代码:
package com.hspedu.file; //节点流
public class FileReader_ extends Reader_{
public void readFile() {
System.out.println("对文件进行读取...");
}
}
StringReader_ 类代码:
package com.hspedu.file; //节点流
public class StringReader_ extends Reader_{
public void readString() {
System.out.println("读取字符串");
}
}
BufferedReader_ 类代码:
package com.hspedu.file; //做成处理流/包装流
public class BufferedReader_ extends Reader_{
private Reader_ reader_;//属性是 Reader_ 类型 //接收Reader_ 子类对象
public BufferedReader_(Reader_ reader_) {
this.reader_ = reader_;
} //让方法更加灵活,多次读取文件,或者加缓冲char[]
public void readFiles(int num) {
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
reader_.readFile();
}
} //扩展 readString,批量处理字符串数据
public void readStrings(int num) {
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
reader_.readString();
}
}
}
Test_ 类代码:
package com.hspedu.file;
public class Test_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader_ bufferedReader = new BufferedReader_(new FileReader_());
bufferedReader.readFiles(3);
//这次希望通过 BufferedReader_ 多次读取字符串
BufferedReader_ bufferedReader1 = new BufferedReader_(new StringReader_());
bufferedReader1.readStrings(3);
}
}
运行结果:

623,BufferedReader
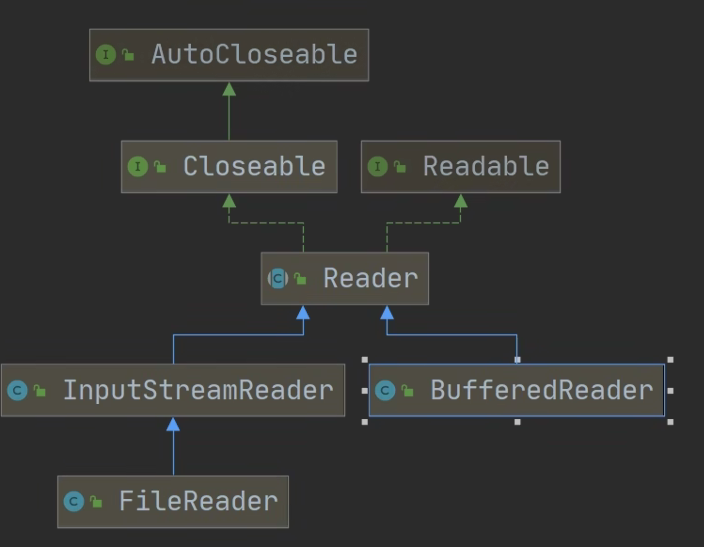

package com.hspedu.file; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException; //演示 bufferedReader 使用
public class BufferedReader_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "d:\\story.txt"; //创建 bufferedReader
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath)); //读取
String line;//按行读取, 效率高
//说明
//1. bufferedReader.readLine() 是按行读取文件
//2. 当返回 null 时, 表示文件读取完毕
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
} //关闭流, 这里注意, 只需要关闭 BufferedReader , 因为底层会自动的去关闭 节点流 FileReader。
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
624,BufferedWriter
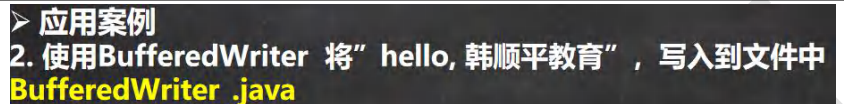
package com.hspedu.file; import java.io.*; //演示 BufferedWriter 的使用
public class BufferedWriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "d:\\story.txt"; //创建 bufferedWriter//说明:
//1. new FileWriter(filePath, true) 表示以追加的方式写入
//2. new FileWriter(filePath) , 表示以覆盖的方式写入
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filePath)); bufferedWriter.write("hello, 韩顺平教育");
bufferedWriter.newLine();//插入一个和系统相关的换行
bufferedWriter.write("hello, 韩顺平教育");
bufferedWriter.newLine(); //说明: 关闭外层流即可 , 传入的 new FileWriter(filePath) ,会在底层关闭
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}
625,Buffered拷贝

package com.hspedu.file;
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedCopy_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter 是安装字符操作
//2. 不要去操作 二进制文件[声音, 视频, doc, pdf ], 可能造成文件损坏
String srcFilePath = "d:\\story.txt";
String destFilePath = "d:\\1.txt";
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcFilePath));
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destFilePath));
String line;
//说明: readLine 读取一行内容, 但是没有换行
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
//每读取一行, 就写入
bufferedWriter.write(line);
//插入一个换行
bufferedWriter.newLine();
}
System.out.println("拷贝成功");
//关闭流
if(bufferedReader != null) {
bufferedReader.close();
}
if(bufferedWriter != null) {
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}
}
627,字节处理流拷贝文件
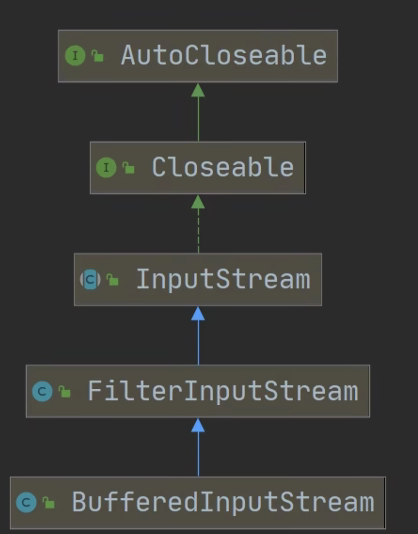
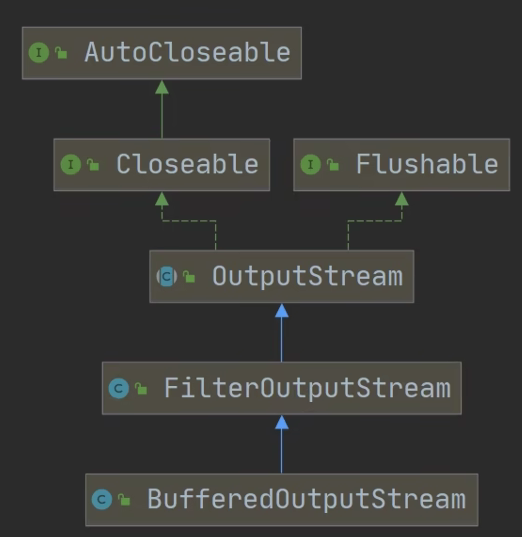

package com.hspedu.file; import java.io.*; /*
*演示使用 BufferedOutputStream 和 BufferedInputStream 使用
* 使用他们, 可以完成二进制文件拷贝.
* 思考: 字节流可以操作二进制文件, 可以操作文本文件吗? 当然可以
*/
public class BufferedCopy_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter 是安装字符操作
//2. 不要去操作 二进制文件[声音, 视频, doc, pdf ], 可能造成文件损坏
String srcFilePath = "d:\\图片\\4.jpg";
String destFilePath = "d:\\1.jpg"; //创建 BufferedOutputStream 对象 BufferedInputStream 对象
//因为 FileInputStream 是 InputStream 子类
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFilePath));
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFilePath)); //循环的读取文件,并写入到 destFilePath
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
int readLen = 0; //当返回 -1 时, 就表示文件读取完毕
while ((readLen = bufferedInputStream.read(buff)) != -1) {
bufferedOutputStream.write(buff, 0, readLen);
}
System.out.println("拷贝成功"); //关闭流 , 关闭外层的处理流即可, 底层会去关闭节点流
if(bufferedInputStream != null) {
bufferedInputStream.close();
}
if(bufferedOutputStream != null) {
bufferedOutputStream.close();
}
}
}
629,ObjectOutputStream
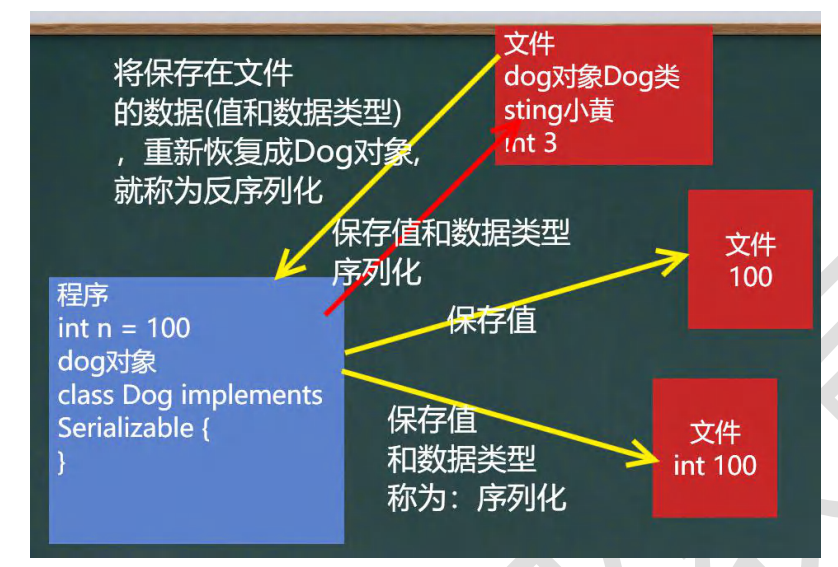
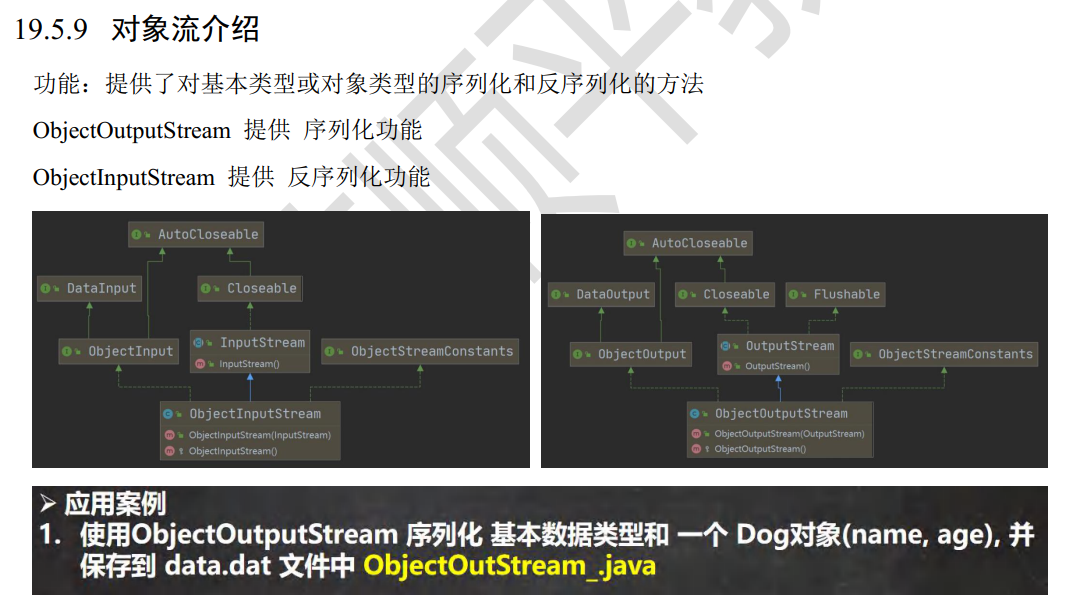
Dog 类
package com.hspedu.file;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Dog implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
ObjectOutputStream_ 类:
package com.hspedu.file; import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; //演示 ObjectOutputStream 的使用,完成数据的序列化
public class ObjectOutputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//序列化后,保存的文件格式不是纯文本的,而是按照它的格式来保存的
String filePath = "d:\\data.dat"; ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath));
//序列化数据到d:\data.dat
oos.writeInt(100);//int -> Integer(Integer实现了Serializable)
oos.writeBoolean(true);//boolean -> Boolean(Boolean实现了Serializable)
oos.writeChar('a');//char -> Character(Character实现了Serializable)
oos.writeDouble(9.6);//double -> Double(Double实现了Serializable)
oos.writeUTF("兔年顶呱呱");//String(String实现了Serializable)
//保存一个dog对象
oos.writeObject(new Dog("旺财", 10));
oos.close();
System.out.println("数据保存完毕(序列化形式)···");
}
}
630,ObjectInputStream

写本节代码时,不能把上一节代码删了,要保留,重新新建一个类,写本节代码。
ObjectInputStream_ 类:
package com.hspedu.file; import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream; //演示 ObjectInputStream 的使用,完成数据的反序列化
public class ObjectInputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//指定反序列化的文件
String filePath = "d:\\data.dat"; ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath)); //读取(反序列化)的顺序需要和保存数据(序列化)的顺序一致,否则会出现异常
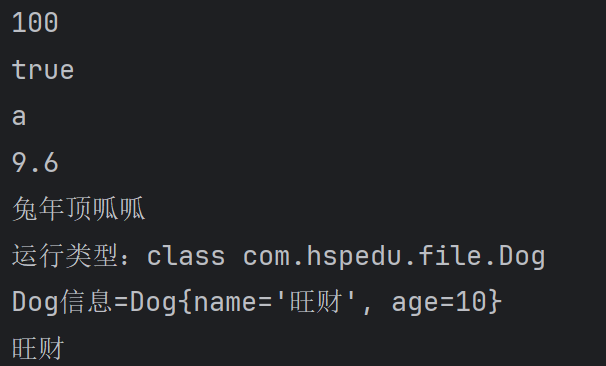
System.out.println(ois.readInt());
System.out.println(ois.readBoolean());
System.out.println(ois.readChar());
System.out.println(ois.readDouble());
System.out.println(ois.readUTF()); //dog的编译类型是Object,dog的运行类型是 Dog
Object dog = ois.readObject();
System.out.println("运行类型:" + dog.getClass());
System.out.println("Dog信息=" + dog);//底层 Object -> Dog //重要细节
//1.如果我们希望调用Dog的方法,需要向下转型
//2.需要我们将Dog类的定义,放在可以引用的位置
Dog dog2 = (Dog) dog;
System.out.println(dog2.getName());//只输出旺柴 //关闭流,关闭外层流即可,底层会自动关闭
ois.close();
}
}
632,标准输入输出流

package com.hspedu.file; import java.sql.SQLOutput;
import java.util.Scanner; public class InputAndOutput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//System 类 的 public final static InputStream in = null;
//System.in 编译类型 InputStream
//System.in 运行类型 BufferedInputStream
// 表示的是标准输入 键盘
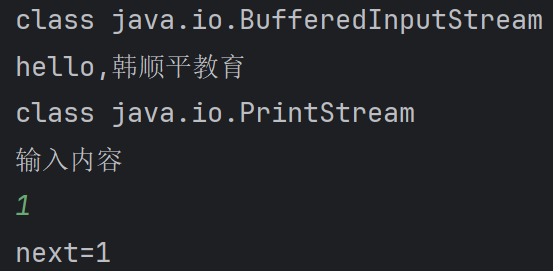
System.out.println(System.in.getClass());
System.out.println("hello,韩顺平教育");
System.out.println(System.out.getClass()); //1,System.out.public final static PrintStream out = null;
//2,编译类型 PrintStream
//3,运行类型 PrintStream
//4,表示标准输出 显示器
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入内容");
String next = scanner.next();
System.out.println("next=" + next);
}
}
633,乱码引出转换流

package com.hspedu.file; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.SQLOutput;
import java.util.Scanner; public class CodeQuestion {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//读取d:\\1.txt 文件到程序
//思路:
//1,创建字符输入流 BufferedReader[处理流]
//2,使用 BufferedReader 对象读取 a.txt
//3,默认情况下,读取文件时按照 utf-8 编码
String filePath = "d:\\1.txt";
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath)); String s = br.readLine();
System.out.println("读取到的内容:" + s);
br.close();
}
}
这是UTF-8的编码,输出结果:

这是改成国标码 ANSI,也就是gbk 码的输出结果:

634,InputStreamReader

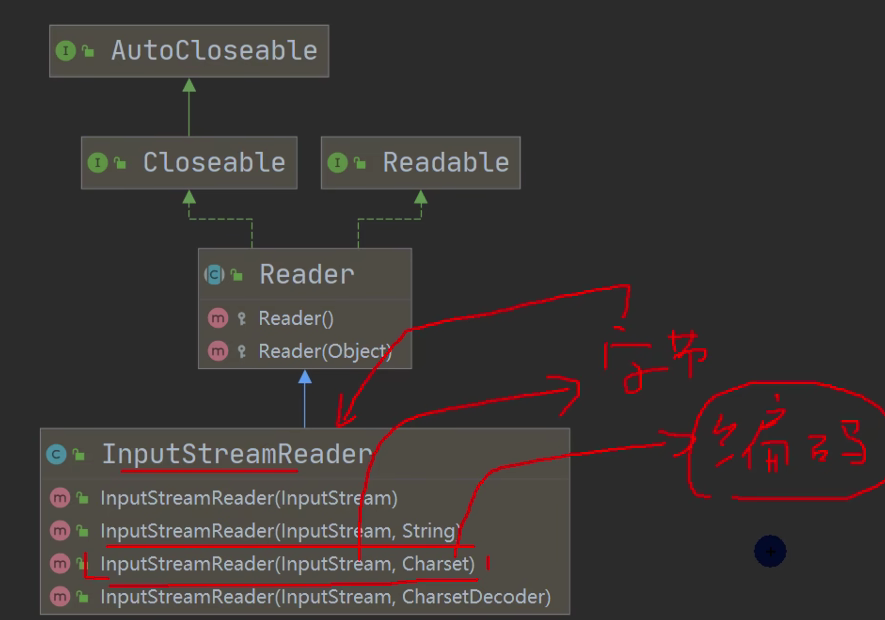
package com.hspedu.file; import java.io.*; //演示使用 InputStreamReader 转换流解决中文乱码问题
//* 将字节流 FileInputStream 转成字符流 InputStreamReader, 指定编码 gbk/utf-8
public class InputStreamReader_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "d:\\1.txt"; //1. 把 FileInputStream 转成 InputStreamReader
//2. 指定编码 gbk
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filePath), "gbk"); //3. 把 InputStreamReader 传入 BufferedReader
//将 2 和 3 合在一起
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
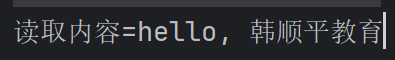
String s = br.readLine(); System.out.println("读取内容=" + s); //5. 关闭外层流
br.close(); }
}
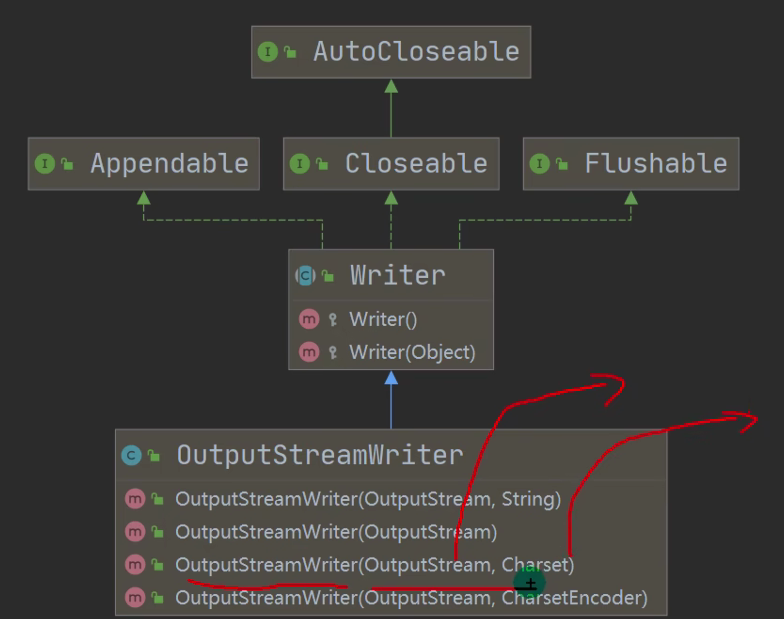
635,OutputStreamWriter

package com.hspedu.file; import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset; //演示使用 OutputStreamWriter 使用
//将字节流 FileOutputStream 转成字符流 OutputStreamWriter,
//指定处理的编码 gbk/utf-8/utf8
public class OutputStreamWriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "d:\\2.txt";
String charSet = "utf-8";
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(filePath), charSet);
osw.write("hi,韩顺平");
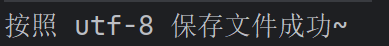
osw.close(); System.out.println("按照 " + charSet + " 保存文件成功~");
}
}
636,PrintStream, PrintStream
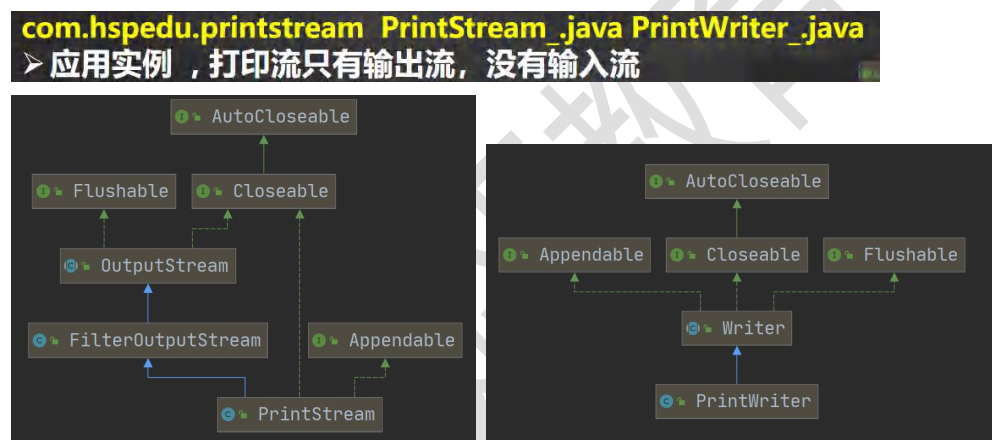
PrintStrean 字节打印流
package com.hspedu.file; import java.io.*; // 演示 PrintStream (字节打印流/输出流)
public class PrintStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { PrintStream out = System.out;
//在默认情况下, PrintStream 输出数据的位置是 标准输出, 即显示器
out.print("john, hello");
//因为 print 底层使用的是 write , 所以我们可以直接调用 write 进行打印/输出
out.write("韩顺平,你好".getBytes());
out.close(); //我们可以去修改打印流输出的位置/设备
//1. 输出修改成到 "e:\\f1.txt"
//2. "hello, 韩顺平教育~" 就会输出到 e:\f1.txt
System.setOut(new PrintStream("d:\\f1.txt"));
System.out.println("hello, 韩顺平教育~");
}
}
package com.hspedu.file; import java.io.*; //演示 PrintWriter 使用方式
public class PrintStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(System.out)
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("d:\\f2.txt"));
printWriter.print("hi, 北京你好~~~");
//flush + 关闭流, 才会将数据写入到文件..
printWriter.close();
}
}
638,配置文件引出Properties

用传统的方法
先在src 下创建一个 properties文件,文件名叫 mysql.properties
ip=192.168.100.100
user=root
pwd=12345
主文件代码:
注意 这个路径没有冒号
package com.hspedu.file.properties_; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException; public class Properties01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //读取 mysql.properties 文件, 并得到 ip, user 和 pwd
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\mysql.properties"));
String line = "";
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { //循环读取
String[] split = line.split("=");
//System.out.println(split[0] + "值是:" + split[1]); //如果我们要求指定的 ip 值
if("ip".equals(split[0])) {
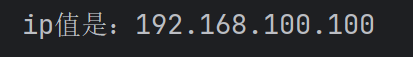
System.out.println(split[0] + "值是:" + split[1]);
}
}
br.close();
}
}
639,Properties读文件

package com.hspedu.file.properties_; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties; public class Properties01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//使用 Properties 类来读取 mysql.properties 文件
//1. 创建 Properties 对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
//2. 加载指定配置文件
properties.load(new FileReader("src\\mysql.properties"));
//3. 把 k-v 显示控制台
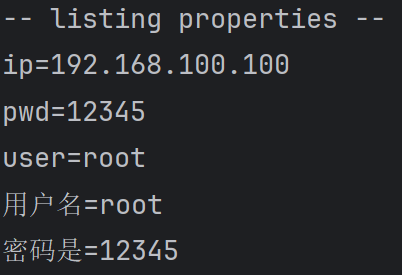
properties.list(System.out);
//4. 根据 key 获取对应的值
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String pwd = properties.getProperty("pwd");
System.out.println("用户名=" + user);
System.out.println("密码是=" + pwd);
}
}
640,Properties修改文件

package com.hspedu.file.properties_; import java.io.*;
import java.util.Properties; public class Properties01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//使用 Properties 类来创建 配置文件, 修改配置文件内容
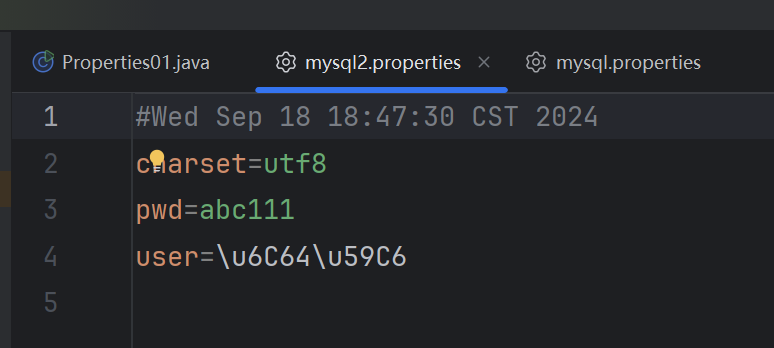
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("charset", "utf8");//注意保存时, 是中文的 unicode 码值
properties.setProperty("user", "汤姆");
properties.setProperty("pwd", "abc111");
//将 k-v 存储文件中即可
properties.store(new FileOutputStream("src\\mysql2.properties"), null);
System.out.println("保存配置文件成功~");
}
}

641,本章家庭作业01

package com.hspedu.file.homework; import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException; public class Homework01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String directoryPath = "d:\\mytemp";
File file = new File(directoryPath);
if (!file.exists()) {
//创建目录
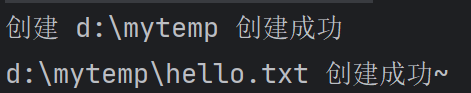
if(file.mkdirs()) {
System.out.println("创建 " + directoryPath + " 创建成功");
} else {
System.out.println("创建 " + directoryPath + " 创建失败");
}
} String filePath = directoryPath + "\\hello.txt"; // d:\mytemp\hello.txt
file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
//创建文件
if (file.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println(filePath + " 创建成功~"); //如果文件存在,我们就使用BufferedWriter 字符输入流写入内容
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
bufferedWriter.write("hello, world~~ 韩顺平教育");
bufferedWriter.close(); } else {
System.out.println(filePath + " 创建失败");
}
} else {
//如果文件已经存在,给出提示信息
System.out.println(filePath + " 已经存在,不存在重复创建...");
}
}
}
642,本章家庭作业02

package com.hspedu.file.homework;
import java.io.*;
public class Homework02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "d:\\story.txt";
BufferedReader br = null;
String line = "";
int lineNum = 0;
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath));
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {//循环读取
System.out.println(++lineNum + " " + line);
}
if (br != null) {
br.close();
}
}
}

643,本章家庭作业03

package com.hspedu.file.homework; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import java.io.*;
import java.util.Properties; public class Homework03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "src\\dog.properties";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileReader(filePath));
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
int age = Integer.parseInt(properties.getProperty("age"));// String -> int
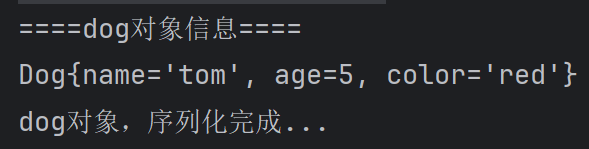
String color = properties.getProperty("color"); Dog dog = new Dog(name, age, color);
System.out.println("====dog对象信息====");
System.out.println(dog); //将创建的Dog对象,序列化到文件 d:dog.dat
String serFilePath = "d:\\dog.dat";
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(serFilePath));
oos.writeObject(dog); //关闭流
oos.close();
System.out.println("dog对象,序列化完成...");
} @Test
public void m1() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String serFilePath = "d:\\dog.dat";
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(serFilePath));
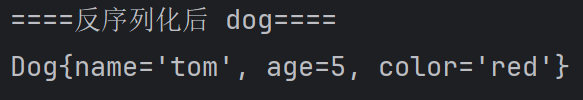
Dog dog = (Dog)ois.readObject(); System.out.println("====反序列化后 dog====");
System.out.println(dog); ois.close();
}
} class Dog implements Serializable{
private String name;
private int age;
private String color; public Dog(String name, int age, String color) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.color = color;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
运行 m1方法后的结果:
java基础 -IO流笔记的更多相关文章
- Java基础-IO流对象之字节流(Stream)
Java基础-IO流对象之字节流(Stream) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 在前面我分享的笔记中,我们一直都是在操作文件或者文件夹,并没有给文件中写任何数据.现 ...
- Java基础IO流(二)字节流小案例
JAVA基础IO流(一)https://www.cnblogs.com/deepSleeping/p/9693601.html ①读取指定文件内容,按照16进制输出到控制台 其中,Integer.to ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之压缩流(ZipOutputStream)与解压缩流(ZipInputStream)
Java基础-IO流对象之压缩流(ZipOutputStream)与解压缩流(ZipInputStream) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 之前我已经分享过很多的J ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之随机访问文件(RandomAccessFile)
Java基础-IO流对象之随机访问文件(RandomAccessFile) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.RandomAccessFile简介 此类的实例支持对 ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之内存操作流(ByteArrayOutputStream与ByteArrayInputStream)
Java基础-IO流对象之内存操作流(ByteArrayOutputStream与ByteArrayInputStream) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.内存 ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之数据流(DataOutputStream与DataInputStream)
Java基础-IO流对象之数据流(DataOutputStream与DataInputStream) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.数据流特点 操作基本数据类型 ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之打印流(PrintStream与PrintWriter)
Java基础-IO流对象之打印流(PrintStream与PrintWriter) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.打印流的特性 打印对象有两个,即字节打印流(P ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之序列化(ObjectOutputStream)与反序列化(ObjectInputStream)
Java基础-IO流对象之序列化(ObjectOutputStream)与反序列化(ObjectInputStream) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.对象的序 ...
- java基础-IO流对象之Properties集合
java基础-IO流对象之Properties集合 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.Properties集合的特点 Properties类表示了一个持久的属性集. ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之字符缓冲流(BufferedWriter与BufferedReader)
Java基础-IO流对象之字符缓冲流(BufferedWriter与BufferedReader) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.字符缓冲流 字符缓冲流根据流的 ...
随机推荐
- 从基础到高级应用,详解用Python实现容器化和微服务架构
本文分享自华为云社区<Python微服务与容器化实践详解[从基础到高级应用]>,作者: 柠檬味拥抱. Python中的容器化和微服务架构实践 在现代软件开发中,容器化和微服务架构已经成为主 ...
- oeasy教您玩转vim - 26 - 缩进设置
缩进设置 回忆上节课内容 这次了解了颜色的细节 设置 256 色模式 :set t_Co=256 然后确定了具体的各种颜色 还可以生成网页 :TOhtml 还有什么好玩的么? 缩进设置 在 ...
- 阅读翻译Mathematics for Machine Learning之2.5 Linear Independence
阅读翻译Mathematics for Machine Learning之2.5 Linear Independence 关于: 首次发表日期:2024-07-18 Mathematics for M ...
- Docker 容器开发:虚拟化
Docker 容器开发:虚拟化 Docker 的核心价值在于虚拟化或者说环境隔离[通过虚拟化技术实现虚拟环境],解决环境配置和部署的依赖问题实现解耦 我对虚拟化的理解源自<Operating S ...
- Vue 打包后自定义样式无法覆盖elementUI组件原有样式问题
Vue 打包后自定义样式无法覆盖elementUI组件原有样式问题 by:授客 QQ:1033553122 开发环境 Win 10 node-v10.15.3-x64.msi 下载地址 ...
- 10、Git之国内项目托管平台(Gitee码云)
10.1.简介 众所周知,GitHub 服务器在国外,如果网络不好的话,严重影响使用体验,甚至会出现登录不上的情况. 针对这个情况,可以使用国内的项目托管平台-- Gitee 码云,来替代 Githu ...
- 使用lanczos算法进行的预处理共轭梯度算法(Preconditioned Conjugate Gradients Method)
构造预处理矩阵M(对称正定) 下图来自:预处理共轭梯度法(1) 下图来自:预处理(Preconditioning) 根据上面的对于预处理共轭梯度法的介绍,我们可以得到使用lanczos算法进行的预处理 ...
- CCF A类会议 —— CVPR 2022 论文审稿模板
============================================= Edit ReviewThank you for accepting to serve as a revie ...
- 微信支付java版(含视频讲解)
1.背景 实际开发中用到微信支付的概率非常大, 至于为什么这里不必要我多少...... 微信支付大体需要对接的核心接口有 其实大部分支付都是这些,就像上一节我们讲的支付宝支付一样 这里以常用的H5支付 ...
- 亚信科技基于 Apache SeaTunnel 的二次开发应用实践
亚信科技在Apache SeaTunnel的实践分享 自我介绍 各位同学好,很荣幸通过Apache SeaTunnel社区和大家进行分享交流.我是来自亚信科技的潘志宏,主要负责公司内部数据中台产品的开 ...
