python全栈开发笔记---基本数据类型--字符串魔法
字符串:
def capitalize(self, *args, **kwargs)
test = "aLxs"
v = test.capitalize() #capitalize() 把字符串中首字母大写,其他为小写。
print(v) #输出结果 Alxs
def casefold(self, *args, **kwargs)
test = "aLxs"
v1 =test.casefold() #所有变小写,未知相对应的也变。casefold()更强
print(v1) #输出结果 alxs
v2 =test.lower() #所有变小写
print(v2) #输出结果 alxs
def center(self, *args, **kwargs)
test ="alxs"
v = test.center(20,'&') #def center(*args, **kwargs) 可以传2个参数,第一个是长度,第二个占位符
print(v) #输出结果&&&&&&&&alxs&&&&&&&&
def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None)
test = "alxsalxs"
v = test.count('a') #def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None) 从字符串中查找有包含多少个。后面可以定义开始结束位置。
print(v) # 输出结果 2
def endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None)
test = "alxs"
v = test.endswith("s") #判断字符串是不是以s结尾,返回布尔值
print(v)
def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None)
def index(self, sub, start=None, end=None)
test = "alxsalxs"
v = test.find('x') #查找字符在字符串中的位置,以零开始,从左到右,找到第一个及返回,找不到返回-1.
print(v) # 输出结果 2 同index() index()如果找不到会报错
def format(self, *args, **kwargs)格式化用法
test ='i am {name},age{a}'
v = test.format(name='kang',a='') #格式化数据赋值方式赋值
print(v)
test ='i am {0},age{1}'
v = test.format('kang','') #格式化数据索引方式赋值
print(v)
def format_map(self, mapping)
test ='i am {name},age{a}'
v = test.format_map({"name":'kang',"a":19}) #成对出现,好比字典
print(v)
def isalnum(self, *args, **kwargs)
test = 'abdcd891'
v = test.isalnum() #isalnum 判断字符串是否为 数字+字母组合, 返回布尔值
print(v) #输出结果 true
def expandtabs(self, *args, **kwargs)
test = 'username\temail\tage\ntianlu\ttianlu@qq.com\t19\ntianlu\ttianlu@qq.com\t19\ntianlu\ttianlu@qq.com\t19'
v = test.expandtabs(20) #expandtabs() 下面设置的20为 以\t结束的字符串长度,如果不够拿空格填充。
print(v)
输出结果:\t填充,\n换行
username email age
tianlu tianlu@qq.com 19
tianlu tianlu@qq.com 19
tianlu tianlu@qq.com 19
def isalpha(self, *args, **kwargs)
test = 'abcd'
v = test.isalpha() #isalpha()判断字符串是不是只有字母组成,返回结果布尔值。
print(v)
def isdecimal(self, *args, **kwargs)
def isdigit(self, *args, **kwargs)
def isnumeric(self, *args, **kwargs)
test = '②'
v = test.isdecimal() #判断字符串是否为数字,只能判断十进制的数字,如:123456
v1 = test.isdigit() #判断字符串是否为数字,可以判断更多小数,如:② 返回true
v3 = test.isnumeric() #判断字符串是否为数字,可以判断更多中文数字,如: 二
print(v,v1)
输出结果:
False True
应用领域:
可以用来做文件查找筛选。

def isalpha(self, *args, **kwargs)
test = 'abcd'
v = test.isalpha() #isalpha()判断字符串是不是只有字母组成,返回结果布尔值。
print(v)
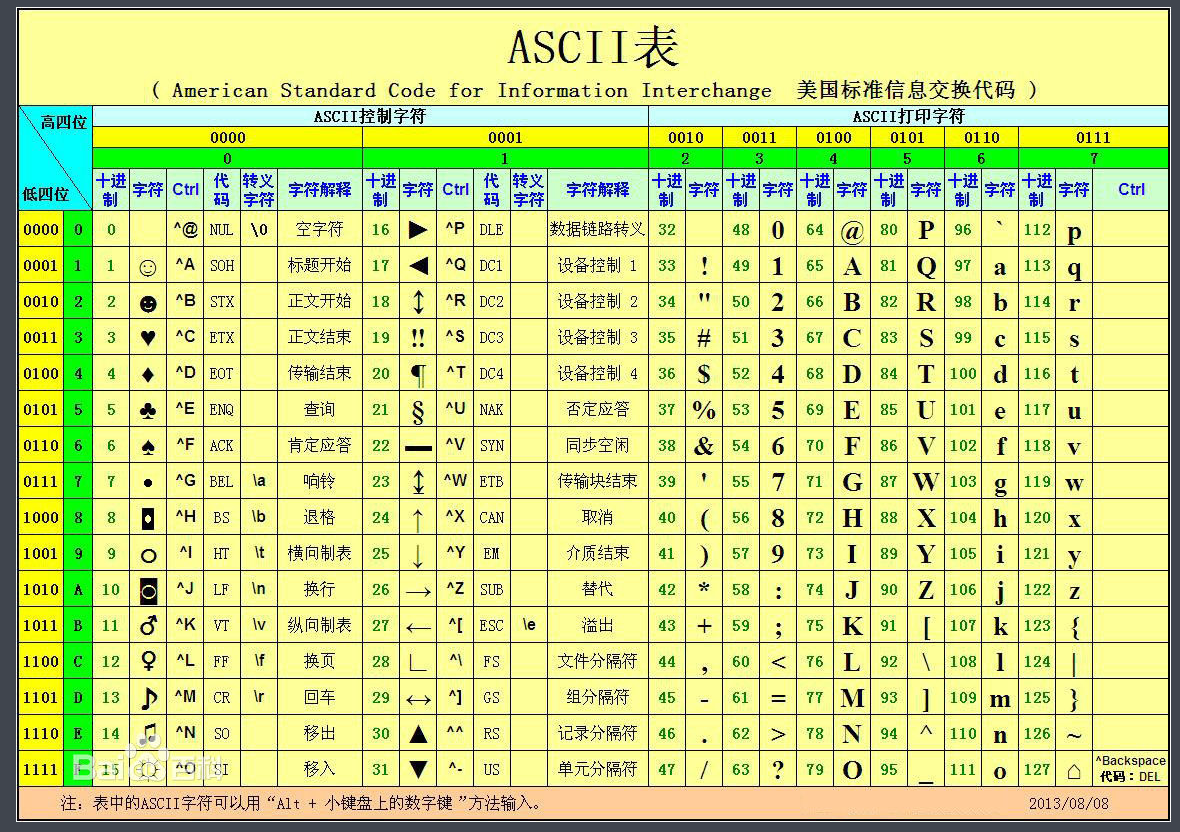
def isascii(self, *args, **kwargs) 如果字符串为空或字符串中的所有字符都是ASCII,则返回true,否则返回false。ASCII字符的代码点范围为U + 0000-U + 007F
更多介绍:https://baike.baidu.com/item/ASCII/309296?fr=aladdin
test = 'ETX'
v =test.isascii() #输出结果 true
print(v)
def islower(self, *args, **kwargs)
def isupper(self, *args, **kwargs)
# islower() 判断字符串是否全部是小写
print('Hello,world'.islower()) # False
# isupper() 判断字符串是否全部为大写
print('Hello,world'.isupper()) # False
def isidentifier(self, *args, **kwargs)
# isidentifier() 判断是不是一个合法的标识符
print('test'.isidentifier()) # True
print(''.isidentifier()) # False
print('_aa'.isidentifier()) # True
swapcase() 方法用于对字符串的大小写字母进行转换。
返回值:把字符串中的大写变成小写,小写的变成大写后生成新的字符串。
#!/usr/bin/python str = "this is string example....wow!!!";
print str.swapcase(); str = "THIS IS STRING EXAMPLE....WOW!!!";
print str.swapcase();
输出结果:
THIS IS STRING EXAMPLE....WOW!!!
this is string example....wow!!!
def isidentifier(self, *args, **kwargs)
标识符:数字,字母,下划线,不能以数字开头。返回结果为布尔值
test = 'alxs'
v = test.isidentifier() #返回结果 true
print(v)
def isprintable(self, *args, **kwargs)
test = 'ojkl;j\tfdsaf'
v = test.isprintable() #字符串中含有比如\t,\n 这样打印出来后,不可见的字符串时返回false
print(v) #返回结果为false
def isspace(self, *args, **kwargs)
test = ' '
v = test.isspace() #判断字符串里面是否全部都是空格,如果'a bc',这样则返回false
print(v) #输出结果 true
def istitle(self, *args, **kwargs)
def title(self, *args, **kwargs)
test = 'Return True if the string'
v1 = test.title() #把字符串变成标题形式(首字母大写)
print(v1) #Return True If The String
v2 = test.istitle() #如果经过title()转换后,那么打印结果就为真了。
print(v2) #输出结果 false
def join(self, ab=None, pq=None, rs=None)
test = '今天的阳光格外的明媚'
print(test) #输出结果 :今天的阳光格外的明媚
t = ' '
v = t.join(test) #用于将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串。
print(v) #输出结果 :今 天 的 阳 光 格 外 的 明 媚
def ljust(self, *args, **kwargs)
一个原字符串左对齐,并使用空格填充至指定长度的新字符串。如果指定的长度小于原字符串的长度则返回原字符串。
def rjust(self, *args, **kwargs)
一个原字符串右对齐,并使用空格填充至指定长度的新字符串。如果指定的长度小于原字符串的长度则返回原字符串。
test = 'alex'
v = test.ljust(20,"*")
print(v) #输入结果:alex**************** test = "alex"
v = test.rjust(20,"*")
print(v) #输出结果:****************alex
def lstrip(self, *args, **kwargs)
def rstrip(self, *args, **kwargs)
def strip(self, *args, **kwargs)
#strip()用法
# 1.可以移除空格
# 2.可以移除换行符,制表符
# 3.可以移除指定字符串 优先最多匹配 例:v4
test = "abcdefgh"
# v1 = test.lstrip() #移除左边空格
# v2 = test.rstrip() #移除右边空格
# v3 = test.strip() #移除左右两边边空格
v4 = test.rstrip('hgef') #输出结果:abcd
print(v4)
def maketrans(self, *args, **kwargs)
用于创建字符映射的转换表,对于接受两个参数的最简单的调用方式,第一个参数是字符串,表示需要转换的字符,第二个参数也是字符串表示转换的目标。
注:两个字符串的长度必须相同,为一一对应的关系。
def translate(self, *args, **kwargs)
方法根据参数table给出的表(包含 256 个字符)转换字符串的字符, 要过滤掉的字符放到 del 参数中。
参数
- table -- 翻译表,翻译表是通过maketrans方法转换而来。
- deletechars -- 字符串中要过滤的字符列表。
v = "abcdefgh"
m = str.maketrans("aced","")
new_v = v.translate(m)
print(new_v) #输出结果:1b243fgh
def partition(self, *args, **kwargs)
test ="testasdsddfg"
v = test.partition('s') #字符串拆分(分割),如果字符串包含指定的分隔符,则返回一个3元的元组,第一个为分隔符左边的子串,第二个为分隔符本身,第三个为分隔符右边的子串。
#print(v) #('te', 's', 'tasdsddfg')
def rpartition(self, *args, **kwargs)
rpartition() 方法类似于 partition() 方法,只是该方法是从目标字符串的末尾也就是右边开始搜索分割符。。
如果字符串包含指定的分隔符,则返回一个3元的元组,第一个为分隔符左边的子串,第二个为分隔符本身,第三个为分隔符右边的子串。
test ="testasdsddfg"
v = test.rpartition('s') #字符串分割,从右侧开始。
print(v) #('testasd', 's', 'ddfg')
def split(self, *args, **kwargs)
test ="testasdsddfg"
v = test.split('s') #字符串分割,后面可加参数,默认全部分割,也可以指定分割几次split('s',1)
print(v) # 输出结果 :['te', 'ta', 'd', 'ddfg']
def rsplit(self, *args, **kwargs)
方法同split类似,只是这个是以右侧开始分割。
def splitlines(self, *args, **kwargs)
按照行('\r', '\r\n', \n')分隔,返回一个包含各行作为元素的列表,如果参数 keepends 为 False,不包含换行符,如果为 True,则保留换行符。
str1 = 'ab c\n\nde fg\rkl\r\n'
print str1.splitlines(); str2 = 'ab c\n\nde fg\rkl\r\n'
print str2.splitlines(True)
输出结果:
['ab c', '', 'de fg', 'kl']
['ab c\n', '\n', 'de fg\r', 'kl\r\n']
def startswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None)
def endswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None) 用法和startswith相同,一个是开始匹配,一个是结束匹配
用于检查字符串是否是以指定子字符串开头,如果是则返回 True,否则返回 False。如果参数 start 和 end 指定值,则在指定范围内检查。
str = "this is string example....wow!!!";
print str.startswith( 'this' );
print str.startswith( 'is', 2, 4 );
print str.startswith( 'this', 2, 4 );
输出结果:
True
True
False
def replace(self, *args, **kwargs)
字符串中的 old(旧字符串) 替换成 new(新字符串),如果指定第三个参数max,则替换不超过 max 次。
str = "this is string example....wow!!! this is really string";
print str.replace("is", "was");
print str.replace("is", "was", 3);
输出结果:
thwas was string example....wow!!! thwas was really string 1 2 3
thwas was string example....wow!!! thwas is really string
重点:join(),split(),find(),strip(),upper(),lower(),replace()
####通用魔法####
1.循环
test = "村里有个姑娘长的很漂亮"
#一个一个截取输出
index = 0
while index < len(test):
v = test[index]
print(v)
index += 1
print('========') #另一种实现方式
for key in test:
print(key)
2.索引,下标,获取字符串中某一个值 从0开始
test = "村里有个姑娘长的很漂亮"
v = test[3]
print(v) #输出结果 :个
3.切片
test = "村里有个姑娘长的很漂亮"
v = test[0:1] #从0位置开始取,取到1位置不包括1
print(v) #输出结果:村
4.join()
方法用于将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串。
str = "-";
seq = ("a", "b", "c"); # 字符串序列
print str.join( seq );
输出结果:
a-b-c
len('abc')获取字符串长度
Ps:字符串一旦创建,不可以修改。
一旦修改或者拼接,都好造成从新生成字符串
python全栈开发笔记---基本数据类型--字符串魔法的更多相关文章
- python全栈开发笔记----基本数据类型---列表List
#list 是 类 ,列表 序列是Python中最基本的数据结构.序列中的每个元素都分配一个数字 - 它的位置,或索引,第一个索引是0,第二个索引是1,依此类推. Python有6个序列的内置类型,但 ...
- python全栈开发笔记----基本数据类型---列表方法
#list 类中提供的方法 #参数 1.def append(self, *args, **kwargs)原来值最后追加#对象..方法(..) #li对象调用append方法 li = [11,22, ...
- python全栈开发笔记---基本数据类型--数字型魔法
数字 int a1 =123 a2=456 int 讲字符串转换为数字 a = " #字符串 b = int(a) #将字符串转换成整形 b = b + 1000 #只有整形的时候才可以进 ...
- python全栈开发笔记---------基本数据类型
基本数据类似包括: 字符串(str) 数字(int) 列表(list) 元祖(tuple) 字典(dict) 布尔值(bool) 字符串(引号): name = "我是某某某" n ...
- python全栈开发笔记---数据类型--综合练习题
一.有两个列表 l1 = [11,22,33] l2 = [22,33,44] a. 获取内容相同的元素列表 for item in l1: if item in l2: print(it ...
- python全栈开发笔记---------字符串格式化
字符串格式化 %s 可以接收任何值, %d只能接收整形 .其他类型报错 msg ='i am %s my body' %'ales' print(msg) #i am ales my body msg ...
- python全栈开发笔记---------数据类型-----集合set
定义:由不同元素组成的集合,集合中是一组无序排列的可hash值,可以作为字典的key 1.不同元素组成 2.无序 3.集合中元素必须是不可变类型(数字,字符串,元组) 特性:集合的目的是讲不同的值放到 ...
- python全栈开发笔记---------数据类型****整理****
一.数字 int(..) 二.字符串 replace/find/join/strip/startswith/split/upper/lower/format tempalet ='i am {name ...
- python全栈开发笔记---------数据类型---字典方法
def clear(self) 清空字典里所有元素 # info = { # "k1":18, # "k2":True, # "k3":[ ...
随机推荐
- What is a working set and how do I use it?
//http://www.avajava.com/tutorials/lessons/what-is-a-working-set-and-how-do-i-use-it.html Working se ...
- Node版本管理nvm, npm
nvm(node version manger) Node版本管理 nvm是一个简单的bash script来管理多个活动的node.js版本. 安装nvm: 具体看git:https://githu ...
- android -------- java虚拟机和Dalvik虚拟机
java虚拟机 虚拟机是一种抽象化的计算机,通过在实际的计算机上仿真模拟各种计算机功能来实现的.Java虚拟机有自己完善的硬体架构,如处理器.堆栈.寄存器等,还具有相应的指令系统.Java虚拟机屏蔽了 ...
- CF1129C Morse Code
pro: 维护一个01字符串,支持在结尾动态加字符. 每一个长度<=4的01串可以对应一个字母(有几个特例除外) 每次操作后询问,这个字符串的所有子串一共可以对应出多少种本质不同的字符串. so ...
- mac下 配置homebrew 和java home
1.terminal下输入 /usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/insta ...
- Mybatis中int insertSelective()的相关问题
1.selective的意思是:选择性2.insertSelective--选择性保存数据:比如User里面有三个字段:id,name,age,password但是我只设置了一个字段:User u=n ...
- IntelliJ IDEA的调试方法
快捷键F9 resume programe 恢复程序 Alt+F10 show execution point 显示执行断点 F8 S ...
- 我的第一个C语言程序
从自学开始到现在应该有块一个月了,之前一直想要写博客一直没想好要自己建博客还是找平台来写.现在想想 其实都一样,不论在哪里,都可以记录自己学习的成长记录.这是我的第一篇关于C语言学习的博客,希望这只是 ...
- element upload 一次性上传多张图片(包含自定义上传不走action)
最重要的都圈出来了
- QQ企业邮箱接口
我推荐的这篇文章很好:http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url=KQIMyrECGb8GS_0fag4PRG64M8Z7wOLbsU1f3BhydXAyYJDC2JMHEuVcy ...