第四十二课 KMP算法的应用
思考:

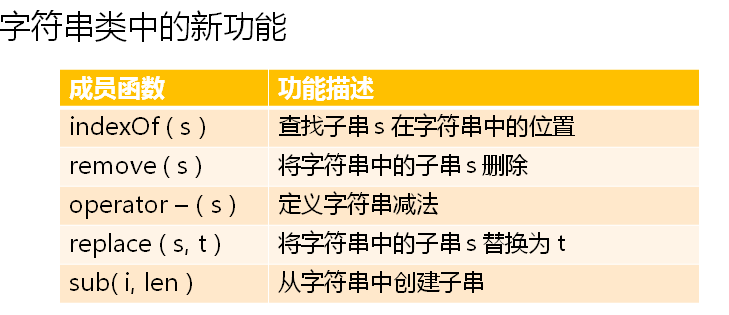




replace图解:
程序完善:
DTString.h:
#ifndef DTSTRING_H
#define DTSTRING_H #include "Object.h" namespace DTLib
{ class String : Object
{
protected:
char* m_str;
int m_length; void init(const char* s);
bool equal(const char* l, const char* r, int len) const; static int* make_pmt(const char* p);
static int kmp(const char* s, const char* p); public:
String();
String(char c);
String(const char* s);
String(const String& s); int length() const;
const char* str() const; bool startWith(const char* s) const;
bool startWith(const String& s) const;
bool endOf(const char* s) const;
bool endOf(const String& s) const; String& insert(int i, const char* s);
String& insert(int i, const String& s); String& trim(); int indexOf(const char* s) const;
int indexOf(const String& s) const; String& remove(int i, int len); //删除指定下标,指定长度的子串
String& remove(const char* s);
String& remove(const String& s); String& replace(const char* t, const char* s);
String& replace(const String& t, const char* s);
String& replace(const char* t, const String& s);
String& replace(const String& t, const String& s); String sub(int i, int len) const; char& operator [] (int i);
char operator [] (int i) const; bool operator == (const String& s) const;
bool operator == (const char* s) const; bool operator != (const String& s) const;
bool operator != (const char* s) const; bool operator > (const String& s) const;
bool operator > (const char* s) const; bool operator < (const String& s) const;
bool operator < (const char* s) const; bool operator >= (const String& s) const;
bool operator >= (const char* s) const; bool operator <= (const String& s) const;
bool operator <= (const char* s) const; String operator + (const String& s) const;
String operator + (const char* s) const;
String& operator += (const String& s);
String& operator += (const char* s); String operator - (const char* s) const;
String operator - (const String& s) const;
String& operator -= (const char* s);
String& operator -= (const String& s); String& operator = (const String& s);
String& operator = (const char* s);
String& operator = (char c); ~String();
}; } #endif // DTSTRING_H
DTString.cpp:
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "DTString.h"
#include "Exception.h" using namespace std; namespace DTLib
{ int* String::make_pmt(const char* p) // O(m)
{
int len = strlen(p); int* ret = static_cast<int*>(malloc(sizeof(int) * len)); if( ret != NULL )
{
int ll = ; ret[] = ; // 第0个元素(长度为1的字符串)的ll值为0 for(int i = ; i < len; i++)
{
//不成功的情况
while( (ll > ) && (p[ll] != p[i]) )
{
ll = ret[ll];
} // 假设最理想的情况成立
//在前一个ll值的基础行进行扩展,只需比对最后扩展的字符是否相等
//相等的话ll值加1,并写入到部分匹配表
if( p[ll] == p[i] )
{
ll++;
} ret[i] = ll; // 将ll值写入匹配表 }
} return ret;
} int String::kmp(const char* s, const char* p) //O(m) + O(n) = O(m + n)
{
int ret = -; int sl = strlen(s);
int pl = strlen(p); //子串 int* pmt = make_pmt(p); //O(m) if( (pmt != NULL) && ( < pl) && (pl <= sl))
{
for( int i = ,j = ; i < sl; i++ )
{
while( (j > ) && (s[i] != p[j]) ) // j小于等于0时要退出
{
j = pmt[j];
} if( s[i] == p[j] )
{
j++;
} if( j == pl ) // j的值如果最后就是子串的长度,意味着查找到了
{
ret = i + - pl; // 匹配成功时i的值停在最后一个匹配的字符上
break;
}
}
} free(pmt); return ret;
} void String::init(const char* s)
{
m_str = strdup(s); if( m_str )
{
m_length = strlen(m_str);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to create string object ...");
}
} bool String::equal(const char* l, const char* r, int len) const
{
bool ret = true; for(int i = ; i < len && ret; i++)
{
ret = ret && (l[i] == r[i]);
} return ret;
} String::String()
{
init("");
} String::String(const char* s)
{
init(s ? s : ""); //空指针就转换成空字符串
} String::String(const String& s)
{
init(s.m_str);
} String::String(char c)
{
char s[] = {c, '\0'}; init(s);
} int String::length() const
{
return m_length;
} const char* String::str() const
{
return m_str;
} bool String::startWith(const char* s) const
{
bool ret = ( s != NULL ); if( ret )
{
int len = strlen(s); ret = (len < m_length) && equal(m_str, s, len); } return ret;
} bool String::startWith(const String& s) const
{
return startWith(s.m_str);
} bool String::endOf(const char* s) const
{
bool ret = ( s != NULL ); if( ret )
{
int len = strlen(s); char* str = m_str + (m_length - len); ret = (len < m_length) && equal(str, s, len); } return ret;
} bool String::endOf(const String& s) const
{
return endOf(s.m_str);
} String& String::insert(int i, const char* s)
{
if( ( <= i) && (i <= m_length) )
{
if( ( s != NULL) && ( s[] != '\0' ) )
{
int len = strlen(s);
char* str = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(m_length + len + )); if( str != NULL )
{
strncpy(str, m_str, i);
strncpy(str + i, s, len);
strncpy(str + i + len, m_str + i, m_length - i); str[m_length + len] = '\0'; free(m_str); m_str = str;
m_length = m_length + len;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to create str object...");
}
}
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "parameter i is invalid...");
} return *this;
} String& String::insert(int i, const String& s)
{
return insert(i, s.m_str);
} String& String::trim()
{
int b = ;
int e = m_length - ; while( m_str[b] == ' ')b++;
while( m_str[e] == ' ')e--; if( b == )
{
m_str[e + ] = '\0'; m_length = e + ;
}
else
{
for(int i = ,j = b; j <= e; i++, j++)
{
m_str[i] = m_str[j];
} m_str[e - b + ] = '\0';
m_length = e - b + ;
} return *this;
} int String::indexOf(const char* s) const
{
return kmp(m_str, s ? s : "");
} int String::indexOf(const String& s) const
{
return kmp(m_str, s.m_str);
} String& String::remove(int i, int len)
{
if( ( <= i) && (i < m_length) )
{
int n = i;
int m = i + len; while( (n < m) && (m < m_length) )
{
m_str[n++] = m_str[m++];
} m_str[n] = '\0';
m_length = n;
} return *this;
} String& String::remove(const char* s)
{
return remove(indexOf(s), s ? strlen(s) : );
} String& String::remove(const String& s)
{
return remove(indexOf(s), s.length());
} String& String::replace(const char* t, const char* s)
{
int index = indexOf(t); if( index >= )
{
remove(t);
insert(index, s);
} return *this;
} String& String::replace(const String& t, const char* s)
{
return replace(t.m_str, s);
} String& String::replace(const char* t, const String& s)
{
return replace(t, s.m_str);
} String& String::replace(const String& t, const String& s)
{
return replace(t.m_str, s.m_str);
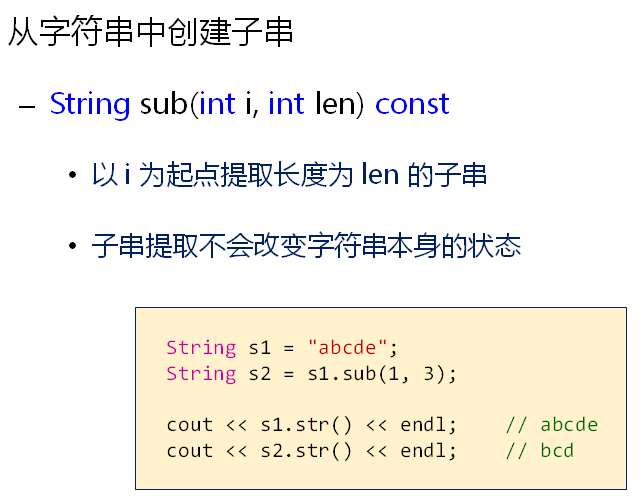
} String String::sub(int i, int len) const
{
String ret; if( ( <= i) && (i<m_length) )
{
if( len < ) len = ;
if(len + i > m_length) len = m_length - i; char* str = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(len + )); strncpy(str, m_str + i, len); str[len] = '\0'; ret = str;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "parameter i is invalid...");
} return ret;
} char& String::operator [] (int i)
{
if( ( <= i) && (i < m_length) )
{
return m_str[i];
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "parameter i is invalid ...");
}
} char String::operator [] (int i) const
{
return (const_cast<String&>(*this))[i];
} bool String::operator == (const String& s) const
{
return ( strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) == );
} bool String::operator == (const char* s) const
{
return ( strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") == );
} bool String::operator != (const String& s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
} bool String::operator != (const char* s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
} bool String::operator > (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) > );
} bool String::operator > (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") > );
} bool String::operator < (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) < );
} bool String::operator < (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") < );
} bool String::operator >= (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) >= );
} bool String::operator >= (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") >= );
} bool String::operator <= (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) <= );
} bool String::operator <= (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") <= );
} String String::operator + (const String& s) const
{
return (*this + s.m_str);
} String String::operator + (const char* s) const
{
String ret; int len = m_length + strlen(s ? s : ""); char* str = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(len + )); if( str )
{
strcpy(str, m_str);
strcat(str, s ? s : ""); free(ret.m_str); ret.m_str = str;
ret.m_length = len;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to create str object...");
} return ret;
} String& String::operator += (const String& s)
{
return (*this = *this + s.m_str);
} String& String::operator += (const char* s)
{
return (*this = *this + s);
} String String::operator - (const char* s) const
{
return String(*this).remove(s);
} String String::operator - (const String& s) const
{
return String(*this).remove(s);
} String& String::operator -= (const char* s)
{
return remove(s);
} String& String::operator -= (const String& s)
{
return remove(s);
} String& String::operator = (const String& s)
{
return (*this = s.m_str);
} String& String::operator = (const char* s)
{
if( m_str != s )
{
char* str = strdup(s ? s: ""); if( str )
{
free(m_str); m_str = str;
m_length = strlen(m_str);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to create str object...");
}
} return *this;
} String& String::operator = (char c)
{
char s[] = {c, '\0'}; return (*this = s);
} String::~String()
{
free(m_str);
} }
小结:

第四十二课 KMP算法的应用的更多相关文章
- NeHe OpenGL教程 第四十二课:多重视口
转自[翻译]NeHe OpenGL 教程 前言 声明,此 NeHe OpenGL教程系列文章由51博客yarin翻译(2010-08-19),本博客为转载并稍加整理与修改.对NeHe的OpenGL管线 ...
- 第四十二课:基于CSS的动画引擎
由于低版本浏览器不支持css3 animation,因此我们需要根据浏览器来选择不同的动画引擎.如果浏览器支持css3 animation,那么就使用此动画引擎,如果不支持,就使用javascript ...
- 潭州课堂25班:Ph201805201 django 项目 第四十二课 后台 课程相关,用户组管理 (课堂笔记)
在线课程: 当点击进入页面时,显示所有课程 def get(self, request): courses = Course.objects.select_related('category', 't ...
- python第四十二课——__str__(self)函数
4.__str__(self): 作用: 创建完对象,直接打印对象名/引用名我们得到的是对象的内存信息(十六进制的地址信息), 这串数据我们程序员并不关心,我们更希望看到的是属性赋值以后的内容(属性赋 ...
- NeHe OpenGL教程 第四十八课:轨迹球
转自[翻译]NeHe OpenGL 教程 前言 声明,此 NeHe OpenGL教程系列文章由51博客yarin翻译(2010-08-19),本博客为转载并稍加整理与修改.对NeHe的OpenGL管线 ...
- centos shell编程6一些工作中实践脚本 nagios监控脚本 自定义zabbix脚本 mysql备份脚本 zabbix错误日志 直接送给bc做计算 gzip innobackupex/Xtrabackup 第四十节课
centos shell编程6一些工作中实践脚本 nagios监控脚本 自定义zabbix脚本 mysql备份脚本 zabbix错误日志 直接送给bc做计算 gzip innobacku ...
- NeHe OpenGL教程 第三十二课:拾取游戏
转自[翻译]NeHe OpenGL 教程 前言 声明,此 NeHe OpenGL教程系列文章由51博客yarin翻译(2010-08-19),本博客为转载并稍加整理与修改.对NeHe的OpenGL管线 ...
- NeHe OpenGL教程 第二十二课:凹凸映射
转自[翻译]NeHe OpenGL 教程 前言 声明,此 NeHe OpenGL教程系列文章由51博客yarin翻译(2010-08-19),本博客为转载并稍加整理与修改.对NeHe的OpenGL管线 ...
- 第四十二个知识点:看看你的C代码为蒙哥马利乘法,你能确定它可能在哪里泄漏侧信道路吗?
第四十二个知识点:看看你的C代码为蒙哥马利乘法,你能确定它可能在哪里泄漏侧信道路吗? 几个月前(回到3月份),您可能还记得我在这个系列的52件东西中发布了第23件(可以在这里找到).这篇文章的标题是& ...
随机推荐
- 四、持久层框架(Hibernate)
一.一级缓存与二级缓存 1.一级缓存:Hibernate默认是开启一级缓存的,一级缓存存放在session里,一个Session做一次查询操作,会把这个操作的结果放在一级缓存中,如果短时间内这个ses ...
- 洛谷P1075 质因数分解
题目描述 已知正整数n是两个不同的质数的乘积,试求出两者中较大的那个质数. 输入输出格式 输入格式: 一个正整数n. 输出格式: 一个正整数p,即较大的那个质数. 输入输出样例 输入样例#1: 复制 ...
- Microsoft SQL Server Trace Flags
Complete list of Microsoft SQL Server trace flags (585 trace flags) REMEMBER: Be extremely careful w ...
- SpringBoot鸡汤(注解集合)
1.(ConfigBean.java :是一个带有属性的bean类) @Configuration @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “com.md”) @Prope ...
- npm run build 打包后,如何运行在本地查看效果(Apache服务)
目前,使用vue-cli脚手架写了一个前端项目,之前一直是使用npm run dev 在8080端口上进行本地调试.项目已经进行一半了,今天有时间突然想使用npm run build进行上线打包,试试 ...
- python QMainWindow QWidget
from PyQt5 import QtWidgetsfrom untitled import Ui_MainWindowfrom PyQt5.QtWidgets import QFileDialog ...
- XIA.人机猜拳
package test1_game; /** * 电脑玩家类 * * @author ljj * */ import java.util.Scanner; public class Computer ...
- 逆袭之旅DAY09.东软实训.接口
2018年7月5日 package day0705.teacher.test1usb; /** * 测试类 * @author Administrator * */ public class UsbI ...
- 《Python》并发编程
手工操作 —— 穿孔卡片 1946年第一台计算机诞生--20世纪50年代中期,计算机工作还在采用手工操作方式.此时还没有操作系统的概念. 程序员将对应于程序和数据的已穿孔的纸带(或卡片)装入输 ...
- :组合模式:Component
#ifndef __COMPONENT_H__ #define __COMPONENT_H__ #include <iostream> #include <vector> us ...
