10 (OC)* Coretext
CoreText实现
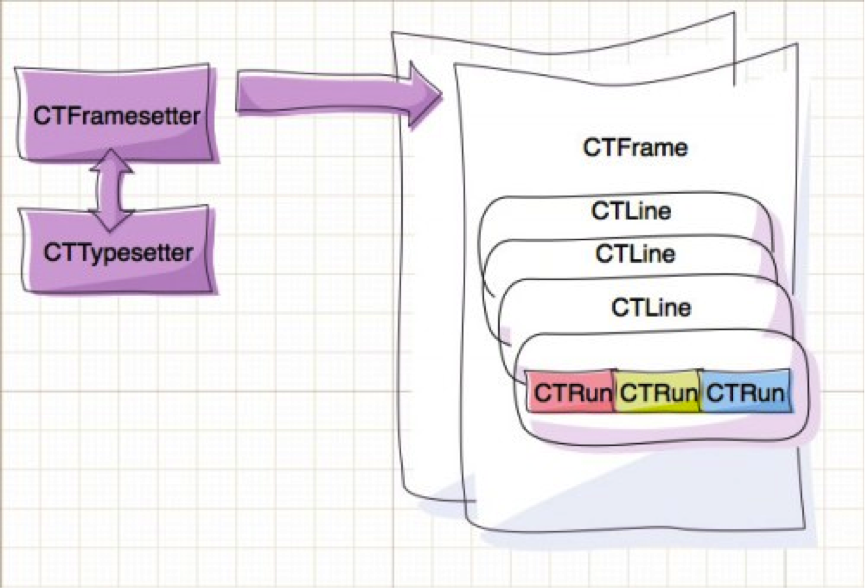
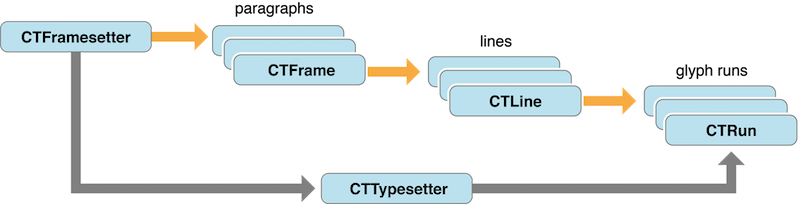
看上图,我们可以知道,一个View包括CTFrame,CTFrame中间包括许多行CTLine,而一个CTLine中包括许多CTRun
我们主要说说CTLine和CTRun
CTLine其实比较好理解,当我们用UILabel显示文本内容时,一行就是一个CTLine,一个CTLine中有一个或者多个CTRun,CTRun的个数取决于文本的具体内容,如果一行里面有两种大小的文字或者两种颜色不通的文字,可以简单的认为这一行就有两个CTRun,其中CTRun还可以是图片
1. CoreText框架基础
CoreText是Mac OS和iOS系统中处理文本的low-level API, 不管是使用OC还是swift, 实际我们使用CoreText都还是间接或直接使用C语言在写代码。CoreText是iOS和Mac OS中文本处理的根基, TextKit和WebKit都是构建于其上。
常用类、属性
CTFrameRef
CTFramesetterRef
CTLineRef
CTRunRef
CTTypesetterRef
CTGlyphInfoRef (NSGlyphInfo)
CTParagraphStyleRef (NSParagraphStyle)
CTFontRef (UIFont)
CFArrayRef (NSArray)
分析:
coreText 属于怎样一套API?
字体结构:
当我们进行字体绘制的时候很重要。
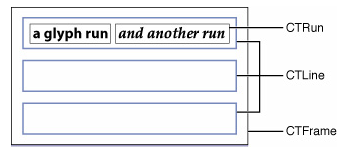
- CTFrame可以想象成画布, 画布的大小范围由CGPath决定
- CTFrame由很多CTLine组成, CTLine表示为一行
- CTLine由多个CTRun组成, CTRun相当于一行中的多个块, 但是CTRun不需要你自己创建, 由NSAttributedString的属性决定, 系统自动生成。每个CTRun对应不同属性。
- CTFramesetter是一个工厂, 创建CTFrame, 一个界面上可以有多个CTFrame
- CTFrame就是一个基本画布,然后一行一行绘制。 CoreText会自动根据传入的NSAttributedString属性创建CTRun,包括字体样式,颜色,间距等
更多详细的基础知识见末尾参考。
流程
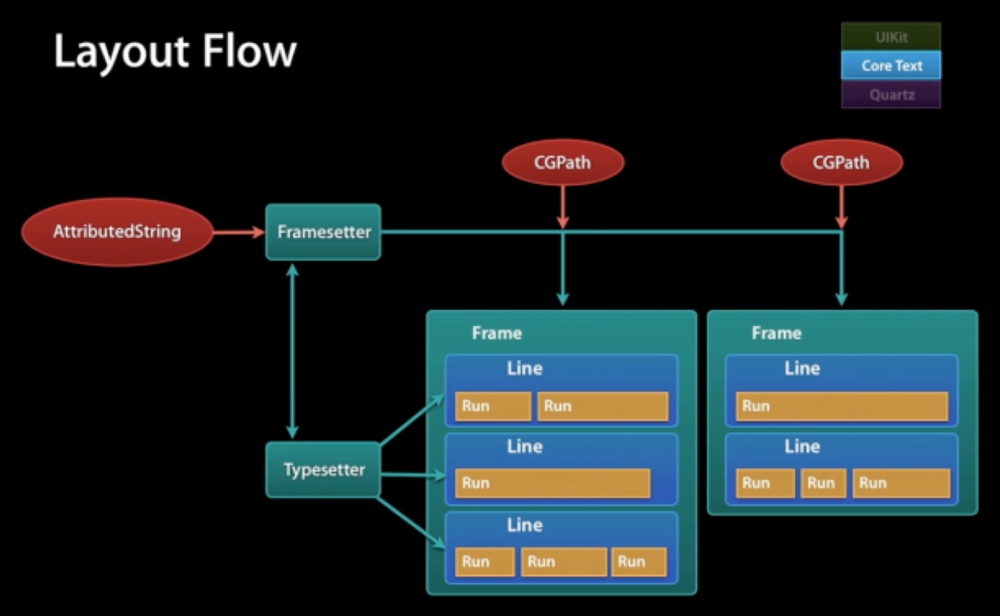
如下图所示,这就是CoreText的基本处理流程:
1、创建AttributedString,定义样式
2、通过 CFAttributedStringRef 生成 CTFramesetter
3、通过CTFramesetter得到CTFrame
4、绘制 (CTFrameDraw)
5、如果有图片存在,先在AttributedString 对应位置添加占位符
6、通过回调函数确定图片的宽高(CTRunDelegateCallbacks)
7、遍历到对应CTRun上、获取对应CGRect、绘制图片(CGContextDrawImage)
2. 基本的文本样式实操
CoreText是需要自己处理绘制,不像UILabel等最上层的控件 ,所以我们必须在drawRect中绘制,为了更好地使用,我们稍微封装一下,自定义一个UIView。
我们在使用上层的控件时,坐标系的原点在左上角,而底层的Core Graphics的坐标系原点则是在左下角,以下是一个最基本的绘制示例:
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
[super drawRect:rect];
//step 1:获取当前画布的上下文
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
//step 2:
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable();
CGPathAddRect(path, NULL, self.bounds);
//step 3:
NSMutableAttributedString *attributedString = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] initWithString:@"xXHhofiyYI这是一段中文,前面是大小写"];
//step 4:
CTFramesetterRef framesetter = CTFramesetterCreateWithAttributedString((CFAttributedStringRef)attributedString);
CTFrameRef frame = CTFramesetterCreateFrame(framesetter, CFRangeMake(0, [attributedString length]), path, NULL);
//step 5:
CTFrameDraw(frame,context);
//step 6:
CFRelease(frame);
CFRelease(path);
CFRelease(framesetter);
//使用Create函数建立的对象引用,必须要使用CFRelease掉。
}
效果如下:
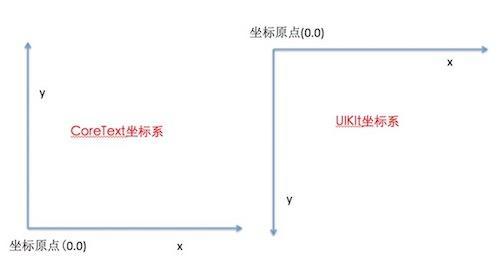
结果分析:发现文案是反的。原因就是因为coreText的坐标系是和UIKit的坐标系不一样的:
如上图,CoreText是基于CoreGraphics的,所以坐标系原点是左下角,我们需要进行翻转。将Y轴从向上转换为向下。
CGContextSetTextMatrix(context, CGAffineTransformIdentity);
CGContextTranslateCTM(context, 0, self.bounds.size.height);
CGContextScaleCTM(context, 1.0, -1.0);
翻转后,下面来进行一个最基本的富文本示例:
step 4 添加
[attr addAttribute:(NSString *)kCTBackgroundColorAttributeName value:[UIColor redColor] range:NSMakeRange(0, 10)];
[attr addAttribute:(NSString *)kCTFontAttributeName value:(__bridge id _Nonnull)(fontRef) range:NSMakeRange(0, 10)];
效果如下:

上面的绘制方式是基于CTFrame绘制,还可以按行和按run绘制:
按CTLine绘制
// 1.获得CTLine数组
let lines = CTFrameGetLines(frame)
// 2.获得行数
let numberOfLines = CFArrayGetCount(lines)
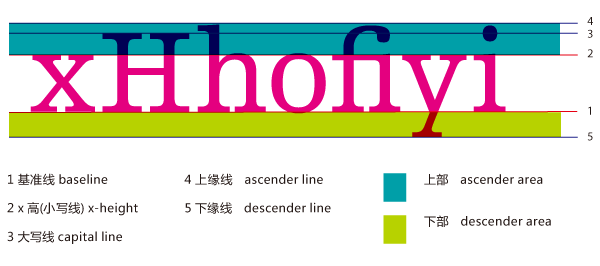
// 3.获得每一行的origin, CoreText的origin是在字形的baseLine处的, 请参考字形图
var lineOrigins = [CGPoint](count: numberOfLines, repeatedValue: CGPointZero)
CTFrameGetLineOrigins(frame, CFRangeMake(0, 0), &lineOrigins)
// 4.遍历每一行进行绘制
for index in 0..<numberOfLines {
let origin = lineOrigins[index]
// 参考: http://swifter.tips/unsafe/
let line = unsafeBitCast(CFArrayGetValueAtIndex(lines, index), CTLine.self)
// 设置每一行的位置
CGContextSetTextPosition(context, origin.x, origin.y)
// 开始一行的绘制
CTLineDraw(line, context)
}
按CTRun绘制
用下面函数替换CTLineDraw(line, context)这一句就可以了, 效果也如上面。
// 画一行
func drawLine(line: CTLine, context: CGContext) {
let runs = CTLineGetGlyphRuns(line) as Array
runs.forEach { run in
CTRunDraw(run as! CTRun, context, CFRangeMake(0, 0))
}
}
}
3. 图文混排
CoreText本身是不提供UIImage的绘制,所以UIImage肯定只能通过Core Graphics绘制,但是绘制时双必须要知道此绘制单元的长宽,庆幸的是CoreText绘制的最小单元CTRun提供了CTRunDelegate,也就是当设置了kCTRunDelegateAttributeName过后,CTRun的绘制时所需的参考(长宽等)将可从委托中获取,我们即可通过此方法实现图片的绘制。在需要绘制图片的位置,提前预留空白占位。
CTRun有几个委托用以实现CTRun的几个参数的获取。
以下是CTRunDelegateCallbacks的几个委托代理 。
typedef struct
{
CFIndex version;
CTRunDelegateDeallocateCallback dealloc;
CTRunDelegateGetAscentCallback getAscent;
CTRunDelegateGetDescentCallback getDescent;
CTRunDelegateGetWidthCallback getWidth;
} CTRunDelegateCallbacks;
以下是一个最基本的图片绘制原型:遍历查询图片,即查找含有imgName attribute的CTRun,并绘制。
step 4 前面添加:
CTRunDelegateCallbacks imageCallBacks;
imageCallBacks.version = kCTRunDelegateCurrentVersion;
imageCallBacks.dealloc = ImgRunDelegateDeallocCallback;
imageCallBacks.getAscent = ImgRunDelegateGetAscentCallback;
imageCallBacks.getDescent = ImgRunDelegateGetDescentCallback;
imageCallBacks.getWidth = ImgRunDelegateGetWidthCallback;
NSString *imgName = @"test.jpg";
CTRunDelegateRef imgRunDelegate = CTRunDelegateCreate(&imageCallBacks, (__bridge void * _Nullable)(imgName));//我们也可以传入其它参数
NSMutableAttributedString *imgAttributedStr = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc]initWithString:@" "];
[imgAttributedStr addAttribute:(NSString *)kCTRunDelegateAttributeName value:(__bridge id)imgRunDelegate range:NSMakeRange(0, 1)];
CFRelease(imgRunDelegate);
#define kImgName @"imgName"
//图片占位符添加
[imgAttributedStr addAttribute:kImgName value:imgName range:NSMakeRange(0, 1)];
[attributedString insertAttributedString:imgAttributedStr atIndex:30];
step 5 后面添加:
//绘制图片
CFArrayRef lines = CTFrameGetLines(frame);
CGPoint lineOrigins[CFArrayGetCount(lines)];
CTFrameGetLineOrigins(frame, CFRangeMake(0, 0), lineOrigins);//获取第行的起始点
for (int i = 0; i < CFArrayGetCount(lines); i++) {
CTLineRef line = CFArrayGetValueAtIndex(lines, i);
CGFloat lineAscent;//上缘线
CGFloat lineDescent;//下缘线
CGFloat lineLeading;//行间距
CTLineGetTypographicBounds(line, &lineAscent, &lineDescent, &lineLeading);//获取此行的字形参数
//获取此行中每个CTRun
CFArrayRef runs = CTLineGetGlyphRuns(line);
for(int j = 0;j< CFArrayGetCount(runs);j++){
CGFloat runAscent;//此CTRun上缘线
CGFloat runDescent;//此CTRun下缘线
CGPoint lineOrigin = lineOrigins[i];//此行起点
CTRunRef run = CFArrayGetValueAtIndex(runs, j);//获取此CTRun
NSDictionary *attributes = (NSDictionary *)CTRunGetAttributes(run);
CGRect runRect;
//获取此CTRun的上缘线,下缘线,并由此获取CTRun和宽度
runRect.size.width = CTRunGetTypographicBounds(run, CFRangeMake(0, 0), &runAscent, &runDescent, NULL);
//CTRun的X坐标
CGFloat runOrgX = lineOrigin.x + CTLineGetOffsetForStringIndex(line, CTRunGetStringRange(run).location, NULL);
runRect = CGRectMake(runOrgX,lineOrigin.y-runDescent,runRect.size.width,runAscent+runDescent );
NSString *imgName = [attributes objectForKey:kImgName];
if (imgName) {
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:imgName];
if(image){
CGRect imageRect ;
imageRect.size = image.size;
imageRect.origin.x = runRect.origin.x + lineOrigin.x;
imageRect.origin.y = lineOrigin.y;
CGContextDrawImage(context, imageRect, image.CGImage);
}
}
}
}
代理函数:
#pragma mark - CTRunDelegateCallbacks
void ImgRunDelegateDeallocCallback( void* refCon ){
}
CGFloat ImgRunDelegateGetAscentCallback( void *refCon ){
NSString *imageName = (__bridge NSString *)refCon;
return [UIImage imageNamed:imageName].size.height;
}
CGFloat ImgRunDelegateGetDescentCallback(void *refCon){
return 0;
}
CGFloat ImgRunDelegateGetWidthCallback(void *refCon){
NSString *imageName = (__bridge NSString *)refCon;
return [UIImage imageNamed:imageName].size.width;
}
效果如下:

基于以上这个原型,我们可以封装一个比较完整的富文本控件,比如定义HTML协议或者JSON,然后在内部进行解析,然后根据类型与相应的属性进行绘制。
4. 图片点击事件
CoreText就是将内容绘制到画布上,自然没有事件处理,我们要实现图片与链接的点击效果就需要使用触摸事件了。当点击的位置在图片的Rect中,那我们做相应的操作即可,所以基本步骤如下:
记录所有图片所在画布中作为一个CTRun的位置 -> 获取每个图片所在画布中所占的Rect矩形区域 -> 当点击事件发生时,判断点击的点是否在某个需要处理的图片Rect内。
这里为了演示的简单,我们直接在drawRect中记录图片的相应坐标,但是一般我们会在CTRichView渲染之前对数据进行相应的处理,比如处理传入的样式数据、记录图片与链接等信息。
用于记录图片信息类
@interface CTImageData : NSObject
@property (nonatomic,strong) NSString *imgHolder;
@property (nonatomic,strong) NSURL *imgPath;
@property (nonatomic) NSInteger idx;
@property (nonatomic) CGRect imageRect;
@end
//记录图片信息
//以下操作仅仅是演示示例,实战时请在渲染之前处理数据,做到最佳实践。
if(!_imageDataArray){
_imageDataArray = [[NSMutableArray alloc]init];
}
BOOL imgExist = NO;
for (CTImageData *ctImageData in _imageDataArray) {
if (ctImageData.idx == idx) {
imgExist = YES;
break;
}
}
if(!imgExist){
CTImageData *ctImageData = [[CTImageData alloc]init];
ctImageData.imgHolder = imgName;
ctImageData.imageRect = imageRect;
ctImageData.idx = idx;
[_imageDataArray addObject:ctImageData];
}
- (void)setupEvents{
UITapGestureRecognizer *tapRecognizer = [[UITapGestureRecognizer alloc]initWithTarget:self action:@selector(userTapGestureDetected:)];
[self addGestureRecognizer:tapRecognizer];
self.userInteractionEnabled = YES;
}
- (void)userTapGestureDetected:(UIGestureRecognizer *)recognizer{
CGPoint point = [recognizer locationInView:self];
//先判断是否是点击的图片Rect
for(CTImageData *imageData in _imageDataArray){
CGRect imageRect = imageData.imageRect;
CGFloat imageOriginY = self.bounds.size.height - imageRect.origin.y - imageRect.size.height;
CGRect rect = CGRectMake(imageRect.origin.x,imageOriginY, imageRect.size.width, imageRect.size.height);
if(CGRectContainsPoint(rect, point)){
NSLog(@"tap image handle");
return;
}
}
//再判断链接
}
5. 链接点击事件
记录链接信息类
@interface CTLinkData : NSObject
@property (nonatomic ,strong) NSString *text;
@property (nonatomic ,strong) NSString *url;
@property (nonatomic ,assign) NSRange range;
@end
记录链接信息
if(!_linkDataArray){
_linkDataArray = [[NSMutableArray alloc]init];
}
CTLinkData *ctLinkData = [[CTLinkData alloc]init];
ctLinkData.text = [attributedString.string substringWithRange:linkRange];
ctLinkData.url = @"http://www.baidu.com";
ctLinkData.range = linkRange;
[_linkDataArray addObject:ctLinkData];
处理链接事件
- (void)userTapGestureDetected:(UIGestureRecognizer *)recognizer{
CGPoint point = [recognizer locationInView:self];
//先判断是否是点击的图片Rect
//......
//再判断链接
CFIndex idx = [self touchPointOffset:point];
if (idx != -1) {
for(CTLinkData *linkData in _linkDataArray){
if (NSLocationInRange(idx, linkData.range)) {
NSLog(@"tap link handle,url:%@",linkData.url);
break;
}
}
}
}
根据点击点获取字符串偏移
- (CFIndex)touchPointOffset:(CGPoint)point{
//获取所有行
CFArrayRef lines = CTFrameGetLines(_ctFrame);
if(lines == nil){
return -1;
}
CFIndex count = CFArrayGetCount(lines);
//获取每行起点
CGPoint origins[count];
CTFrameGetLineOrigins(_ctFrame, CFRangeMake(0, 0), origins);
//Flip
CGAffineTransform transform = CGAffineTransformMakeTranslation(0, self.bounds.size.height);
transform = CGAffineTransformScale(transform, 1.f, -1.f);
CFIndex idx = -1;
for (int i = 0; i< count; i++) {
CGPoint lineOrigin = origins[i];
CTLineRef line = CFArrayGetValueAtIndex(lines, i);
//获取每一行Rect
CGFloat ascent = 0.0f;
CGFloat descent = 0.0f;
CGFloat leading = 0.0f;
CGFloat width = (CGFloat)CTLineGetTypographicBounds(line, &ascent, &descent, &leading);
CGRect lineRect = CGRectMake(lineOrigin.x, lineOrigin.y - descent, width, ascent + descent);
lineRect = CGRectApplyAffineTransform(lineRect, transform);
if(CGRectContainsPoint(lineRect,point)){
//将point相对于view的坐标转换为相对于该行的坐标
CGPoint linePoint = CGPointMake(point.x-lineRect.origin.x, point.y-lineRect.origin.y);
//根据当前行的坐标获取相对整个CoreText串的偏移
idx = CTLineGetStringIndexForPosition(line, linePoint);
}
}
return idx;
}
6、微博类型富文本实现异步绘制
当我们涉及到图文混排时候的高度计算
http://www.jianshu.com/p/a7f55e456539
YYLable
1、解析@、超链接、图片、表情
2、逐行逐Run异步绘制,
3、点击高亮背景绘制
3、点击效果、事件
参考
10 (OC)* Coretext的更多相关文章
- 10.OC中retainCount返回值不准的原因
翻看该方法的参考文档,苹果对retainCount方法的描述如下: retainCount Do not use this method. (required) - (NSUInteger)retai ...
- Swift与OC区别
一.Swift与OC区别: 1.swift程序的入口是UIApplicationMain; 2.OC的类是以.h和.m组成的;swift是一.swift结尾的; 3.OC的类是以@interface和 ...
- OC 面试问题汇总
OC 问题汇总: 1. 你如何理解 iOS 内存管理 1. new alloc copy retain这些对象我们都要主动的release或者 autorelease 2. 如果是类方法创建的 ...
- IOS学习之路--OC的基础知识
1.项目经验 2.基础问题 3.指南认识 4.解决思路 ios开发三大块: 1.Oc基础 2.CocoaTouch框架 3.Xcode使用 -------------------- CocoaTouc ...
- Swift-常量变量
OC 用NSLog输出日志 swift 用print输出日志 swift语句结束不需要加:号 常量和变量: OC 定义常量 const int a = 10; swift 定义常量 let a = 1 ...
- js封装、简单实例源码记录
1.运动封装:doMove ( obj, attr, dir, target, endFn ) 加入回调.&&.||用法注释 <script> var oBtn1 = d ...
- Swift 初步了解
Swift 初步了解 前言: 本篇博客会结合OC对Swift进行简单介绍. OC 用NSLog输出日志 NSLog(@"旭宝爱吃鱼"); Swift 用print输出日志 prin ...
- iOS开发——面试笔试精华(一)
面试笔试精华(一) 1. #import 跟#include.@class有什么区别?#import<> 跟 #import”"又什么区别? 1> #imp ...
- Objective-C 学习 (一):Objective-C 概述
1. OC在C的基础上新增了一些面向对象的语法,将C的复杂的.繁琐的语法封装的更为简单.且OC完全兼容C语言. 2. OC程序的源文件的后缀名是.m, m 代表message,代表OC中最重要的一个机 ...
随机推荐
- Mybatis mapper动态代理的原理详解
在开始动态代理的原理讲解以前,我们先看一下集成mybatis以后dao层不使用动态代理以及使用动态代理的两种实现方式,通过对比我们自己实现dao层接口以及mybatis动态代理可以更加直观的展现出my ...
- python学习之路(3)---列表
列表定义: 列表就是一个数据的集合,列表是可以重复的,可以对存储的数据进行增删改查, 列表的写法: list_name = ['ljwang','wangwu'] 列表的嵌套 a = ['1',['2 ...
- Zabbix监控华为路由器配置
zabbix监控华为路由器 一.配置路由器界面: 开启snmpv2c功能,同时勾选v2c版本(不要勾v1,不安全,其实v2也不安全,如果很注重安全的话,一定要只配置v3). 手里没有路由器登录账号,大 ...
- Django之ORM-model模型关系
模型类关系 1)一对多关系例:图书类-英雄类 models.ForeignKey() 定义在多的类中. 2)多对多关系例:新闻类-新闻类型类 体育新闻 国际新闻models.ManyToManyFie ...
- Linux环境搭建 | 手把手教你安装Linux虚拟机
前言 作为一名Linux工程师,不管是运维.应用.驱动方向,在工作中肯定会需要Linux环境.想要获得Linux环境,一个办法就是将电脑系统直接换成Linux系统,但我们平常用惯了Windows系统, ...
- 百度地图获取定位,实现拖动marker定位,返回具体的位置名
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content ...
- Oracle - Tables
创建表 a: Sql语句创建 -- Create table create table Table_Name ( 字段1 VARCHAR2(50), 字段2 VARCHAR2(50) not null ...
- H5调用相机和相册更换头像
需求:H5调用手机的相机和相册从而实现更换头像的功能 这个功能是很常用的一个功能,因此做一个记录. 1.在头像img下加一个文件输入框 <input type="file" ...
- WebApi使用OAuth2认证
本篇文章实现了四种认证方式中的客户端模式和密码模式,未实现token持久化 未介绍OAuth2的相关概念,全部是干货,可自己在网上搜索OAuth2相关知识,在这不做过多阐述 一.引用OAuth2所需的 ...
- P1726 上白泽慧音 tarjan 模板
P1726 上白泽慧音 这是一道用tarjan做的模板,要求找到有向图中最大的联通块. #include <algorithm> #include <iterator> #in ...