Spark Streaming源码分析 – DStream
A Discretized Stream (DStream), the basic abstraction in Spark Streaming, is a continuous sequence of RDDs (of the same type) representing a continuous stream of data.
Dstream本质就是离散化的stream,将stream离散化成一组RDD的list,所以基本的操作仍然是以RDD为基础
下面看到DStream的基本定义,对于普通的RDD而言,时间对于DStream是更为重要的因素
将stream切分成RDD的interval时间,stream开始的时间,DStream需要保留的RDD的时间,每个RDD所对于的时间key……
DStream抽象定义
/**
* A Discretized Stream (DStream), the basic abstraction in Spark Streaming, is a continuous
* sequence of RDDs (of the same type) representing a continuous stream of data (see
* org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD in the Spark core documentation for more details on RDDs).
* DStreams can either be created from live data (such as, data from TCP sockets, Kafka, Flume,
* etc.) using a [[org.apache.spark.streaming.StreamingContext]] or it can be generated by
* transforming existing DStreams using operations such as `map`,
* `window` and `reduceByKeyAndWindow`. While a Spark Streaming program is running, each DStream
* periodically generates a RDD, either from live data or by transforming the RDD generated by a
* parent DStream.
*
* This class contains the basic operations available on all DStreams, such as `map`, `filter` and
* `window`. In addition, [[org.apache.spark.streaming.dstream.PairDStreamFunctions]] contains
* operations available only on DStreams of key-value pairs, such as `groupByKeyAndWindow` and
* `join`. These operations are automatically available on any DStream of pairs
* (e.g., DStream[(Int, Int)] through implicit conversions when
* `org.apache.spark.streaming.StreamingContext._` is imported.
*
* DStreams internally is characterized by a few basic properties:
* - A list of other DStreams that the DStream depends on
* - A time interval at which the DStream generates an RDD
* - A function that is used to generate an RDD after each time interval
*/ abstract class DStream[T: ClassTag] (
@transient private[streaming] var ssc: StreamingContext
) extends Serializable with Logging { // =======================================================================
// Methods that should be implemented by subclasses of DStream
// ======================================================================= /** Time interval after which the DStream generates a RDD */
def slideDuration: Duration // 将stream切分成RDD的interval /** List of parent DStreams on which this DStream depends on */
def dependencies: List[DStream[_]] // 和RDD一样,DStream之间也存在dependency关系 /** Method that generates a RDD for the given time */
def compute (validTime: Time): Option[RDD[T]] // RDD的生成逻辑 // =======================================================================
// Methods and fields available on all DStreams
// ======================================================================= // RDDs generated, marked as private[streaming] so that testsuites can access it
@transient
private[streaming] var generatedRDDs = new HashMap[Time, RDD[T]] () // 最为核心的结构,可以看到DStream就是以time为key的RDD的hashmap // Time zero for the DStream
private[streaming] var zeroTime: Time = null // Stream开始的时间 // Duration for which the DStream will remember each RDD created
private[streaming] var rememberDuration: Duration = null // Stream是无限的,而在DStream不可能保留所有的RDD,所以设置DStream需要remember的duration // Storage level of the RDDs in the stream
private[streaming] var storageLevel: StorageLevel = StorageLevel.NONE // Checkpoint details
private[streaming] val mustCheckpoint = false
private[streaming] var checkpointDuration: Duration = null
private[streaming] val checkpointData = new DStreamCheckpointData(this) // Reference to whole DStream graph
private[streaming] var graph: DStreamGraph = null // DStreamGraph // Duration for which the DStream requires its parent DStream to remember each RDD created
private[streaming] def parentRememberDuration = rememberDuration /** Return the StreamingContext associated with this DStream */
def context = ssc /** Persist the RDDs of this DStream with the given storage level */
def persist(level: StorageLevel): DStream[T] = {
this.storageLevel = level
this
} /** Persist RDDs of this DStream with the default storage level (MEMORY_ONLY_SER) */
def persist(): DStream[T] = persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY_SER) /** Persist RDDs of this DStream with the default storage level (MEMORY_ONLY_SER) */
def cache(): DStream[T] = persist() /**
* Enable periodic checkpointing of RDDs of this DStream
* @param interval Time interval after which generated RDD will be checkpointed
*/
def checkpoint(interval: Duration): DStream[T] = {
persist()
checkpointDuration = interval
this
}
}
getOrCompute
注意的是,这里是产生RDD对象,而不是真正的进行计算,只有在runjob时才会做真正的计算
Spark RDD本身是不包含具体数据的,只是定义了workflow(依赖关系),处理逻辑
/**
* Retrieve a precomputed RDD of this DStream, or computes the RDD. This is an internal
* method that should not be called directly.
*/
private[streaming] def getOrCompute(time: Time): Option[RDD[T]] = {
// If this DStream was not initialized (i.e., zeroTime not set), then do it
// If RDD was already generated, then retrieve it from HashMap
generatedRDDs.get(time) match { // If an RDD was already generated and is being reused, then
// probably all RDDs in this DStream will be reused and hence should be cached
case Some(oldRDD) => Some(oldRDD) // if RDD was not generated, and if the time is valid
// (based on sliding time of this DStream), then generate the RDD
case None => { // 需要compute
if (isTimeValid(time)) { // invalid的定义,(time <= zeroTime || ! (time - zeroTime).isMultipleOf(slideDuration)
compute(time) match { // 使用compute生成RDD对象
case Some(newRDD) =>
if (storageLevel != StorageLevel.NONE) {
newRDD.persist(storageLevel) // 设置persist level
}
if (checkpointDuration != null &&
(time - zeroTime).isMultipleOf(checkpointDuration)) {
newRDD.checkpoint() // 设置checkpoint
}
generatedRDDs.put(time, newRDD) // 将产生的RDD对象放入generatedRDDs
Some(newRDD)
case None =>
None
}
} else {
None
}
}
}
}
generateJob
对于用getOrCompute产生的RDD对象,需要封装成job
而Job的关键,jobFunc,其实就是想Spark集群提交一个job
这里只是使用了emptyFunc,具体的output逻辑是需要被具体的outputDStream改写的
/**
* Generate a SparkStreaming job for the given time. This is an internal method that
* should not be called directly. This default implementation creates a job
* that materializes the corresponding RDD. Subclasses of DStream may override this
* to generate their own jobs.
*/
private[streaming] def generateJob(time: Time): Option[Job] = {
getOrCompute(time) match {
case Some(rdd) => {
val jobFunc = () => {
val emptyFunc = { (iterator: Iterator[T]) => {} }
context.sparkContext.runJob(rdd, emptyFunc)
}
Some(new Job(time, jobFunc))
}
case None => None
}
}
clearMetadata
清除过时的RDD对象,其中还会做unpersist,以及调用dependencies的clearMetadata
/**
* Clear metadata that are older than `rememberDuration` of this DStream.
* This is an internal method that should not be called directly. This default
* implementation clears the old generated RDDs. Subclasses of DStream may override
* this to clear their own metadata along with the generated RDDs.
*/
private[streaming] def clearMetadata(time: Time) {
val oldRDDs = generatedRDDs.filter(_._1 <= (time - rememberDuration))
generatedRDDs --= oldRDDs.keys
if (ssc.conf.getBoolean("spark.streaming.unpersist", false)) {
oldRDDs.values.foreach(_.unpersist(false))
}
dependencies.foreach(_.clearMetadata(time))
}
具体DStream的定义
FilteredDStream
package org.apache.spark.streaming.dstream private[streaming]
class FilteredDStream[T: ClassTag](
parent: DStream[T],
filterFunc: T => Boolean
) extends DStream[T](parent.ssc) { override def dependencies = List(parent) override def slideDuration: Duration = parent.slideDuration override def compute(validTime: Time): Option[RDD[T]] = {
parent.getOrCompute(validTime).map(_.filter(filterFunc))
}
}
WindowedDStream
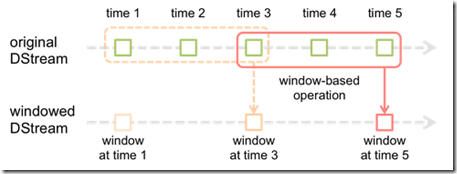
private[streaming]
class WindowedDStream[T: ClassTag](
parent: DStream[T],
_windowDuration: Duration,
_slideDuration: Duration)
extends DStream[T](parent.ssc) { // Persist parent level by default, as those RDDs are going to be obviously reused.
parent.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY_SER) //默认将parentRDD设置persist,因为parent RDD会在window slide中被反复读到 def windowDuration: Duration = _windowDuration // Windows大小 override def dependencies = List(parent) override def slideDuration: Duration = _slideDuration // Windows滑动 override def parentRememberDuration: Duration = rememberDuration + windowDuration // 保证RememberDuratioin一定大于windowDuration override def persist(level: StorageLevel): DStream[T] = {
// Do not let this windowed DStream be persisted as windowed (union-ed) RDDs share underlying
// RDDs and persisting the windowed RDDs would store numerous copies of the underlying data.
// Instead control the persistence of the parent DStream.
// 不要直接persist windowed RDDS,而是去persist parent RDD,原因是各个windows RDDs之间有大量的重复数据,直接persist浪费空间
parent.persist(level)
this
} override def compute(validTime: Time): Option[RDD[T]] = {
val currentWindow = new Interval(validTime - windowDuration + parent.slideDuration, validTime) //计算窗口inteval
val rddsInWindow = parent.slice(currentWindow)
val windowRDD = if (rddsInWindow.flatMap(_.partitioner).distinct.length == 1) {
new PartitionerAwareUnionRDD(ssc.sc, rddsInWindow)
} else {
new UnionRDD(ssc.sc,rddsInWindow) //本质就是把parent DStream窗口内的RDD做union
}
Some(windowRDD)
}
}
ShuffledDStream
private[streaming]
class ShuffledDStream[K: ClassTag, V: ClassTag, C: ClassTag](
parent: DStream[(K,V)],
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiner: (C, C) => C,
partitioner: Partitioner,
mapSideCombine: Boolean = true
) extends DStream[(K,C)] (parent.ssc) { override def dependencies = List(parent) override def slideDuration: Duration = parent.slideDuration override def compute(validTime: Time): Option[RDD[(K,C)]] = {
parent.getOrCompute(validTime) match {
case Some(rdd) => Some(rdd.combineByKey[C](
createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiner, partitioner, mapSideCombine))
case None => None
}
}
}
PairDStreamFunctions
以groupByKey为例,和普通Spark里面没啥区别,依赖是基于combineByKey实现
比较有特点是提供groupByKeyAndWindow,其实就是先使用WindowedDStream将windows中的RDD union,然后再使用combineByKey
/**
* Extra functions available on DStream of (key, value) pairs through an implicit conversion.
* Import `org.apache.spark.streaming.StreamingContext._` at the top of your program to use
* these functions.
*/
class PairDStreamFunctions[K: ClassTag, V: ClassTag](self: DStream[(K,V)])
extends Serializable { private[streaming] def ssc = self.ssc private[streaming] def defaultPartitioner(numPartitions: Int = self.ssc.sc.defaultParallelism)
= {new HashPartitioner(numPartitions)} /**
* Return a new DStream by applying `groupByKey` on each RDD. The supplied
* [[org.apache.spark.Partitioner]] is used to control the partitioning of each RDD.
*/
def groupByKey(partitioner: Partitioner): DStream[(K, Seq[V])] = {
val createCombiner = (v: V) => ArrayBuffer[V](v)
val mergeValue = (c: ArrayBuffer[V], v: V) => (c += v)
val mergeCombiner = (c1: ArrayBuffer[V], c2: ArrayBuffer[V]) => (c1 ++ c2)
combineByKey(createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiner, partitioner)
.asInstanceOf[DStream[(K, Seq[V])]]
} /**
* Combine elements of each key in DStream's RDDs using custom functions. This is similar to the
* combineByKey for RDDs. Please refer to combineByKey in
* org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions in the Spark core documentation for more information.
*/
def combineByKey[C: ClassTag](
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiner: (C, C) => C,
partitioner: Partitioner,
mapSideCombine: Boolean = true): DStream[(K, C)] = {
new ShuffledDStream[K, V, C](self, createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiner, partitioner,
mapSideCombine)
}
}
groupByKeyAndWindow
/**
* Create a new DStream by applying `groupByKey` over a sliding window on `this` DStream.
* Similar to `DStream.groupByKey()`, but applies it over a sliding window.
* @param windowDuration width of the window; must be a multiple of this DStream's
* batching interval
* @param slideDuration sliding interval of the window (i.e., the interval after which
* the new DStream will generate RDDs); must be a multiple of this
* DStream's batching interval
* @param partitioner partitioner for controlling the partitioning of each RDD in the new
* DStream.
*/
def groupByKeyAndWindow(
windowDuration: Duration,
slideDuration: Duration,
partitioner: Partitioner
): DStream[(K, Seq[V])] = {
val createCombiner = (v: Seq[V]) => new ArrayBuffer[V] ++= v
val mergeValue = (buf: ArrayBuffer[V], v: Seq[V]) => buf ++= v
val mergeCombiner = (buf1: ArrayBuffer[V], buf2: ArrayBuffer[V]) => buf1 ++= buf2
self.groupByKey(partitioner)
.window(windowDuration, slideDuration) // DStream.window会将当前的dstream封装成WindowedDStream,见下面的代码
.combineByKey[ArrayBuffer[V]](createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiner, partitioner)
.asInstanceOf[DStream[(K, Seq[V])]]
}
/**
* Return a new DStream in which each RDD contains all the elements in seen in a
* sliding window of time over this DStream.
* @param windowDuration width of the window; must be a multiple of this DStream's
* batching interval
* @param slideDuration sliding interval of the window (i.e., the interval after which
* the new DStream will generate RDDs); must be a multiple of this
* DStream's batching interval
*/
def window(windowDuration: Duration, slideDuration: Duration): DStream[T] = {
new WindowedDStream(this, windowDuration, slideDuration)
}
updateStateByKey
/**
* Return a new "state" DStream where the state for each key is updated by applying
* the given function on the previous state of the key and the new values of each key.
* [[org.apache.spark.Partitioner]] is used to control the partitioning of each RDD.
* @param updateFunc State update function. If `this` function returns None, then
* corresponding state key-value pair will be eliminated. Note, that
* this function may generate a different a tuple with a different key
* than the input key. It is up to the developer to decide whether to
* remember the partitioner despite the key being changed.
* @param partitioner Partitioner for controlling the partitioning of each RDD in the new
* DStream
* @param rememberPartitioner Whether to remember the paritioner object in the generated RDDs.
* @tparam S State type
*/
def updateStateByKey[S: ClassTag](
updateFunc: (Iterator[(K, Seq[V], Option[S])]) => Iterator[(K, S)],
partitioner: Partitioner,
rememberPartitioner: Boolean
): DStream[(K, S)] = {
new StateDStream(self, ssc.sc.clean(updateFunc), partitioner, rememberPartitioner)
}
StateDStream
普通的DStream,都是直接从ParentRDD通过compute来得到当前的RDD
而StateDStream的特别之处,除了ParentRDD,还需要参考PreviousRDD,这个只存在在stream场景下,只有这个场景下,RDD之间才存在时间关系
PreviousRDD = getOrCompute(validTime - slideDuration),即在DStream的generatedRDDs上前一个时间interval上的RDD
处理函数,val finalFunc = (iterator: Iterator[(K, (Seq[V], Seq[S]))]) => { },需要3个参数,key,ParentRDD上的value,PreviousRDD上的value
处理函数需要考虑,当ParentRDD或PreviousRDD为空的情况
注意StateDStream,默认需要做persist和checkpoint
private[streaming]
class StateDStream[K: ClassTag, V: ClassTag, S: ClassTag](
parent: DStream[(K, V)],
updateFunc: (Iterator[(K, Seq[V], Option[S])]) => Iterator[(K, S)],
partitioner: Partitioner,
preservePartitioning: Boolean
) extends DStream[(K, S)](parent.ssc) { super.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY_SER) // RDD persist默认设为memory,因为后面的RDD需要用到 override def dependencies = List(parent) override def slideDuration: Duration = parent.slideDuration override val mustCheckpoint = true // 默认需要checkpoint,需要保持状态 override def compute(validTime: Time): Option[RDD[(K, S)]] = { // Try to get the previous state RDD
getOrCompute(validTime - slideDuration) match { case Some(prevStateRDD) => { // If previous state RDD exists // Try to get the parent RDD
parent.getOrCompute(validTime) match { // 既有PreviousRDD,又有ParentRDD的case
case Some(parentRDD) => { // If parent RDD exists, then compute as usual // Define the function for the mapPartition operation on cogrouped RDD;
// first map the cogrouped tuple to tuples of required type,
// and then apply the update function
val updateFuncLocal = updateFunc
val finalFunc = (iterator: Iterator[(K, (Seq[V], Seq[S]))]) => {
val i = iterator.map(t => {
(t._1, t._2._1, t._2._2.headOption)
})
updateFuncLocal(i)
}
val cogroupedRDD = parentRDD.cogroup(prevStateRDD, partitioner) //`(k, a) cogroup (k, b)` produces k -> Seq(ArrayBuffer as, ArrayBuffer bs)
val stateRDD = cogroupedRDD.mapPartitions(finalFunc, preservePartitioning)
Some(stateRDD)
}
case None => { // If parent RDD does not exist,ParentRDD不存在 // Re-apply the update function to the old state RDD
val updateFuncLocal = updateFunc
val finalFunc = (iterator: Iterator[(K, S)]) => {
val i = iterator.map(t => (t._1, Seq[V](), Option(t._2))) // 直接把ParentRDD置空,Seq[V]()
updateFuncLocal(i)
}
val stateRDD = prevStateRDD.mapPartitions(finalFunc, preservePartitioning)
Some(stateRDD)
}
}
} case None => { // If previous session RDD does not exist (first input data) // Try to get the parent RDD
parent.getOrCompute(validTime) match {
case Some(parentRDD) => { // If parent RDD exists, then compute as usual,PreviousRDD为空的case,说明是第一个state RDD // Define the function for the mapPartition operation on grouped RDD;
// first map the grouped tuple to tuples of required type,
// and then apply the update function
val updateFuncLocal = updateFunc
val finalFunc = (iterator: Iterator[(K, Seq[V])]) => {
updateFuncLocal(iterator.map(tuple => (tuple._1, tuple._2, None))) // 把PreviousRDD置为None
} val groupedRDD = parentRDD.groupByKey(partitioner)
val sessionRDD = groupedRDD.mapPartitions(finalFunc, preservePartitioning)
//logDebug("Generating state RDD for time " + validTime + " (first)")
Some(sessionRDD)
}
case None => { // If parent RDD does not exist, then nothing to do!,previous和parent都没有,当然啥也做不了
//logDebug("Not generating state RDD (no previous state, no parent)")
None
}
}
}
}
}
}
TransformedDStream
首先这是个比较通用的operation,可以通过自定义的transformFunc,将一组parentRDDs计算出当前的RDD
需要注意的是,这些parentRDDs必须在同一个streamContext下,并且有相同的slideDuration
在DStream接口中,可以提供transform和transformWith两种,参考下面源码
private[streaming]
class TransformedDStream[U: ClassTag] (
parents: Seq[DStream[_]],
transformFunc: (Seq[RDD[_]], Time) => RDD[U]
) extends DStream[U](parents.head.ssc) { require(parents.length > 0, "List of DStreams to transform is empty")
require(parents.map(_.ssc).distinct.size == 1, "Some of the DStreams have different contexts")
require(parents.map(_.slideDuration).distinct.size == 1,
"Some of the DStreams have different slide durations") override def dependencies = parents.toList override def slideDuration: Duration = parents.head.slideDuration override def compute(validTime: Time): Option[RDD[U]] = {
val parentRDDs = parents.map(_.getOrCompute(validTime).orNull).toSeq
Some(transformFunc(parentRDDs, validTime))
}
}
/**
* Return a new DStream in which each RDD is generated by applying a function
* on each RDD of 'this' DStream.
*/
def transform[U: ClassTag](transformFunc: (RDD[T], Time) => RDD[U]): DStream[U] = {
val cleanedF = context.sparkContext.clean(transformFunc)
val realTransformFunc = (rdds: Seq[RDD[_]], time: Time) => {
assert(rdds.length == 1)
cleanedF(rdds.head.asInstanceOf[RDD[T]], time)
}
new TransformedDStream[U](Seq(this), realTransformFunc) // this,单个RDD
}
/**
* Return a new DStream in which each RDD is generated by applying a function
* on each RDD of 'this' DStream and 'other' DStream.
*/
def transformWith[U: ClassTag, V: ClassTag](
other: DStream[U], transformFunc: (RDD[T], RDD[U], Time) => RDD[V]
): DStream[V] = {
val cleanedF = ssc.sparkContext.clean(transformFunc)
val realTransformFunc = (rdds: Seq[RDD[_]], time: Time) => {
assert(rdds.length == 2)
val rdd1 = rdds(0).asInstanceOf[RDD[T]]
val rdd2 = rdds(1).asInstanceOf[RDD[U]]
cleanedF(rdd1, rdd2, time)
}
new TransformedDStream[V](Seq(this, other), realTransformFunc) // this and other,多个RDDs
}
Spark Streaming源码分析 – DStream的更多相关文章
- 10.Spark Streaming源码分析:Receiver数据接收全过程详解
原创文章,转载请注明:转载自 听风居士博客(http://www.cnblogs.com/zhouyf/) 在上一篇中介绍了Receiver的整体架构和设计原理,本篇内容主要介绍Receiver在 ...
- Spark Streaming源码分析 – Checkpoint
PersistenceStreaming没有做特别的事情,DStream最终还是以其中的每个RDD作为job进行调度的,所以persistence就以RDD为单位按照原先Spark的方式去做就可以了, ...
- Spark Streaming源码分析 – JobScheduler
先给出一个job从被generate到被执行的整个过程在JobGenerator中,需要定时的发起GenerateJobs事件,而每个job其实就是针对DStream中的一个RDD,发起一个Spark ...
- Spark Streaming源码分析 – InputDStream
对于NetworkInputDStream而言,其实不是真正的流方式,将数据读出来后不是直接去处理,而是先写到blocks中,后面的RDD再从blocks中读取数据继续处理这就是一个将stream离散 ...
- Spark Streaming源码解读之JobScheduler内幕实现和深度思考
本期内容 : JobScheduler内幕实现 JobScheduler深度思考 JobScheduler 是整个Spark Streaming调度的核心,需要设置多线程,一条用于接收数据不断的循环, ...
- 第十一篇:Spark SQL 源码分析之 External DataSource外部数据源
上周Spark1.2刚发布,周末在家没事,把这个特性给了解一下,顺便分析下源码,看一看这个特性是如何设计及实现的. /** Spark SQL源码分析系列文章*/ (Ps: External Data ...
- 第十篇:Spark SQL 源码分析之 In-Memory Columnar Storage源码分析之 query
/** Spark SQL源码分析系列文章*/ 前面讲到了Spark SQL In-Memory Columnar Storage的存储结构是基于列存储的. 那么基于以上存储结构,我们查询cache在 ...
- 第九篇:Spark SQL 源码分析之 In-Memory Columnar Storage源码分析之 cache table
/** Spark SQL源码分析系列文章*/ Spark SQL 可以将数据缓存到内存中,我们可以见到的通过调用cache table tableName即可将一张表缓存到内存中,来极大的提高查询效 ...
- 第七篇:Spark SQL 源码分析之Physical Plan 到 RDD的具体实现
/** Spark SQL源码分析系列文章*/ 接上一篇文章Spark SQL Catalyst源码分析之Physical Plan,本文将介绍Physical Plan的toRDD的具体实现细节: ...
随机推荐
- python爬虫请求库之selenium模块
一 介绍 selenium最初是一个自动化测试工具,而爬虫中使用它主要是为了解决requests无法直接执行JavaScript代码的问题 selenium本质是通过驱动浏览器,完全模拟浏览器 ...
- js中如何判断一个字符串包含另外一个字符串?
js中判断一个字符串包含另外一个字符串的方式比较多? 比如indexOf()方法,注意O是大写. var test="this is a test"; if(test.indexO ...
- 网页尺寸offsetHeight,offsetWidth
网页尺寸offsetHeight offsetHeight和offsetWidth,获取网页内容高度和宽度(包括滚动条等边线,会随窗口的显示大小改变). 一.值 offsetHeight = clie ...
- lua工具库penlight--07函数编程(二)
列表压缩 列表压缩是以紧凑的方式通过指定的元素创建表.在 Python里,你可以说: ls = [x for x in range(5)] # == [0,1,2,3,4] 在 Lua,使用pl.c ...
- Ubuntu 12.04 Subversion及GUI客户端RabbitVCS安装
(经过一天的使用,发现pygtk的内存泄漏问题严重影响使用,需要打一下deepin ui做的补丁:https://github.com/linuxdeepin/deepin-ui) 1. 类似Tort ...
- jquery设置radio选中
<script type="text/javascript"> $(document).ready(function(){ $("input[type=rad ...
- ImportError: No module named mysql 报错python引用mysql报错
需要安装 pip2.7 install MySQL-python pip2.7 install mysql-connector
- EasyUI 表单 tree
第一步:创建HTML标记 <divid="dlg"style="padding:20px;"> <h2>Account Info ...
- 通过http输出流的方式从将html写入到Excel
private void HtmlResponseToExecl() { //将数据(html)导入到Excel中 Response.Charset = "gb2312"; Res ...
- Python使用pycurl获取http的响应时间
最近需要对节点到源站自己做个监控,简单的ping可以检测到一些东西,但是http请求的检查也要进行,于是就研究了下pycurlpycurl是个用c语言实现的python 库,虽然据说不是那么pytho ...
