Saltstack_使用指南06_远程执行-指定目标
1. 主机规划
Targeting Minions文档
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/contents.html
另请参见:自动化运维神器之saltstack (三)节点组及复合匹配器
注意事项
修改了master或者minion的配置文件,那么必须重启对应的服务。
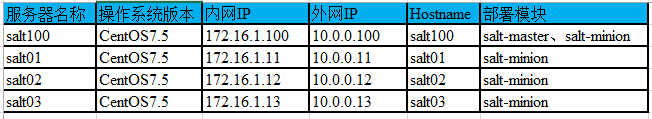
2. 目标指定方式
|
Letter |
Match Type |
Example |
|
|
G |
Grains glob |
G@os:Ubuntu |
Yes |
|
E |
PCRE Minion ID |
E@web\d+\.(dev|qa|prod)\.loc |
No |
|
P |
Grains PCRE |
P@os:(RedHat|Fedora|CentOS) |
Yes |
|
L |
List of minions |
L@minion1.example.com,minion3.domain.com or bl*.domain.com |
No |
|
I |
Pillar glob |
I@pdata:foobar |
Yes |
|
J |
Pillar PCRE |
J@pdata:^(foo|bar)$ |
Yes |
|
S |
Subnet/IP address |
S@192.168.1.0/24 or S@192.168.1.100 |
No |
|
R |
Range cluster |
R@%foo.bar |
No |
Matchers can be joined using boolean and, or, and not operators. 【复合匹配的时候】
2.1. 当前有哪些minion
[root@salt100 ~]# salt '*' test.ping
salt02:
True
salt100:
True
salt03:
True
salt01:
True
3. 通过minion id匹配
3.1. 通配符匹配
在 top file 中也仍然适用。【推荐使用】
# Match all minions:
salt '*' test.ping # Match all minions in the example.net domain or any of the example domains:
salt '*.example.net' test.ping
salt '*.example.*' test.ping # Match all the 「webN」 minions in the example.net domain (web1.example.net, web2.example.net … webN.example.net):
salt 'web?.example.net' test.ping # Match the 「web1」 through 「web5」 minions:
salt 'web[1-5]' test.ping # Match the 「web1」 and 「web3」 minions:
salt 'web[1,3]' test.ping # Match the 「web-x」, 「web-y」, and 「web-z」 minions:
salt 'web-[x-z]' test.ping
3.2. 正则表达式(-E)
使用较少,因为正则写错的几率会大些。
正则规则参见:
https://blog.csdn.net/woshizhangliang999/article/details/46859161
# Match both 「web1-prod」 and 「web1-devel」 minions:
salt -E 'web1-(prod|devel)' test.ping
3.2.1. 在 top file 中的使用
base:
'web1-(prod|devel)':
- match: pcre # 使用正则匹配
- webserver
3.3. 列表匹配(-L)
salt -L 'web1,web2,web3' test.ping
4. 使用grains指定(-G)
# For example, the following matches all CentOS minions:
salt -G 'os:CentOS' test.ping # Match all minions with -bit CPUs, and return number of CPU cores for each matching minion:
salt -G 'cpuarch:x86_64' grains.item num_cpus
4.1. 嵌套匹配【细粒度匹配】
[root@salt100 ~]# salt -G 'ip_interfaces:eth0' test.ping
salt01:
True
salt02:
True
salt03:
True
salt100:
True
[root@salt100 ~]# salt -G 'ip_interfaces:eth0:*11*' test.ping
salt01:
True
5. 使用pillar指定(-I)
像grains匹配一样,也支持嵌套匹配。
# 具体匹配
salt -I 'somekey:specialvalue' test.ping
5.1. 嵌套匹配【细粒度匹配】
[root@salt100 ~]# salt -I 'level1:level2:my_user:*zhang*' test.ping
salt03:
True
salt02:
True
6. 子网/IP 地址匹配(-S)
# Minions can easily be matched based on IP address, or by subnet
salt -S 172.16.1.11 test.ping # 具体地址
salt -S 172.16.1.0/ test.ping # 网段
salt -S fe80::20c:29ff:fe95:1b7a test.ping # IPv 具体配置
salt -S :db8::/ test.ping # IPv 网段配置
6.1. 用于复合匹配
# Ipcidr matching can also be used in compound matches
salt -C 'S@10.0.0.0/24 and G@os:Debian' test.ping
6.2. 用于pillar和状态的top file匹配
'172.16.0.0/12':
- match: ipcidr # 匹配方式
- internal
7. 复合匹配(-C)
Matchers can be joined using boolean and, or, and not operators. 【复合匹配的时候】
# the following string matches all 「Debian minions」 with a hostname that begins with 「webserv」, as well as any minions that have a hostname which matches the regular expression 「web-dc1-srv.* 」:
salt -C 'webserv* and G@os:Debian or E@web-dc1-srv.*' test.ping # Excluding a minion based on its ID is also possible:
salt -C 'not web-dc1-srv' test.ping # Versions prior to 2015.8. a leading 「not」 was not supported in compound matches. Instead, something like the following was required:
salt -C '* and not G@kernel:Darwin' test.ping # Excluding a minion based on its ID was also possible:
salt -C '* and not web-dc1-srv' test.ping
7.1. 在 top file 中的使用
base:
'webserv* and G@os:Debian or E@web-dc1-srv.*':
- match: compound # 复合匹配
- webserver
7.2. 优先匹配
# 可以使用括号实现优先匹配
# 一定要注意括号和目标之间需要「空格」。不遵守此规则可能导致错误的目标!
salt -C '( ms-1 or G@id:ms-3 ) and G@id:ms-3' test.ping
7.3. 替换分隔符
# 默认为 「:」 改为其他字符分割
salt -C 'J|@foo|bar|^foo:bar$ or J!@gitrepo!https://github.com:example/project.git' test.ping
案例1
[root@salt100 ~]# salt -C 'G@os:redhat03' test.ping
salt01:
True
[root@salt100 ~]#
[root@salt100 ~]# salt -C 'G|@os|redhat03' test.ping # 将分隔符从「:」 改为「|」
salt01:
True
[root@salt100 ~]# salt -C 'G!@os!redhat03' test.ping #将分隔符从「:」 改为「!」
salt01:
True
[root@salt100 ~]# salt -C 'G!@os!redhat03 or salt02' test.ping
salt02:
True
salt01:
True
案例2
[root@salt-master- ~]# salt '*' pillar.item getos
10.0.0.112:
----------
getos:
----------
apache:
httpd
git:
git
172.16.1.111:
----------
getos:
----------
apache:
apache2:kkk
git:
git-core
salt-master-:
----------
getos:
----------
apache:
httpd
git:
git
[root@salt-master- ~]# salt -I 'getos:apache:apache2:kkk' test.ping
172.16.1.111:
True
[root@salt-master- ~]# salt -C 'I@getos:apache:apache2:kkk' test.ping # 因为有 apache2:kkk ,所以在某些情况下会出现错误
172.16.1.111:
True
[root@salt-master- ~]#
[root@salt-master- ~]# salt -C 'I#@getos#apache#apache2:kkk' test.ping # 表示使用 # 作为分隔符,而不是 :
172.16.1.111:
True
8. 节点组(-N)
备注:
、当向主配置文件添加或修改节点组时,必须重新启动master,以便完全识别这些更改。
、在不重启的情况下,可以使用命令行中 -N 作为目标的有限功能。
8.1. /etc/salt/master 配置
# The nodegroups master config file parameter is used to define nodegroups. Here's an example nodegroup configuration within 「/etc/salt/master」:
nodegroups:
group1: 'L@foo.domain.com,bar.domain.com,baz.domain.com or bl*.domain.com'
group2: 'G@os:Debian and foo.domain.com'
group3: 'G@os:Debian and N@group1'
group4:
- 'G@foo:bar'
- 'or'
- 'G@foo:baz' # As of the 2017.7. release of Salt, group names can also be prepended with a dash【破折号】. This brings the usage in line with many other areas of Salt. For example:
# 组节点也可以使用 如下方式。 组名前面到破折号「-」
nodegroups:
- group1: 'L@foo.domain.com,bar.domain.com,baz.domain.com or bl*.domain.com' 注意:
Nodegroups可以参考group3中看到的其他Nodegroups,确保没有循环引用。循环引用将被检测到,并导致部分扩展产生日志错误消息。
注意:
「N@」 不能在命令行和top file中使用,只能在master config 中使用
8.2. 命令行匹配
salt -N group1 test.ping
8.3. 在 top file 中的使用
base:
group1:
- match: nodegroup # 使用节点组匹配
- webserver
8.4. 根据列表的minion IDs定义为节点组
# 常规的定义方式
nodegroups:
group1: L@host1,host2,host3 # YAML 定义方式
nodegroups:
group1:
- host1
- host2
- host3
9. 批量大小(-b)
# The 「-b」 (or 「--batch-size」) option allows commands to be executed on only a specified number of minions at a time.
# 同一时间执行多少 minion,支持百分比和数字。
salt '*' -b test.ping # 同一时间执行 台,完毕后执行另外 台,依次执行下去
salt '*' -b % test.ping # 同一时间执行 % 的minion 端,完毕后执行另外 %【实际是最后的 %】。
salt -G 'os:RedHat' --batch-size % apache.signal restart # # --batch-wait minion返回后,等待多少秒在发送命令给新的minion
salt '*' -b % --batch-wait test.ping # 第一批minion反馈后,等待 秒后,在发送命令给下一批的minion。

Saltstack_使用指南06_远程执行-指定目标的更多相关文章
- Saltstack_使用指南07_远程执行-执行模块
1. 主机规划 远程执行教程文档 https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/tutorials/modules.html 所有模块文档 https://d ...
- Saltstack_使用指南02_远程执行-验证
1. 主机规划 2. Master与哪些minion通信 2.1. Master与哪些minion正常通信 [root@salt100 ~]# salt '*' test.ping salt100: ...
- Saltstack_使用指南08_远程执行-返回程序
1. 主机规划 salt 版本 [root@salt100 ~]# salt --version salt (Oxygen) [root@salt100 ~]# salt-minion --versi ...
- Saltstack_使用指南09_远程执行-编写执行模块
1. 主机规划 salt 版本 [root@salt100 ~]# salt --version salt (Oxygen) [root@salt100 ~]# salt-minion --versi ...
- expect脚本同步文件 expect脚本指定host和要同步的文件 构建文件分发系统 批量远程执行命令
自动同步文件 #!/usr/bin/expect set " spawn rsync -av root@.txt /tmp/ expect { "yes/no" { se ...
- expect脚本同步文件、expect脚本指定host和要同步的文件、构建文件分发系统、批量远程执行命令
7月20日任务 20.31 expect脚本同步文件20.32 expect脚本指定host和要同步的文件20.33 构建文件分发系统20.34 批量远程执行命令扩展:shell多线程 http:// ...
- 使用CreateRemoteThread把代码远程注入指定exe执行
由于本人也是新手,如果有朋友不懂windows api相关知识,我相信查阅书籍或者百度会比我说有帮助的多,下面就我所做简单复述一下过程,欢迎指正缺点. 效果图示如下: 做的这个例子首先是创建了一个MF ...
- 【DB2】报错:-30090 25000 指定的操作对远程执行失败
场景描述: 数据库:DB_1,DB_2 现在在DB_1中建立NICKNAME为CST_INFO_NICK,并且该别名指向数据库DB_2的CST_INFO表,在DB_1中建立存储过程,该存储过程需要 ...
- 03 深入远程执行:target目标、模块modules、返回returns
0.学习目的 http://docs.saltstack.cn/topics/execution/index.html 官方文档 0.1 命令解释 [root@host---- ~]# salt ' ...
随机推荐
- Spring Boot 2.0 教程 | AOP 切面统一打印请求日志
欢迎关注微信公众号: 小哈学Java 文章首发于个人网站 https://www.exception.site/springboot/spring-boot-aop-web-request 本节中,您 ...
- 『追捕盗贼 Tarjan算法』
追捕盗贼(COCI2007) Description 为了帮助警察抓住在逃的罪犯,你发明了一个新的计算机系统.警察控制的区域有N个城市,城市之间有E条双向边连接,城市编号为1到N. 警察经常想在罪犯从 ...
- 使用ML.NET + Azure DevOps + Azure Container Instances打造机器学习生产化
介绍 Azure DevOps,以前称为Visual Studio Team Services(VSTS),可帮助个人和组织更快地规划,协作和发布产品.其中一项值得注意的服务是Azure Pipeli ...
- asp.net core系列 33 EF查询数据 (2)
一. 原生SQL查询 接着上篇讲.通过 Entity Framework Core 可以在使用关系数据库时下降到原始 SQL 查询. 在无法使用 LINQ 表达要执行的查询时,或因使用 LINQ 查询 ...
- asp.net core 系列 9 环境(Development、Staging 、Production)
一.在asp.net core中使用多个环境 ASP.NET Core 配置是基于运行时环境, 使用环境变量.ASP.NET Core 在应用启动时读取环境变量ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONME ...
- 带着新人学springboot的应用05(springboot+RabbitMQ 上)
这次就来说说RabbitMQ,这个应该不陌生了,随便一查就知道这个是用来做消息队列的.(注意:这一节很多都是概念的东西,需要操作的比较少) 至于AMQP协议(Advanced Message Queu ...
- 简单的了解一下AQS吧
什么是AQS AQS,即AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,是一套定义了多线程访问共享资源的同步器框架.在JDK的并发包中很多类都是基于AQS进行实现的,比如ReentrantLoc ...
- 阿里云弹性容器实例产品 ECI ——云原生时代的基础设施
阿里云弹性容器实例产品 ECI ——云原生时代的基础设施 1. 什么是 ECI 弹性容器实例 ECI (Elastic Container Instance) 是阿里云在云原生时代为用户提供的基础计算 ...
- 在数据采集器中用TensorFlow进行实时机器学习
最新DataOps平台的真正价值,只有在业务用户和应用程序能够从各种数据源来访问原始数据和聚合数据,并且及时地产生数据驱动的认识时,才能够实现.利用机器学习(Machine Learning),分析师 ...
- 支持异步写入的日志类,支持Framework2.0
因为工作需要需要在XP上运行一个C#编写的Winform插件,我就用Framework2.0,因为存在接口交互所以想保留交易过程的入参出参. 考虑到插件本身实施的因素,就没有使用Log4.NLog等成 ...
