OHDSI——数据标准化
Home › Data Standardization
Data Standardization
Data standardization is the critical process of bringing data into a common format that allows for collaborative research, large-scale analytics, and sharing of sophisticated tools and methodologies【美[.meθə'dɑlədʒi],方法论;研究法;【生】分类法】. Why is it so important?
Healthcare data can vary greatly from one organization to the next. Data are collected for different purposes, such as provider reimbursement【英[ˌri:ɪm'bɜ:smənt],补偿;付还】, clinical research, and direct patient care. These data may be stored in different formats using different database systems and information models. And despite the growing use of standard terminologies in healthcare, the same concept (e.g., blood glucose) may be represented in a variety of ways from one setting to the next.
We at OHDSI are deeply involved in the evolution 【evolutionary [,ev·o'lu·tion·ar·y || ‚evə'luːʃənərɪ /ɪːv-]adj. 发展的; 渐进的; 进化的】and adoption【n. 采纳, 采用; 收养; 正式通过
】 of a Common Data Model known as the OMOP Common Data Model. We provide resources to convert a wide variety of datasets into the CDM, as well as a plethora【美['pleθərə],过多的】 of tools to take advantage of your data once it is in CDM format.
Most importantly, we have an active community that has done many data conversions (often called ETLs) with members who are eager to help you with your CDM conversion and maintenance.
OMOP Common Data Model
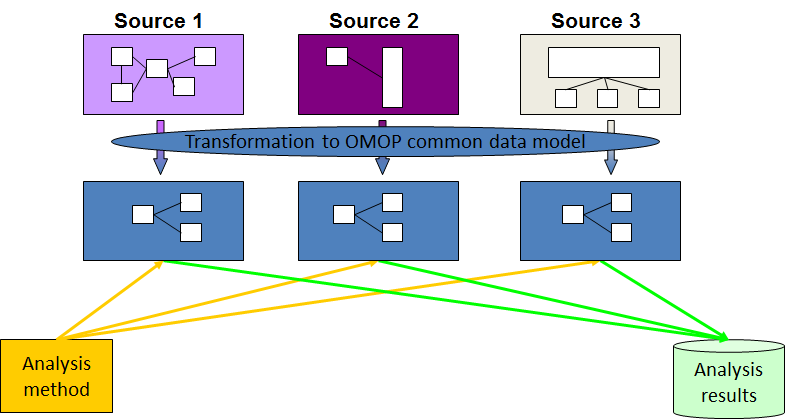
What is the OMOP Common Data Model (CDM)?
The OMOP Common Data Model allows for the systematic analysis of disparate 【disparate [dis·pa·rate || 'dɪspərət],不同的】observational databases. The concept behind this approach is to transform data contained within those databases into a common format (data model) as well as a common representation (表述)(terminologies【terminology [ter·mi·nol·o·gy |用词,术语】, vocabularies(词汇), coding schemes), and then perform systematic analyses using a library of standard analytic routines that have been written based on the common format.
Why do we need a CDM?
Observational databases differ in both purpose and design. Electronic Medical Records (EMR) are aimed at supporting clinical practice at the point of care, while administrative (adj. 管理的; 行政的)claims data are built for the insurance reimbursement 【reimbursement [,re·im'burse·ment ]补偿,赔偿】processes. Each has been collected for a different purpose, resulting in different logical organizations and physical formats, and the terminologies used to describe the medicinal products and clinical conditions vary from source to source.
The CDM can accommodate【[ac·com·mo·date || ə'kɒmədeɪt]v. 调节, 使适应, 和解; 供应; 适应】 both administrative claims and EHR, allowing users to generate evidence from a wide variety of sources. It would also support collaborative research across data sources both within and outside the United States, in addition to being manageable for data owners and useful for data users.
Why use the OMOP CDM?
The Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership (OMOP) CDM, now in its version 5.0.1, offers a solution unlike any other. OMOP found that disparate coding systems can be harmonized(和谐)—with minimal information loss—to a standardized vocabulary.
Once a database has been converted to the OMOP CDM, evidence can be generated using standardized analytics tools. We at OHDSI are currently developing Open Source tools for data quality and characterization(特征描述), medical product safety surveillance, comparative effectiveness, quality of care, and patient-level predictive modeling, but there are also other sources of such tools, some of them commercial.
For more information about the CDM please read the documentation, download the DDL for various database dialects and learn about the Standardized Vocabularies. If you have qustions post them at the OHDSI Forum.
Vocabulary Resources
The Standard Vocabulary is a foundational tool initially developed by some of us at OMOP that enables transparent and consistent content across disparate observational databases, and serves to support the OHDSI research community in conducting efficient and reproducible observational research.
To download the standard vocabularies, please visit our Athena download site:
Building your CDM
Building your CDM is a process that necessitates proper planning and execution, and we are here to help. Successful use of an observational data network requires a collaborative, interdisciplinary approach that includes:
- Local knowledge of the source data: underlying data capture process and its role in the healthcare system
- Clinical understanding of medical products and disease
- Domain expertise in the analytical use cases: epidemiology, pharmacovigilance, health economics and outcomes research
- Command of advanced statistical techniques for large-scale modeling and exploratory analysis
- Informatics experience with ontology management and leveraging standard terminologies for analysis
- Technical/programming skills to implement design and develop a scalable solution
Getting Started
Ready to get started on the conversion (ETL) process? Here are some recommended steps for an effective process:
- Train on OMOP CDM and Vocabulary
- Discuss analysis opportunities (Why are we doing this? What do you want to be able to do once CDM is done?)
- Evaluate technology requirements and infrastructure
- Discuss data dictionary and documentation on raw database
- Perform a systematic scan of raw database
- Draft Business Logic
a. Table level
b. Variable level
c. Value level (mapping)
d. Capture what will not be captured (lost) in the transformation - Create data sample to allow initial development
- DON’T START IMPLEMENTING UNTIL THE DESIGN IS COMPLETE
- don't start implementing ustil design is complete
Helpful Hints
Having gone through the ETL process with several databases over the past few years, we know that there will be obstacles to overcome and challenges to solve. Here are some helpful hints and lessons learned from the OHDSI collaborative:
- A successful ETL requires a village; don’t make one person try to be the hero and do it all themselves
- Team design
- Team implementation
- Team testing
- Document early and often, the more details the better
- Data quality checking is required at every step of the process
- Don’t make assumptions about source data based on documentation; verify by looking at the data
- Good design and comprehensive specifications should save unnecessary iterations and thrash during implementation
- ETL design/documentation/implementation is a living process. It will never be done and it can always be better. But don’t let the perfect be the enemy of the good
For more information, check out the documentation on our wiki page: www.ohdsi.org/web/wiki
And remember, the OHDSI community is here to help! Contact us at contact@ohdsi.org.
A 100k sample of CMS SynPUF data in CDM Version 5.2 is available to download on LTS Computing LLC’s download site:
OHDSI——数据标准化的更多相关文章
- 数据标准化 Normalization
数据的标准化(normalization)是将数据按比例缩放,使之落入一个小的特定区间.在某些比较和评价的指标处理中经常会用到,去除数据的单位限制,将其转化为无量纲的纯数值,便于不同单位或量级的指标能 ...
- 利用 pandas 进行数据的预处理——离散数据哑编码、连续数据标准化
数据的标准化 数据标准化就是将不同取值范围的数据,在保留各自数据相对大小顺序不变的情况下,整体映射到一个固定的区间中.根据具体的实现方法不同,有的时候会映射到 [ 0 ,1 ],有时映射到 0 附近的 ...
- 数据标准化/归一化normalization
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/52247379 基础知识参考: [均值.方差与协方差矩阵] [矩阵论:向量范数和矩阵范数] 数据的标准化 ...
- R实战 第九篇:数据标准化
数据标准化处理是数据分析的一项基础工作,不同评价指标往往具有不同的量纲,数据之间的差别可能很大,不进行处理会影响到数据分析的结果.为了消除指标之间的量纲和取值范围差异对数据分析结果的影响,需要对数据进 ...
- sklearn5_preprocessing数据标准化
sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博主亲自录制视频) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003& ...
- 转:数据标准化/归一化normalization
转自:数据标准化/归一化normalization 这里主要讲连续型特征归一化的常用方法.离散参考[数据预处理:独热编码(One-Hot Encoding)]. 基础知识参考: [均值.方差与协方差矩 ...
- 数据标准化方法及其Python代码实现
数据的标准化(normalization)是将数据按比例缩放,使之落入一个小的特定区间.目前数据标准化方法有多种,归结起来可以分为直线型方法(如极值法.标准差法).折线型方法(如三折线法).曲线型方法 ...
- python数据标准化
def datastandard(): from sklearn import preprocessing import numpy as np x = np.array([ [ 1., -1., 2 ...
- Matlab数据标准化——mapstd、mapminmax
Matlab神经网络工具箱中提供了两个自带的数据标准化处理的函数——mapstd和mapminmax,本文试图解析一下这两个函数的用法. 一.mapstd mapstd对应我们数学建模中常使用的Z-S ...
随机推荐
- 请使用千位分隔符(逗号)表示web网页中的大数字
方法一:使用正则表达式 语法如下: String(Number).replace(/(\d)(?=(\d{3})+$)/g, "$1,"); 举例: String(12345678 ...
- LCA算法解析-Tarjan&倍增&RMQ
原文链接http://www.cnblogs.com/zhouzhendong/p/7256007.html UPD(2018-5-13) : 细节修改以及使用了Latex代码,公式更加美观.改的过程 ...
- Redis数据库 02事务| 持久化| 主从复制| 集群
1. Redis事务 Redis不支持事务,此事务不是关系型数据库中的事务: Redis事务是一个单独的隔离操作:事务中的所有命令都会序列化.按顺序地执行.事务在执行的过程中,不会被其他客户端发送来的 ...
- busybox linux-2.6.2 编译安装中碰到的若干问题
Q1 /busybox-1.18.4/scripts/gcc-version.sh: line 11: arm-linux-gcc: command not found 1.问题:/home/ub ...
- os2
1. os.getcwd() 显示当前路径 2. a = os.name 显示当前操作系统 3. a = listdir(path) 显示该路径的所有内容,类似与ls 4. os.chdir(&quo ...
- fastAdmin进阶
基本知识流程一栏链接 bootstrapTable fastadmin系统配置(符内置规则): fastadmin默认的controller已实现的方法 一张图解析fastadmin的表格: fast ...
- 在Visual Sutdio 2017中使用boost库
在Visual Sutdio 2017中使用boost库 转载 https://blog.csdn.net/u011054333/article/details/78648294 对C++有一 ...
- js获取form元素,不使用id
<form method="post" name="form"> <input type="text" name=&quo ...
- 前端之html、css
一.什么是前端 前端即网站前台部分,运行在PC端.移动端等浏览器上展现给用户浏览的网页.前端技术一般分为前端设计和前端开发,前端设计一般可以理解为网站的视觉设计,前端开发则是网站的前台代码实现,包括基 ...
- C# 使用PrintDocument 绘制表格 完成 打印预览
C# 使用PrintDocument 绘制表格 完成 打印预览 DataTable 经过不断的Google与baidu,最终整理出来的打印类 主要是根据两个参考的类组合而成,稍微修改了一下,参考代 ...

 ATHENA
ATHENA