6LoWPAN - Transmission of IPv6 Packets over IEEE 802.15.4 Networks
6LoWPAN covered topics include the following:
- Frame format for transmission of IPv6 packets
- Method of forming IPv6 link-local addresses
- Statelessly autoconfigured addresses on IEEE 802.15.4 networks
- Simple header compression scheme using shared context
- Provisions for packet delivery in IEEE 802.15.4 meshes
IEEE 802.15.4 Mode for IP
- IEEE 802.15.4 defines four types of frames: beacon frames, MAC command frames, acknowledgement frames, and data frames.
- IPv6 packets MUST be carried on data frames.
- IEEE 802.15.4 networks can either be nonbeacon-enabled or beaconenabled.
- 6LoWPAN does not require that IEEE networks run in beacon-enabled mode.
- Beacons are still useful for link-layer device discovery to aid in association and disassociation events.
- 6LoWPAN requires both source and destination addresses be included in the IEEE 802.15.4 frame header.
- The source or destination PAN ID fields may also be included.
Addressing Modes
- IEEE 802.15.4 defines several addressing modes: IEEE 64-bit extended addresses or 16-bit short addresses unique within the PAN.
- 6LoWPAN supports both 64-bit extended addresses, and 16-bit short addresses.
- 6LoWPAN assumes that a PAN maps to a specific IPv6 link.
- Multicast is not supported natively in IEEE 802.15.4.
- IPv6 level multicast packets MUST be carried as link-layer broadcast frames in IEEE 802.15.4 networks.
- Broadcast frames are only heeded by devices within the specific PAN of the link:
- A destination PAN identifier is included in the frame, and it MUST match the PAN ID of the link in question.
- A short destination address is included in the frame, and it MUST match the broadcast address (0xffff).
- Hosts learn IPv6 prefixes via router advertisements.
Maximum Transmission Unit
- IEEE 802.15.4 frame sizes:
- Maximum physical layer packet size of 127 octets (aMaxPHYPacketSize) –
- Maximum frame overhead of 25 (aMaxFrameOverhead) –
- Link-layer security overhead (21 octets in AES-CCM-128, 9 and 13 in AES-CCM-32 and AES-CCM-64)
- leaves only 81 octets for IPv6 -
- IPv6 header of 40 octets
- leaves only 41 octets for upper-layer protocols, like UDP
- UDP uses 8 octets in the header
- leaves only 33 octets for application data.
- fragmentation and reassembly layer will use even more octets.
- Fragmention and reassembly adaptation layer must be provided at the layer below IP.
LoWPAN Adaptation Layer and Frame Format
- All LoWPAN encapsulated datagrams transported over IEEE 802.15.4 are prefixed by an encapsulation header stack.
- LoWPAN header sequence is mesh (L2) addressing, hop-by-hop options (including L2 broadcast/multicast), fragmentation, and finally payload.


- When more than one LoWPAN header is used in the same packet, they MUST appear in the following order:
- Mesh Addressing Header
- Broadcast Header
- Fragmentation Header
Dispatch Type and Header

 、
、

Mesh Addressing Type and Header


Fragmentation Type and Header
- All link fragments for a datagram except the last one MUST be multiples of eight bytes in length.




Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
- All 802.15.4 devices have an IEEE EUI-64 address, but 16-bit short addresses are also possible.
- Interface Identifier is formed from the EUI-64 according to the "IPv6 over Ethernet" specification.
- When 16-bit short addressing is used, a "pseudo 48-bit address" is formed as follows:
- First, the left-most 32 bits are formed by concatenating 16 zero bits to the 16-bit PAN ID (or 16 zero bits) - 16_bit_PAN:16_zero_bits.
- Then, these 32 bits are concatenated with the 16-bit short address - 32_bits_as_specified_previously:16_bit_short_address.
- A different MAC address set manually or by software MAY be used to derive the Interface Identifier.
IPv6 Link Local Address

Unicast Address Mapping
- The Source/Target Link-layer Address option has the following forms when the link layer is IEEE 802.15.4 and the addresses are EUI-64 or 16-bit short addresses, respectively.


Multicast Address Mapping
- An IPv6 packet with a multicast destination address (DST), consisting of the sixteen octets DST[1] through DST[16], is transmitted to the following 802.15.4 16-bit multicast address:

Header Compression
Encoding of IPv6 Header Fields
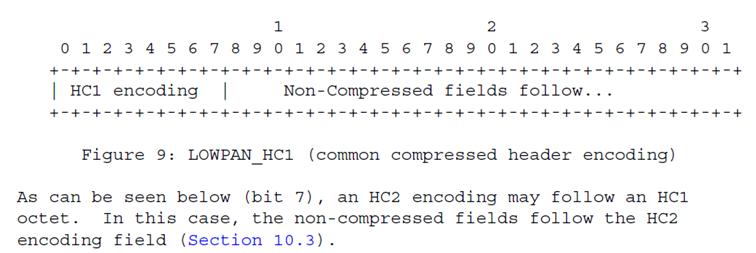
- A packet is compressible via the LOWPAN_HC1 format by using a Dispatch value of LOWPAN_HC1 followed by a LOWPAN_HC1 header "HC1 encoding" field (8 bits) to encode the different combinations as shown below.
- This header may be preceded by a fragmentation header, which may be preceded by a mesh header.\



Encoding of UDP Header Fields


6LoWPAN - Transmission of IPv6 Packets over IEEE 802.15.4 Networks的更多相关文章
- 蓝牙(Bluetooth) IEEE 802.15.1 协议学习
catalogue . 蓝牙概念 . 配对和连接 . 机密安全性 . 蓝牙协议分类 . 蓝牙协议栈 1. 蓝牙概念 蓝牙(Bluetooth)是一种无线技术标准,可实现固定设备.移动设备和楼宇个人域网 ...
- IEEE 802.15介绍
1. 无线通信 无线通信主要是利用无线电(Radio)射频(RF)技术的通信方式,无线网络是采用无线通信技术实现的网络无线网络可为两种: 近距离无线网络和远距离无线网络 近距离无线网络主要可分为如下两 ...
- IEEE 802.15.4协议学习之物理层
在详细讲述IEEE 802.15.4协议之前,谈谈自己这两个星期看协议过程中的一点心得,或者是收获吧. 看协议文档,一定要看有书签的,边看边在旁边做些备注,以便于后期整理.对于协议层次相关的,最好在纸 ...
- IEEE 802.15.4协议学习之MAC层
MAC负责建立于网络的同步,支持关联和取消关联.MAC层的安全以及控制物理信道访问机制.信道访问机制主要有以下几种: 1. 有序的物理无线信道访问机制 2. 协调器启动和维 ...
- 计算机网络六:无线局域网、IEEE 802.11、WIFI和蓝牙
无线局域网.IEEE 802.11.WIFI和蓝牙 ㈠无线局域网 1.定义 无线局域网络(Wireless Local Area Networks),简称WLAN.它是相当便利的数据传输系 ...
- XBee 802.15.4/Digimesh FAQs:如何为2.4G模块选择合适的信道
XBee 802.15.4模块和XBee Digimesh模块在硬件上完全相同,只是出厂带有不同固件,如果测试需要,这两个固件可以都可以互换烧入模块中. 如何为2.4G模块选择合适的信道 IEEE 8 ...
- IEEE 802.3 Ethernet
Introduction Ethernet 是过去30年以来最为成功的局域网(local area networking)技术. 1. First widely used LAN technology ...
- IEEE 802.11p (WAVE,Wireless Access in the Vehicular Environment)
IEEE 802.11p(又称WAVE,Wireless Access in the Vehicular Environment)是一个由IEEE 802.11标准扩充的通讯协定.这个通讯协定主要用在 ...
- IEEE 802.11 标准列表
IEEE 802.11 标准列表 IEEE 802.11,1997年,原始标准(2Mbit/s,播在2.4GHz). IEEE 802.11a,1999年,物理层补充(54Mbit/s,播在5GHz) ...
随机推荐
- iOS_06_基本运算符
一.算术运算 c语言一共有34种运算符,包括了常见的加减乘除 1.加法运算+ # 除了能做加法运算,还能表示正号:+5.+90 2.减法运算- # 除了能做减法运算,还能表示符号:-10.-200 3 ...
- 并发知识与concurrent包
要想进入一线互联网公司,这部分内容必须要会,否则的话,你始终都只能停留在比较low的段位. 关于并发知识,最重要的两个概念一定要搞清楚,那就是可见性和原子性.其中可见性与前面提到的volatile关键 ...
- WPF 支持分组互斥的 RadioButton 式单选菜单
扩展 MenuItem 为同组互斥的 RadioMenuItem,并且将对勾符号修改为圆点. http://stackoverflow.com/a/35692688/5972372 这个问题下还有其他 ...
- 基于StringUtils工具类的常用方法介绍(必看篇)
前言:工作中看到项目组里的大牛写代码大量的用到了StringUtils工具类来做字符串的操作,便学习整理了一下,方便查阅. isEmpty(String str) 是否为空,空格字符为false is ...
- 适用android的MVP:怎样组织展示层
原文 MVP for Android:How to organize presentation layer http://antonioleiva.com/mvp-android/ 译文 MVP(Mo ...
- <转> Intel VTune分析结果中的名词释译
原文转自http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26000296-id-3369740.html Elapsed Time(执行耗时): the total time your t ...
- 恢复SLAVE上的某几张表的简要方法
同步报错是遇到最多的一个问题,如果你修复后发现还没有解决,通常的方法就是在Master上重新dump出一份,然后在slave上恢复.这个方法是针对整个库不是很大的情况下使用的,那如果是较大,全部dum ...
- 26、从零写UVC驱动之分析描述符
指令:lsusb 可以查看usb设备的描述符信息,当然lsusb指令要带一些参数 一个usb设备有多个config配置+设备描述符,一个config有多个接口和association.config描述 ...
- 轻松掌握ISO8583报文协议
http://www.itpub.net/thread-419521-1-1.html 我刚进入金融行业时,就知道了IS08583报文协议,我想可能我还没进入这个行业都已经听过了,可知ISO8583的 ...
- UE4制作插件的插件神器pluginCreator
本文章由cartzhang编写,转载请注明出处. 所有权利保留. 文章链接:http://blog.csdn.net/cartzhang/article/details/45644007 作者:car ...
