C++与C的区别二
1. new,delete的局部重载:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; int objs = ; class myclass
{
public:
myclass()
{
//objs++;
cout << "create" << endl;
}
~myclass()
{
//objs--;
cout << "delete" << endl;
}
//operator重载,针对new重新作出一种解释,只针对当前类
static void * operator new(size_t size)
{
objs++;
cout << "new-call" << endl;
myclass *p = ::new myclass; //全局new
return p;
}
static void operator delete(void *p)
{
objs--;
cout << "delete-call" << endl;
::delete p;
}
};
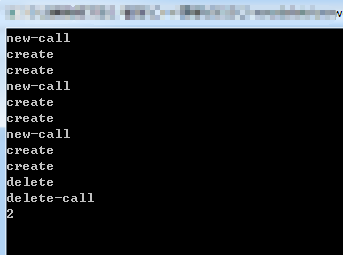
//功能1:无法在堆上被创建的类
void main()
{
myclass *p1 = new myclass;
myclass *p2 = new myclass;
myclass *p3 = new myclass;
delete p1; int *p = new int(); //此时new重载对于这一句无效 cout << objs << endl; cin.get();
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; int objs = ;
void *g_p = nullptr; class myclass
{
public:
myclass()
{
//objs++;
cout << "create" << endl;
}
~myclass()
{
//objs--;
cout << "delete" << endl;
} //operator重载,针对new重新作出一种解释,只针对当前类
static void * operator new(size_t size)
{
if (g_p==nullptr)
{
objs++;
cout << "new-call" << endl;
myclass *p = ::new myclass; //全局new
g_p = p; //单例,堆上创建对象只有一个
return p;
}
else
{
return g_p;
}
} static void operator delete(void *p)
{
if (g_p!=nullptr)
{
objs--;
cout << "delete-call" << endl;
::delete p;
g_p = nullptr;
}
}
};
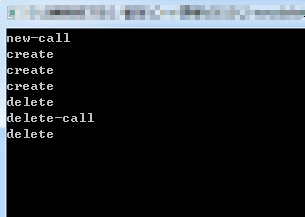
//功能1:无法在堆上被创建的类
//功能2:实现统计分配内存,释放内存的次数
//实现单例设计模式,实现避免反复delete出错
//new delete在内部,只针对当前类,int double 无影响
void main()
{
myclass *p1 = new myclass;
myclass *p2 = new myclass; delete p1;
delete p1; //规避了两次delete的错误 cin.get();
}
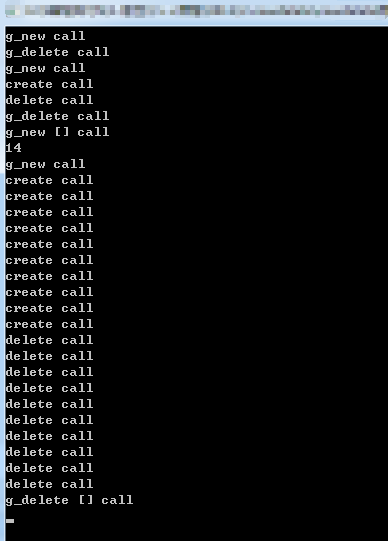
2. 全局new,delete重载:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; //全局内存管理,统计释放内存,分配内存
//new new [] delete delete []
//分配内存优先于构造
//析构优先于释放内存
void * operator new(size_t size)
{
cout << "g_new call" << endl;
void *p = malloc(size); //全局的new,只能使用malloc
return p;
}
void * operator new [](size_t size)
{
cout << "g_new [] call" << endl;
cout << size << endl;
return operator new(size); //每个元素调用一次new
} void operator delete(void *p)
{
cout << "g_delete call" << endl;
free(p);
}
void operator delete [](void *p)
{
cout << "g_delete [] call" << endl;
free(p);
} class myclass
{
public:
myclass()
{
cout << "create call" << endl;
}
~myclass()
{
cout << "delete call" << endl;
}
}; void main()
{
int *p1 = new int();
delete p1; myclass *p2 = new myclass;
delete p2; myclass *px = new myclass[];
delete[]px; cin.get();
}
3. 绑定类成员函数:
#include <iostream>
#include <functional> using namespace std;
using namespace std::placeholders;//站位 struct MyStruct
{
void add1(int a)
{
cout << a << endl;
}
void add2(int a, int b)
{
cout << a << b << endl;
}
void add3(int a, int b, int c)
{
cout << a << b << c << endl;
}
}; void main()
{
MyStruct my1;
//my1.add(10); //绑定包装器,包装类成员函数,用于使用
auto fun1 = bind(&MyStruct::add1, &my1, _1);//有1个参数 函数名、对象地址、参数
fun1(); auto fun2 = bind(&MyStruct::add2, &my1, _1,_2);//有2个参数
fun2(,); auto fun3 = bind(&MyStruct::add3, &my1, _1,_2,_3);//有3个参数
fun3(,,); cin.get();
}
4. 绑定lambda表达式以及仿函数:
#include <iostream>
#include <functional> using namespace std;
using namespace std::placeholders; int add(int a, int b,int c)
{
return a + b+c;
} struct MyStruct
{
int operator()(int a,int b) //仿函数
{
return a + b;
}
}; void main()
{
auto fun1 = bind(add, ,, _1);//适配器模式
cout << fun1() << endl; // auto fun2 = bind([](int a, int b)->int {return a + b; }, , _1);
cout << fun2() << endl; // MyStruct my1;
cout << my1(, ) << endl; //
auto fun3 = bind(my1, , _1); //绑定
cout << fun3() << endl; // cin.get();
}
5. 静态断言:
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std; int divv(int a, int b)
{
assert(b != ); //断言
return a / b;
} void main()
{
cout << divv(, ) << endl; cin.get();
}
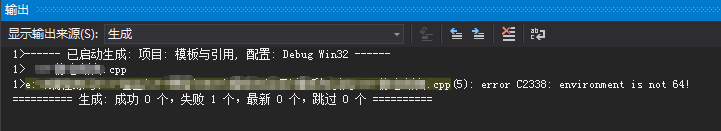
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std; static_assert(sizeof(void *) >= , "environment is not 64!"); void main()
{ cin.get();
}
6. 内联函数:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std; #define f(x) x*x*x //C语言内联,C++要求类型严格匹配 inline int get(int x) //C++的内联函数
{
return x*x*x;
}
//提高程序运行速度 //inline 只是对于编译器的建议
//一般情况下,我们对内联函数做如下的限制:
//(1)不能有递归;
//(2)不能包含静态数据;
//(3)不能包含循环;
//(4)不能包含switch和goto语句;
//(5)不能包含数组。
//若一个内联函数定义不满足以上限制,则编译系统把它当做普通函数对待 template<class T>
inline T go(T t)
{
return t*t;
} void main()
{
get(); go(); //优化为内联函数 auto fun = []() {}; //lambda表达式实际上也是内联函数 cin.get();
}
7. CPP处理转义字符:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> using namespace std; void main()
{
//string str("\"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Google\\Chrome\\Application\\chrome.exe\"");
string str(R"("C:\Program Files (x86)\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exe")"); // R"(......)" system(str.c_str()); cin.get();
}
C++与C的区别二的更多相关文章
- C#中抽象类和接口的区别(二)
一.抽象类: 抽象类是特殊的类,只是不能被实例化:除此以外,具有类的其他特性:重要的是抽象类可以包括抽象方法,这是普通类所不能的.抽象方法只能声明于抽象类中,且不包含任何实现,派生类必须覆盖它们.另外 ...
- Python协程与Go协程的区别二
写在前面 世界是复杂的,每一种思想都是为了解决某些现实问题而简化成的模型,想解决就得先面对,面对就需要选择角度,角度决定了模型的质量, 喜欢此UP主汤质看本质的哲学科普,其中简洁又不失细节的介绍了人类 ...
- vue1.0和vue2.0的区别(二)
这篇我们继续之前的vue1.0和vue2.0的区别(一)继续说 四.循环 学过vue的同学应该知道vue1.0是不能添加重复数据的,否则它会报错,想让它重复添加也不是不可以,不过需要定义别的东西 而v ...
- Linux内存管理--虚拟地址、逻辑地址、线性地址和物理地址的区别(二)【转】
本文转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/yusiguyuan/article/details/9668363 这篇文章中介绍了四个名词的概念,下面针对四个地址的转换进行分析 CPU将一个 ...
- java集合对象区别二
集合包是Java中最常用的包,它最常用的有Collection和Map两个接口的实现类,Collection用于存放多个单对象,Map用于存放Key-Value形式的键值对. Collection中常 ...
- OC与Swift的区别二(常量、变量、运算符)
4.常量与变量声明 oc的变量声明使用 类型 变量名 = 变量值的方式,其中类型为系统内置数据类型或自定义类型,变量名需由英文字母开头且不能包含特殊字符 swift变量声明使用 var 变量名 = ...
- 传统IO与NIO区别二
nio是new io的简称,从jdk1.4就被引入了.现在的jdk已经到了1.6了,可以说不是什么新东西了.但其中的一些思想值得我来研究.这两天,我研究了下其中的套接字部分,有一些心得,在此分享. ...
- Cocos2d中update与fixedUpdate的区别(二)
关于update:方法的目的 update:方法的目的在于给你一个更新你的游戏(你游戏中的所有对象,标签等待)的机会,在它们被渲染到屏幕之前. 换句话说,如果你想要一些游戏对象显示在屏幕的特定位置,你 ...
- java static成员变量方法和非static成员变量方法的区别 ( 二 )
原创文章,未经作者允许,禁止转载!!! 静态成员变量不用new对象,在类加载的过程中就已经初始化存放在数据区域,静态成员变量是类和所有对象共有的,类和对象都可以改变它的值,每一次改变值之后,静态成员变 ...
随机推荐
- 使用net Manager工具配置远程连接oracle
一,在服务端配置oracle端口在命令行中输入netca命令,打开相关配置默认端口号为1521 二,配置端口后使用Telnet工具调试端口是否联通 在命令行输入telnet 服务器ip 端口号 三,找 ...
- Golang之反射(重点!!)
1.反射:可以在运行时动态获取变量的相关信息 Import(“reflect”) 两个函数: reflect.TypeOf()//获取变量的类型,返回reflect.Type类型reflect.Val ...
- Hbase 系列(一)基本概念
Hbase 系列(一)基本概念 HBase 是 Apache 旗下一个高可靠性.高性能.面向列.可伸缩的分布式存储系统.利用 HBase 技术可在廉价 PC 服务器上搭建起大规模的存储化集群.使用 H ...
- Android使用ListView使用方法
Android使用ListView应该注意的地方 在ListView中设置Selector为null会报空指针? mListView.setSelector(null);//空指针 试试下面这种: ...
- 2014 ACM/ICPC 鞍山赛区网络赛(清华命题)
为迎接10月17号清华命题的鞍山现场赛 杭电上的题目 Biconnected(hdu4997) 状态压缩DP Rotate(hdu4998) 相对任一点的旋转 Overt(hdu4999 ...
- git 回退到某个特定提交
1.先用git log commit aba290c570d3894f4f39a1fdf52aa512c0231525 Author: huzhengbo <@qq.com> Date: ...
- context:propertyPlaceholder
Activates replacement of ${...} placeholders by registering a PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer w ...
- Ubuntu下的apache2的配置过程
参考apache2的中文文档:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/ 安装apache2: apt-get install apache2 安装apache2doc文档:a ...
- 编译语言 vs 解释语言
编译语言 vs 解释语言 阅读: 评论: 作者:Rybby 日期: 来源:rybby.com 一直以为,编译语言的性能绝对比解释语言快,因为就理论而言,解释语言要一边解释(将脚本语言翻译成计算 ...
- daylyknowledge1
1.数据库截取字符串:toFixed():四舍五入substring(cp_introduce,0,11) cp_introduce前台截取: field: 'an_content', title: ...
