C++解析(17):操作符重载
0.目录
1.操作符重载
2.完善的复数类
3.小结
1.操作符重载
下面的复数解决方案是否可行?
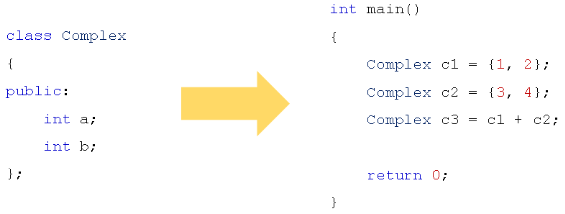
示例1——原有的解决方案:
#include <stdio.h>
class Complex
{
int a;
int b;
public:
Complex(int a = 0, int b = 0)
{
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
}
int getA() { return a; }
int getB() { return b; }
friend Complex Add(const Complex& p1, const Complex& p2);
};
Complex Add(const Complex& p1, const Complex& p2)
{
Complex ret;
ret.a = p1.a + p2.a;
ret.b = p1.b + p2.b;
return ret;
}
int main()
{
Complex c1(1, 2);
Complex c2(3, 4);
Complex c3 = Add(c1, c2); // c1 + c2
printf("c3.a = %d, c3.b = %d\n", c3.getA(), c3.getB());
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
[root@bogon Desktop]# g++ test.cpp
[root@bogon Desktop]# ./a.out
c3.a = 4, c3.b = 6
操作符重载:
- C++中的重载能够扩展操作符的功能
- 操作符的重载以函数的方式进行
- 本质——用特殊形式的函数扩展操作符的功能
通过operator关键字可以定义特殊的函数
operator的本质是通过函数重载操作符
语法:

示例2——使用操作符重载函数代替原有函数:
#include <stdio.h>
class Complex
{
int a;
int b;
public:
Complex(int a = 0, int b = 0)
{
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
}
int getA() { return a; }
int getB() { return b; }
friend Complex operator + (const Complex& p1, const Complex& p2);
};
Complex operator + (const Complex& p1, const Complex& p2)
{
Complex ret;
ret.a = p1.a + p2.a;
ret.b = p1.b + p2.b;
return ret;
}
int main()
{
Complex c1(1, 2);
Complex c2(3, 4);
Complex c3 = operator + (c1, c2); // c1 + c2
printf("c3.a = %d, c3.b = %d\n", c3.getA(), c3.getB());
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
[root@bogon Desktop]# g++ test.cpp
[root@bogon Desktop]# ./a.out
c3.a = 4, c3.b = 6
可以将操作符重载函数定义为类的成员函数:
- 比全局操作符重载函数少一个参数(左操作符)
- 不需要依赖友元就可以完成操作符重载
- 编译器优先在成员函数中寻找操作符重载函数

示例3——不使用友元,而是使用类的成员函数(编译器优先在成员函数中寻找操作符重载函数):
#include <stdio.h>
class Complex
{
int a;
int b;
public:
Complex(int a = 0, int b = 0)
{
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
}
int getA() { return a; }
int getB() { return b; }
Complex operator + (const Complex& p)
{
Complex ret;
printf("Complex operator + (const Complex& p)\n");
ret.a = this->a + p.a;
ret.b = this->b + p.b;
return ret;
}
friend Complex operator + (const Complex& p1, const Complex& p2);
};
Complex operator + (const Complex& p1, const Complex& p2)
{
Complex ret;
printf("Complex operator + (const Complex& p1, const Complex& p2)\n");
ret.a = p1.a + p2.a;
ret.b = p1.b + p2.b;
return ret;
}
int main()
{
Complex c1(1, 2);
Complex c2(3, 4);
Complex c3 = c1 + c2; // c1.operator + (c2)
printf("c3.a = %d, c3.b = %d\n", c3.getA(), c3.getB());
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
[root@bogon Desktop]# g++ test.cpp
[root@bogon Desktop]# ./a.out
Complex operator + (const Complex& p)
c3.a = 4, c3.b = 6
2.完善的复数类
复数类应该具有的操作:

利用操作符重载:
- 统一复数与实数的运算方式
- 统一复数与实数的比较方式
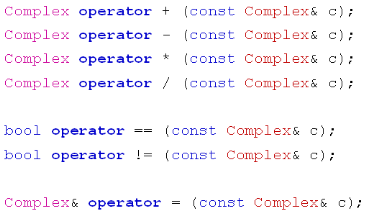
先实现Complex.h头文件:
// Complex.h
#ifndef _COMPLEX_H_
#define _COMPLEX_H_
class Complex
{
double a;
double b;
public:
Complex(double a = 0, double b = 0);
double getA();
double getB();
double getModulus();
Complex operator + (const Complex& c);
Complex operator - (const Complex& c);
Complex operator * (const Complex& c);
Complex operator / (const Complex& c);
bool operator == (const Complex& c);
bool operator != (const Complex& c);
Complex& operator = (const Complex& c);
};
#endif
再实现Complex.cpp具体操作:
// Complex.cpp
#include "Complex.h"
#include "math.h"
Complex::Complex(double a, double b)
{
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
}
double Complex::getA()
{
return a;
}
double Complex::getB()
{
return b;
}
double Complex::getModulus()
{
return sqrt(a * a + b * b);
}
Complex Complex::operator + (const Complex& c)
{
double na = a + c.a;
double nb = b + c.b;
Complex ret(na, nb);
return ret;
}
Complex Complex::operator - (const Complex& c)
{
double na = a - c.a;
double nb = b - c.b;
Complex ret(na, nb);
return ret;
}
Complex Complex::operator * (const Complex& c)
{
double na = a * c.a - b * c.b;
double nb = a * c.b + b * c.a;
Complex ret(na, nb);
return ret;
}
Complex Complex::operator / (const Complex& c)
{
double cm = c.a * c.a + c.b * c.b;
double na = (a * c.a + b * c.b) / cm;
double nb = (b * c.a - a * c.b) / cm;
Complex ret(na, nb);
return ret;
}
bool Complex::operator == (const Complex& c)
{
return (a == c.a) && (b == c.b);
}
bool Complex::operator != (const Complex& c)
{
return !(*this == c);
}
Complex& Complex::operator = (const Complex& c)
{
if( this != &c )
{
a = c.a;
b = c.b;
}
return *this;
}
最后实现main函数:
// test.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include "Complex.h"
int main()
{
Complex c1(1, 2);
Complex c2(3, 6);
Complex c3 = c2 - c1;
Complex c4 = c1 * c3;
Complex c5 = c2 / c1;
printf("c3.a = %f, c3.b = %f\n", c3.getA(), c3.getB());
printf("c4.a = %f, c4.b = %f\n", c4.getA(), c4.getB());
printf("c5.a = %f, c5.b = %f\n", c5.getA(), c5.getB());
Complex c6(2, 4);
printf("c3 == c6 : %d\n", c3 == c6);
printf("c3 != c4 : %d\n", c3 != c4);
(c3 = c2) = c1;
printf("c1.a = %f, c1.b = %f\n", c1.getA(), c1.getB());
printf("c2.a = %f, c2.b = %f\n", c2.getA(), c2.getB());
printf("c3.a = %f, c3.b = %f\n", c3.getA(), c3.getB());
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
[root@bogon Desktop]# g++ test.cpp Complex.cpp
[root@bogon Desktop]# ./a.out
c3.a = 2.000000, c3.b = 4.000000
c4.a = -6.000000, c4.b = 8.000000
c5.a = 3.000000, c5.b = 0.000000
c3 == c6 : 1
c3 != c4 : 1
c1.a = 1.000000, c1.b = 2.000000
c2.a = 3.000000, c2.b = 6.000000
c3.a = 1.000000, c3.b = 2.000000
注意事项:
- C++规定赋值操作符(=)只能重载为成员函数
- 操作符重载不能改变原操作符的优先级
- 操作符重载不能改变操作符的个数
- 操作符重载不应改变操作符的原有语义
3.小结
- 操作符重载是C++的强大特性之一
- 操作符重载的本质是通过函数扩展操作符的功能
- operator关键字是实现操作符重载的关键
- 操作符重载遵循相同的函数重载规则
- 全局函数和成员函数都可以实现对操作符的重载
- 复数的概念可以通过自定义类实现
- 复数中的运算操作可以通过操作符重载实现
- 赋值操作符只能通过成员函数实现
- 操作符重载的本质为函数定义
C++解析(17):操作符重载的更多相关文章
- Kotlin操作符重载:把标准操作加入到任何类中(KAD 17)
作者:Antonio Leiva 时间:Mar 21, 2017 原文链接:https://antonioleiva.com/operator-overload-kotlin/ 就像其他每种语言一样, ...
- 析构函数-复制构造函数-赋值操作符重载-默认构造函数<代码解析>
通过下面primer中的一道习题,可以更深刻的了解,析构函数,复制构造函数,赋值操作符重载,默认构造函数的使用. 但是我的结果与primer习题解答里面的并不相同,可能是编译器不同的原因导致. // ...
- lua 14 metatable (类似操作符重载)
转自:http://www.runoob.com/lua/lua-metatables.html 感性认识: “Lua中Metatable这个概念, 国内将他翻译为元表. 元表为重定义Lua中任意一个 ...
- 【转】Python3 操作符重载方法
Python3 操作符重载方法 本文由 Luzhuo 编写,转发请保留该信息. 原文: http://blog.csdn.net/Rozol/article/details/70769628 以下代码 ...
- 5.1 C++基本操作符重载
参考:http://www.weixueyuan.net/view/6379.html 总结: 操作符重载指的是将C++提供的操作符进行重新定义,使之满足我们所需要的一些功能. 长度运算符“sizeo ...
- 侯捷STL学习(四)--OOP-GP/操作符重载-泛化特化
C++标准库第二讲 体系结构与内核分析 第1-7节为第一讲 读源代码前的准备 第八节:源代码分布 C++基本语法 模板的使用 数据结构和算法 本课程主要使用:Gnu C 2.9.1与Gun C 4.9 ...
- C++ 操作符重载 (operator)
重载不能改变操作符的优先级 如果一个内建操作符是一元的,那么所有对它的重载仍是一元的.如果是二元的重载后也是二元的 下面看一个有代表性的例子:: 头文件Complex.h: #includeusing ...
- c++ 操作符重载和友元
操作符重载(operator overloading)是C++中的一种多态,C++允许用户自定义函数名称相同但参数列表不同的函数,这被称为函数重载或函数多态.操作符重载函数的格式一般为: operat ...
- paip.操作符重载的缺失 Java 的一个大缺点
paip.操作符重载的缺失 Java 的一个大缺点 #----操作符重载的作用 1.提升用户体验 操作符重载..可以让代码更加自然.... 2.轻松实现代码代码移植 例如 java代码会直接移植到 ...
随机推荐
- Yii2 使用 faker 生成假数据
测试过程中有时候需要生成大量的假数据,faker 是一个生成假数据的类库,可以生成姓名,电话,IP地址,密码,ISBN等等你能想到的或者你想不到的各种类型的假数据. Yii2.0已经集成该类库,不用再 ...
- 《Flutter实战》开源电子书
<Flutter实战>开源电子书 <Flutter实战> 开源了,本书为 Flutter中文网开源电子书项目,本书系统介绍了Flutter技术的各个方面,本书属于原创书籍(并非 ...
- Awesome TensorFlow
Awesome TensorFlow A curated list of awesome TensorFlow experiments, libraries, and projects. Inspi ...
- charles录制https请求
之前一直用windows系统,抓包什么的都是用的fiddler或者wireshark,操作比较简单,扩展性也比较强,现在因为工作原因换了mac,在网上一直没有找到fiddler的mac版本,就只能切换 ...
- 探寻ASP.NET MVC鲜为人知的奥秘(3):寻找多语言的最佳实践方式
如果你的网站需要被世界各地的人访问,访问者会使用各种不同的语言和文字书写习惯,那么创建一个支持多语言的网站就是十分必要的了,这一篇文章就讲述怎么快速合理的创建网站对多语言的支持.接下来通过一个实例来讲 ...
- Mac下重置MySQL密码
第一步要先停止掉mysql服务: brew services stop mysql 第二步查看mysql安装路径: brew info mysql //我这里是brew管理的所以我用brew查看mys ...
- Jmeter接口测试(九)授权
下面应该是jmeter的授权设置,但是由于本人目前对这块了解还不深,暂时写个标题,以后有时间再来补充,大家可以先看下一篇内容
- 记录一下自己申请并使用VPS的全过程
在学习REST API的时候,想要阅读一下谷歌爸爸的api design guide,无奈无情被墙,正好在学习云相关的技术,就想到申请一个VPS来用用. 这次我选择的是hostmybytes,原因有两 ...
- SQL判断是否存在
判断数据库是否存在 ifexists(select*frommaster..sysdatabaseswherename=N’库名’) print’exists’ else print’notexist ...
- Python模块random使用详情
python常用模块目录 1.random.random()#用于生成一个0到1的随机浮点数:0<= n < 1.0 import random mcw = random.random() ...
