2014年亚洲区域赛北京赛区现场赛A,D,H,I,K题解(hdu5112,5115,5119,5220,5122)
转载请注明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/fraud/ ——by fraud
下午在HDU上打了一下今年北京区域赛的重现,过了5题,看来单挑只能拿拿铜牌,呜呜。
先将这五题的题解放上来,剩余题目等搞出来再补上
A题
A Curious Matt
Time Limit: 2000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 512000/512000 K (Java/Others)
One day, Matt's best friend Ted is wandering on the non-negative half
of the number line. Matt finds it interesting to know the maximal
speed Ted may reach. In order to do so, Matt takes records of Ted’s
position. Now Matt has a great deal of records. Please help him to find
out the maximal speed Ted may reach, assuming Ted moves with a constant
speed between two consecutive records.
For each test case, the first line contains an integer N (2 ≤ N ≤ 10000),indicating the number of records.
Each of the following N lines contains two integers ti and xi (0 ≤ ti, xi ≤ 106),
indicating the time when this record is taken and Ted’s corresponding
position. Note that records may be unsorted by time. It’s guaranteed
that all ti would be distinct.
case number (starting from 1), and y is the maximal speed Ted may
reach. The result should be rounded to two decimal places.
In the first sample, Ted moves from 2 to 4 in 1 time unit. The speed 2/1 is maximal.
In the second sample, Ted moves from 5 to 0 in 1 time unit. The speed 5/1 is maximal.
题目要求求出最大的速度
分析:以时间为key值,排序,然后遍历一遍
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[];
int b[];
double c[];
int id[];
bool cmp(int x,int y)
{
return a[x]<=a[y];
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
int n;
int cas=;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
cin>>n;
a[]=,b[]=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i]>>b[i];
id[i]=i;
}
sort(id,id+n,cmp);
double maxx=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
maxx=max(maxx,fabs((b[id[i]]-b[id[i-]])*1.0/((a[id[i]]-a[id[i-]])*1.0)));
}
cout<<"Case #"<<cas++<<": ";
cout<<fixed<<setprecision()<<maxx<<endl;
}
return ;
}
代码君
D题
Dire Wolf
Time Limit: 5000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 512000/512000 K (Java/Others)
powerful wolves. Many, if not all, Dire Wolves appear to originate from
Draenor.
Dire wolves look like normal wolves, but these creatures
are of nearly twice the size. These powerful beasts, 8 - 9 feet long
and weighing 600 - 800 pounds, are the most well-known orc mounts. As
tall as a man, these great wolves have long tusked jaws that look like
they could snap an iron bar. They have burning red eyes. Dire wolves are
mottled gray or black in color. Dire wolves thrive in the northern
regions of Kalimdor and in Mulgore.
Dire wolves are efficient pack
hunters that kill anything they catch. They prefer to attack in packs,
surrounding and flanking a foe when they can.
— Wowpedia, Your wiki guide to the World of Warcra
Matt, an adventurer from the Eastern Kingdoms, meets a pack of dire
wolves. There are N wolves standing in a row (numbered with 1 to N from
left to right). Matt has to defeat all of them to survive.
Once Matt defeats a dire wolf, he will take some damage which is equal
to the wolf’s current attack. As gregarious beasts, each dire wolf i can
increase its adjacent wolves’ attack by bi. Thus, each dire
wolf i’s current attack consists of two parts, its basic attack ai and
the extra attack provided by the current adjacent wolves. The increase
of attack is temporary. Once a wolf is defeated, its adjacent wolves
will no longer get extra attack from it. However, these two wolves (if
exist) will become adjacent to each other now.
For example,
suppose there are 3 dire wolves standing in a row, whose basic attacks
ai are (3, 5, 7), respectively. The extra attacks bi they can
provide are (8, 2, 0). Thus, the current attacks of them are (5, 13,
9). If Matt defeats the second wolf first, he will get 13 points of
damage and the alive wolves’ current attacks become (3, 15).
As an alert and resourceful adventurer, Matt can decide the order of the
dire wolves he defeats. Therefore, he wants to know the least damage he
has to take to defeat all the wolves.
number of test cases. For each test case, the first line contains only
one integer N (2 ≤ N ≤ 200).
The second line contains N integers ai (0 ≤ ai ≤ 100000), denoting the basic attack of each dire wolf.
The third line contains N integers bi (0 ≤ bi ≤ 50000), denoting the extra attack each dire wolf can provide.
case number (starting from 1), y is the least damage Matt needs to
take.
In the first sample, Matt defeats the dire wolves from left to right. He takes 5 + 5 + 7 = 17 points of damage which is the least damage he has to take.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int a[],b[];
int dp[][];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t,n;
cin>>t;
int cas=;
while(t--)
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i];
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)cin>>b[i];
b[]=b[n+]=;
for(int p=;p<n;p++)
{
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int j=i+p;
if(i==j)
{
dp[i][j]=a[i]+b[i-]+b[i+];
continue;
}
if(j>n)break;
dp[i][j]=min(a[i]+dp[i+][j],a[j]+dp[i][j-]);
int temp=;
for(int k=i+;k<j;k++)
{
dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][j],dp[i][k-]+a[k]+dp[k+][j]);
}
dp[i][j]+=b[i-]+b[j+];
}
}
cout<<"Case #"<<cas++<<": ";
cout<<dp[][n]<<endl;
}
return ;
}
代码君
H题
Happy Matt Friends
Time Limit: 6000/6000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 510000/510000 K (Java/Others)
Each of Matt’s friends has a magic number. In the game, Matt selects
some (could be zero) of his friends. If the xor (exclusive-or) sum of
the selected friends’magic numbers is no less than M , Matt wins.
Matt wants to know the number of ways to win.
For each test case, the first line contains two integers N, M (1 ≤ N ≤ 40, 0 ≤ M ≤ 106).
In the second line, there are N integers ki (0 ≤ ki ≤ 106), indicating the i-th friend’s magic number.
case number (starting from 1) and y indicates the number of ways where
Matt can win.
In the first sample, Matt can win by selecting:
friend with number 1 and friend with number 2. The xor sum is 3.
friend with number 1 and friend with number 3. The xor sum is 2.
friend with number 2. The xor sum is 2.
friend with number 3. The xor sum is 3. Hence, the answer is 4.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int a[];
long long dp[][(<<)+];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin>>t;
int cas=;
while(t--)
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
memset(dp,,sizeof(dp));
for(int i=;i<n;i++)cin>>a[i];
cout<<"Case #"<<cas++<<": ";
dp[][]=;
int k;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<(<<);j++)dp[i&][j]=dp[!(i&)][j];
for(int j=;j<(<<);j++)
{
k=a[i]^j;
dp[i&][k]+=dp[!(i&)][j];
}
}
long long ans=;
for(int i=m;i<(<<);i++)ans+=dp[!(n&)][i];
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return ;
}
代码君
I题
Intersection
Time Limit: 4000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 512000/512000 K (Java/Others)
made up by rings. The following figures are some famous examples you
may know.

A ring is a 2-D figure bounded by two circles sharing the common
center. The radius for these circles are denoted by r and R (r < R).
For more details, refer to the gray part in the illustration below.
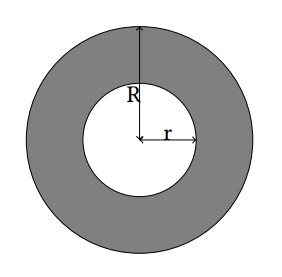
Matt just designed a new logo consisting of two rings with the same
size in the 2-D plane. For his interests, Matt would like to know the
area of the intersection of these two rings.
Each of the following two lines contains two integers xi, yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 20) indicating the coordinates of the center of each ring.
case number (starting from 1) and y is the area of intersection rounded
to 6 decimal places.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std; #define PI acos(-1.0)
double area(double x1,double y1,double r1,double x2,double y2,double r2)
{
double d=(x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2);
if(d>=(r1+r2)*(r1+r2))return ;
if(d<=(r1-r2)*(r1-r2))return r1<r2 ? PI*r1*r1 : PI*r2*r2;
d=sqrt(d);
double a1=acos((r1*r1+d*d-r2*r2)/(2.0*r1*d));
double a2=acos((r2*r2+d*d-r1*r1)/(2.0*r2*d));
double s1=a1*r1*r1;
double s2=a2*r2*r2;
double t=(r1+r2+d)/2.0;
t=2.0*sqrt(t*(t-r1)*(t-r2)*(t-d));
return s1+s2-t;
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
double r1,r2,x1,y1,x2,y2;
scanf("%d",&t);
int cas=;
while(t--)
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf",&r1,&r2,&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
double ans=;
ans-=area(x1,y1,r2,x2,y2,r1)*;
ans+=area(x1,y1,r2,x2,y2,r2);
ans+=area(x1,y1,r1,x2,y2,r1);
printf("Case #%d: ",cas++);
printf("%.6lf\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
代码君
K题
K.Bro Sorting
Time Limit: 2000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 512000/512000 K (Java/Others)
Yesterday, K.Bro learnt an algorithm: Bubble sort. Bubble sort will
compare each pair of adjacent items and swap them if they are in the
wrong order. The process repeats until no swap is needed.
Today, K.Bro comes up with a new algorithm and names it K.Bro Sorting.
There are many rounds in K.Bro Sorting. For each round, K.Bro chooses
a number, and keeps swapping it with its next number while the next
number is less than it. For example, if the sequence is “1 4 3 2 5”, and
K.Bro chooses “4”, he will get “1 3 2 4 5” after this round. K.Bro
Sorting is similar to Bubble sort, but it’s a randomized algorithm
because K.Bro will choose a random number at the beginning of each
round. K.Bro wants to know that, for a given sequence, how many rounds
are needed to sort this sequence in the best situation. In other words,
you should answer the minimal number of rounds needed to sort the
sequence into ascending order. To simplify the problem, K.Bro promises
that the sequence is a permutation of 1, 2, . . . , N .
the number of test cases. For each test case, the first line contains
an integer N (1 ≤ N ≤ 106).
The second line contains N integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ N ), denoting the sequence K.Bro gives you.
The sum of N in all test cases would not exceed 3 × 106.
case number (starting from 1), y is the minimal number of rounds needed
to sort the sequence.
In the second sample, we choose “5” so that after the first round, sequence becomes “1 2 3 4 5”, and the algorithm completes.
题意:求题目完成排序需要题目所述的最小的round次数
分析:每次把不符合排序的最大的数进行swap,那么,这个数在经过一个round之后,所有大于等于它的数一定是最终的排列。
由此,可以将问题转化为判断一个数的右边是否有必该数小的数,若有,则需要一次round。
对于此问题,只需要从右往左统计,并且不断更新最小值,若当前数为最小值,则将最小值更新为当前数,否则round+1
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int a[];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
int t;
int cas=;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
int k,s=,m=;
int ans=;
int minn=1e7;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
for(int i=n;i>;i--)
{
if(a[i]<minn)minn=a[i];
else ans++;
}
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",cas++,ans); }
return ;
}
代码君
2014年亚洲区域赛北京赛区现场赛A,D,H,I,K题解(hdu5112,5115,5119,5220,5122)的更多相关文章
- ACM总结——2017ACM-ICPC北京赛区现场赛总结
现在距离比赛结束已经过了一个多星期了,也是终于有时间写下心得了.回来就是被压着做项目,也是够够的. 这次比赛一样是我和两个学弟(虽然是学弟,但我的实力才是最弱的T_T)一起参加的,成绩的话打铁,算是情 ...
- HDU 5120 A Curious Matt(2014北京赛区现场赛A题 简单模拟)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5112 解题报告:扫一遍 #include<cstdio> #include<cstr ...
- HDU 5120 Intersection(2014北京赛区现场赛I题 计算几何)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5120 解题报告:给你两个完全相同的圆环,要你求这两个圆环相交的部分面积是多少? 题意看了好久没懂.圆环 ...
- 2013区域赛长沙赛区现场赛 K - Pocket Cube
K - Pocket Cube Time Limit:10000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Su ...
- [hdu5113]Black And White2014北京赛区现场赛B题(搜索加剪枝)
转载请注明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/fraud/ ——by fraud Black And White Time Limit: 2000/2000 MS ...
- UVALive7261(2015ACM/ICPC北京赛区现场赛A)
题目链接:https://icpcarchive.ecs.baylor.edu/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=8&page=show_ ...
- HDU 4041 Eliminate Witches! (模拟题 ACM ICPC 2011亚洲北京赛区网络赛)
HDU 4041 Eliminate Witches! (模拟题 ACM ICPC 2011 亚洲北京赛区网络赛题目) Eliminate Witches! Time Limit: 2000/1000 ...
- HDU 4046 Panda (ACM ICPC 2011北京赛区网络赛)
HDU 4046 Panda (ACM ICPC 2011北京赛区网络赛) Panda Time Limit: 10000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: ...
- 2014 ACM/ICPC 鞍山赛区现场赛 D&I 解题报告
鞍山现场赛结束了呢-- 我们出的是D+E+I三道题-- 吾辈AC掉的是D和I两道,趁着还记得.先在这里写一写我写的两道水题D&I的解题报告吧^_^. D题的意思呢是说星云内有一堆排成一条直线的 ...
随机推荐
- C++智能指针初学小结
本篇随笔仅作为个人学习<C++ Primer>智能指针一节后的部分小结,抄书严重,伴随个人理解.主要介绍shared_ptr.make_shared.weak_ptr的用法和联系. C++ ...
- C#按键打开文件选择对话框,并把选择好的路径保存/显示到textBox
1.选择文件夹 FolderBrowserDialog fbd = new FolderBrowserDialog(); fbd.SelectedPath = "D:";//默认路 ...
- mysql to sql sersver
USE SCK_PARA GO /****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[syncdata_mysql2sqlserver] Script Date: 08 ...
- php环境安装及搭建
最近由于项目需要 转战 PHP . 在做了差不多两年java后 说实话看php代码还是有些难受的. 毕竟不习惯.废话不说 先说一下 PHP环境的部署等等,也就是最近几天学习的心得吧.方便以后参考. ...
- py2exe生成exe后,运行exe时提示No module named * 的解决办法
一个pymssql 的程序在解释器上运行正常,但是用py2exe打包后,提示 ImportError: No module named _mssql 百度了半天无果,然后bing,结果bing还是比百 ...
- python导入matplotlib模块出错
我的系统是linux mint.用新立得软件包安装了numpy和matplotlib.在导入matplotlib.pyplot时出错.说是没有python3-tk包. 于是就在shell中装了一下. ...
- memcached的安装
最近在研究怎么让Discuz!去应用Memcache去做一些事情,记录下Memcache安装的过程. Linux下Memcache服务器端的安装 服务器端主要是安装memcache服务器端,目前的最新 ...
- 自定义Filter服务
自定义一个用户Email长度超过12个字符后值截取前12个然后添加“...”显示. 例如: index.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html ng-app=" ...
- delphi 打开文件夹并定位到一个文件(关键是/select参数)
strFileName := FcxLV[nIndex].Items.Item[FcxLV[nIndex].ItemIndex].SubItems.Strings[0]; //路径 ShellExe ...
- c++ 05
一.单例模式 二.成员指针 class Student { public: string m_name; void print (void) { ... } }; 1.指向成员变量的指针 成员 ...
