第三十三篇 玩转数据结构——红黑树(Read Black Tree)
1.. 图解2-3树维持绝对平衡的原理:
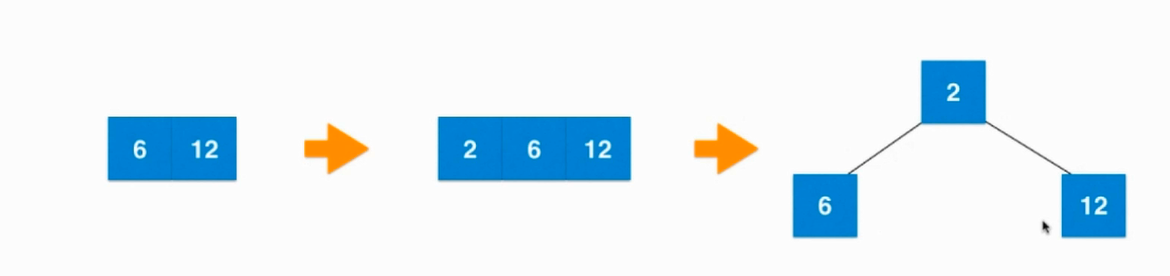
2.. 红黑树与2-3树是等价的
3.. 红黑树的特点
- 简要概括如下:
- 所有节点非黑即红;根节点为黑;NULL节点为黑;红节点孩子为黑;黑平衡
4.. 实现红黑树的业务逻辑
import java.util.ArrayList; public class RBTree<K extends Comparable<K>, V> { private static final boolean RED = true;
private static final boolean BLACK = false; private class Node{
public K key;
public V value;
public Node left, right;
public boolean color; public Node(K key, V value){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
left = null;
right = null;
color = RED;
}
} private Node root;
private int size; public RBTree(){
root = null;
size = 0;
} public int getSize(){
return size;
} public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
} // 判断节点node的颜色
private boolean isRed(Node node){
if(node == null)
return BLACK;
return node.color;
} // node x
// / \ 左旋转 / \
// T1 x ---------> node T3
// / \ / \
// T2 T3 T1 T2
private Node leftRotate(Node node){ Node x = node.right; // 左旋转
node.right = x.left;
x.left = node; x.color = node.color;
node.color = RED; return x;
} // node x
// / \ 右旋转 / \
// x T2 -------> y node
// / \ / \
// y T1 T1 T2
private Node rightRotate(Node node){ Node x = node.left; // 右旋转
node.left = x.right;
x.right = node; x.color = node.color;
node.color = RED; return x;
} // 颜色翻转
private void flipColors(Node node){ node.color = RED;
node.left.color = BLACK;
node.right.color = BLACK;
} // 向红黑树中添加新的元素(key, value)
public void add(K key, V value){
root = add(root, key, value);
root.color = BLACK; // 最终根节点为黑色节点
} // 向以node为根的红黑树中插入元素(key, value),递归算法
// 返回插入新节点后红黑树的根
private Node add(Node node, K key, V value){ if(node == null){
size ++;
return new Node(key, value); // 默认插入红色节点
} if(key.compareTo(node.key) < 0)
node.left = add(node.left, key, value);
else if(key.compareTo(node.key) > 0)
node.right = add(node.right, key, value);
else // key.compareTo(node.key) == 0
node.value = value; if (isRed(node.right) && !isRed(node.left))
node = leftRotate(node); if (isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.left.left))
node = rightRotate(node); if (isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.right))
flipColors(node); return node;
} // 返回以node为根节点的二分搜索树中,key所在的节点
private Node getNode(Node node, K key){ if(node == null)
return null; if(key.equals(node.key))
return node;
else if(key.compareTo(node.key) < 0)
return getNode(node.left, key);
else // if(key.compareTo(node.key) > 0)
return getNode(node.right, key);
} public boolean contains(K key){
return getNode(root, key) != null;
} public V get(K key){ Node node = getNode(root, key);
return node == null ? null : node.value;
} public void set(K key, V newValue){
Node node = getNode(root, key);
if(node == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + " doesn't exist!"); node.value = newValue;
} // 返回以node为根的二分搜索树的最小值所在的节点
private Node minimum(Node node){
if(node.left == null)
return node;
return minimum(node.left);
} // 删除掉以node为根的二分搜索树中的最小节点
// 返回删除节点后新的二分搜索树的根
private Node removeMin(Node node){ if(node.left == null){
Node rightNode = node.right;
node.right = null;
size --;
return rightNode;
} node.left = removeMin(node.left);
return node;
} // 从二分搜索树中删除键为key的节点
public V remove(K key){ Node node = getNode(root, key);
if(node != null){
root = remove(root, key);
return node.value;
}
return null;
} private Node remove(Node node, K key){ if( node == null )
return null; if( key.compareTo(node.key) < 0 ){
node.left = remove(node.left , key);
return node;
}
else if(key.compareTo(node.key) > 0 ){
node.right = remove(node.right, key);
return node;
}
else{ // key.compareTo(node.key) == 0 // 待删除节点左子树为空的情况
if(node.left == null){
Node rightNode = node.right;
node.right = null;
size --;
return rightNode;
} // 待删除节点右子树为空的情况
if(node.right == null){
Node leftNode = node.left;
node.left = null;
size --;
return leftNode;
} // 待删除节点左右子树均不为空的情况 // 找到比待删除节点大的最小节点, 即待删除节点右子树的最小节点
// 用这个节点顶替待删除节点的位置
Node successor = minimum(node.right);
successor.right = removeMin(node.right);
successor.left = node.left; node.left = node.right = null; return successor;
}
} public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("Pride and Prejudice"); ArrayList<String> words = new ArrayList<>();
if(FileOperation.readFile("pride-and-prejudice.txt", words)) {
System.out.println("Total words: " + words.size()); RBTree<String, Integer> map = new RBTree<>();
for (String word : words) {
if (map.contains(word))
map.set(word, map.get(word) + 1);
else
map.add(word, 1);
} System.out.println("Total different words: " + map.getSize());
System.out.println("Frequency of PRIDE: " + map.get("pride"));
System.out.println("Frequency of PREJUDICE: " + map.get("prejudice"));
} System.out.println();
}
}
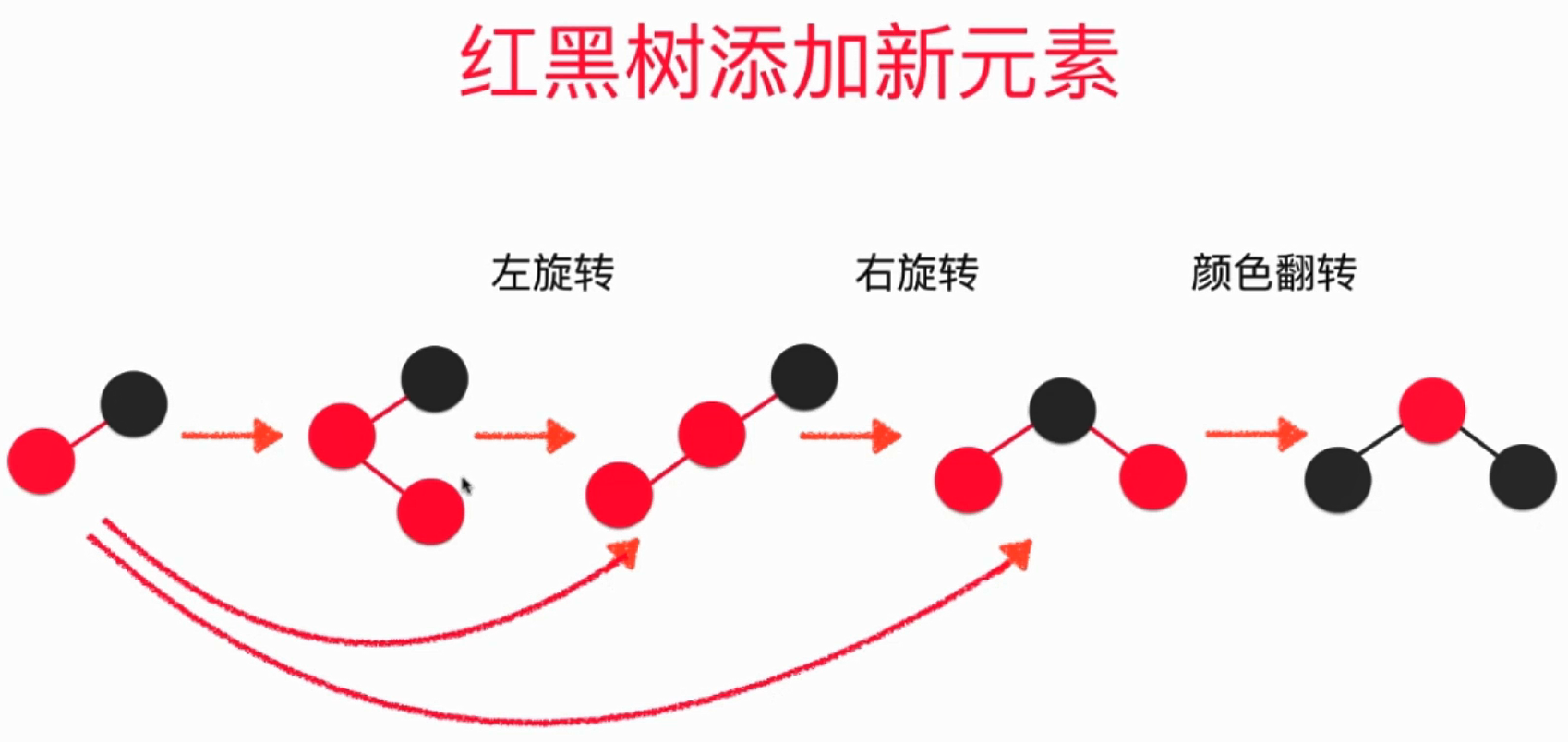
5.. 向红黑树中添加新元素之后需要进行维护的过程示意图
第三十三篇 玩转数据结构——红黑树(Read Black Tree)的更多相关文章
- java数据结构——红黑树(R-B Tree)
红黑树相比平衡二叉树(AVL)是一种弱平衡树,且具有以下特性: 1.每个节点非红即黑; 2.根节点是黑的; 3.每个叶节点(叶节点即树尾端NULL指针或NULL节点)都是黑的; 4.如图所示,如果一个 ...
- 第二十三篇 玩转数据结构——栈(Stack)
1.. 栈的特点: 栈也是一种线性结构: 相比数组,栈所对应的操作是数组的子集: 栈只能从一端添加元素,也只能从这一端取出元素,这一端通常称之为"栈顶": 向栈中添加元 ...
- 第三十二篇 玩转数据结构——AVL树(AVL Tree)
1.. 平衡二叉树 平衡二叉树要求,对于任意一个节点,左子树和右子树的高度差不能超过1. 平衡二叉树的高度和节点数量之间的关系也是O(logn) 为二叉树标注节点高度并计算平衡因子 AVL ...
- 第三十一篇 玩转数据结构——并查集(Union Find)
1.. 并查集的应用场景 查看"网络"中节点的连接状态,这里的网络是广义上的网络 数学中的集合类的实现 2.. 并查集所支持的操作 对于一组数据,并查集主要支持两种操作:合并两 ...
- 第三十篇 玩转数据结构——字典树(Trie)
1.. Trie通常被称为"字典树"或"前缀树" Trie的形象化描述如下图: Trie的优势和适用场景 2.. 实现Trie 实现Trie的业务无 ...
- 第二十九篇 玩转数据结构——线段树(Segment Tree)
1.. 线段树引入 线段树也称为区间树 为什么要使用线段树:对于某些问题,我们只关心区间(线段) 经典的线段树问题:区间染色,有一面长度为n的墙,每次选择一段墙进行染色(染色允许覆盖),问 ...
- 树-红黑树(R-B Tree)
红黑树概念 特殊的二叉查找树,每个节点上都有存储位表示节点的颜色是红(Red)或黑(Black).时间复杂度是O(lgn),效率高. 特性: (1)每个节点或者是黑色,或者是红色. (2)根节点是黑色 ...
- 红黑树(R-B Tree)
R-B Tree简介 R-B Tree,全称是Red-Black Tree,又称为“红黑树”,它一种特殊的二叉查找树.红黑树的每个节点上都有存储位表示节点的颜色,可以是红(Red)或黑(Black). ...
- 笔试算法题(51):简介 - 红黑树(RedBlack Tree)
红黑树(Red-Black Tree) 红黑树是一种BST,但是每个节点上增加一个存储位表示该节点的颜色(R或者B):通过对任何一条从root到leaf的路径上节点着色方式的显示,红黑树确保所有路径的 ...
随机推荐
- ASP.NET常用内置对象(二)Response
response翻译为中文:响应. 将数据作为请求的结果从服务器发送到客户浏览器中,并提供有关响应的消息.它可用来在页面中输出数据,在页面中跳转,还可以传递各个页面的参数. Response对象是Sy ...
- Selenium3+python自动化014-自动化常用设计模式页面对象模型 (Page Object)
一.概 念: PO(Page Object)设计模式是一种面向对象(页面对象)的设计模式,将测试对象及单个的测试步骤封装在每个Page对象中,以page为单位进行管理. 二.优点可以使代码复用,降低维 ...
- JVM内存模型以及HotSpot的GC策略
概述 想要进一步掌握Java语言,必须要深入了解一下Java程序的运行环境.本文会对JVM的内存模型.Java内存自动管理机制.以及Oracle官方虚拟机HotSpot在GC方面的实现策略进行大概的梳 ...
- 刷题22. Generate Parentheses
一.题目说明 这个题目是22. Generate Parentheses,简单来说,输入一个数字n,输出n对匹配的小括号. 简单考虑了一下,n=0,输出"";n=1,输出" ...
- Sql Server2008忘记sa登陆密码
Sql的sa登陆密码忘记解决方法: 语句执行的前提: 1.系统可以登陆进去(当不记得sa密码的时候,可以使用windows用户验证的方式进行登陆) 2.平时用sa登陆,点了记住密码但是不记得密码是多少 ...
- git 命令 总结
1.添加所有文件 git add . 2.添加某个文件 git add filename 3.commit 注释 git commit -m'commit 注释' 4.修改commit 注释 git ...
- canvas-文字粒子化(小程序)
有2张画板,1张渲染文字为获取文字数组,另一张用来渲染粒子根据拿到的数组. step1:渲染文字,根据canvasGetImageData拿到rgba数组 step2:遍历rgba数组拿到粒子的坐标 ...
- Java代码手段防止非法请求——防盗链
Java代码手段防止非法请求,思路如下: 1. 获取到当前请求的域名,如www.a.com 2. 获取到请求资源的上一个地址 3. 判断上一个地址是否为空,如 ...
- Ora-00906:missing left parenthesis
问题描述 Ora-00906:missing left parenthesis 问题原因 varchar和varchar2 必须指定长度,不然会报错
- JS全选按钮练习
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...