老齐python-基础1
1、基本对象类型
1.1数:
>>> 3 #基本数字
3
>>> 3333
3333
>>> 3.222
3.222
>>> id(3) #查看变量的内存地址
139725613539392
>>> id(4)
139725613539424
>>> help(id) #查看帮助
Help on built-in function id in module builtins: id(...)
id(object) -> integer Return the identity of an object. This is guaranteed to be unique among
simultaneously existing objects. (Hint: it's the object's memory address.) >>> type(3) #查看变量类型
<class 'int'> #返回为int类型
>>> type(3.0)
<class 'float'>
>>> type(3.22222) #返回为浮点类型
<class 'float'>
1.2变量:
python一个重要特征---对象有类型,变量无类型
>>> x = 5
>>> x
5
>>> x = 6
>>> x
6
1.3四则运算:
在计算机中,四则运算和数学中学习过的四则运算规则是一样的
>>> x = 5
>>> x
5
>>> x = 6
>>> x
6
>>> 2 + 5
7
>>> 5 - 2
3
>>> 10/2
5.0
>>> 10 / 5 + 1
3.0
>>> 2 * 3 - 4
在计算机中,整数不可以无限大,如果计算机结果超出计算机最大数,问题被称为“整数溢出问题”
推荐阅读:http://zhaoweizhuanshuo.blog.163.com/blog/static/148055262201093151439742
1.4大整数:
大整数乘法相关阅读:https://github.com/qiwsir/algorithm/blob/master/big_int.md
>>> 123123123123123213123546546980 * 6712376213576781238976172683168723
826448722992937633540194134897988240054845522368696291386106540
整数,用int表示,来自单词:integer
浮点数,用float表示,即单词:float
1.5浮点数:
遇到非常大或是非常小的浮点数,这时通常会使用一种叫做“科学计数法”的方式来表示。
>>> 9.8 ** -7.2
7.297468937055047e-08
e-08表示10的-8次方,这就是科学记数法。当然也可也使用这种方法写数字
>>> a = 2e3
>>> a
2000.0
超出浮点数范围溢出错误
>>> 500.0 ** 100000
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
OverflowError: (34, 'Numerical result out of range')
1.6除法:
整数除以整数
>>> 2 / 5
0.4
>>> 2.0 / 5
0.4
>>> 2 / 5.0
0.4
>>> 2.0 / 5.0
0.4
Python3整数除以整数不管什么类型都返回的是浮点数
>>> 5 // 2
2
整除取整,不四舍五入
1.7异常计算:
>>> 10.0 / 3
3.3333333333333335 #python主动结束运算
>>> 0.1 + 0.2
0.30000000000000004
>>> 0.1 + 0.1 - 0.2
0.0
>>> 0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1 - 0.3
5.551115123125783e-17
>>> 0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1 - 0.2
0.10000000000000003
原因是计算机存储位数显示导致0.1转换为二进制后的数不会精确的为10进制0.1就出现了上述现象
python的浮点数而言大多数计算机每次计算误差不超过2的53次方分支1,对于大多数任务来说已经足够了,但是要谨记这不是十进制算法,每个浮点数计算可能会带来一个新的舍入错误。一般情况下,只要简单地将最终显示的结果"四舍五入"到所期望的十进制位数,就会得到满意的最终结果。
对于需要非常精确的情况,可以使用decimal模块
另外,fractions模块支持另外一种形式的运算,他实现的运算基于有理数(因此1/3这样的数字可以精确的表示)。还可以使用NumPy包和其它的数学统计包。
《浮点数算法:争议和限制》:https://docs.python.org/2/tutorial/floatingpoint.html#tut-fp-issues
1.8引用模块解决除法问题:
python中又各种"轮子"供我们使用,那些"轮子"在python中叫"模块"或者“库”,有人承接其他的语言名称,叫做"类库"。
用法:
形式1: import module-name. import后面跟空格,然后是模块名称,如import os
形式2: from modue1 import module11. module1是一个大模块(可以称之为“库”),里面还有子模块module11,只想用module11就这么写
>>> import decimal
>>> a = decimal.Decimal("10.0")
>>> b = decimal.Decimal("")
>>> a / b
Decimal('3.333333333333333333333333333') >>> from fractions import Fraction
>>> Fraction(10,3)
Fraction(10, 3)
>>> Fraction(10,8)
Fraction(5, 4)
>>> Fraction(10,6)
Fraction(5, 3)
1.9余数
>>> 5 % 2
1
>>> 6 % 4
2
>>> 5.0 % 2
1.0
divmod
>>> help(divmod)
Help on built-in function divmod in module builtins: divmod(...)
divmod(x, y) -> (div, mod) Return the tuple ((x-x%y)/y, x%y). Invariant: div*y + mod == x. >>> divmod(5,2)
(2, 1)
>>> divmod(9,2)
(4, 1)
>>> divmod(5.0,2)
(2.0, 1.0)
1.10四舍五入
>>> round(1.234567,2)
1.23
>>> round(1.234567,3)
1.235
>>> round(10.0/3,4)
3.3333
>>> round(1.2345,3)
1.234 #没有四舍五入,还是转换2进制的问题
>>> round(2.235,2)
2.23
推荐阅读:https://github.com/qiwsir/algorithm/blob/master/divide.py
1.11常用数学函数和运算优先级
math模块:
>>> import math
>>> math.pi
3.141592653589793
>>> dir(math)
['__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'acos', 'acosh', 'asin', 'asinh', 'atan', 'atan2', 'atanh', 'ceil', 'copysign', 'cos', 'cosh', 'degrees', 'e', 'erf', 'erfc', 'exp', 'expm1', 'fabs', 'factorial', 'floor', 'fmod', 'frexp', 'fsum', 'gamma', 'hypot', 'isfinite', 'isinf', 'isnan', 'ldexp', 'lgamma', 'log', 'log10', 'log1p', 'log2', 'modf', 'pi', 'pow', 'radians', 'sin', 'sinh', 'sqrt', 'tan', 'tanh', 'trunc']
dir() 内建函数
help(dir)
Help on built-in function dir in module builtins: dir(...)
dir([object]) -> list of strings If called without an argument, return the names in the current scope.
Else, return an alphabetized list of names comprising (some of) the attributes
of the given object, and of attributes reachable from it.
If the object supplies a method named __dir__, it will be used; otherwise
the default dir() logic is used and returns:
for a module object: the module's attributes.
for a class object: its attributes, and recursively the attributes
of its bases.
for any other object: its attributes, its class's attributes, and
recursively the attributes of its class's base classes.
使用help()
>>> help(math.pow)
Help on built-in function pow in module math:
#交互模式下输入上面的指令,然后回车键,就会看到下面的信息
pow(...)
pow(x, y) Return x**y (x to the power of y).
#这里展示了math种的pow()函数的使用方法和相关说明
#pow(x,y):表示这个函数的参数有两个,也是函数的调用方式。
#Return x**y(x to the power of y):是对函数的说明,返回x**y的结果,并且在后面解释了x**y的含义(x的y次方
>>> 4 ** 2
16
>>> math.pow(4,2)
16.0
>>> 4 * 2
8
>>> math.sqrt(9)
3.0
>>> math.floor(3.14) #四舍五入
3
>>> math.floor(3.92)
3
>>> math.fabs(-2) #绝对值
2.0
>>> abs(-2)
2
>>> math.fmod(5,3) #取余
2.0
>>> 5 % 3
2
1.12运算优先级
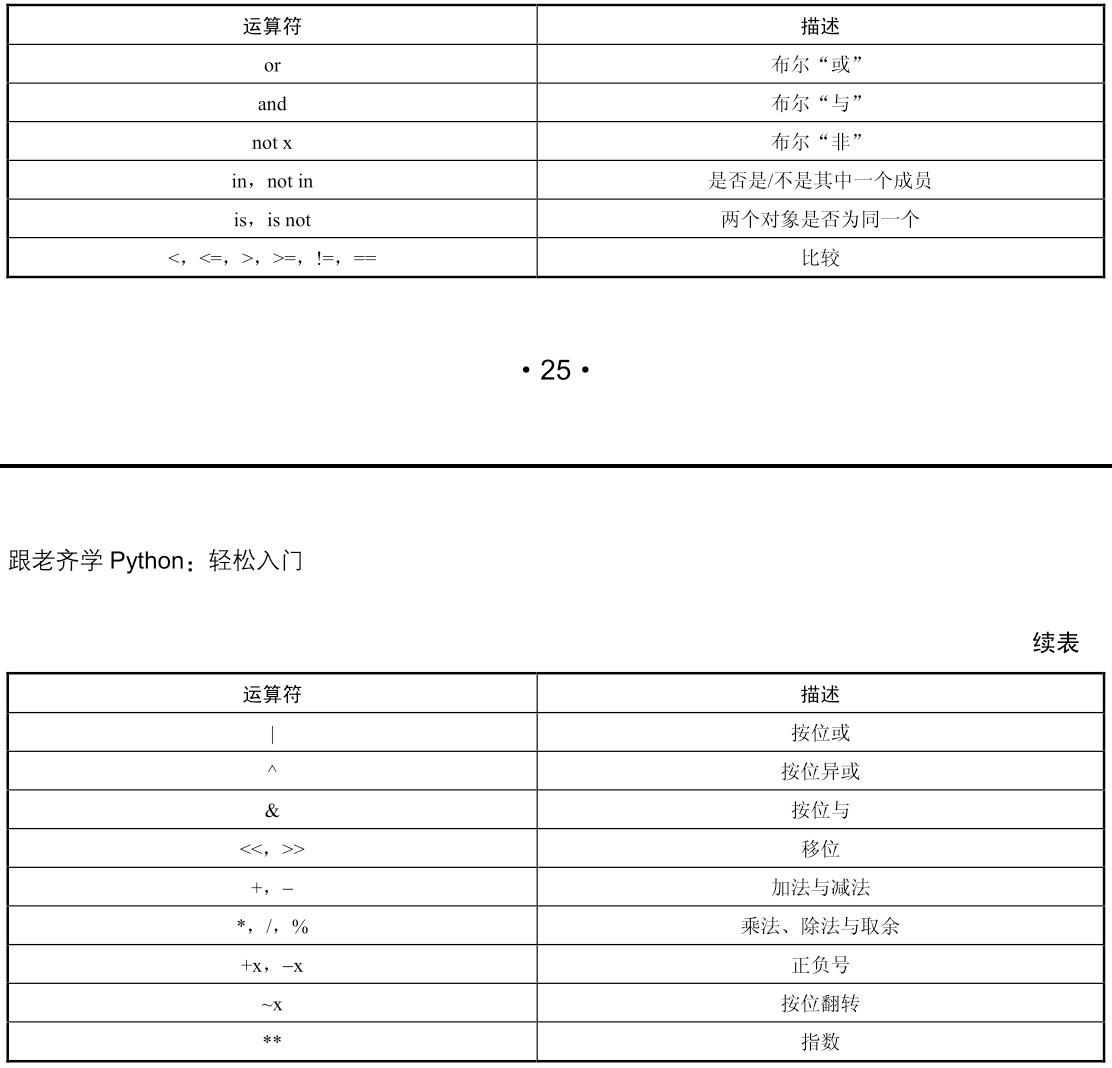
1.13程序
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding=utf-8 print("Hello, World")
#!/usr/bin/env python3 #pyhton解释器
#coding:utf-8 #编码指定,python3中默认是utf8,python2中需要指定 """
请计算:19+2*4-8/2
""" a = 19 + 2 * 4 - 8 / 2
print(a)
程序编译执行过程
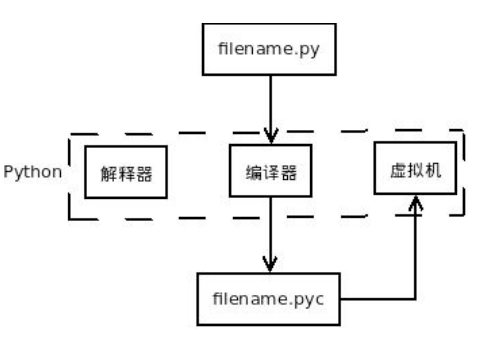
1.14字符串
>>> "I love Python."
'I love Python.'
>>> "I LOVE PYTHON."
'I LOVE PYTHON.'
>>> type(250)
<class 'int'>
>>> type("") #注意加引号后的类型
<class 'str'>
>>> print("good good study, day day up")
good good study, day day up
print特殊字符处理
>>> 'What's your name?'
File "<stdin>", line 1
'What's your name?'
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
>>> "What's your name?" #方法1双引号
"What's your name?"
>>> 'What\'s your name?' #方法2转译符
"What's your name?
变量和字符
>>> b = "hello,world"
>>> b
'hello,world'
>>> print(b)
hello,world
>>> type(b)
<class 'str'
连接字符串
>>> "py" + "thon"
'python'
>>> "py" - "thon" #str类型不支持减
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for -: 'str' and 'str'
>>> a = 1989
>>> b = "free"
>>> a + b
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'int' and 'str'
>>> b + str(a) #转换之后相加
'free1989'
>>> b + repr(a) #另一种方法
'free1989
>>> a = ""
>>> b = int(a)
>>> b
250
>>> type(b)
<class 'int'>
1.15python转义符
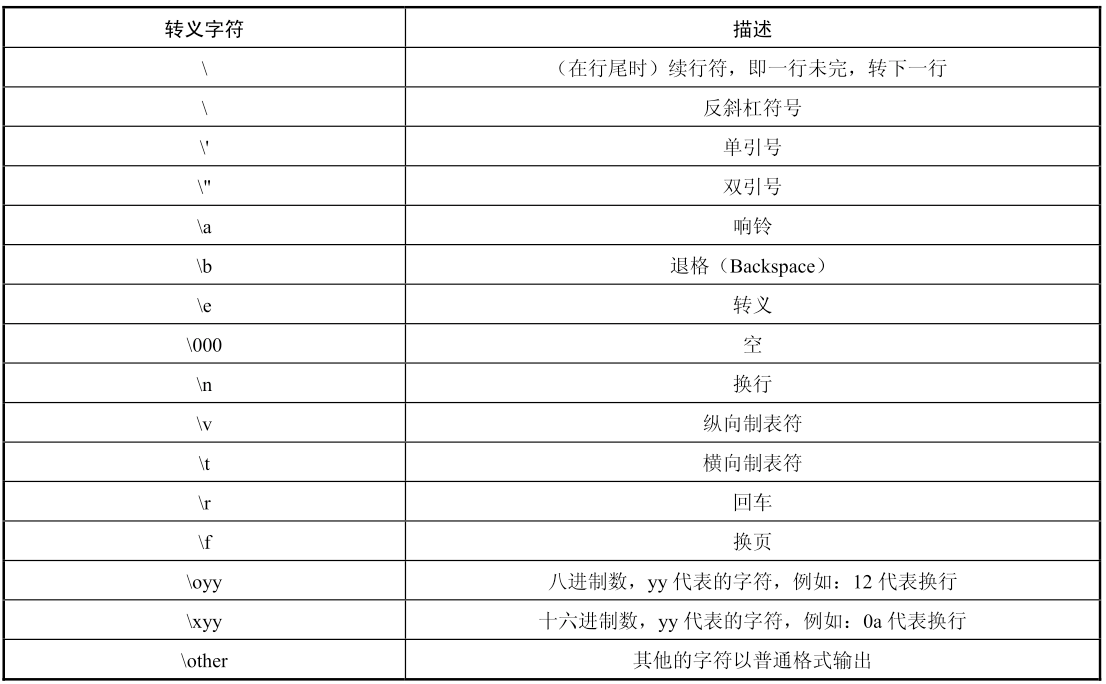
>>> print("hello. I am qiwsir.\
... My website is 'http://qiwsir.github.io'.")
hello. I am qiwsir.My website is 'http://qiwsir.github.io'.
>>> print("you can connect me by qq\\weibo\\gmail")
you can connect me by qq\weibo\gmail
1.16 键盘输入
内建函数:https://docs.python.org/3.5/library/functions.html
help(input)
Help on built-in function input in module builtins: input(prompt=None, /)
Read a string from standard input. The trailing newline is stripped. The prompt string, if given, is printed to standard output without a
trailing newline before reading input. If the user hits EOF (*nix: Ctrl-D, Windows: Ctrl-Z+Return), raise EOFError.
On *nix systems, readline is used if available.
(END)
>>> input("input your name:")
input your name:python #提示输入内容,通过键盘输入python
'python'
>>>
>>> name = input("input your name:")
input your name:python #将输入信息传入变量
>>> name
'python'
>>> type(name)
<class 'str'>
>>> age = input("How old are you?")
How old are you?10
>>> age
''
>>> type(age)
<class 'str'>
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding=utf-8 name = input("What is your name?")
age = input("How old are you?") print("Your name is:", name)
print("You are" + age + "years old.") after_ten = int(age) + 10
print("You will be " + str(after_ten) + "years old after ten years.")
字符输入小程序
1.17原始字符串
>>> print("I like \npython")
I like #\n换行
python
>>> dos = "c:\news"
>>> dos
'c:\news' #打印后出现的问题
>>> print(dos)
c:
ews
#解决方法1
>>> dos = "c:\\news"
>>> print(dos)
c:\news
>>> dos = r"c:\news"
#解决方法2
>>> print(dos)
c:\news
>>> print(r"c:\news\python")
c:\news\python
python保留字:某些变量名,文件名,函数,类等命名是不能被使用的
>>> import keyword
>>> keyword.kwlist
['False', 'None', 'True', 'and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'nonlocal', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
>>>
老齐python-基础1的更多相关文章
- 《跟老齐学Python:从入门到精通》齐伟(编著)epub+mobi+azw3
内容简介 <跟老齐学Python:从入门到精通>是面向编程零基础读者的Python入门教程,内容涵盖了Python的基础知识和初步应用.以比较轻快的风格,向零基础的学习者介绍一门时下比较流 ...
- 老王Python培训视频教程(价值500元)【基础进阶项目篇 – 完整版】
老王Python培训视频教程(价值500元)[基础进阶项目篇 – 完整版] 教学大纲python基础篇1-25课时1.虚拟机安装ubuntu开发环境,第一个程序:hello python! (配置开发 ...
- 从零开始部署Django生产环境(适用:《跟老齐学Python Django实战》)
<跟老齐学Python Django实战>作为市面上少有的Django通俗实战书籍,给了我学习Django很大的帮助.作为一名新入门的菜鸟,全书我重复练习了至少三遍,每次都有新的收获. 前 ...
- Pyhton开发【第五篇】:Python基础之杂货铺
Python开发[第五篇]:Python基础之杂货铺 字符串格式化 Python的字符串格式化有两种方式: 百分号方式.format方式 百分号的方式相对来说比较老,而format方式则是比较先进 ...
- python 基础部分重点复习整理--从意识那天开始进阶--已结
pythonic 风格编码 入门python好博客 进阶大纲 有趣的灵魂 老齐的教程 老齐还整理了很多精华 听说 fluent python + pro python 这两本书还不错! 元组三种遍历, ...
- python基础之dict、set及字符
python基础之dict.set及字符串处理 本节内容 字典介绍及内置方法 集合介绍 字符串处理 1.字典介绍及内置方法 字典是python中唯一的映射类型,采用键值对(key-value)的形式存 ...
- python基础之循环结构以及列表
python基础之编译器选择,循环结构,列表 本节内容 python IDE的选择 字符串的格式化输出 数据类型 循环结构 列表 简单购物车的编写 1.python IDE的选择 IDE的全称叫做集成 ...
- Python基础:序列(字符串)
一.概述 字符串 类似于C中的字符数组(功能上更像C++中的string),它是由一个个 字符 组成的序列.与C/C++不同的是,Python中没有 字符 这个类型,而是用 长度为1的字符串 来表示字 ...
- 第四篇:python基础之dict、set及字符
python基础之dict.set及字符 python基础之dict.set及字符串处理 本节内容 字典介绍及内置方法 集合介绍 字符串处理 1.字典介绍及内置方法 字典是python中唯一的映射 ...
- 第五篇:python基础之循环结构以及列表
python基础之循环结构以及列表 python基础之编译器选择,循环结构,列表 本节内容 python IDE的选择 字符串的格式化输出 数据类型 循环结构 列表 简单购物车的编写 1.pyth ...
随机推荐
- Moore majority vote algorithm(摩尔投票算法)
Boyer-Moore majority vote algorithm(摩尔投票算法) 简介 Boyer-Moore majority vote algorithm(摩尔投票算法)是一种在线性时间O( ...
- Spring与CXF整合
1.首先引入CXF相关jar包以及spring相关jar包,因项目是maven项目,所以直接在pom.xml文件中引入以下依赖即可(以下只是CXF的依赖包,Spring的也要引入,相关的依赖参考我博客 ...
- Pandas统计函数
统计方法有助于理解和分析数据的行为.现在我们将学习一些统计函数,可以将这些函数应用到Pandas的对象上. pct_change()函数 系列,DatFrames和Panel都有pct_change( ...
- selenium学习笔记(xpath和css定位)
简单的介绍下xpath和css的定位 理论知识就不罗列了 还是利用博客园的首页.直接附上代码: 这个是xpath #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf_8 - ...
- UIElement.IsMouseCaptured属性的应用
一个只读属性,该值描述了此元素是否捕获到了鼠标,如果该值为true,则说明此元素捕获到了鼠标:否则,未捕获到(例如:当鼠标进入到一个Button的可视化范围之内,当Button按钮外观效果发生了变化时 ...
- mysql必会必知
select distinct CHARACTER_SET_NAME from CHARACTER_SETS limit 12 offset 30;select distinct CHARACTER_ ...
- 音悦台mv视频下载
需要获取的页面: 参考了此处,做了修改,代码如下: #coding:utf-8 import urllib2 import urllib import re import sys import os ...
- MongoDB GridFS——本质上是将一个文件分割为大小为256KB的chunks 每个chunk里会放md5标识 取文件的时候会将这些chunks合并为一个整体返回
MongoDB GridFS GridFS 用于存储和恢复那些超过16M(BSON文件限制)的文件(如:图片.音频.视频等). GridFS 也是文件存储的一种方式,但是它是存储在MonoDB的集合中 ...
- ubuntu下搭建hadoop平台
终于把单击模式跟伪分布式模式搭建起来了,记录于此. 1.SSH无密码验证配置 因为伪分布模式下DataNode和NameNode均是本身,所以必须配置SSH localhost的无密码验证. 第一步, ...
- transition 总结
详情:http://www.css88.com/book/css/properties/transition/transition-property.htm left不能进行transition
