recastnavigation计算三角形离给定点最近位置方法简单注释
三角形
在recastnavigation中,三角形是最基础的元素,很多逻辑都是基于三角形进行的,其中比较常见的一个操作就是计算指定点到某三角形上的最近距离。由于三角形通常代表行走面,而给定点P可能是场景中的任意位置,所以这个操作通常会用来计算可行走面的最近距离。
recastnavigation的计算
主体代码在dtClosestPtPointTriangle函数,代码风格一直简洁明快,但是注释也说明了关键思路和步骤。
void dtClosestPtPointTriangle(float* closest, const float* p,
const float* a, const float* b, const float* c)
{
// Check if P in vertex region outside A
float ab[3], ac[3], ap[3];
dtVsub(ab, b, a);
dtVsub(ac, c, a);
dtVsub(ap, p, a);
float d1 = dtVdot(ab, ap);
float d2 = dtVdot(ac, ap);
if (d1 <= 0.0f && d2 <= 0.0f)
{
// barycentric coordinates (1,0,0)
dtVcopy(closest, a);
return;
}
// Check if P in vertex region outside B
float bp[3];
dtVsub(bp, p, b);
float d3 = dtVdot(ab, bp);
float d4 = dtVdot(ac, bp);
if (d3 >= 0.0f && d4 <= d3)
{
// barycentric coordinates (0,1,0)
dtVcopy(closest, b);
return;
}
// Check if P in edge region of AB, if so return projection of P onto AB
float vc = d1*d4 - d3*d2;
if (vc <= 0.0f && d1 >= 0.0f && d3 <= 0.0f)
{
// barycentric coordinates (1-v,v,0)
float v = d1 / (d1 - d3);
closest[0] = a[0] + v * ab[0];
closest[1] = a[1] + v * ab[1];
closest[2] = a[2] + v * ab[2];
return;
}
// Check if P in vertex region outside C
float cp[3];
dtVsub(cp, p, c);
float d5 = dtVdot(ab, cp);
float d6 = dtVdot(ac, cp);
if (d6 >= 0.0f && d5 <= d6)
{
// barycentric coordinates (0,0,1)
dtVcopy(closest, c);
return;
}
// Check if P in edge region of AC, if so return projection of P onto AC
float vb = d5*d2 - d1*d6;
if (vb <= 0.0f && d2 >= 0.0f && d6 <= 0.0f)
{
// barycentric coordinates (1-w,0,w)
float w = d2 / (d2 - d6);
closest[0] = a[0] + w * ac[0];
closest[1] = a[1] + w * ac[1];
closest[2] = a[2] + w * ac[2];
return;
}
// Check if P in edge region of BC, if so return projection of P onto BC
float va = d3*d6 - d5*d4;
if (va <= 0.0f && (d4 - d3) >= 0.0f && (d5 - d6) >= 0.0f)
{
// barycentric coordinates (0,1-w,w)
float w = (d4 - d3) / ((d4 - d3) + (d5 - d6));
closest[0] = b[0] + w * (c[0] - b[0]);
closest[1] = b[1] + w * (c[1] - b[1]);
closest[2] = b[2] + w * (c[2] - b[2]);
return;
}
// P inside face region. Compute Q through its barycentric coordinates (u,v,w)
float denom = 1.0f / (va + vb + vc);
float v = vb * denom;
float w = vc * denom;
closest[0] = a[0] + ab[0] * v + ac[0] * w;
closest[1] = a[1] + ab[1] * v + ac[1] * w;
closest[2] = a[2] + ab[2] * v + ac[2] * w;
}
为了便于理解,简单画了一个示意图,图中1——6个区域分别对应了函数中的6个返回点(前5个return和最后一个自然退出)。
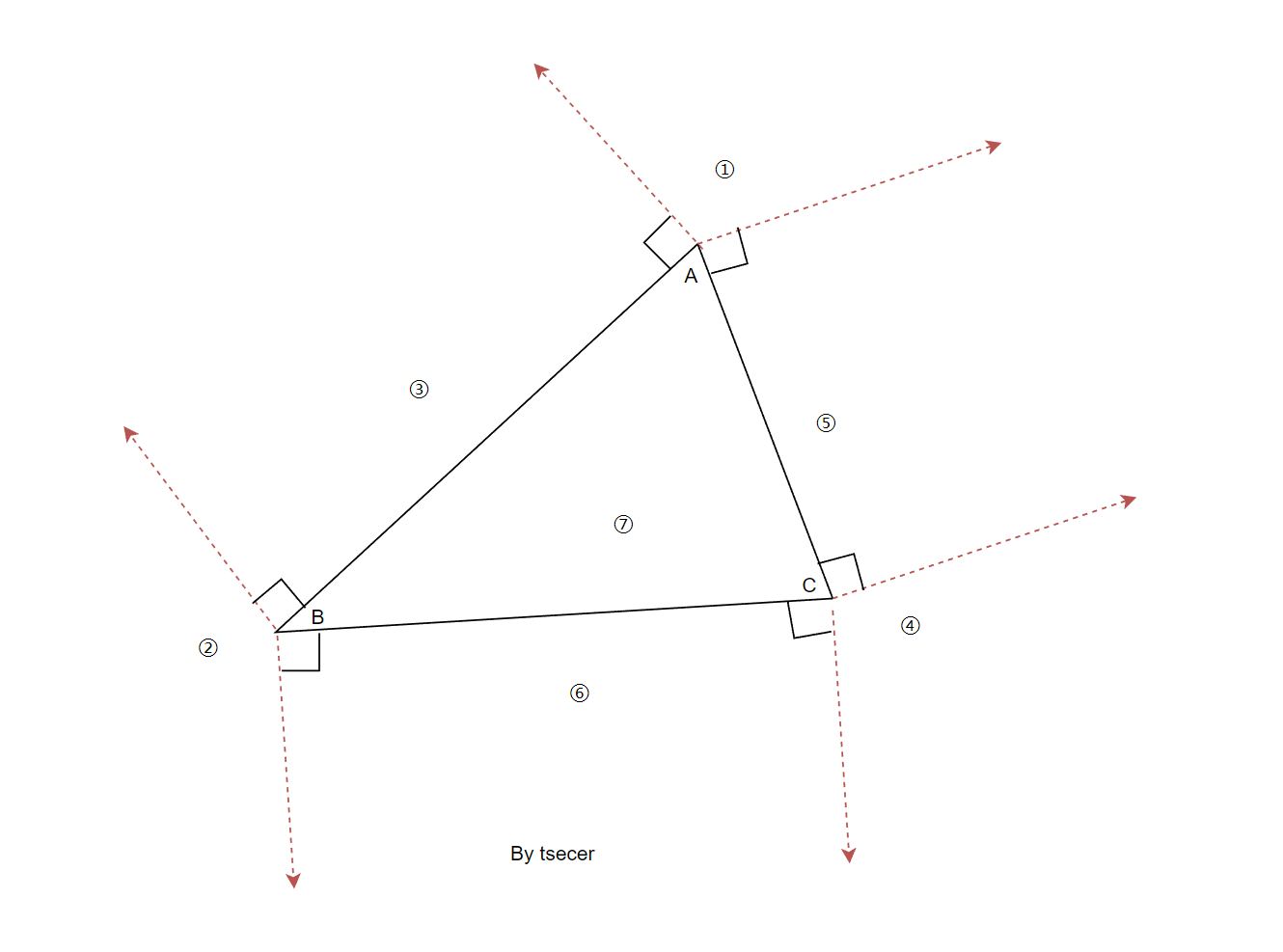
d1 <= 0.0f && d2 <= 0.0f
点乘有一个优良的几何性质,点乘的结果表示了两个向量夹角的cos值,该结果的正负表示了两个向量之间的夹角是否大于90度。如果点乘结果小于0,表示两个向量夹角大于90度。
这里另个判断表示点P在AB向量反方向,并且也在AC向量反方向,所以对应的就是图中的区域①。
d3 >= 0.0f && d4 <= d3
这里的 d4 <= d3 看起来不太直观:这个地方应该是P应该在CB向量的正方向,也就是CB*PB >= 0。
这里只是使用了一个简单的向量等式CB = (AB - AC) ,所以CB * PB >=0 等价于 (AB - AC) * PB >= 0 等价于 AB * PB >= AC * PB。
由于
float d3 = dtVdot(ab, bp);
并且
float d4 = dtVdot(ac, bp);
所以 AB * PB >= AC * PB <==> d3 >= d4。
vc <= 0.0f
一个基于极坐标的解释,由于网站规模比较小,文章数量也不多,恐怕哪天就不见了,所以还是整段全部拷贝过来。同样的问题,还有一个pdf格式的描述,看起来更舒服些。
The advantage of the method above is that it's very simple to understand so that once you read it you should be able to remember it forever and code it up at any time without having to refer back to anything. It's just - hey the point has to be on the same side of each line as the triangle point that's not in the line. Cake.
Well, there's another method that is also as easy conceptually but executes faster. The downside is there's a little more math involved, but once you see it worked out it should be no problem.
So remember that the three points of the triangle define a plane in space. Pick one of the points and we can consider all other locations on the plane as relative to that point. Let's go with A -- it'll be our origin on the plane. Now what we need are basis vectors so we can give coordinate values to all the locations on the plane. We'll pick the two edges of the triangle that touch A, (C - A) and (B - A). Now we can get to any point on the plane just by starting at A and walking some distance along (C - A) and then from there walking some more in the direction (B - A).
With that in mind we can now describe any point on the plane as
P = A + u * (C - A) + v * (B - A)
Notice now that if u or v < 0 then we've walked in the wrong direction and must be outside the triangle. Also if u or v > 1 then we've walked too far in a direction and are outside the triangle. Finally if u + v > 1 then we've crossed the edge BC again leaving the triangle.
Given u and v we can easily calculate the point P with the above equation, but how can we go in the reverse direction and calculate u and v from a given point P? Time for some math!
P = A + u * (C - A) + v * (B - A) // Original equation
(P - A) = u * (C - A) + v * (B - A) // Subtract A from both sides
v2 = u * v0 + v * v1 // Substitute v0, v1, v2 for less writing
// We have two unknowns (u and v) so we need two equations to solve
// for them. Dot both sides by v0 to get one and dot both sides by
// v1 to get a second.
(v2) . v0 = (u * v0 + v * v1) . v0
(v2) . v1 = (u * v0 + v * v1) . v1
// Distribute v0 and v1
v2 . v0 = u * (v0 . v0) + v * (v1 . v0)
v2 . v1 = u * (v0 . v1) + v * (v1 . v1)
// Now we have two equations and two unknowns and can solve one
// equation for one variable and substitute into the other. Or
// if you're lazy like me, fire up Mathematica and save yourself
// some handwriting.
Solve[v2.v0 == {u(v0.v0) + v(v1.v0), v2.v1 == u(v0.v1) + v(v1.v1)}, {u, v}]
u = ((v1.v1)(v2.v0)-(v1.v0)(v2.v1)) / ((v0.v0)(v1.v1) - (v0.v1)(v1.v0))
v = ((v0.v0)(v2.v1)-(v0.v1)(v2.v0)) / ((v0.v0)(v1.v1) - (v0.v1)(v1.v0))
Here's an implementation in Flash that you can play with. :)
// Compute vectors
v0 = C - A
v1 = B - A
v2 = P - A
// Compute dot products
dot00 = dot(v0, v0)
dot01 = dot(v0, v1)
dot02 = dot(v0, v2)
dot11 = dot(v1, v1)
dot12 = dot(v1, v2)
// Compute barycentric coordinates
invDenom = 1 / (dot00 * dot11 - dot01 * dot01)
u = (dot11 * dot02 - dot01 * dot12) * invDenom
v = (dot00 * dot12 - dot01 * dot02) * invDenom
// Check if point is in triangle
return (u >= 0) && (v >= 0) && (u + v < 1)
但是无论如何,两者说明的内容都是和代码中的不完全相同,不过也只是格式不同,本质是一样的,遗憾的是我还是没办法理解这种实现的直观(intuitive)解释:-(。
想让recastnavigation和文档中的内容相同,只需要做简单的向量转换即可,把代码中的BP根据向量减法替换为(AP - AB),然后带入
const float vc = d1*d4 - d3*d2;
d1d4 - d3d2 = (ABAP) * (ACBP) - (AB * BP) * (AC * AP) = AB * AP (AC * (AP - AB)) - (AB * (AP - AB)) * AC * AP = AB * AP * AC * AP - AB * AP * AC * AB - AB * AP * AC * AP + AB * AB * AC * AP
由于第1项和第3项内容相同,符号相反,所以可以抵消掉,剩余内容为
-AB * AP * AC * AB + AB * AB * AC * AP = AB * AB * AC * AP - AB * AP * AC * AB = dot11 * dot02 - dot12 * dot01
由于点乘双方顺序无关,所以上面值和前面的u值相同。
根据u的定义,P点一定是在AC的反方向分量上(加上另一个ABv分量,无论这个ABv分量是多少,P一定在AB的外侧:因为P点是通过两个基向量AC和AB与U和v标量获得,也就是沿AC移动u然后再沿着AB移动v个距离),所以在AB的外侧。
另外,embree库的closestPointTriangle函数实现,PhysX库也都使用了相同的方法。
UE的实现
UE的实现比较直观,就是计算垂线,然后判断方向,这个是最直观的实现方法,也最容易理解。
FVector FMath::ClosestPointOnTriangleToPoint(const FVector& Point, const FVector& A, const FVector& B, const FVector& C)
{
//Figure out what region the point is in and compare against that "point" or "edge"
const FVector BA = A - B;
const FVector AC = C - A;
const FVector CB = B - C;
const FVector TriNormal = BA ^ CB;
// Get the planes that define this triangle
// edges BA, AC, BC with normals perpendicular to the edges facing outward
const FPlane Planes[3] = { FPlane(B, TriNormal ^ BA), FPlane(A, TriNormal ^ AC), FPlane(C, TriNormal ^ CB) };
int32 PlaneHalfspaceBitmask = 0;
//Determine which side of each plane the test point exists
for (int32 i=0; i<3; i++)
{
if (Planes[i].PlaneDot(Point) > 0.0f)
{
PlaneHalfspaceBitmask |= (1 << i);
}
}
FVector Result(Point.X, Point.Y, Point.Z);
switch (PlaneHalfspaceBitmask)
{
case 0: //000 Inside
return FVector::PointPlaneProject(Point, A, B, C);
case 1: //001 Segment BA
Result = FMath::ClosestPointOnSegment(Point, B, A);
break;
case 2: //010 Segment AC
Result = FMath::ClosestPointOnSegment(Point, A, C);
break;
case 3: //011 point A
return A;
case 4: //100 Segment BC
Result = FMath::ClosestPointOnSegment(Point, B, C);
break;
case 5: //101 point B
return B;
case 6: //110 point C
return C;
default:
UE_LOG(LogUnrealMath, Log, TEXT("Impossible result in FMath::ClosestPointOnTriangleToPoint"));
break;
}
return Result;
}
recastnavigation计算三角形离给定点最近位置方法简单注释的更多相关文章
- OpenJudge计算概论-计算三角形面积【海伦公式】
/*============================================== 计算三角形面积 总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 65536kB 描述 平面上有一个三角形,它的 ...
- PHP图形计算器(计算三角形矩形周长面积)
运用PHP面向对象的知识设计一个图形计算器,同时也运用到了抽象类知识,这个计算器可以计算三角形的周长和面积以及矩形的周长和面积.本图形计算器有4个页面:1.PHP图形计算器主页index.php; ...
- 计算概论(A)/基础编程练习2(8题)/3:计算三角形面积
#include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> int main() { // 声明三角形的三个顶点坐标和面积 float x1, y1, x2, y2, ...
- Java入门:基础算法之计算三角形面积
本部分介绍如何计算三角形面积. /** * @author: 理工云课堂 * @description: 程序计算三角形的面积.三角形的底和高由用户输入 */ import java.util.Sca ...
- JavaScript中的内置对象-8--1.Array(数组)-Array构造函数; 数组的栈方法; 数组的转换方法; 数组的操作方法; 删除-插入-替换数组项; ECMAScript为数组实例添加的两个位置方法;
JavaScript内置对象-1Array(数组) 学习目标 1.掌握任何创建数组 2.掌握数值元素的读和写 3.掌握数组的length属性 如何创建数组 创建数组的基本方式有两种: 1.使用Arra ...
- C++11用于计算函数对象返回类型的统一方法
[C++11用于计算函数对象返回类型的统一方法] 模板 std::result_of 被TR1 引进且被 C++11 所采纳,可允许我们决定和使用一个仿函数其回返值的类别.底下,CalculusVer ...
- JS高程5.引用类型(6)Array类型的位置方法,迭代方法,归并方法
一.位置方法 ECMAScript5为数组实例添加了两个位置:indexOf()和 lastIndexOf().这两个方法接收两个参数:要查找的项和(可选的)表示查找起点位置的索引(如在数组[7,8, ...
- JS_高程5.引用类型(6)Array类型的位置方法,迭代方法,归并方法
一.位置方法 ECMAScript5为数组实例添加了两个位置:indexOf()和 lastIndexOf().这两个方法接收两个参数:要查找的项和(可选的)表示查找起点位置的索引(如在数组[7,8, ...
- C#中准确跟踪错误异常所在的文件位置方法
准确跟踪错误异常所在的文件位置方法是在发布改文件所在的DLL时候,把对应的pdb文件也一同发布. pdb文件是:PDB全称Program Database,不知道中文翻译叫什么.相信使用过VS的人对于 ...
- Mist 转移默认区块存储位置方法
http://8btc.com/thread-35325-1-1.html 看了bunaifeiqq 发的帖子“Mist 转移区块存储位置方法”,综合帖子下面的发言,自己做了测试,可行.电脑系统win ...
随机推荐
- cannot import name 'detail_route' from 'rest_framework.decorators'的解决办法
原因 es7不能使用3.1.1版本的django-haystack 解决办法 如果你是在弄elasticsearch,那么这个适合你,否则应该用不了. 终端执行django-haystack的更新 p ...
- Mybaits属性和元素
元素有select . insert . delect . updatae属性有: restType:主要用于查找返回的结果类型 parameterTpye:主要用于增删改返回的结果类型 以下关于re ...
- Flutter 登录与list列表demo
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() => runApp(DemoApp()); class DemoApp extends S ...
- 安全测试-WEB安全渗透测试基础知识(五)
1.5. 代码审计 1.5.1. 简介 代码审计是找到应用缺陷的过程.其通常有白盒.黑盒.灰盒等方式.白盒指通过对源代码的分析找到应用缺陷,黑盒通常不涉及到源代码,多使用模糊测试的方式,而灰盒则是黑白 ...
- docker搭建图片压测QPS3000+服务器(ftp+nginx)
docker搭建图片压测QPS3000+服务器(ftp+nginx) 在针对图片算法服务进行压力测试时,需要高性能的图片服务器 自己编写的图片应用性能不一定能达到要求 可能因为图片应用自身达不到压测要 ...
- VM部署服务后设置局域网内其他人访问
第一种方式:虚拟机设置中,网络适配器选择桥接模式,此时虚拟机IP号段与局域网处于同一号段,局域网内其他人使用虚拟机IP+端口即可访问服务 将虚拟机IP设为静态IP,我的虚拟机系统为Ubuntu20.0 ...
- C++ 手动创建二叉树,并实现前序、中序、后序、层次遍历
二叉树的创建是个麻烦事,我的思路是:首先将一个普通的二叉树转化为满二叉树,其中的空节点用一些标识数据来代替,如此一来,就可以用数组索引来描述数据在二叉树的什么位置了. 比如,数组[2,4,3,1,5, ...
- PHP日志组件Monolog的使用
1.首先安装日志组件 composer require monolog/monolog 2.创建日志类 3.使用 4.结果
- Linux网络第六章:PXE高效批量网络装机及kickstart无人值守安装
目录 一.PXE基础知识 二.PXE使用服务 三.高效批量网络装机实操 1.环境准备 2.配置dhcpd服务 3.配置FTP服务 4.配置TFTP服务 5.配置kickstart无人值守 6.启动服务 ...
- PostgreSQL权限管理
一旦一个对象被创建,它会被分配一个所有者.所有者通常是执行创建语句的角色.对于大部分类型的对象,初始状态下只有所有者(或者超级用户)能够对该对象做任何事情.为了允许其他角色使用它,必须分配权限. 1 ...
