《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example6.29

代码:
% The following funciton computes the filter
% coefficients shown in Table 6.2
b = firpm(30, [0, 0.3, 0.5, 1], [1, 1, 0, 0]);
w = [0:500]*pi/500; H = freqz(b, 1, w);
magH = abs(H); magHdb = 20*log10(magH); % 16-bit word-length quantization
N1 = 15; [bhat1, L1, B1] = QCoeff(b, N1);
TITLE1 = sprintf('%i-bits (1+%i+%i) ', N1+1, L1, B1);
%bhat1 = bahat(1, :); ahat1 = bahat(2, :);
Hhat1 = freqz(bhat1, 1, w); magHhat1 = abs(Hhat1);
magHhat1db = 20*log10(magHhat1); zhat1 = roots(bhat1); % 8-bit word-length quantization
N2 = 7; [bhat2, L2, B2] = QCoeff(b, N2);
TITLE2 = sprintf('%i-bits (1+%i+%i) ', N2+1, L2, B2);
%bhat2 = bahat(1, :); ahat2 = bahat(2, :);
Hhat2 = freqz(bhat2, 1, w); magHhat2 = abs(Hhat2);
magHhat2db = 20*log10(magHhat2); zhat2 = roots(bhat2); % Comparison of Magnitude Plots
Hf_1 = figure('paperunits', 'inches', 'paperposition', [0, 0, 6, 5], 'NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple 6.29');
%figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple 6.26a')
set(gcf,'Color','white'); % Comparison of Log-Magnitude Response: 16 bits
subplot(2, 2, 1); plot(w/pi, magHdb, 'g', 'linewidth', 1.5); axis([0, 1, -80, 5]);
hold on; plot(w/pi, magHhat1db, 'r', 'linewidth', 1); hold off;
xlabel('Digital Frequency in \pi units', 'fontsize', 10);
ylabel('Decibels', 'fontsize', 10); grid on;
title(['Log-mag Plot: ', TITLE1], 'fontsize', 10, 'fontweight', 'bold'); % Comparison of Pole-Zero Plots: 16 bits
subplot(2, 2, 3); [HZ, HP, Hl] = zplane([b], [1]); axis([-2, 2, -2, 2]); hold on;
set(HZ, 'color', 'g', 'linewidth', 1, 'markersize', 4);
set(HP, 'color', 'g', 'linewidth', 1, 'markersize', 4);
plot(real(zhat1), imag(zhat1), 'r+', 'linewidth', 1); grid on;
title(['PZ Plot: ' TITLE1], 'fontsize', 10, 'fontweight', 'bold'); hold off; % Comparison of Log-Magnitude Response: 8 bits
subplot(2, 2, 2); plot(w/pi, magHdb, 'g', 'linewidth', 1.5); axis([0, 1, -80, 5]);
hold on; plot(w/pi, magHhat2db, 'r', 'linewidth', 1); hold off;
xlabel('Digital Frequency in \pi units', 'fontsize', 10);
ylabel('Decibels', 'fontsize', 10); grid on;
title(['Log-mag Plot: ', TITLE2], 'fontsize', 10, 'fontweight', 'bold'); % Comparison of Pole-Zero Plots: 8 bits
subplot(2, 2, 4); [HZ, HP, Hl] = zplane([b], [1]); axis([-2, 2, -2, 2]); hold on;
set(HZ, 'color', 'g', 'linewidth', 1, 'markersize', 4);
set(HP, 'color', 'g', 'linewidth', 1, 'markersize', 4);
plot(real(zhat2), imag(zhat2), 'r+', 'linewidth', 1); grid on;
title(['PZ Plot: ' TITLE2], 'fontsize', 10, 'fontweight', 'bold'); hold off;
运行结果:
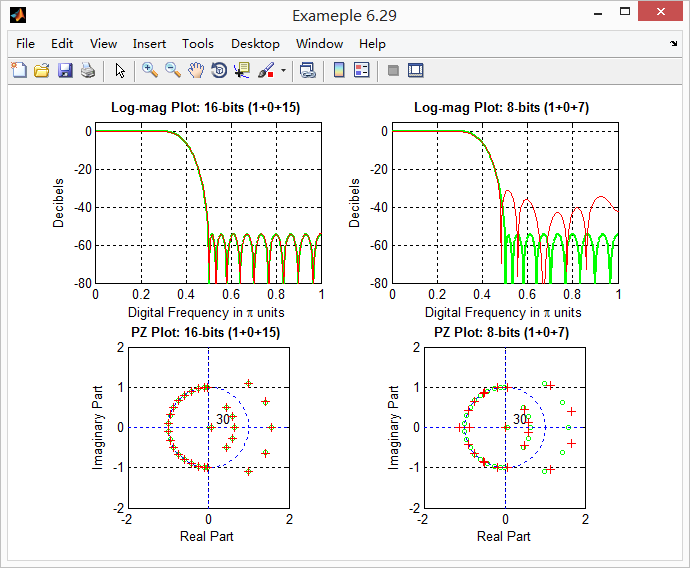
《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example6.29的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.22
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x2(n) Ts = 0.001; n = -5:1:5; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*abs(nT ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.17
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.16
代码: b = [0.0181, 0.0543, 0.0543, 0.0181]; % filter coefficient array b a = [1.0000, -1.7600, 1.1829, ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.15
上代码: subplot(1,1,1); b = 1; a = [1, -0.8]; n = [0:100]; x = cos(0.05*pi*n); y = filter(b,a,x); figur ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.13
上代码: w = [0:1:500]*pi/500; % freqency between 0 and +pi, [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. H = ex ...
随机推荐
- thinkphp3.2.3 + nginx 配置二级域名
使用的是阿里云centOS.74 第一步: 配置urlpath server { listen ; server_name www.xxxx.com xxxx.com; root /data/www/ ...
- 数据库原理及应用-数据库管理系统 DBMS
2018-02-20 14:35:34 数据库管理系统(英语:database management system,缩写:DBMS) 是一种针对对象数据库,为管理数据库而设计的大型电脑软件管理系统.具 ...
- 解决silk-v3-decoder-master转换wav时,百度语音解析问题
$cur_dir/silk/decoder >& if [ ! -f "$1.pcm" ]; then /usr/local/ffmpeg/bin/ffmpeg -y ...
- mysql数据库优化课程---17、mysql索引优化
mysql数据库优化课程---17.mysql索引优化 一.总结 一句话总结:一些字段可能会使索引失效,比如like,or等 1.check表监测的使用场景是什么? 视图 视图建立在两个表上, 删除了 ...
- 搞懂分布式技术3:初探分布式协调服务zookeeper
搞懂分布式技术3:初探分布式协调服务zookeeper 1.Zookeepr是什么 Zookeeper是一个典型的分布式数据一致性的解决方案,分布式应用程序可以基于它实现诸如数据发布/订阅,负载均衡, ...
- opencv画图
#coding=utf-8 import cv2 import numpy as np img = cv2.imread("2.png",cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) cv2 ...
- 捕获enter键盘事件绑定到登录按钮
/** *捕获enter键盘事件绑定到登录按钮 */ function keyLogin(event) { if (event.keyCode == 13) { document.getElement ...
- OLT配置学习
1.console连接跟一般交换机一样,不赘述 2.修改系统名称 Add Hostname/Device Name: huawei(config)#system sys-info descriptio ...
- RabbitMQ(6) 集群部署
单节点部署 rabbitmq单节点部署比较简单,可以使用apt-get等工具快速安装部署. wget -O- https://www.rabbitmq.com/rabbitmq-release-sig ...
- 将VS2010环境设置为VC6.0样式(字体、前景色、背景色、Visual Assist X等)
一.设置字体. 使用字体:Fixedsys Excelsior 3.01. 步骤1:下载字体. 步骤2:安装字体,控制面板->字体,复制下载的字体进去. 步骤3:打开VS2010,选择菜单:To ...
