java集合遍历删除指定元素异常分析总结
在使用集合的过程中,我们经常会有遍历集合元素,删除指定的元素的需求,而对于这种需求我们往往使用会犯些小错误,导致程序抛异常或者与预期结果不对,本人很早之前就遇到过这个坑,当时没注意总结,结果前段时间又遇到了这个问题,因此,总结下遍历集合的同时如何删除集合中指定的元素;
1.错误场景复原
public class ListRemoveTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("liu1",24));
users.add(new User("liu2",24));
users.add(new User("liu3",24));
users.add(new User("liu4",24));
Iterator<User> iterator = users.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
User user = iterator.next();
if(user.getName().equals("liu2")) {
users.remove(user);
}
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
或者如下代码
public class ListRemoveTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("liu1",24));
users.add(new User("liu2",24));
users.add(new User("liu3",24));
users.add(new User("liu4",24));
for (User user : users) {
if(user.getName().equals("liu2")) {
users.remove(user);
}
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
以上两种用法都会跑出如下异常:
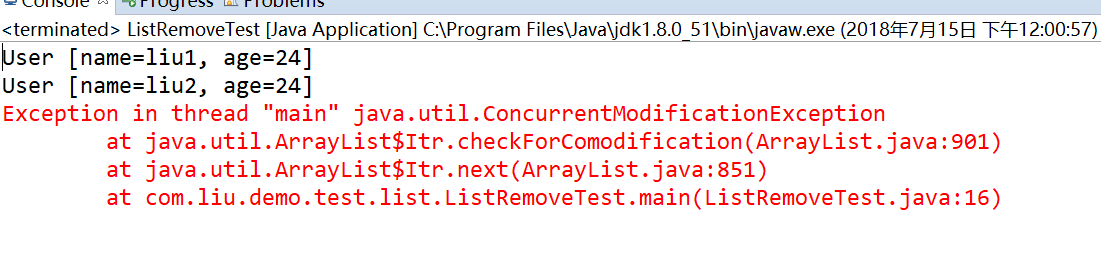
2.原因分析
上面两种错误,我想很多人都遇到过,这是我们很容易犯的错误,但是为啥会出现上述异常呢,我们又该如何正确遍历集合的同时,删除指定的元素呢!
2.1 原因解析
首先,对于foreach循环遍历,本质上还是迭代器的模式,上面的for语句等价于如下代码:
for (Iterator<User> iterator = users.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
User user = iterator.next();
if(user.getName().equals("liu2")) {
users.remove(user);
}
System.out.println(user);
}
因此,上述错误的本质,就要看迭代器iterator的源码啦
在ArrayList中,它的修改操作(add/remove)都会对modCount这个字段+1,modCount可以看作一个版本号,每次集合中的元素被修改后,都会+1(即使溢出)。
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
接下来再看看AbsrtactList中iteraor方法
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
它返回一个内部类,这个类实现了iterator接口,代码如下:
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor = 0;
int lastRet = -1;
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size();
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
try {
E next = get(cursor);
lastRet = cursor++;
return next;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
checkForComodification();
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet);
if (lastRet < cursor)
cursor--;
lastRet = -1;
// 修改expectedModCount 的值
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
在内部类Itr中,有一个字段expectedModCount ,初始化时等于modCount,即当我们调用list.iterator()返回迭代器时,该字段被初始化为等于modCount。在类Itr中next/remove方法都有调用checkForComodification()方法,在该方法中检测modCount == expectedModCount,如果不相等则抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
前面说过,在集合的修改操作(add/remove)中,都对modCount进行了+1。
在迭代过程中,执行list.remove(val),使得modCount+1,当下一次循环时,执行
it.next(),checkForComodification方法发现modCount != expectedModCount,则抛出异常。
2.2 预期结果不对,但是不抛异常
注意:还有一种更坑的场景,当删除集合的倒数第二个元素时,程序不会抛出任何异常,只是结果与预期的不相符,如果在应用过程中不认真观察,很难发现该错误!
错误实例如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("liu1",24));
users.add(new User("liu2",24));
users.add(new User("liu3",24));
users.add(new User("liu4",24));
Iterator<User> iterator = users.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
User user = iterator.next();
if(user.getName().equals("liu3")) {
users.remove(user);
}
System.out.println(user);
}
}
运行结果如下:
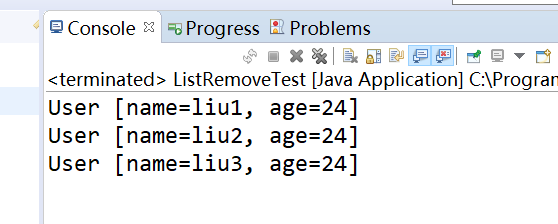
遍历过程删除了倒数第二个元素,那么最后一个元素就永远遍历不到了,这个主要原因就是Iterator源码中hasNext方法中,判断当前元素下标和集合大小是否相等
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
当删除倒数第二个元素后,当前元素下标和集合的大小相等了,跳出了循环,就会遍历最后一个集合元素了;
3.正确用法
要想在集合遍历的过程中删除指定元素,就务必使用迭代器自身的remove方法;
再来看看内部类Itr的remove()方法,在删除元素后,有这么一句expectedModCount
= modCount,同步修改expectedModCount
的值。所以,如果需要在使用迭代器迭代时,删除元素,可以使用迭代器提供的remove方法。
其他集合(Map/Set)使用迭代器迭代也是一样。
所以 Iterator 在工作的时候是不允许被迭代的对象被改变的。
但你可以使用 Iterator 本身的方法 remove() 来删除对象, Iterator.remove() 方法会在删除当前迭代对象的同时维护索引的一致
具体正确用法代码如下:
public class ListRemoveTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("liu1",24));
users.add(new User("liu2",24));
users.add(new User("liu3",24));
users.add(new User("liu4",24));
Iterator<User> iterator = users.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
User user = iterator.next();
if(user.getName().equals("liu2")) {
iterator.remove();
}
System.out.println(user);
}
System.out.println(users);
}
}
运行结果如下:

与预期结果一致;
java集合遍历删除指定元素异常分析总结的更多相关文章
- vector list map 遍历删除指定元素
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <vector> #include <list> #in ...
- Java集合——遍历集合元素并修改
Java集合——遍历集合元素并修改 摘要:本文主要总结了遍历集合的方式,以及在遍历时修改集合要注意的问题. 遍历Collection 对List和Set的遍历,有四种方式,下面以ArrayList为例 ...
- java集合系列之ArrayList源码分析
java集合系列之ArrayList源码分析(基于jdk1.8) ArrayList简介 ArrayList时List接口的一个非常重要的实现子类,它的底层是通过动态数组实现的,因此它具备查询速度快, ...
- Java集合系列[4]----LinkedHashMap源码分析
这篇文章我们开始分析LinkedHashMap的源码,LinkedHashMap继承了HashMap,也就是说LinkedHashMap是在HashMap的基础上扩展而来的,因此在看LinkedHas ...
- java集合系列之LinkedList源码分析
java集合系列之LinkedList源码分析 LinkedList数据结构简介 LinkedList底层是通过双端双向链表实现的,其基本数据结构如下,每一个节点类为Node对象,每个Node节点包含 ...
- jquery数组删除指定元素的方法:grep()
jquery数组删除指定元素的方法:grep() 金刚 数组 jquery javascript 元素 遇到的问题 今天遇到一个问题,删除数组中的一个指定元素,并返回新的数组. 我定义的js数组是这样 ...
- java集合循环删除
java集合循环删除,java list集合操作,java循环.分享牛,分享牛原创.java集合删除方法. 2.6.1.第一种方式 list.add("1"); list.add( ...
- List 循环删除 指定元素的 方法
使用Iterator进行循环,在删除指定元素.如果使用for 或 foreach 在删除指定下标是,list.size 会相应的缩短且下标前移,导致相邻满足条件的元素未删除 Iterator<S ...
- ES6数组中删除指定元素
知识点: ES6从数组中删除指定元素 findIndex()方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数的第一个元素的索引.否则返回-1. arr.splice(arr.findIndex(item => ...
随机推荐
- 日尼玛(。・∀・)ノ゙嗨 关于使用netstat时:::*
关于使用netstat时 # netstat -tlnp | grep :22 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1444/sshd tcp6 0 0 :::22 ...
- yii2.0 使用不同语言
1.建立语言目录.文件.项目根目录建立messages文件夹.存放不同语言对应的目录文件. 例如中文和英文 message 下建立两个文件夹 en.zh_CN 里面可以对应着多个翻译文件 2.在mai ...
- Xen,VMware ESXi,Hyper-V和KVM等虚拟化技术的原理解析
Xen,VMware ESXi,Hyper-V和KVM等虚拟化技术的原理解析 2018年04月03日 13:51:55 阅读数:936 XEN 与 VMware ESXi,Hyper-V 以及 K ...
- Linux .o a .so .la .lo的区别
o: 编译的目标文件a: 静态库,其实就是把若干o文件打了个包so: 动态链接库(共享库) lo: 使用libtool编译出的目标文件,其实就是在o文件中添加了一些信息la: 使用libtool编译出 ...
- Unity内存优化技术测试案例
笔者介绍:姜雪伟,IT公司技术合伙人,IT高级讲师,CSDN社区专家,特邀编辑,畅销书作者,已出版书籍:<手把手教你架构3D游戏引擎>电子工业出版社和<Unity3D实战核心技术详解 ...
- Android版本的"Wannacry"文件加密病毒样本分析(附带锁机)
一.前言 之前一个Wannacry病毒样本在PC端肆意了很久,就是RSA加密文件,勒索钱财.不给钱就删除.但是现在移动设备如此之多,就有一些不法分子想把这个病毒扩散到移动设备了,这几天一个哥们给了一个 ...
- strip()函数和 split()函数
一:python strip()函数介绍 函数原型:strip可以删除字符串的某些字符 声明:s为字符串,rm为要删除的字符序列 s.strip(rm) 删除s字符串中开头.结尾处,位于 ...
- 安全性测试AppScan工具使用实战20150920
Appscan是做安全性测试的一款工具,网上资料比较少,项目需要做安全性测试,用它做了web的扫描,可以发现一些问题,并且有原因分析和修复建议,感觉还不错,现在实战 1.打开工具,点击[文件]下的[新 ...
- iOS-AFNetworking3.0上传大量(1000张)图片到服务器
背景: 最近项目要做上传图片功能,图片必须是高清的,所以不让压缩,上传图片是大量的,比如几百张,这个如果是用afn,将图片直接for循环加入到formData里会出现一个问题,临时变量太多,导致内存紧 ...
- Java面试题收集以及参考答案(100道)
不积跬步无以至千里,这里会不断收集和更新Java基础相关的面试题,目前已收集100题. 1.什么是B/S架构?什么是C/S架构 B/S(Browser/Server),浏览器/服务器程序 C/S(Cl ...
