Popular HashMap and ConcurrentHashMap Interview Questions
http://howtodoinjava.com/core-java/collections/popular-hashmap-and-concurrenthashmap-interview-questions/
Popular HashMap and ConcurrentHashMap Interview Questions
June 14, 2013 by Lokesh Gupta
In this post, I will try to cover some related interview questionsusually occur next in chain:
Topics covered in this post:
- How you will design a good key for HashMap?
- Difference between HashMap and ConcurrentHashMap?
- Difference between HashMap and Collections.synchronizedMap(HashMap)?
- Difference between ConcurrentHashMap and Collections.synchronizedMap(HashMap)?
- Difference between HashMap and HashTable?
- Difference between HashTable and Collections.synchronized(HashMap)?
- Impact of random/fixed hashCode() value for key?
- Using HashMap in non-synchronized code in multi-threaded application?
Lets start the discussion without wasting time on unnecessary things.
1) How to design a good key for HashMap
The very basic need for designing a good key is that “we should be able to retrieve the value object back from the map without failure”, right?? Otherwise no matter how fancy data structure you build, it will be of no use. To decide that we have created a good key, we MUST know that “how HashMap works?“. I will leave, how hashmap works, part on you to read from linked post, but in summary it works on principle of Hashing.
Key’s hash code is used primarily in conjunction to its equals() method, for putting a key in map and then searching it back from map. So if hash code of key object changes after we have put a key-value pair in map, then its almost impossible to fetch the value object back from map. It is a case of memory leak. To avoid this, map keys should be immutable. These are few things to create an immutable of class.
This is the main reason why immutable classes like String, Integer or other wrapper classes are a good key object candidate.
But remember that immutability is recommended and not mandatory. If you want to make a mutable object as key in hashmap, then you have to make sure that state change for key object does not change the hash code of object. This can be done by overriding the hashCode() method. Also, key class must honor the hashCode() and equals() methods contract to avoid the undesired and surprising behavior on run time. Read more about this contract in linked post.
A more detailed information is available in here.
2) Difference between HashMap and ConcurrentHashMap
To better visualize the ConcurrentHashMap, let it consider as a group of HashMaps. To get and put key-value pairs from hashmap, you have to calculate the hashcode and look for correct bucket location in array of Collection.Entry. Rest you have read on previous related article on how hashmap works.
In concurrentHashMap, the difference lies in internal structure to store these key-value pairs. ConcurrentHashMap has an addition concept of segments. It will be easier to understand it you think of one segment equal to one HashMap [conceptually]. A concurrentHashMap is divided into number of segments [default 16] on initialization. ConcurrentHashMap allows similar number (16) of threads to access these segments concurrently so that each thread work on a specific segment during high concurrency.
This way, if when your key-value pair is stored in segment 10; code does not need to block other 15 segments additionally. This structure provides a very high level of concurrency.
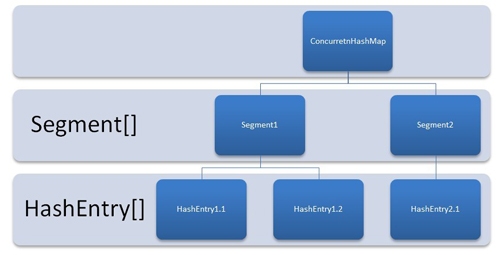 ConcurrentHashMap Internal Structure
ConcurrentHashMap Internal Structure
In other words, ConcurrentHashMap uses a multitude of locks, each lock controls one segment of the map. When setting data in a particular segment, the lock for that segment is obtained. So essentially update operations are synchronized.
When getting data, a volatile read is used without any synchronization. If the volatile read results in a miss, then the lock for that segment is obtained and entry is again searched in synchronized block.
I will go further deeper into this concept in my coming post. I will suggest you to subscribe email updates to get notified.
3) Difference between HashMap and Collections.synchronizedMap(HashMap)
It’s easy question, right !! HashMap is non-synchronized and Collections.synchronizedMap() returns a wrapped instance of HashMap which has all get, put methods synchronized.
Essentially, Collections.synchronizedMap() returns the reference of internally created inner-class “SynchronizedMap”, which contains key-value pairs of input HashMap, passed as argument.
This instance of inner class has nothing to do with original parameter HashMap instance and is completely independent.
4) Difference between ConcurrentHashMap and Collections.synchronizedMap( HashMap )
This one is slightly tougher. Both are synchronized version of HashMap, with difference in their core functionality and internal structure.
As stated above, ConcurrentHashMap is consist of internal segments which can be viewed as independent HashMaps, conceptually. All such segments can be locked by separate threads in high concurrent executions. In this way,multiple threads can get/put key-value pairs from ConcurrentHashMap without blocking/waiting for each other.
In Collections.synchronizedMap(), we get a synchronized version of HashMap and it is accessed in blocking manner. This means if multiple threads try to access synchronizedMap at same time, they will be allowed to get/put key-value pairs one at a time in synchronized manner.
5) Difference between HashMap and HashTable
It is also very easy question. The major difference is that HashTable is synchronized and HashMap is not.
If asked for other reasons, tell them, HashTable is legacy class (part of JDK 1.0) which was promoted into collections framework by implementing Map interface later. It still has some extra features like Enumerator with it, which HashMap lacks.
Another minor reason can be: HashMap supports null key (mapped to zero bucket), HashTable does not support null keys and throws NullPointerException on such attempt.
6) Difference between HashTable and Collections.synchronized(HashMap)
So far you must have got the core idea of the similarities between them. Both are synchronized version of collection. Both have synchronized methods inside class. Both are blocking in nature i.e. multiple threads will need to wait for getting the lock on instance before putting/getting anything out of it.
So what is the difference. Well, NO major difference for above said reasons. Performance is also same for both collections.
Only thing which separates them is the fact HashTable is legacy class promoted into collection framework. It got its own extra features like enumerators.
7) Impact of random/fixed hashcode() value for key
The impact of both cases (fixed hashcode or random hashcode for keys) will have same result and that is “unexpected behavior“. The very basic need of hashcode in HashMap is to identify the bucket location where to put the key-value pair, and from where it has to be retrieved.
If the hashcode of key object changes every time, the exact location of key-value pair will be calculated different, every time. This way, one object stored in HashMap will be lost forever and there will be very minimum possibility to get it back from map.
For this same reason, key are suggested to be immutable, so that they return a unique and same hashcode each time requested on same key object.
8) Using HashMap in non-synchronized code in multi-threaded application
In normal cases, it can leave the hashmap in inconsistent state where key-value pairs added and retrieved can be different. Apart from this, other surprising behavior like NullPointerException can come into picture.
In worst case, It can cause infinite loop. YES. You got it right. It can cause infinite loop. What did you asked, How?? Well, here is the reason.
HashMap has the concept of rehashing when it reaches to its upper limit of size. This rehashing is the process of creating a new memory area, and copying all the already present key-value pairs in new memory are. Lets say Thread A tried to put a key-value pair in map and then rehashing started. At the same time, thread B came and started manipulating the buckets using put operation.
Here while rehashing process, there are chances to generate the cyclic dependency where one element in linked list [in any bucket] can point to any previous node in same bucket. This will result in infinite loop, because rehashing code contains a “while(true) { //get next node; }” block and in cyclic dependency it will run infinite.
To watch closely, look art source code of transfer method which is used in rehashing:
public Object get(Object key) { Object k = maskNull(key); int hash = hash(k); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); Entry e = table[i]; //While true is always a bad practice and cause infinite loops while (true) { if (e == null) return e; if (e.hash == hash && eq(k, e.key)) return e.value; e = e.next; }} |
I will write a more detailed article on this in future.
I hope I was able to put some more items on your knowledge bucket. If you find this article helpful, please consider it sharing with your friends.
Happy Learning !!
Popular HashMap and ConcurrentHashMap Interview Questions的更多相关文章
- Top 25 Most Frequently Asked Interview Core Java Interview Questions And Answers
We are sharing 25 java interview questions , these questions are frequently asked by the recruiters. ...
- 115 Java Interview Questions and Answers – The ULTIMATE List--reference
In this tutorial we will discuss about different types of questions that can be used in a Java inter ...
- 69 Spring Interview Questions and Answers – The ULTIMATE List--reference
This is a summary of some of the most important questions concerning the Spring Framework, that you ...
- Verilog Tips and Interview Questions
Verilog Interiew Quetions Collection : What is the difference between $display and $monitor and $wr ...
- 安卓面试题 Android interview questions
安卓面试题 Android interview questions 作者:韩梦飞沙 2017年7月3日,14:52:44 1. 要做一个尽可能流畅的ListView,你平时在 ...
- WCF学习系列二---【WCF Interview Questions – Part 2 翻译系列】
http://www.topwcftutorials.net/2012/09/wcf-faqs-part2.html WCF Interview Questions – Part 2 This WCF ...
- [译]Node.js Interview Questions and Answers (2017 Edition)
原文 Node.js Interview Questions for 2017 什么是error-first callback? 如何避免无止境的callback? 什么是Promises? 用什么工 ...
- WCF学习系列三--【WCF Interview Questions – Part 3 翻译系列】
http://www.topwcftutorials.net/2012/10/wcf-faqs-part3.html WCF Interview Questions – Part 3 This WCF ...
- WCF学习系列四--【WCF Interview Questions – Part 4 翻译系列】
WCF Interview Questions – Part 4 This WCF service tutorial is part-4 in series of WCF Interview Qu ...
随机推荐
- Android模拟器Intel Atom下载安装配置
https://software.intel.com 在Android x86模拟器Intel Atom x86 System Image时提示Intel execute disable bit(xd ...
- 20145329 《Java程序设计》第三周学习总结
教材学习内容总结 java并非完整的面向对象程序语言 定义 1:class:定义类 2.char:类型声明变量 3.new:新建对象 4.名称 X:参考 5.=:可用于指定参考至新建变量 6.构造函数 ...
- MYSQL数据库里面的所有密码批量MD5加密
如果你的字段够长度的话:UPDATE users SET password = MD5(password);如果长度不够,可以先增加长度后再做,或者多建一列,完成后删除原来的列!(如passwd)UP ...
- zabbix分布式监控系统安装配置
zabbix简介: zabbix(音同 zæbix)是一个基于WEB界面的提供分布式系统监视以及网络监视功能的企业级的开源解决方案. zabbix能监视各种网络参数,保证服务器系统的安全运营:并提供灵 ...
- Docker容器可以使用容器平台管理自动重启实现自修复吗?
容器的自修复功能是经常被吹嘘的.因为容器是衣服,人躺下了,衣服也躺下了,容器平台能够马上发现人躺下了,于是可以迅速将人重新唤醒工作. 而虚拟机是房子,人躺下了,房子还站着.因而虚拟机管理平台不知道里面 ...
- 【链接】Eclipse的Debug调试技巧
Eclipse的Debug调试技巧大全 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bORg9YxJiby2WenYRrXY-w 使用Eclipse调试Java程序的10个技巧 https: ...
- Grunt Part 2
Objectives and Outcomes In this exercise, you will continue to learn to use Grunt, the task runner. ...
- 利用Object.defineProperty实现Vue数据双向绑定
body部分很简单,一个输入框和一个展示的div <div> <p>你好,<input id='nickName'></p> <div id=&q ...
- Redis可以做哪些事儿?
Redis可以作为数据库,提供高速缓存,消息队列等功能,这里介绍Redis可以做的其中两件事: 1.提供缓存功能,作为缓存服务器; 2.轻量级的消息队列(MQ)进行使用. /// <summar ...
- 修改sublime侧边栏的颜色
Ctrl+Shift+P -> install -> 搜索安装包SyncedSidebarBg,自动同步侧边栏底色为编辑窗口底色.
