第五章 dubbo源码解析目录
一 netty的线程模型

在netty中存在两种线程:boss线程和worker线程。
1 boss线程
作用:
- accept客户端的连接;
- 将接收到的连接注册到一个worker线程上
个数:
- 通常情况下,服务端每绑定一个端口,开启一个boss线程
2 worker线程
作用:
- 处理注册在其身上的连接connection上的各种io事件
个数:
- 默认是:核数+1
注意:
- 一个worker线程可以注册多个connection
- 一个connection只能注册在一个worker线程上
二 dubbo的事件派发策略和线程池
1、dubbo基于netty。有5种派发策略:
- 默认是all:所有消息都派发到线程池,包括请求,响应,连接事件,断开事件,心跳等。 即worker线程接收到事件后,将该事件提交到业务线程池中,自己再去处理其他事。
- direct:worker线程接收到事件后,由worker执行到底。
- message:只有请求响应消息派发到线程池,其它连接断开事件,心跳等消息,直接在 IO线程上执行
- execution:只请求消息派发到线程池,不含响应(客户端线程池),响应和其它连接断开事件,心跳等消息,直接在 IO 线程上执行
- connection:在 IO 线程上,将连接断开事件放入队列,有序逐个执行,其它消息派发到线程池。
2、业务线程池:
- fixed:固定大小线程池,启动时建立线程,不关闭,一直持有。(缺省)
- coresize:200
- maxsize:200
- 队列:SynchronousQueue
- 回绝策略:AbortPolicyWithReport - 打印线程信息jstack,之后抛出异常
- cached:缓存线程池,空闲一分钟自动删除,需要时重建。
- limited:可伸缩线程池,但池中的线程数只会增长不会收缩。只增长不收缩的目的是为了避免收缩时突然来了大流量引起的性能问题。
三 服务端
两种线程池:
- io线程池:netty的boss和worker线程池。
- boss:建立connection
- worker:处理注册在其身上的连接connection上的各种io事件
- 业务线程池:fixedThreadPool():“DubboServerHandler-10.10.10.11:20880” 见“二 dubbo的事件派发策略和线程池”
- 与worker配合处理各种请求
四 客户端
两种线程池:
- io线程池:netty的boss和worker线程池
- 同上
- 业务线程池:cachedThreadPool:“DubboClientHandler-10.10.10.10:20880”
- 与worker配合处理各种响应,最后得到响应后唤醒被阻塞的主线程
五 dubbo线程模型图
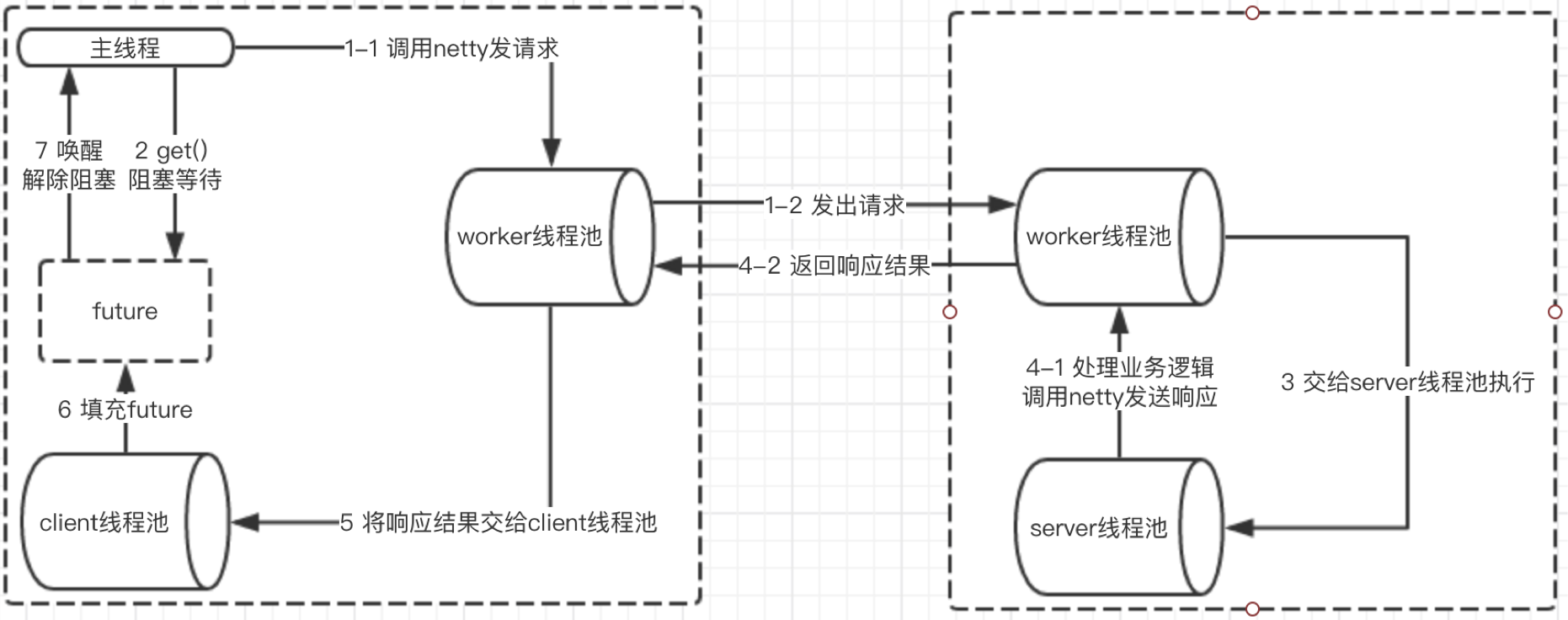
整体步骤:(受限于派发策略,以默认的all为例, 以netty4为例)
- 客户端的主线程发出一个请求后获得future,在执行get时进行阻塞等待;
- 服务端使用worker线程(netty通信模型)接收到请求后,将请求提交到server线程池中进行处理
- server线程处理完成之后,将相应结果返回给客户端的worker线程池(netty通信模型),最后,worker线程将响应结果提交到client线程池进行处理
- client线程将响应结果填充到future中,然后唤醒等待的主线程,主线程获取结果,返回给客户端
netty4是2.5.6引入的,2.5.6之前的netty用的是netty3。在dubbo源码中相较于netty3,添加netty4主要仅仅改了两个类:NettyServer,NettyClient。还有就是编解码。
使用方式:
服务端:
1 <dubbo:provider server="netty4"/>
客户端:
1 <dubbo:consumer client="netty4" />
一、服务端 - NettyServer

1 package com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4;
2
3 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.Constants;
4 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL;
5 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.Logger;
6 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.LoggerFactory;
7 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.utils.ExecutorUtil;
8 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.utils.NetUtils;
9 import com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Channel;
10 import com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.ChannelHandler;
11 import com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.RemotingException;
12 import com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Server;
13 import com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.AbstractServer;
14 import com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.dispatcher.ChannelHandlers;
15 import com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4.logging.NettyHelper;
16
17 import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
18 import io.netty.buffer.PooledByteBufAllocator;
19 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
20 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
21 import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
22 import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
23 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
24 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
25 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
26 import io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultThreadFactory;
27
28 import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
29 import java.util.Collection;
30 import java.util.HashSet;
31 import java.util.Map;
32
33 public class NettyServer extends AbstractServer implements Server {
34
35 private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(NettyServer.class);
36
37 private Map<String, Channel> channels; // <ip:port, channel>
38
39 private ServerBootstrap bootstrap;
40
41 private io.netty.channel.Channel channel;
42
43 private EventLoopGroup bossGroup;
44 private EventLoopGroup workerGroup;
45
46 public NettyServer(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
47 super(url, ChannelHandlers.wrap(handler, ExecutorUtil.setThreadName(url, SERVER_THREAD_POOL_NAME)));
48 }
49
50 @Override
51 protected void doOpen() throws Throwable {
52 NettyHelper.setNettyLoggerFactory();
53
54 bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
55
56 bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1, new DefaultThreadFactory("NettyServerBoss", true));
57 workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(getUrl().getPositiveParameter(Constants.IO_THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_IO_THREADS),
58 new DefaultThreadFactory("NettyServerWorker", true));
59
60 final NettyServerHandler nettyServerHandler = new NettyServerHandler(getUrl(), this);
61 channels = nettyServerHandler.getChannels();
62
63 bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
64 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
65 .childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, Boolean.TRUE)
66 .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, Boolean.TRUE)
67 .childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
68 .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
69 @Override
70 protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
71 NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyServer.this);
72 ch.pipeline()//.addLast("logging",new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))//for debug
73 .addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder())
74 .addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder())
75 .addLast("handler", nettyServerHandler);
76 }
77 });
78 // bind
79 ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(getBindAddress());
80 channelFuture.syncUninterruptibly();
81 channel = channelFuture.channel();
82
83 }
84
85 @Override
86 protected void doClose() throws Throwable {
87 try {
88 if (channel != null) {
89 // unbind.
90 channel.close();
91 }
92 } catch (Throwable e) {
93 logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
94 }
95 try {
96 Collection<com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Channel> channels = getChannels();
97 if (channels != null && channels.size() > 0) {
98 for (com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Channel channel : channels) {
99 try {
100 channel.close();
101 } catch (Throwable e) {
102 logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
103 }
104 }
105 }
106 } catch (Throwable e) {
107 logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
108 }
109 try {
110 if (bootstrap != null) {
111 bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
112 workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
113 }
114 } catch (Throwable e) {
115 logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
116 }
117 try {
118 if (channels != null) {
119 channels.clear();
120 }
121 } catch (Throwable e) {
122 logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
123 }
124 }
125
126 public Collection<Channel> getChannels() {
127 Collection<Channel> chs = new HashSet<Channel>();
128 for (Channel channel : this.channels.values()) {
129 if (channel.isConnected()) {
130 chs.add(channel);
131 } else {
132 channels.remove(NetUtils.toAddressString(channel.getRemoteAddress()));
133 }
134 }
135 return chs;
136 }
137
138 public Channel getChannel(InetSocketAddress remoteAddress) {
139 return channels.get(NetUtils.toAddressString(remoteAddress));
140 }
141
142 public boolean isBound() {
143 return channel.isActive();
144 }
145 }

netty4的写法与netty3有很大不同,下面是netty3:(http://www.cnblogs.com/java-zhao/p/7625596.html)

1 /**
2 * 启动netty服务,监听客户端连接
3 */
4 @Override
5 protected void doOpen() throws Throwable {
6 NettyHelper.setNettyLoggerFactory();
7 ExecutorService boss = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(new NamedThreadFactory("NettyServerBoss", true));
8 ExecutorService worker = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(new NamedThreadFactory("NettyServerWorker", true));
9 ChannelFactory channelFactory = new NioServerSocketChannelFactory(boss, worker, getUrl().getPositiveParameter(Constants.IO_THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_IO_THREADS));
10 bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(channelFactory);
11
12 final NettyHandler nettyHandler = new NettyHandler(getUrl(), this);
13 channels = nettyHandler.getChannels();
14 // https://issues.jboss.org/browse/NETTY-365
15 // https://issues.jboss.org/browse/NETTY-379
16 // final Timer timer = new HashedWheelTimer(new NamedThreadFactory("NettyIdleTimer", true));
17 bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory() {
18 public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() {
19 NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyServer.this);
20 ChannelPipeline pipeline = Channels.pipeline();
21 /*int idleTimeout = getIdleTimeout();
22 if (idleTimeout > 10000) {
23 pipeline.addLast("timer", new IdleStateHandler(timer, idleTimeout / 1000, 0, 0));
24 }*/
25 pipeline.addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder());
26 pipeline.addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder());
27 pipeline.addLast("handler", nettyHandler);
28 return pipeline;
29 }
30 });
31 // bind
32 channel = bootstrap.bind(getBindAddress());
33 }

二、客户端 - NettyClient

1 package com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4;
2
3 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.Constants;
4 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL;
5 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.Version;
6 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.Logger;
7 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.LoggerFactory;
8 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.utils.NetUtils;
9 import com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.ChannelHandler;
10 import com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.RemotingException;
11 import com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.AbstractClient;
12 import com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4.logging.NettyHelper;
13
14 import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
15 import io.netty.buffer.PooledByteBufAllocator;
16 import io.netty.channel.Channel;
17 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
18 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
19 import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
20 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
21 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
22 import io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultThreadFactory;
23
24 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
25
26 public class NettyClient extends AbstractClient {
27
28 private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(NettyClient.class);
29
30 private static final NioEventLoopGroup nioEventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(Constants.DEFAULT_IO_THREADS, new DefaultThreadFactory("NettyClientWorker", true));
31
32 private Bootstrap bootstrap;
33
34 private volatile Channel channel; // volatile, please copy reference to use
35
36 public NettyClient(final URL url, final ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
37 super(url, wrapChannelHandler(url, handler));
38 }
39
40 @Override
41 protected void doOpen() throws Throwable {
42 NettyHelper.setNettyLoggerFactory();
43 final NettyClientHandler nettyClientHandler = new NettyClientHandler(getUrl(), this);
44 bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
45 bootstrap.group(nioEventLoopGroup)
46 .option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
47 .option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
48 .option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
49 //.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, getTimeout())
50 .channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
51
52 if (getTimeout() < 3000) {
53 bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 3000);
54 } else {
55 bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, getTimeout());
56 }
57
58 bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
59 protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
60 NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyClient.this);
61 ch.pipeline()//.addLast("logging",new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))//for debug
62 .addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder())
63 .addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder())
64 .addLast("handler", nettyClientHandler);
65 }
66 });
67 }
68
69 protected void doConnect() throws Throwable {
70 long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
71 ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(getConnectAddress());
72 try {
73 boolean ret = future.awaitUninterruptibly(3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
74
75 if (ret && future.isSuccess()) {
76 Channel newChannel = future.channel();
77 try {
78 // Close old channel
79 Channel oldChannel = NettyClient.this.channel; // copy reference
80 if (oldChannel != null) {
81 try {
82 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
83 logger.info("Close old netty channel " + oldChannel + " on create new netty channel " + newChannel);
84 }
85 oldChannel.close();
86 } finally {
87 NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(oldChannel);
88 }
89 }
90 } finally {
91 if (NettyClient.this.isClosed()) {
92 try {
93 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
94 logger.info("Close new netty channel " + newChannel + ", because the client closed.");
95 }
96 newChannel.close();
97 } finally {
98 NettyClient.this.channel = null;
99 NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(newChannel);
100 }
101 } else {
102 NettyClient.this.channel = newChannel;
103 }
104 }
105 } else if (future.cause() != null) {
106 throw new RemotingException(this, "client(url: " + getUrl() + ") failed to connect to server "
107 + getRemoteAddress() + ", error message is:" + future.cause().getMessage(), future.cause());
108 } else {
109 throw new RemotingException(this, "client(url: " + getUrl() + ") failed to connect to server "
110 + getRemoteAddress() + " client-side timeout "
111 + getConnectTimeout() + "ms (elapsed: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms) from netty client "
112 + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using dubbo version " + Version.getVersion());
113 }
114 } finally {
115 if (!isConnected()) {
116 //future.cancel(true);
117 }
118 }
119 }
120
121 @Override
122 protected void doDisConnect() throws Throwable {
123 try {
124 NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(channel);
125 } catch (Throwable t) {
126 logger.warn(t.getMessage());
127 }
128 }
129
130 @Override
131 protected void doClose() throws Throwable {
132 //can't shutdown nioEventLoopGroup
133 //nioEventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
134 }
135
136 @Override
137 protected com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Channel getChannel() {
138 Channel c = channel;
139 if (c == null || !c.isActive())
140 return null;
141 return NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(c, getUrl(), this);
142 }
143 }

netty3:http://www.cnblogs.com/java-zhao/p/7811040.html

1 protected void doOpen() throws Throwable {
2 NettyHelper.setNettyLoggerFactory();
3 bootstrap = new ClientBootstrap(channelFactory);
4 // config
5 // @see org.jboss.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannelConfig
6 bootstrap.setOption("keepAlive", true);
7 bootstrap.setOption("tcpNoDelay", true);
8 bootstrap.setOption("connectTimeoutMillis", getTimeout());
9 final NettyHandler nettyHandler = new NettyHandler(getUrl(), this);
10 bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory() {
11 public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() {
12 NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyClient.this);
13 ChannelPipeline pipeline = Channels.pipeline();
14 pipeline.addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder());
15 pipeline.addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder());
16 pipeline.addLast("handler", nettyHandler);
17 return pipeline;
18 }
19 });
20 }
21
22 protected void doConnect() throws Throwable {
23 long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
24 ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(getConnectAddress());
25 try {
26 boolean ret = future.awaitUninterruptibly(getConnectTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
27
28 if (ret && future.isSuccess()) {
29 Channel newChannel = future.getChannel();
30 newChannel.setInterestOps(Channel.OP_READ_WRITE);
31 try {
32 // 关闭旧的连接
33 Channel oldChannel = NettyClient.this.channel; // copy reference
34 if (oldChannel != null) {
35 try {
36 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
37 logger.info("Close old netty channel " + oldChannel + " on create new netty channel " + newChannel);
38 }
39 oldChannel.close();
40 } finally {
41 NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(oldChannel);
42 }
43 }
44 } finally {
45 if (NettyClient.this.isClosed()) {
46 try {
47 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
48 logger.info("Close new netty channel " + newChannel + ", because the client closed.");
49 }
50 newChannel.close();
51 } finally {
52 NettyClient.this.channel = null;
53 NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(newChannel);
54 }
55 } else {
56 NettyClient.this.channel = newChannel;
57 }
58 }
59 } else if (future.getCause() != null) {
60 throw new RemotingException(this, "client(url: " + getUrl() + ") failed to connect to server "
61 + getRemoteAddress() + ", error message is:" + future.getCause().getMessage(), future.getCause());
62 } else {
63 throw new RemotingException(this, "client(url: " + getUrl() + ") failed to connect to server "
64 + getRemoteAddress() + " client-side timeout "
65 + getConnectTimeout() + "ms (elapsed: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms) from netty client "
66 + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using dubbo version " + Version.getVersion());
67 }
68 } finally {
69 if (!isConnected()) {
70 future.cancel();
71 }
72 }
73 }

还有就是编解码。
后续会做netty4源码阅读计划。
以dubbo使用netty4为通信框架来进行分析。
客户端请求编码总体流程如下:

1 NettyCodecAdapter$InternalEncoder.encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Channel ch, Object msg)
2 -->new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(ByteBuf buffer) // 创建一个buffer
3 -->NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(io.netty.channel.Channel ch, URL url, ChannelHandler handler)
4 -->DubboCountCodec.encode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Object msg)
5 -->ExchangeCodec.encode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Object msg)
6 -->encodeRequest(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Request req)
7 -->getSerialization(Channel channel) //获取Hessian2Serialization序列化实例
8 -->CodecSupport.getSerialization(URL url)
9 -->ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Serialization.class).getExtension(url.getParameter("serialization", "hessian2"))
10 <!-- 构造一个16字节的byte[16] header -->
11 -->byte[] header = new byte[16]
12 -->Bytes.short2bytes(MAGIC, header) //设置前两个字节为魔数[-38, -69, 0, ..., 0]
13 <!-- 第三个字节:表示消息是req,序列化协议ID,twoway/event -->
14 -->header[2] = (byte) (FLAG_REQUEST | serialization.getContentTypeId());
15 if (req.isTwoWay()) header[2] |= FLAG_TWOWAY;
16 if (req.isEvent()) header[2] |= FLAG_EVENT;
17 <!-- 设置第5~12个字节(long是64bit,即8byte):requestID -->
18 -->Bytes.long2bytes(req.getId(), header, 4);
19 <!-- 下面序列化请求体数据 -->
20 -->new Hessian2ObjectOutput(out)
21 -->DubboCodec.encodeRequestData(Channel channel, ObjectOutput out, Object data)
22 -->Bytes.int2bytes(len, header, 12); // 设置第13~16个字节(int是32位,4个字节):消息体长度
23 -->buffer.writeBytes(header); // 将header写入buffer的前16位

总体流程很简单:
- 创建一个buffer
- 创建一个16位的byte[16] header,将魔数、请求标志、序列化协议ID、twoway/event标志、requestID、请求体长度写入header
- 之后序列化请求体,从buffer的第17位向后写入序列化后的请求体字节数组
- 最后,将header中的内容写入buffer的前16位
- 最后发送buffer
首先来看一下netty编解码的入口:com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4:

1 @Override
2 protected void doOpen() throws Throwable {
3 NettyHelper.setNettyLoggerFactory();
4 final NettyClientHandler nettyClientHandler = new NettyClientHandler(getUrl(), this);
5 bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
6 bootstrap.group(nioEventLoopGroup)
7 .option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
8 .option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
9 .option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
10 //.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, getTimeout())
11 .channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
12
13 if (getTimeout() < 3000) {
14 bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 3000);
15 } else {
16 bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, getTimeout());
17 }
18
19 bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
20
21 protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
22 NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyClient.this);
23 ch.pipeline()//.addLast("logging",new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))//for debug
24 .addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder())
25 .addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder())
26 .addLast("handler", nettyClientHandler);
27 }
28 });
29 }

NettyCodecAdapter:

1 final class NettyCodecAdapter {
2 private final ChannelHandler encoder = new InternalEncoder();
3 private final ChannelHandler decoder = new InternalDecoder();
4 private final Codec2 codec;
5 private final URL url;
6 private final com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.ChannelHandler handler;
7
8 public NettyCodecAdapter(Codec2 codec, URL url, com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.ChannelHandler handler) {
9 this.codec = codec;
10 this.url = url;
11 this.handler = handler;
12 }
13
14 public ChannelHandler getEncoder() {
15 return encoder;
16 }
17
18 public ChannelHandler getDecoder() {
19 return decoder;
20 }
21
22 private class InternalEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder {
23 protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
24 com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.buffer.ChannelBuffer buffer = new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(out);
25 Channel ch = ctx.channel();
26 NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ch, url, handler);
27 try {
28 codec.encode(channel, buffer, msg);
29 } finally {
30 NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(ch);
31 }
32 }
33 }
34
35 private class InternalDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
36 protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf input, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
37 ChannelBuffer message = new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(input);
38 NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ctx.channel(), url, handler);
39 Object msg;
40 int saveReaderIndex;
41
42 try {
43 // decode object.
44 do {
45 saveReaderIndex = message.readerIndex();
46 try {
47 msg = codec.decode(channel, message);
48 } catch (IOException e) {
49 throw e;
50 }
51 if (msg == Codec2.DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT) {
52 message.readerIndex(saveReaderIndex);
53 break;
54 } else {
55 //is it possible to go here ?
56 if (saveReaderIndex == message.readerIndex()) {
57 throw new IOException("Decode without read data.");
58 }
59 if (msg != null) {
60 out.add(msg);
61 }
62 }
63 } while (message.readable());
64 } finally {
65 NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(ctx.channel());
66 }
67 }
68 }
69 }

一、创建ChannelBuffer
1 com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.buffer.ChannelBuffer buffer = new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(out);
这里的out是:
1 ByteBuf buffer = SimpleLeakAwareByteBuf
2 -->ByteBuf buf = PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf
NettyBackedChannelBuffer:
1 private ByteBuf buffer;
2
3 public NettyBackedChannelBuffer(ByteBuf buffer) {
4 Assert.notNull(buffer, "buffer == null");
5 this.buffer = buffer;
6 }
最终的buffer:
1 NettyBackedChannelBuffer
2 -->ByteBuf buffer = SimpleLeakAwareByteBuf
3 -->ByteBuf buf = PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf
二、获取NettyChannel
之后从获取io.netty.channel实例,然后包装在NettyChannel中。
1 NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ch, url, handler);

1 private static final ConcurrentMap<Channel, NettyChannel> channelMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<Channel, NettyChannel>();
2 private final Channel channel;
3
4 private NettyChannel(Channel channel, URL url, ChannelHandler handler) {
5 super(url, handler);
6 if (channel == null) {
7 throw new IllegalArgumentException("netty channel == null;");
8 }
9 this.channel = channel;
10 }
11
12 static NettyChannel getOrAddChannel(Channel ch, URL url, ChannelHandler handler) {
13 if (ch == null) {
14 return null;
15 }
16 NettyChannel ret = channelMap.get(ch);
17 if (ret == null) {
18 NettyChannel nettyChannel = new NettyChannel(ch, url, handler);
19 if (ch.isActive()) {
20 ret = channelMap.putIfAbsent(ch, nettyChannel);
21 }
22 if (ret == null) {
23 ret = nettyChannel;
24 }
25 }
26 return ret;
27 }

首先从缓存ConcurrentMap<Channel, NettyChannel> channelMap中获取key=io.netty.channel的NettyChannel,有则返回,没有则新建并返回。
最终获取到的NettyChannel实例如下:
1 -->Channel channel = NioSocketChannel
2 -->ChannelHandler handler = NettyClient
3 -->URL url = dubbo://10.10.10.10:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=demo-consumer&check=false&codec=dubbo&default.client=netty4&default.server=netty4&dubbo=2.0.0&generic=false&heartbeat=60000&interface=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=sayHello&pid=2204®ister.ip=10.10.10.10&remote.timestamp=1514958356359&side=consumer&timeout=6000000×tamp=1514959413199
三、进行编码
1 codec.encode(channel, buffer, msg)
这里的codec是:
1 Codec2 codec =
2 DubboCountCodec
3 -->DubboCodec codec = new DubboCodec()
DubboCountCodec
1 private DubboCodec codec = new DubboCodec();
2
3 public void encode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Object msg) throws IOException {
4 codec.encode(channel, buffer, msg);
5 }
入参:
- channel:上述的NettyChannel对象
- buffer:上述的NettyBackedChannelBuffer对象
- msg:Request对象,其属性如下:

1 long mId = 0
2 String mVersion = "2.0.0"
3 boolean mTwoWay = true
4 boolean mEvent = false
5 boolean mBroken = false
6 Object mData = RpcInvocation对象
7 -->String methodName = "sayHello"
8 -->Class<?>[] parameterTypes = [java.lang.String]
9 -->Object[] arguments = ["world"]
10 -->Map<String, String> attachments = {
11 "path" -> "com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService"
12 "interface" -> "com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService"
13 "version" -> "0.0.0"
14 "timeout" -> "6000000"
15 }
16 -->Invoker<?> invoker = DubboInvoker对象
之后调用DubboCodec.encode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Object msg),该方法位于其父类ExchangeCodec中。

1 public void encode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Object msg) throws IOException {
2 if (msg instanceof Request) {
3 encodeRequest(channel, buffer, (Request) msg);
4 } else if (msg instanceof Response) {
5 encodeResponse(channel, buffer, (Response) msg);
6 } else {
7 super.encode(channel, buffer, msg);
8 }
9 }
10
11 protected void encodeRequest(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Request req) throws IOException {
12 Serialization serialization = getSerialization(channel);
13 // header.
14 byte[] header = new byte[HEADER_LENGTH];
15 // set magic number.
16 Bytes.short2bytes(MAGIC, header);
17
18 // set request and serialization flag.
19 header[2] = (byte) (FLAG_REQUEST | serialization.getContentTypeId());
20
21 if (req.isTwoWay()) header[2] |= FLAG_TWOWAY;
22 if (req.isEvent()) header[2] |= FLAG_EVENT;
23
24 // set request id.
25 Bytes.long2bytes(req.getId(), header, 4);
26
27 // encode request data.
28 int savedWriteIndex = buffer.writerIndex();
29 buffer.writerIndex(savedWriteIndex + HEADER_LENGTH);//设置writerIndex为0+16,先输入请求体的字节
30 ChannelBufferOutputStream bos = new ChannelBufferOutputStream(buffer);
31 ObjectOutput out = serialization.serialize(channel.getUrl(), bos);
32 if (req.isEvent()) {
33 encodeEventData(channel, out, req.getData());
34 } else {
35 encodeRequestData(channel, out, req.getData());
36 }
37 out.flushBuffer();
38 bos.flush();
39 bos.close();
40 int len = bos.writtenBytes();
41 checkPayload(channel, len);
42 Bytes.int2bytes(len, header, 12);
43
44 // write
45 buffer.writerIndex(savedWriteIndex);
46 buffer.writeBytes(header); // write header.
47 buffer.writerIndex(savedWriteIndex + HEADER_LENGTH + len);
48 }

1 首先使用spi获取序列化协议
1 Serialization serialization = getSerialization(channel);
getSerialization位于ExchangeCodec的父类AbstractCodec中。
1 protected Serialization getSerialization(Channel channel) {
2 return CodecSupport.getSerialization(channel.getUrl());
3 }
1 public static Serialization getSerialization(URL url) {
2 return ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Serialization.class).getExtension(
3 url.getParameter("serialization", "hessian2"));
4 }
最终获取到的Serialization serialization = Hessian2Serialization对象:

1 public class Hessian2Serialization implements Serialization {
2 public static final byte ID = 2;
3
4 public byte getContentTypeId() {
5 return ID;
6 }
7
8 public String getContentType() {
9 return "x-application/hessian2";
10 }
11
12 public ObjectOutput serialize(URL url, OutputStream out) throws IOException {
13 return new Hessian2ObjectOutput(out);
14 }
15
16 public ObjectInput deserialize(URL url, InputStream is) throws IOException {
17 return new Hessian2ObjectInput(is);
18 }
19 }

注意:hessian2序列化方式的id是2,该序列化方式ID会写在协议头里传给服务端,服务端根据序列化方式ID获取对应的序列化方式来反序列化请求体。
2 创建16字节header字节数组
1 byte[] header = new byte[16];
然后填充第1~2个字节为魔数;填充第3个字节为requestFlag、序列化方式ID(这里是2)、twowayFlag或eventFlag;填充第5~12个字节为requestID(long==64bit==8byte)

1 // set magic number.
2 Bytes.short2bytes(MAGIC, header);
3
4 // set request and serialization flag.
5 header[2] = (byte) (FLAG_REQUEST | serialization.getContentTypeId());
6
7 if (req.isTwoWay()) header[2] |= FLAG_TWOWAY;
8 if (req.isEvent()) header[2] |= FLAG_EVENT;
9
10 // set request id.
11 Bytes.long2bytes(req.getId(), header, 4);

3 序列化请求体
首先设置buffer的writerIndex:
1 int savedWriteIndex = buffer.writerIndex();
2 buffer.writerIndex(savedWriteIndex + HEADER_LENGTH);//设置writerIndex为0+16,先输入请求体的字节
首先存储了buffer当前的writeIndex(可写位置),从该位置开始到“该位置+15”这一段我们会写入header字节数组(例如,[0,15]),从“该位置+16”开始向后写入请求体字节数组(例如,[16, x))。
然后就是设置buffer的writerIndex为当前位置+16,因为接下来我们要先序列化请求体,然后将请求体写入buffer,最后才会将header写入buffer。
序列化请求体:

1 ChannelBufferOutputStream bos = new ChannelBufferOutputStream(buffer);
2 ObjectOutput out = serialization.serialize(channel.getUrl(), bos);
3 if (req.isEvent()) {
4 encodeEventData(channel, out, req.getData());
5 } else {
6 encodeRequestData(channel, out, req.getData());
7 }
8 out.flushBuffer();
9 bos.flush();
10 bos.close();

首先新建一个ChannelBufferOutputStream对象(该对象继承了java.io.OutputStream抽象类):

1 private final ChannelBuffer buffer;
2 private final int startIndex;
3
4 public ChannelBufferOutputStream(ChannelBuffer buffer) {
5 if (buffer == null) {
6 throw new NullPointerException("buffer");
7 }
8 this.buffer = buffer;
9 startIndex = buffer.writerIndex();
10 }

buffer为上述的NettyBackedChannelBuffer对象;startIndex == 16
然后获取ObjectOutput对象:
1 public ObjectOutput serialize(URL url, OutputStream out) throws IOException {
2 return new Hessian2ObjectOutput(out);
3 }
1 private final Hessian2Output mH2o;
2
3 public Hessian2ObjectOutput(OutputStream os) {
4 mH2o = new Hessian2Output(os);
5 mH2o.setSerializerFactory(Hessian2SerializerFactory.SERIALIZER_FACTORY);
6 }

1 public final static int SIZE = 4096;
2 private final byte[] _buffer = new byte[SIZE];
3 protected OutputStream _os;
4
5 public Hessian2Output(OutputStream os) {
6 _os = os;
7 }

最终得到的ObjectOutput对象:
1 Hessian2ObjectOutput
2 -->Hessian2Output mH2o
3 -->byte[] _buffer = new byte[4096]
4 -->OutputStream _os = 上述的ChannelBufferOutputStream对象
5 -->SerializerFactory _serializerFactory = Hessian2SerializerFactory实例
最后执行DubboCodec.encodeRequestData(Channel channel, ObjectOutput out, Object data),该方法是真正的进行请求体序列化的地方。

1 @Override
2 protected void encodeRequestData(Channel channel, ObjectOutput out, Object data) throws IOException {
3 RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) data;
4
5 out.writeUTF(inv.getAttachment(Constants.DUBBO_VERSION_KEY, DUBBO_VERSION));
6 out.writeUTF(inv.getAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY));
7 out.writeUTF(inv.getAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY));
8
9 out.writeUTF(inv.getMethodName());
10 out.writeUTF(ReflectUtils.getDesc(inv.getParameterTypes()));
11 Object[] args = inv.getArguments();
12 if (args != null)
13 for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
14 out.writeObject(encodeInvocationArgument(channel, inv, i));
15 }
16 out.writeObject(inv.getAttachments());
17 }

其中,channel是上述的NettyChannel实例;out是上述的Hessian2ObjectOutput实例;data是Request对象中的data属性

1 Object mData = RpcInvocation对象
2 -->String methodName = "sayHello"
3 -->Class<?>[] parameterTypes = [java.lang.String]
4 -->Object[] arguments = ["world"]
5 -->Map<String, String> attachments = {
6 "path" -> "com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService"
7 "interface" -> "com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService"
8 "version" -> "0.0.0"
9 "timeout" -> "6000000"
10 }
11 -->Invoker<?> invoker = DubboInvoker对象

从DubboCodec.encodeRequestData方法中,我们可以看到只会序列化Request请求体中的RpcInvocation对象的:
- methodName:方法名
- parameterTypes:参数类型
- arguments:参数值
- attachments:附加参数
其中附加参数中的"dubbo"、"path"、"version"还会单独使用out.writeUTF进行序列化。
首先来看一下:
1 Hessian2ObjectOutput.writeUTF(String v)
2 -->Hessian2Output.writeString(String value)
3 -->printString(String v, int strOffset, int length)
通过这个方法,我们将传入的v存储在ObjectOutput对象的byte[] _buffer = new byte[4096]数组中。

1 Hessian2Output:
2 /**
3 * Writes any object to the output stream.
4 */
5 public void writeObject(Object object)
6 throws IOException {
7 if (object == null) {
8 writeNull();
9 return;
10 }
11
12 Serializer serializer = findSerializerFactory().getSerializer(object.getClass());
13 serializer.writeObject(object, this);
14 }
15
16 public final SerializerFactory findSerializerFactory() {
17 SerializerFactory factory = _serializerFactory;
18 if (factory == null)
19 _serializerFactory = factory = new SerializerFactory();
20 return factory;
21 }
22
23 SerializerFactory:
24 private static HashMap _staticSerializerMap;
25 private HashMap _cachedSerializerMap;
26 /**
27 * Returns the serializer for a class.
28 * @param cl the class of the object that needs to be serialized.
29 * @return a serializer object for the serialization.
30 */
31 public Serializer getSerializer(Class cl)
32 throws HessianProtocolException {
33 Serializer serializer;
34
35 serializer = (Serializer) _staticSerializerMap.get(cl);
36 if (serializer != null)
37 return serializer;
38
39 if (_cachedSerializerMap != null) {
40 synchronized (_cachedSerializerMap) {
41 serializer = (Serializer) _cachedSerializerMap.get(cl);
42 }
43
44 if (serializer != null)
45 return serializer;
46 }
47
48 ......
49
50 if (serializer != null) {
51
52 }
53 .......
54 else if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(cl)) {
55 if (_mapSerializer == null)
56 _mapSerializer = new MapSerializer();
57
58 serializer = _mapSerializer;
59 }
60 ......
61 if (serializer == null)
62 serializer = getDefaultSerializer(cl);
63
64 if (_cachedSerializerMap == null)
65 _cachedSerializerMap = new HashMap(8);
66
67 synchronized (_cachedSerializerMap) {
68 _cachedSerializerMap.put(cl, serializer);
69 }
70
71 return serializer;
72 }

out.writeObject(Object object):
首先获取_serializerFactory工厂,这里是Hessian2SerializerFactory实例。其getSerializer(Class cl)方法位于其父类SerializerFactory中:获取序列化器的逻辑是:首先从_staticSerializerMap中获取相关类型的序列化器(_staticSerializerMap中启动时就缓存好一堆类型的序列化器:具体见com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.SerializerFactory),如果有返回,否则从_cachedSerializerMap缓存中获取相关的类加载器,如果没有,根据类型先创建序列化器(new MapSerializer(),当然还有getDefaultSerializer(cl)来兜底),最后放入缓存_cachedSerializerMap中。最后返回创建好的类加载器。
最后调用MapSerializer.writeObject(Object obj, AbstractHessianOutput out)进行序列化。
DubboCodec.encodeRequestData执行完毕之后,我们将所有的信息写入了ObjectOutput对象的byte[] _buffer = new byte[4096]数组中。
注意:
- 如果在将数据写入到_buffer的过程中,字节量超出了4096,会先执行一把Hessian2ObjectOutput.flushBuffer()将_buffer中的数据拷贝到PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf中,之后再往_buffer中写入字节
最后执行Hessian2ObjectOutput.flushBuffer()

1 Hessian2ObjectOutput
2 public void flushBuffer() throws IOException {
3 mH2o.flushBuffer();
4 }
5
6 Hessian2Output
7 public final void flushBuffer()
8 throws IOException {
9 int offset = _offset;
10
11 if (!_isStreaming && offset > 0) {
12 _offset = 0;
13 _os.write(_buffer, 0, offset);
14 } else if (_isStreaming && offset > 3) {
15 int len = offset - 3;
16 _buffer[0] = 'p';
17 _buffer[1] = (byte) (len >> 8);
18 _buffer[2] = (byte) len;
19 _offset = 3;
20 _os.write(_buffer, 0, offset);
21 }
22 }

此处执行ChannelBufferOutputStream.write(byte[] b, int off, int len)

1 @Override
2 public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {
3 if (len == 0) {
4 return;
5 }
6 buffer.writeBytes(b, off, len);
7 }


1 ChannelBuffer:
2 /**
3 * Transfers the specified source array's data to this buffer starting at
4 * the current {@code writerIndex} and increases the {@code writerIndex} by
5 * the number of the transferred bytes (= {@code length}).
6 *
7 * @param index the first index of the source
8 * @param length the number of bytes to transfer
9 */
10 void writeBytes(byte[] src, int index, int length);

就是将ObjectOutput对象的byte[] _buffer = new byte[4096]数组中的数据转移到buf中。(具体方法见:unsafe.copyMemory(Object srcBase, long srcOffset, Object destBase, long destOffset,long bytes))
1 NettyBackedChannelBuffer
2 -->ByteBuf buffer = SimpleLeakAwareByteBuf
3 -->ByteBuf buf = PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf
4 将header写入buffer

1 int len = bos.writtenBytes();//计算请求体长度
2 checkPayload(channel, len);
3 Bytes.int2bytes(len, header, 12);//将请求体长度写入header的第13~16个字节(int=4byte)
4
5 // write
6 buffer.writerIndex(savedWriteIndex);//设置buffer的writerIndex为该次写入的开始位置
7 buffer.writeBytes(header); // 将header数组写入buffer
8 buffer.writerIndex(savedWriteIndex + HEADER_LENGTH + len);//设置buffer的writerIndex,为下一次写入做准备

到此为止,整个编码就结束了。之后存储了<header><body>数据的ByteBuf由netty自己来进行网络传输。
来看一下请求编码的byte[] header的最终结构:
- 1~2 byte:魔数
- 3 byte:requestFlag、序列化方式ID、twowayFlag或eventFlag
- 5~12 byte :requestID
- 13~16:请求体长度
这里有一个小插曲:

1 protected static void checkPayload(Channel channel, long size) throws IOException {
2 int payload = Constants.DEFAULT_PAYLOAD;
3 if (channel != null && channel.getUrl() != null) {
4 payload = channel.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.PAYLOAD_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_PAYLOAD);//8M
5 }
6 if (payload > 0 && size > payload) {
7 ExceedPayloadLimitException e = new ExceedPayloadLimitException("Data length too large: " + size + ", max payload: " + payload + ", channel: " + channel);
8 logger.error(e);
9 throw e;
10 }
11 }

dubbo限制了如果传输的请求体长度大于8M,将会直接抛出异常。
服务端请求解码总体流程:

1 NettyCodecAdapter$InternalDecoder.decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf input, List<Object> out)
2 -->new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(ByteBuf buffer) // 创建一个buffer
3 -->NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(io.netty.channel.Channel ch, URL url, ChannelHandler handler)
4 -->DubboCountCodec.decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer)
5 -->ExchangeCodec.decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer)
6 -->buffer.readBytes(header); //读取header byte[]
7 -->decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, int readable, byte[] header)
8 -->检查魔数、检查总长度是否大于等于16
9 -->获取请求体长度
10 -->new ChannelBufferInputStream(buffer, len)
11 -->DubboCodec.decodeBody(Channel channel, InputStream is, byte[] header)
12 -->CodecSupport.getSerialization(URL url, Byte id) //解析出请求头header[2]中的序列化ID,根据该ID获取与请求编码相同的序列化协议
13 -->Bytes.bytes2long(header, 4) //获取requestID
14 <!-- 之后创建一个新的Request对象,将requestID及后续解析出来的各种request属性塞入该对象中 -->
15 -->new DecodeableRpcInvocation(channel, req, is, proto)
16 -->DecodeableRpcInvocation.decode()
17 -->decode(Channel channel, InputStream input) //解析请求体参数并将其构造为一个DecodeableRpcInvocation,最终塞到Request对象的data属性中
18 -->new Hessian2ObjectInput(InputStream is)
19 -->反序列化:in.readObject()

总体流程:
- 包装请求传过来的ByteBuf为NettyBackedChannelBuffer(简称buffer)
- 从buffer中读取header
- 之后检查魔数、检查header+请求体body总长度是否大于等于16
- 获取请求体body长度
- 解析出请求头header[2]中的序列化ID,根据该ID获取与请求编码相同的序列化协议
- 获取requestID
- 创建Request对象,将requestID及后续解析出来的各种request属性塞入该对象中
- 反序列化请求体body,并将其设在DecodeableRpcInvocation中,最后该对象设在Request对象的data属性中
解码还是在NettyCodecAdapter中:

1 private class InternalDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
2 protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf input, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
3 //获取ChannelBuffer
4 ChannelBuffer message = new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(input);
5 //获取NettyChannel
6 NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ctx.channel(), url, handler);
7 Object msg;
8 int saveReaderIndex;
9
10 try {
11 do {
12 saveReaderIndex = message.readerIndex();
13 try {
14 //解码message
15 msg = codec.decode(channel, message);
16 } catch (IOException e) {
17 throw e;
18 }
19 // 如果接收到的消息发生了拆包,则仅仅设置message的readerIndex为当前的saveReaderIndex
20 if (msg == Codec2.DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT) {
21 message.readerIndex(saveReaderIndex);
22 break;
23 } else {
24 //is it possible to go here ?(没有读到任何数据)
25 if (saveReaderIndex == message.readerIndex()) {
26 throw new IOException("Decode without read data.");
27 }
28 // 如果读到了正常的消息,写入List<Object> out
29 if (msg != null) {
30 out.add(msg);
31 }
32 }
33 } while (message.readable());
34 } finally {
35 NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(ctx.channel());
36 }
37 }
38 }

一、创建ChannelBuffer
1 ChannelBuffer message = new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(input);
与客户端请求编码类似,最终的得到的message:
1 NettyBackedChannelBuffer
2 -->ByteBuf buffer = SimpleLeakAwareByteBuf
3 -->ByteBuf buf = PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf
二、获取NettyChannel
之后从获取io.netty.channel实例,然后包装在NettyChannel中。
1 NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ctx.channel(), url, handler);
与服务端请求解码类似,最终的得到的channel:
1 -->Channel channel = NioSocketChannel
2 -->ChannelHandler handler = NettyServer
3 -->URL url =dubbo://10.10.10.10:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=demo-provider&bind.ip=10.10.10.10&bind.port=20880&channel.readonly.sent=true&codec=dubbo&default.server=netty4&dubbo=2.0.0&generic=false&heartbeat=60000&interface=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=sayHello&pid=7294&side=provider×tamp=1515031737563
三、进行解码
这里的codec是:
1 Codec2 codec =
2 DubboCountCodec
3 -->DubboCodec codec = new DubboCodec()
DubboCountCodec:

1 public Object decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer) throws IOException {
2 int save = buffer.readerIndex();
3 MultiMessage result = MultiMessage.create();
4 do {
5 Object obj = codec.decode(channel, buffer);
6 if (Codec2.DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT == obj) {// 如果发生了拆包,则跳出,在下一次依旧从save处读取
7 buffer.readerIndex(save);
8 break;
9 } else {
10 result.addMessage(obj);// 如果消息正常,添加消息到MultiMessage的List messages中
11 logMessageLength(obj, buffer.readerIndex() - save);
12 save = buffer.readerIndex();
13 }
14 } while (true);
15 if (result.isEmpty()) {
16 return Codec2.DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT;
17 }
18 if (result.size() == 1) {
19 return result.get(0);
20 }
21 return result;
22 }

MultiMessage:
1 private final List messages = new ArrayList();
2
3 public void addMessage(Object msg) {
4 messages.add(msg);
5 }
DubboCodec的父类ExchangeCodec:
1 public Object decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer) throws IOException {
2 int readable = buffer.readableBytes();// 获取buffer所有的可读字节(header + body)
3 byte[] header = new byte[Math.min(readable, HEADER_LENGTH)];
4 buffer.readBytes(header);// 将buffer中的前16个字节读入header
5 return decode(channel, buffer, readable, header);// 反序列化请求体body,构造成DecodeableRpcResult,塞入Request的data属性中
6 }

1 protected Object decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, int readable, byte[] header) throws IOException {
2 // check magic number.
3 if (readable > 0 && header[0] != MAGIC_HIGH
4 || readable > 1 && header[1] != MAGIC_LOW) {//魔数不匹配
5 int length = header.length;
6 if (header.length < readable) {
7 header = Bytes.copyOf(header, readable);
8 buffer.readBytes(header, length, readable - length);
9 }
10 for (int i = 1; i < header.length - 1; i++) {
11 if (header[i] == MAGIC_HIGH && header[i + 1] == MAGIC_LOW) {
12 buffer.readerIndex(buffer.readerIndex() - header.length + i);
13 header = Bytes.copyOf(header, i);
14 break;
15 }
16 }
17 return super.decode(channel, buffer, readable, header);
18 }
19 // check length.
20 if (readable < HEADER_LENGTH) {//header+body的总可读数据<16
21 return DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT;
22 }
23
24 // 从header中获取body长度
25 int len = Bytes.bytes2int(header, 12);
26 checkPayload(channel, len);//检测body是否超8M了
27
28 int tt = len + HEADER_LENGTH;
29 if (readable < tt) {// 如果当前可读的消息<header+body总长度(说明发生了拆包)
30 return DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT;
31 }
32
33 // limit input stream.
34 ChannelBufferInputStream is = new ChannelBufferInputStream(buffer, len);
35
36 try {
37 return decodeBody(channel, is, header);//解码body
38 } finally {
39 if (is.available() > 0) {
40 try {
41 if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
42 logger.warn("Skip input stream " + is.available());
43 }
44 StreamUtils.skipUnusedStream(is);
45 } catch (IOException e) {
46 logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
47 }
48 }
49 }
50 }

DubboCodec:

1 protected Object decodeBody(Channel channel, InputStream is, byte[] header) throws IOException {
2 byte flag = header[2], proto = (byte) (flag & SERIALIZATION_MASK);// proto:序列化方式ID
3 Serialization s = CodecSupport.getSerialization(channel.getUrl(), proto);// 根据序列化方式ID获取序列化方式
4 // get request id.
5 long id = Bytes.bytes2long(header, 4);// 获取reqID
6 if ((flag & FLAG_REQUEST) == 0) {
7 ......
8 return res;
9 } else {
10 // decode request.
11 Request req = new Request(id);
12 req.setVersion("2.0.0");
13 req.setTwoWay((flag & FLAG_TWOWAY) != 0);
14 if ((flag & FLAG_EVENT) != 0) {
15 req.setEvent(Request.HEARTBEAT_EVENT);
16 }
17 try {
18 Object data;
19 if (req.isHeartbeat()) {
20 data = decodeHeartbeatData(channel, deserialize(s, channel.getUrl(), is));
21 } else if (req.isEvent()) {
22 data = decodeEventData(channel, deserialize(s, channel.getUrl(), is));
23 } else {
24 DecodeableRpcInvocation inv;
25 if (channel.getUrl().getParameter(
26 Constants.DECODE_IN_IO_THREAD_KEY,
27 Constants.DEFAULT_DECODE_IN_IO_THREAD)) {
28 inv = new DecodeableRpcInvocation(channel, req, is, proto);
29 inv.decode();// 解码请求体
30 } else {
31 inv = new DecodeableRpcInvocation(channel, req,
32 new UnsafeByteArrayInputStream(readMessageData(is)), proto);
33 }
34 data = inv;
35 }
36 req.setData(data);
37 } catch (Throwable t) {
38 if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
39 log.warn("Decode request failed: " + t.getMessage(), t);
40 }
41 // bad request
42 req.setBroken(true);
43 req.setData(t);
44 }
45 return req;
46 }
47 }

就是构造Request参数,重点构造其中的data属性(实际上是一个DecodeableRpcInvocation实例)
DecodeableRpcInvocation:

1 public void decode() throws Exception {
2 if (!hasDecoded && channel != null && inputStream != null) {
3 try {
4 decode(channel, inputStream);
5 } catch (Throwable e) {
6 if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
7 log.warn("Decode rpc invocation failed: " + e.getMessage(), e);
8 }
9 request.setBroken(true);
10 request.setData(e);
11 } finally {
12 hasDecoded = true;
13 }
14 }
15 }


1 public Object decode(Channel channel, InputStream input) throws IOException {
2 ObjectInput in = CodecSupport.getSerialization(channel.getUrl(), serializationType)
3 .deserialize(channel.getUrl(), input);// 创建Hessian2ObjectInput
4 //下边的读取顺序与序列化时的必须一模一样(我们反序列化"dubbo"=2.0.0时,offset=0, 反序列化"path"=xxx时,offset=6)
5 setAttachment(Constants.DUBBO_VERSION_KEY, in.readUTF());
6 setAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY, in.readUTF());
7 setAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY, in.readUTF());
8
9 setMethodName(in.readUTF());
10 try {
11 Object[] args;
12 Class<?>[] pts;
13 String desc = in.readUTF();
14 if (desc.length() == 0) {
15 pts = DubboCodec.EMPTY_CLASS_ARRAY;
16 args = DubboCodec.EMPTY_OBJECT_ARRAY;
17 } else {
18 pts = ReflectUtils.desc2classArray(desc);
19 args = new Object[pts.length];
20 for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
21 try {
22 args[i] = in.readObject(pts[i]);
23 } catch (Exception e) {
24 if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
25 log.warn("Decode argument failed: " + e.getMessage(), e);
26 }
27 }
28 }
29 }
30 setParameterTypes(pts);
31
32 Map<String, String> map = (Map<String, String>) in.readObject(Map.class);
33 if (map != null && map.size() > 0) {
34 Map<String, String> attachment = getAttachments();
35 if (attachment == null) {
36 attachment = new HashMap<String, String>();
37 }
38 attachment.putAll(map);
39 setAttachments(attachment);
40 }
41 //decode argument ,may be callback
42 for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
43 args[i] = decodeInvocationArgument(channel, this, pts, i, args[i]);
44 }
45
46 setArguments(args);
47
48 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
49 throw new IOException(StringUtils.toString("Read invocation data failed.", e));
50 }
51 return this;
52 }

上述的setXXX方法,实际上就是为当前的DecodeableRpcInvocation设置各种属性,in.readUTF()和in.readobject都是反序列化的方法,前者将byte[]反序列化为String,后者将byte[]反序列化为Object。
到此为止,服务端请求解码就结束了。
服务端响应编码总体流程:

1 NettyCodecAdapter$InternalEncoder.encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ByteBuf out)
2 -->new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(ByteBuf buffer) // 创建一个buffer
3 -->NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(io.netty.channel.Channel ch, URL url, ChannelHandler handler)
4 -->DubboCountCodec.encode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Object msg)
5 -->ExchangeCodec.encode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Object msg)
6 -->encodeResponse(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Response res)
7 -->getSerialization(Channel channel) //获取Hessian2Serialization序列化实例
8 -->CodecSupport.getSerialization(URL url)
9 -->ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Serialization.class).getExtension(url.getParameter("serialization", "hessian2"))
10 <!-- 构造一个16字节的byte[16] header -->
11 -->byte[] header = new byte[16]
12 -->Bytes.short2bytes(MAGIC, header) //设置前两个字节为魔数[-38, -69, 0, ..., 0]
13 <!-- 第三个字节:序列化协议ID,如果响应是心跳,添加eventFlag -->
14 -->header[2] = serialization.getContentTypeId();
15 if (res.isHeartbeat()) header[2] |= FLAG_EVENT;
16 <!-- 第四个字节:响应状态 -->
17 -->header[3] = res.getStatus();
18 <!-- 设置第5~12个字节(long是64bit,即8byte):respID == requestID -->
19 -->Bytes.long2bytes(res.getId(), header, 4);
20 <!-- 下面序列化响应体数据 -->
21 -->new Hessian2ObjectOutput(out)
22 -->DubboCodec.encodeResponseData(Channel channel, ObjectOutput out, Object data)
23 -->Bytes.int2bytes(len, header, 12); // 设置第13~16个字节(int是32位,4个字节):消息体长度
24 -->buffer.writeBytes(header); // 将header写入buffer的前16位

与 12.1 客户端请求编码 极其相似。
注意:响应编码中DubboCodec

1 @Override
2 protected void encodeResponseData(Channel channel, ObjectOutput out, Object data) throws IOException {
3 Result result = (Result) data;
4
5 Throwable th = result.getException();
6 if (th == null) {
7 Object ret = result.getValue();
8 if (ret == null) {
9 out.writeByte(RESPONSE_NULL_VALUE);
10 } else {
11 out.writeByte(RESPONSE_VALUE);
12 out.writeObject(ret);
13 }
14 } else {
15 out.writeByte(RESPONSE_WITH_EXCEPTION);
16 out.writeObject(th);
17 }
18 }

注意:out.writeByte(RESPONSE_VALUE);写入这个响应类型,是为了将来客户端响应解码用的,具体见 12.4 客户端响应解码
请求编码的byte[] header的最终结构:
- 1~2 byte:魔数
- 3 byte:requestFlag、序列化方式ID、twowayFlag或eventFlag
- 5~12 byte :requestID
- 13~16:请求体长度
响应编码的byte[] header的最终结构:
- 1~2 byte:魔数
- 3 byte:序列化方式ID、eventFlag(如果响应信息是心跳信息,添加eventFlag)
- 4 byte:响应状态,20代表成功
- 5~12 byte :reponseID(实际上==requestID)
- 13~16:响应体长度
客户端响应解码整体流程:

1 NettyCodecAdapter$InternalDecoder.decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf input, List<Object> out)
2 -->new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(ByteBuf buffer) // 创建一个buffer
3 -->NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(io.netty.channel.Channel ch, URL url, ChannelHandler handler)
4 -->DubboCountCodec.decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer)
5 -->ExchangeCodec.decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer)
6 -->buffer.readBytes(header); //读取header byte[]
7 -->decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, int readable, byte[] header)
8 -->检查魔数、检查总长度是否大于等于16
9 -->获取请求体长度
10 -->new ChannelBufferInputStream(buffer, len)
11 -->DubboCodec.decodeBody(Channel channel, InputStream is, byte[] header)
12 -->CodecSupport.getSerialization(URL url, Byte id) //解析出请求头header[2]中的序列化ID,根据该ID获取与请求编码相同的序列化协议
13 -->Bytes.bytes2long(header, 4) //获取respID
14 <!-- 之后创建一个新的Response对象,将respID及后续解析出来的各种resp属性塞入该对象中 -->
15 -->new DecodeableRpcResult(Channel channel, Response response, InputStream is, Invocation invocation, byte id)
16 -->DecodeableRpcResult.decode()
17 -->decode(Channel channel, InputStream input) //解析请求体参数并将其构造为一个DecodeableRpcResult,最终塞到Request对象的data属性中
18 -->new Hessian2ObjectInput(InputStream is)
19 -->反序列化:in.readObject()

与 12.2 服务端请求解码 极其相似。
不同的地方是:

1 protected Object decodeBody(Channel channel, InputStream is, byte[] header) throws IOException {
2 byte flag = header[2], proto = (byte) (flag & SERIALIZATION_MASK);
3 Serialization s = CodecSupport.getSerialization(channel.getUrl(), proto);
4 // get request id.
5 long id = Bytes.bytes2long(header, 4);
6 if ((flag & FLAG_REQUEST) == 0) {// 解码服务端的响应
7 // decode response.
8 Response res = new Response(id);
9 if ((flag & FLAG_EVENT) != 0) {
10 res.setEvent(Response.HEARTBEAT_EVENT);
11 }
12 // get status.
13 byte status = header[3];
14 res.setStatus(status);
15 if (status == Response.OK) {
16 try {
17 Object data;
18 if (res.isHeartbeat()) {
19 data = decodeHeartbeatData(channel, deserialize(s, channel.getUrl(), is));
20 } else if (res.isEvent()) {
21 data = decodeEventData(channel, deserialize(s, channel.getUrl(), is));
22 } else {
23 DecodeableRpcResult result;
24 if (channel.getUrl().getParameter(
25 Constants.DECODE_IN_IO_THREAD_KEY,
26 Constants.DEFAULT_DECODE_IN_IO_THREAD)) {
27 result = new DecodeableRpcResult(channel, res, is,
28 (Invocation) getRequestData(id), proto);
29 result.decode();
30 } else {
31 result = new DecodeableRpcResult(channel, res,
32 new UnsafeByteArrayInputStream(readMessageData(is)),
33 (Invocation) getRequestData(id), proto);
34 }
35 data = result;
36 }
37 res.setResult(data);
38 } catch (Throwable t) {
39 if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
40 log.warn("Decode response failed: " + t.getMessage(), t);
41 }
42 res.setStatus(Response.CLIENT_ERROR);
43 res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(t));
44 }
45 } else {
46 res.setErrorMessage(deserialize(s, channel.getUrl(), is).readUTF());
47 }
48 return res;
49 } else { // 解码客户端的请求
50 // decode request.
51 Request req = new Request(id);
52 req.setVersion("2.0.0");
53 req.setTwoWay((flag & FLAG_TWOWAY) != 0);
54 if ((flag & FLAG_EVENT) != 0) {
55 req.setEvent(Request.HEARTBEAT_EVENT);
56 }
57 try {
58 Object data;
59 if (req.isHeartbeat()) {
60 data = decodeHeartbeatData(channel, deserialize(s, channel.getUrl(), is));
61 } else if (req.isEvent()) {
62 data = decodeEventData(channel, deserialize(s, channel.getUrl(), is));
63 } else {
64 DecodeableRpcInvocation inv;
65 if (channel.getUrl().getParameter(
66 Constants.DECODE_IN_IO_THREAD_KEY,
67 Constants.DEFAULT_DECODE_IN_IO_THREAD)) {
68 inv = new DecodeableRpcInvocation(channel, req, is, proto);
69 inv.decode();
70 } else {
71 inv = new DecodeableRpcInvocation(channel, req,
72 new UnsafeByteArrayInputStream(readMessageData(is)), proto);
73 }
74 data = inv;
75 }
76 req.setData(data);
77 } catch (Throwable t) {
78 if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
79 log.warn("Decode request failed: " + t.getMessage(), t);
80 }
81 // bad request
82 req.setBroken(true);
83 req.setData(t);
84 }
85 return req;
86 }
87 }
88
89 private ObjectInput deserialize(Serialization serialization, URL url, InputStream is)
90 throws IOException {
91 return serialization.deserialize(url, is);
92 }
93
94 private byte[] readMessageData(InputStream is) throws IOException {
95 if (is.available() > 0) {
96 byte[] result = new byte[is.available()];
97 is.read(result);
98 return result;
99 }
100 return new byte[]{};
101 }

DecodeableRpcResult:

1 public Object decode(Channel channel, InputStream input) throws IOException {
2 ObjectInput in = CodecSupport.getSerialization(channel.getUrl(), serializationType)
3 .deserialize(channel.getUrl(), input);
4
5 byte flag = in.readByte();
6 switch (flag) {
7 case DubboCodec.RESPONSE_NULL_VALUE:
8 break;
9 case DubboCodec.RESPONSE_VALUE://这个值是响应编码是编码进来的,用来表示响应的返回类型
10 try {
11 Type[] returnType = RpcUtils.getReturnTypes(invocation);
12 setValue(returnType == null || returnType.length == 0 ? in.readObject() :
13 (returnType.length == 1 ? in.readObject((Class<?>) returnType[0])
14 : in.readObject((Class<?>) returnType[0], returnType[1])));
15 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
16 throw new IOException(StringUtils.toString("Read response data failed.", e));
17 }
18 break;
19 case DubboCodec.RESPONSE_WITH_EXCEPTION:
20 try {
21 Object obj = in.readObject();
22 if (obj instanceof Throwable == false)
23 throw new IOException("Response data error, expect Throwable, but get " + obj);
24 setException((Throwable) obj);
25 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
26 throw new IOException(StringUtils.toString("Read response data failed.", e));
27 }
28 break;
29 default:
30 throw new IOException("Unknown result flag, expect '0' '1' '2', get " + flag);
31 }
32 return this;
33 }

setValue:设置DecodeableRpcResult的Object result属性。
响应解码结束。
第五章 dubbo源码解析目录的更多相关文章
- 第零章 dubbo源码解析目录
第一章 第一个dubbo项目 第二章 dubbo内核之spi源码解析 2.1 jdk-spi的实现原理 2.2 dubbo-spi源码解析 第三章 dubbo内核之ioc源码解析 第四章 dubb ...
- 第五章 HashMap源码解析
5.1.对于HashMap需要掌握以下几点 Map的创建:HashMap() 往Map中添加键值对:即put(Object key, Object value)方法 获取Map中的单个对象:即get( ...
- 第五章 ReentrantLock源码解析1--获得非公平锁与公平锁lock()
最常用的方式: int a = 12; //注意:通常情况下,这个会设置成一个类变量,比如说Segement中的段锁与copyOnWriteArrayList中的全局锁 final Reentrant ...
- 第六章 ReentrantLock源码解析2--释放锁unlock()
最常用的方式: int a = 12; //注意:通常情况下,这个会设置成一个类变量,比如说Segement中的段锁与copyOnWriteArrayList中的全局锁 final Reentrant ...
- dubbo源码解析五 --- 集群容错架构设计与原理分析
欢迎来我的 Star Followers 后期后继续更新Dubbo别的文章 Dubbo 源码分析系列之一环境搭建 博客园 Dubbo 入门之二 --- 项目结构解析 博客园 Dubbo 源码分析系列之 ...
- dubbo源码解析-spi(一)
前言 虽然标题是dubbo源码解析,但是本篇并不会出现dubbo的源码,本篇和之前的dubbo源码解析-简单原理.与spring融合一样,为dubbo源码解析专题的知识预热篇. 插播面试题 你是否了解 ...
- Dubbo 源码解析四 —— 负载均衡LoadBalance
欢迎来我的 Star Followers 后期后继续更新Dubbo别的文章 Dubbo 源码分析系列之一环境搭建 Dubbo 入门之二 --- 项目结构解析 Dubbo 源码分析系列之三 -- 架构原 ...
- dubbo源码解析-spi(4)
前言 本篇是spi的第四篇,本篇讲解的是spi中增加的AOP,还是和上一篇一样,我们先从大家熟悉的spring引出AOP. AOP是老生常谈的话题了,思想都不会是一蹴而就的.比如架构设计从All in ...
- dubbo源码解析-spi(3)
前言 在上一篇的末尾,我们提到了dubbo的spi中增加了IoC和AOP的功能.那么本篇就讲一下这个增加的IoC,spi部分预计会有四篇,因为这东西实在是太重要了.温故而知新,我们先来回顾一下,我们之 ...
- 第十四章 Executors源码解析
前边两章介绍了基础线程池ThreadPoolExecutor的使用方式.工作机理.参数详细介绍以及核心源码解析. 具体的介绍请参照: 第十二章 ThreadPoolExecutor使用与工作机理 第十 ...
随机推荐
- MySQL,你只需看这一篇文章就够了!
MySQL--DAY02 distinct 去重 把查询结果去除重复记录[distinct] 注意:原表数据不会被修改,只是查询结果去重. 去重需要使用一个关键字:distinct mysql> ...
- Docker制作私有镜像仓库
构建私有仓库 启动Docker Registry,使用Docker官方提供的Registry镜像就可以搭建本地私有镜像仓库,具体指令如下. docker run -d -p 5000:5000 --r ...
- 精选2款C#/.NET开源且功能强大的网络通信框架
前言 今天大姚给分享2个C#/.NET开源且功能强大的网络通信框架,希望可以帮助到有需要的同学. NetCoreServer NetCoreServer是一个.NET开源.免费(MIT License ...
- floyd 算法——P1119 灾后重建
floyd 算法 是图论中较为简单的最短路算法,但在某些方面远超最短路范围. 算法思路 定义 \(f[x][y]\) 为 \(x\) 到 \(y\) 节点的最短路径. 初始化:若存在边 \((x,y) ...
- Spring AOP实现原理与CGLIB应用
AOP(Aspect Orient Programming),也就是面向方面编程,作为面向对象编程的一种补充,专门用于处理系统中分布于各个模块(不同方法)中的交叉关注点的问题,在 Java EE 应用 ...
- Winform解决跨线程更新UI的问题
最近又拿起了Winform的程序,由于要起socket server,所以需要起线程,这里就遇到了经典的跨线程UI调用的问题. 如果什么都不写,直接由线程更新UI,会报错:线程间操作无效. 这里的解决 ...
- javase学习文档
javase学习文档(更新) javase 学习文档已更新 查看地址:https://lib.stazxr.cn/codenotes/java/javase/
- 小程序 + node koa2 session存储验证码碰到最大的坑,(喜极而泣 /狗头)
问题:session存验证码.本地拿postman测试了半天,都没有问题. 但到了小程序,服务端再获取(ctx.session.verifyCode)就一直提示不存在.undefined 小程序会 ...
- Python 和 Podman
1. Windows 10 上安装 Python 开始在 Windows 上使用 Python(初学者) 2. 使用 pip Python 的 Microsoft Store 安装包括 pip(标准包 ...
- drf知识点
目录 drf知识点 1.web应用模式.API接口.接口测试工具postman.restful规范 2.序列化与反序列化的概念.基于django原生编写5个接口.drf介绍和快速使用.cbv源码分析 ...
