【Zookeeper】源码分析之Watcher机制(三)之Zookeeper
一、前言
前面已经分析了Watcher机制中的大多数类,本篇对于ZKWatchManager的外部类Zookeeper进行分析。
二、ZooKeeper源码分析
2.1 类的内部类
ZooKeeper的内部类框架图如下图所示
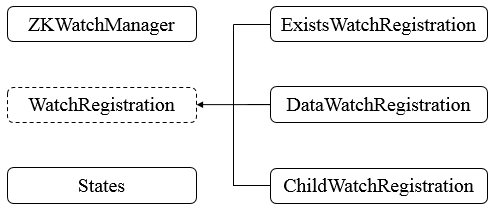
说明:
· ZKWatchManager,Zookeeper的Watcher管理者,其源码在之前已经分析过,不再累赘。
· WatchRegistration,抽象类,用作watch注册。
· ExistsWatchRegistration,存在性watch注册。
· DataWatchRegistration,数据watch注册。
· ChildWatchRegistration,子节点注册。
· States,枚举类型,表示服务器的状态。
1. WatchRegistration
接口类型,表示对路径注册监听。
abstract class WatchRegistration {
// Watcher
private Watcher watcher;
// 客户端路径
private String clientPath;
// 构造函数
public WatchRegistration(Watcher watcher, String clientPath)
{
this.watcher = watcher;
this.clientPath = clientPath;
}
// 获取路径到Watchers集合的键值对,由子类实现
abstract protected Map<String, Set<Watcher>> getWatches(int rc);
/**
* Register the watcher with the set of watches on path.
* @param rc the result code of the operation that attempted to
* add the watch on the path.
*/
// 注册
public void register(int rc) {
if (shouldAddWatch(rc)) { // 应该添加监听
// 获取路径到Watchers集合的键值对,工厂模式
Map<String, Set<Watcher>> watches = getWatches(rc);
synchronized(watches) { // 同步块
// 通过路径获取watcher集合
Set<Watcher> watchers = watches.get(clientPath);
if (watchers == null) { // watcher集合为空
// 新生成集合
watchers = new HashSet<Watcher>();
// 将路径和watchers集合存入
watches.put(clientPath, watchers);
}
// 添加至watchers集合
watchers.add(watcher);
}
}
}
/**
* Determine whether the watch should be added based on return code.
* @param rc the result code of the operation that attempted to add the
* watch on the node
* @return true if the watch should be added, otw false
*/
// 判断是否需要添加,判断rc是否为0
protected boolean shouldAddWatch(int rc) {
return rc == 0;
}
}
说明:可以看到WatchRegistration包含了Watcher和clientPath字段,表示监听和对应的路径,值得注意的是getWatches方式抽象方法,需要子类实现,而在register方法中会调用getWatches方法,实际上调用的是子类的getWatches方法,这是典型的工厂模式。register方法首先会判定是否需要添加监听,然后再进行相应的操作,在WatchRegistration类的默认实现中shouldAddWatch是判定返回码是否为0。
2. ExistsWatchRegistration
class ExistsWatchRegistration extends WatchRegistration {
// 构造函数
public ExistsWatchRegistration(Watcher watcher, String clientPath) {
// 调用父类构造函数
super(watcher, clientPath);
}
@Override
protected Map<String, Set<Watcher>> getWatches(int rc) {
// 根据rc是否为0确定返回dataWatches或existsWatches
return rc == 0 ? watchManager.dataWatches : watchManager.existWatches;
}
@Override
protected boolean shouldAddWatch(int rc) {
// 判断rc是否为0或者rc是否等于NONODE的值
return rc == 0 || rc == KeeperException.Code.NONODE.intValue();
}
}
说明:ExistsWatchRegistration 表示对存在性监听的注册,其实现了getWatches方法,并且重写了shouldAddWatch方法,getWatches方法是根据返回码的值确定返回dataWatches或者是existWatches。
3. DataWatchRegistration
class DataWatchRegistration extends WatchRegistration {
// 构造函数
public DataWatchRegistration(Watcher watcher, String clientPath) {
// 调用父类构造函数
super(watcher, clientPath);
}
@Override
protected Map<String, Set<Watcher>> getWatches(int rc) {
// 直接返回dataWatches
return watchManager.dataWatches;
}
}
说明:DataWatchRegistration表示对数据监听的注册,其实现了getWatches方法,返回dataWatches。
4. ChildWatchRegistration
class ChildWatchRegistration extends WatchRegistration {
// 构造函数
public ChildWatchRegistration(Watcher watcher, String clientPath) {
// 调用父类构造函数
super(watcher, clientPath);
}
@Override
protected Map<String, Set<Watcher>> getWatches(int rc) {
// 直接返回childWatches
return watchManager.childWatches;
}
}
说明:ChildWatchRegistration表示对子节点监听的注册,其实现了getWatches方法,返回childWatches。
5. States
public enum States {
// 代表服务器的状态
CONNECTING, ASSOCIATING, CONNECTED, CONNECTEDREADONLY,
CLOSED, AUTH_FAILED, NOT_CONNECTED;
// 是否存活
public boolean isAlive() {
// 不为关闭状态并且未认证失败
return this != CLOSED && this != AUTH_FAILED;
}
/**
* Returns whether we are connected to a server (which
* could possibly be read-only, if this client is allowed
* to go to read-only mode)
* */
// 是否连接
public boolean isConnected() {
// 已连接或者只读连接
return this == CONNECTED || this == CONNECTEDREADONLY;
}
}
说明:States为枚举类,表示服务器的状态,其有两个方法,判断服务器是否存活和判断客户端是否连接至服务端。
2.2 类的属性
public class ZooKeeper {
// 客户端Socket
public static final String ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_CNXN_SOCKET = "zookeeper.clientCnxnSocket";
// 客户端,用来管理客户端与服务端的连接
protected final ClientCnxn cnxn;
// Logger日志
private static final Logger LOG;
static {
//Keep these two lines together to keep the initialization order explicit
// 初始化
LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ZooKeeper.class);
Environment.logEnv("Client environment:", LOG);
}
private final ZKWatchManager watchManager = new ZKWatchManager();
}
说明:ZooKeeper类存维护一个ClientCnxn类,用来管理客户端与服务端的连接。
2.3 类的构造函数
1. ZooKeeper(String connectString, int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher, boolean canBeReadOnly)型构造函数
public ZooKeeper(String connectString, int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher,
boolean canBeReadOnly)
throws IOException
{
LOG.info("Initiating client connection, connectString=" + connectString
+ " sessionTimeout=" + sessionTimeout + " watcher=" + watcher);
// 初始化默认Watcher
watchManager.defaultWatcher = watcher; // 对传入的connectString进行解析
// connectString 类似于127.0.0.1:3000,127.0.0.1:3001,127.0.0.1:3002未指定根空间的字符串
// 或者是127.0.0.1:3000,127.0.0.1:3001,127.0.0.1:3002/app/a指定根空间的字符串,根为/app/a
ConnectStringParser connectStringParser = new ConnectStringParser(
connectString); // 根据服务器地址列表生成HostProvider
HostProvider hostProvider = new StaticHostProvider(
connectStringParser.getServerAddresses());
// 生成客户端管理
cnxn = new ClientCnxn(connectStringParser.getChrootPath(),
hostProvider, sessionTimeout, this, watchManager,
getClientCnxnSocket(), canBeReadOnly);
// 启动
cnxn.start();
}
说明:该构造函数会初始化WatchManager的defaultWatcher,同时会解析服务端地址和端口号,之后根据服务端的地址生成HostProvider(其会打乱服务器的地址),之后生成客户端管理并启动,注意此时会调用getClientCnxnSocket函数,其源码如下
private static ClientCnxnSocket getClientCnxnSocket() throws IOException {
// 查看是否在系统属性中进行了设置
String clientCnxnSocketName = System
.getProperty(ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_CNXN_SOCKET);
if (clientCnxnSocketName == null) { // 若未进行设置,取得ClientCnxnSocketNIO的类名
clientCnxnSocketName = ClientCnxnSocketNIO.class.getName();
}
try {
// 使用反射新生成实例然后返回
return (ClientCnxnSocket) Class.forName(clientCnxnSocketName)
.newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
IOException ioe = new IOException("Couldn't instantiate "
+ clientCnxnSocketName);
ioe.initCause(e);
throw ioe;
}
}
说明:该函数会利用反射创建ClientCnxnSocketNIO实例
2. public ZooKeeper(String connectString, int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher, long sessionId, byte[] sessionPasswd, boolean canBeReadOnly) throws IOException型构造函数
public ZooKeeper(String connectString, int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher,
long sessionId, byte[] sessionPasswd, boolean canBeReadOnly)
throws IOException
{
LOG.info("Initiating client connection, connectString=" + connectString
+ " sessionTimeout=" + sessionTimeout
+ " watcher=" + watcher
+ " sessionId=" + Long.toHexString(sessionId)
+ " sessionPasswd="
+ (sessionPasswd == null ? "<null>" : "<hidden>")); // 初始化默认Watcher
watchManager.defaultWatcher = watcher; // 对传入的connectString进行解析
// connectString 类似于127.0.0.1:3000,127.0.0.1:3001,127.0.0.1:3002未指定根空间的字符串
// 或者是127.0.0.1:3000,127.0.0.1:3001,127.0.0.1:3002/app/a指定根空间的字符串,根为/app/a
ConnectStringParser connectStringParser = new ConnectStringParser(
connectString); // 根据服务器地址列表生成HostProvider
HostProvider hostProvider = new StaticHostProvider(
connectStringParser.getServerAddresses());
// 生成客户端时使用了session密码
cnxn = new ClientCnxn(connectStringParser.getChrootPath(),
hostProvider, sessionTimeout, this, watchManager,
getClientCnxnSocket(), sessionId, sessionPasswd, canBeReadOnly); // 设置客户端的seenRwServerBefore字段为true(因为用户提供了sessionId,表示肯定已经连接过)
cnxn.seenRwServerBefore = true; // since user has provided sessionId
// 启动
cnxn.start();
}
说明:此型构造函数和之前构造函数的区别在于本构造函数提供了sessionId和sessionPwd,这表明用户已经之前已经连接过服务端,所以能够获取到sessionId,其流程与之前的构造函数类似,不再累赘。
2.4 核心函数分析
1. create函数
函数签名:public String create(final String path, byte data[], List<ACL> acl, CreateMode createMode) throws KeeperException, InterruptedException
public String create(final String path, byte data[], List<ACL> acl,
CreateMode createMode)
throws KeeperException, InterruptedException
{
final String clientPath = path; // 验证路径是否合法
PathUtils.validatePath(clientPath, createMode.isSequential()); // 添加根空间
final String serverPath = prependChroot(clientPath); // 新生请求头
RequestHeader h = new RequestHeader();
// 设置请求头类型
h.setType(ZooDefs.OpCode.create);
// 新生创建节点请求
CreateRequest request = new CreateRequest();
// 新生创建节点响应
CreateResponse response = new CreateResponse();
// 设置请求的数据
request.setData(data);
// 设置请求对应的Flag
request.setFlags(createMode.toFlag());
// 设置服务器路径
request.setPath(serverPath);
if (acl != null && acl.size() == 0) { // ACL不为空但是大小为0,抛出异常
throw new KeeperException.InvalidACLException();
}
// 设置请求的ACL列表
request.setAcl(acl);
// 提交请求
ReplyHeader r = cnxn.submitRequest(h, request, response, null);
if (r.getErr() != 0) { // 请求的响应的错误码不为0,则抛出异常
throw KeeperException.create(KeeperException.Code.get(r.getErr()),
clientPath);
}
if (cnxn.chrootPath == null) { // 根空间为空
// 则返回响应中的路径
return response.getPath();
} else {
// 除去根空间后返回
return response.getPath().substring(cnxn.chrootPath.length());
}
}
说明:该create函数是同步的,主要用作创建节点,其大致步骤如下
① 验证路径是否合法,若不合法,抛出异常,否则进入②
② 添加根空间,生成请求头、请求、响应等,并设置相应字段,进入③
③ 通过客户端提交请求,判断返回码是否为0,若不是,则抛出异常,否则,进入④
④ 除去根空间后,返回响应的路径
其中会调用submitRequest方法,其源码如下
public ReplyHeader submitRequest(RequestHeader h, Record request,
Record response, WatchRegistration watchRegistration)
throws InterruptedException {
// 新生响应头
ReplyHeader r = new ReplyHeader();
// 新生Packet包
Packet packet = queuePacket(h, r, request, response, null, null, null,
null, watchRegistration);
synchronized (packet) { // 同步
while (!packet.finished) { // 如果没有结束
// 则等待
packet.wait();
}
}
// 返回响应头
return r;
}
说明:submitRequest会将请求封装成Packet包,然后一直等待packet包响应结束,然后返回;若没结束,则等待。可以看到其是一个同步方法。
2. create函数
函数签名:public void create(final String path, byte data[], List<ACL> acl, CreateMode createMode, StringCallback cb, Object ctx)
public void create(final String path, byte data[], List<ACL> acl,
CreateMode createMode, StringCallback cb, Object ctx)
{
final String clientPath = path; // 验证路径是否合法
PathUtils.validatePath(clientPath, createMode.isSequential()); // 添加根空间
final String serverPath = prependChroot(clientPath); // 新生请求头
RequestHeader h = new RequestHeader();
// 设置请求头类型
h.setType(ZooDefs.OpCode.create);
// 新生创建节点请求
CreateRequest request = new CreateRequest();
// 新生创建节点响应
CreateResponse response = new CreateResponse();
// 新生响应头
ReplyHeader r = new ReplyHeader();
// 设置请求的数据
request.setData(data);
// 设置请求对应的Flag
request.setFlags(createMode.toFlag());
// 设置服务
request.setPath(serverPath);
// 设置ACL列表
request.setAcl(acl);
// 封装成packet放入队列,等待提交
cnxn.queuePacket(h, r, request, response, cb, clientPath,
serverPath, ctx, null);
}
说明:该create函数是异步的,其大致步骤与同步版的create函数相同,只是最后其会将请求打包成packet,然后放入队列等待提交。
3. delete函数
函数签名:public void delete(final String path, int version) throws InterruptedException, KeeperException
public void delete(final String path, int version)
throws InterruptedException, KeeperException
{
final String clientPath = path;
// 验证路径的合法性
PathUtils.validatePath(clientPath); final String serverPath; // maintain semantics even in chroot case
// specifically - root cannot be deleted
// I think this makes sense even in chroot case.
if (clientPath.equals("/")) { // 判断是否是"/",即zookeeper的根目录,根目录无法删除
// a bit of a hack, but delete(/) will never succeed and ensures
// that the same semantics are maintained
//
serverPath = clientPath;
} else { // 添加根空间
serverPath = prependChroot(clientPath);
} // 新生请求头
RequestHeader h = new RequestHeader();
// 设置请求头类型
h.setType(ZooDefs.OpCode.delete);
// 新生删除请求
DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest();
// 设置路径
request.setPath(serverPath);
// 设置版本号
request.setVersion(version);
// 新生响应头
ReplyHeader r = cnxn.submitRequest(h, request, null, null);
if (r.getErr() != 0) { // 判断返回码
throw KeeperException.create(KeeperException.Code.get(r.getErr()),
clientPath);
}
}
说明:该函数是同步的,其流程与create流程相似,不再累赘。
4. delete函数
函数签名:public void delete(final String path, int version, VoidCallback cb, Object ctx)
public void delete(final String path, int version, VoidCallback cb,
Object ctx)
{
final String clientPath = path; // 验证路径是否合法
PathUtils.validatePath(clientPath); final String serverPath; // maintain semantics even in chroot case
// specifically - root cannot be deleted
// I think this makes sense even in chroot case.
if (clientPath.equals("/")) { // 判断是否是"/",即zookeeper的根目录,根目录无法删除
// a bit of a hack, but delete(/) will never succeed and ensures
// that the same semantics are maintained
serverPath = clientPath;
} else {
serverPath = prependChroot(clientPath);
} // 新生请求头
RequestHeader h = new RequestHeader();
// 设置请求头类型
h.setType(ZooDefs.OpCode.delete);
// 新生删除请求
DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest();
// 设置路径
request.setPath(serverPath);
// 设置版本号
request.setVersion(version);
// 封装成packet放入队列,等待提交
cnxn.queuePacket(h, new ReplyHeader(), request, null, cb, clientPath,
serverPath, ctx, null);
}
说明:该函数是异步的,其流程也相对简单,不再累赘。
5. multi函数
public List<OpResult> multi(Iterable<Op> ops) throws InterruptedException, KeeperException {
for (Op op : ops) { // 验证每个操作是否合法
op.validate();
}
// reconstructing transaction with the chroot prefix
// 新生事务列表
List<Op> transaction = new ArrayList<Op>();
for (Op op : ops) { // 将每个操作添加根空间后添加到事务列表中
transaction.add(withRootPrefix(op));
}
// 调用multiInternal后返回
return multiInternal(new MultiTransactionRecord(transaction));
}
说明:该函数用于执行多个操作或者不执行,其首先会验证每个操作的合法性,然后将每个操作添加根空间后加入到事务列表中,之后会调用multiInternal函数,其源码如下
protected List<OpResult> multiInternal(MultiTransactionRecord request)
throws InterruptedException, KeeperException {
// 新生请求头
RequestHeader h = new RequestHeader();
// 设置请求头类型
h.setType(ZooDefs.OpCode.multi);
// 新生多重响应
MultiResponse response = new MultiResponse();
// 新生响应头
ReplyHeader r = cnxn.submitRequest(h, request, response, null);
if (r.getErr() != 0) { // 判断返回码是否为0
throw KeeperException.create(KeeperException.Code.get(r.getErr()));
} // 获取响应的结果集
List<OpResult> results = response.getResultList(); ErrorResult fatalError = null;
for (OpResult result : results) { // 遍历结果集
if (result instanceof ErrorResult && ((ErrorResult)result).getErr() != KeeperException.Code.OK.intValue()) { //判断结果集中是否出现了异常
fatalError = (ErrorResult) result;
break;
}
} if (fatalError != null) { // 出现了异常
// 新生异常后抛出
KeeperException ex = KeeperException.create(KeeperException.Code.get(fatalError.getErr()));
ex.setMultiResults(results);
throw ex;
} // 返回结果集
return results;
}
说明:multiInternal函数会提交多个操作并且等待响应结果集,然后判断结果集中是否有异常,若有异常则抛出异常,否则返回响应结果集。
6. exists函数
函数签名:public Stat exists(final String path, Watcher watcher) throws KeeperException, InterruptedException
public Stat exists(final String path, Watcher watcher)
throws KeeperException, InterruptedException
{
final String clientPath = path; // 验证路径是否合法
PathUtils.validatePath(clientPath); // the watch contains the un-chroot path
WatchRegistration wcb = null;
if (watcher != null) { // 生成存在性注册
wcb = new ExistsWatchRegistration(watcher, clientPath);
} // 添加根空间
final String serverPath = prependChroot(clientPath); // 新生请求头
RequestHeader h = new RequestHeader();
// 设置请求头类型
h.setType(ZooDefs.OpCode.exists);
// 新生节点存在请求
ExistsRequest request = new ExistsRequest();
// 设置路径
request.setPath(serverPath);
// 设置Watcher
request.setWatch(watcher != null);
// 新生设置数据响应
SetDataResponse response = new SetDataResponse();
// 提交请求
ReplyHeader r = cnxn.submitRequest(h, request, response, wcb);
if (r.getErr() != 0) { // 判断返回码
if (r.getErr() == KeeperException.Code.NONODE.intValue()) {
return null;
}
throw KeeperException.create(KeeperException.Code.get(r.getErr()),
clientPath);
} // 返回结果的状态
return response.getStat().getCzxid() == -1 ? null : response.getStat();
}
说明:该函数是同步的,用于判断指定路径的节点是否存在,值得注意的是,其会对指定路径的结点进行注册监听。
7. exists
函数签名:public void exists(final String path, Watcher watcher, StatCallback cb, Object ctx)
public void exists(final String path, Watcher watcher,
StatCallback cb, Object ctx)
{
final String clientPath = path;
// 验证路径是否合法
PathUtils.validatePath(clientPath); // the watch contains the un-chroot path
WatchRegistration wcb = null;
if (watcher != null) { // 生成存在性注册
wcb = new ExistsWatchRegistration(watcher, clientPath);
} // 添加根空间
final String serverPath = prependChroot(clientPath);
// 新生请求头
RequestHeader h = new RequestHeader();
// 设置请求头类型
h.setType(ZooDefs.OpCode.exists);
// 新生节点存在请求
ExistsRequest request = new ExistsRequest();
// 设置路径
request.setPath(serverPath);
// 设置Watcher
request.setWatch(watcher != null);
// 新生设置数据响应
SetDataResponse response = new SetDataResponse();
// 将请求封装成packet,放入队列,等待执行
cnxn.queuePacket(h, new ReplyHeader(), request, response, cb,
clientPath, serverPath, ctx, wcb);
}
说明:该函数是异步的,与同步的流程相似,不再累赘。
之后的getData、setData、getACL、setACL、getChildren函数均类似,只是生成的响应类别和监听类别不相同,大同小异,不再累赘。
三、总结
本篇博文分析了Watcher机制的ZooKeeper类,该类包括了对服务器的很多事务性操作,并且包含了同步和异步两个版本,但是相对来说,较为简单,也谢谢各位园友的观看~
【Zookeeper】源码分析之Watcher机制(三)之Zookeeper的更多相关文章
- 【Zookeeper】源码分析之Watcher机制(一)
一.前言 前面已经分析了Zookeeper持久话相关的类,下面接着分析Zookeeper中的Watcher机制所涉及到的类. 二.总体框图 对于Watcher机制而言,主要涉及的类主要如下. 说明: ...
- 【Zookeeper】源码分析之Watcher机制(二)
一.前言 前面已经分析了Watcher机制中的第一部分,即在org.apache.zookeeper下的相关类,接着来分析org.apache.zookeeper.server下的WatchManag ...
- 【Zookeeper】源码分析之Watcher机制(二)之WatchManager
一.前言 前面已经分析了Watcher机制中的第一部分,即在org.apache.zookeeper下的相关类,接着来分析org.apache.zookeeper.server下的WatchManag ...
- zookeeper源码分析之六session机制
zookeeper中session意味着一个物理连接,客户端连接服务器成功之后,会发送一个连接型请求,此时就会有session 产生. session由sessionTracker产生的,sessio ...
- Zookeeper 源码分析-启动
Zookeeper 源码分析-启动 博客分类: Zookeeper 本文主要介绍了zookeeper启动的过程 运行zkServer.sh start命令可以启动zookeeper.入口的main ...
- zookeeper源码分析之五服务端(集群leader)处理请求流程
leader的实现类为LeaderZooKeeperServer,它间接继承自标准ZookeeperServer.它规定了请求到达leader时需要经历的路径: PrepRequestProcesso ...
- zookeeper源码分析之四服务端(单机)处理请求流程
上文: zookeeper源码分析之一服务端启动过程 中,我们介绍了zookeeper服务器的启动过程,其中单机是ZookeeperServer启动,集群使用QuorumPeer启动,那么这次我们分析 ...
- zookeeper源码分析之三客户端发送请求流程
znode 可以被监控,包括这个目录节点中存储的数据的修改,子节点目录的变化等,一旦变化可以通知设置监控的客户端,这个功能是zookeeper对于应用最重要的特性,通过这个特性可以实现的功能包括配置的 ...
- 【JUC】JDK1.8源码分析之ArrayBlockingQueue(三)
一.前言 在完成Map下的并发集合后,现在来分析ArrayBlockingQueue,ArrayBlockingQueue可以用作一个阻塞型队列,支持多任务并发操作,有了之前看源码的积累,再看Arra ...
随机推荐
- Java设计模式--Java Builder模式
1.Java Builder模式主要是用一个内部类去实例化一个对象,避免一个类出现过多构造函数,而且构造函数如果出现默认参数的话,很容易出错. public Person(String name) P ...
- springmvc配置首页的方式
<mvc:view-controller path="/" view-name="redirect:/user/loginUI" />
- 有两个数据库A和B,数据库A中有表a,如何把表a映射到数据库B中,sql 2005
select * into B.dbo.a from A.dbo.a 就把表同步过去如果只同步表结构select * into B.dbo.a from A.dbo.a where 1<> ...
- 考分鄙视(exam)
考分鄙视(exam) 题目描述 Whence这个学期考了n次试,每一次都有一个0-20000之间的整数分数.Whence本来的状态应该是每一次考试都比前一次多一分(除第一次),但由于他很不稳定,偏差可 ...
- JS——无缝滚动
1.描述——无缝滚动图片 2.代码 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" ...
- bzoj1562【Noi2009】变换序列
题意:http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1562 给一个序列Di表示min(|i-Ti|,n-|i-Ti|),求一个字典序最小的序列Ti ...
- nginx 防 webshell 跨目录
对于在一台服务器上有多个虚拟主机的人来说,Apache有一个很好用的地方---配置php_admin_value,在里面配置一下 open_basedir就可以了. 但是Nginx却没有这样的设置 ...
- (中等) POJ 1703 Find them, Catch them,带权并查集。
Description The police office in Tadu City decides to say ends to the chaos, as launch actions to ro ...
- LPC1788的EMC驱动norflash
Norflash型号为sst39vf32 #ifndef __NORFLASH_H_ #define __NORFLASH_H_ #include "common.h" #incl ...
- 完美分割字符串,实现字符串的splict功能
class Str:Client_C { string val; string[] str = new string[100]; public void StrT1() { //1.正常情况 //2. ...
