python之数据库编程
python之数据库编程
sqlite
1.前期准备工作
导入模块:
import sqlite3
连接数据库
conn = sqlite3.connect("test.db") #test为数据库名称,若不存在此数据库,会自动创建
测试是否创建或连接数据库成功
print(conn) #打印结果为connection对象
pycharm端显示出数据库:
- 1.打开pycharm->右端database->点击+号
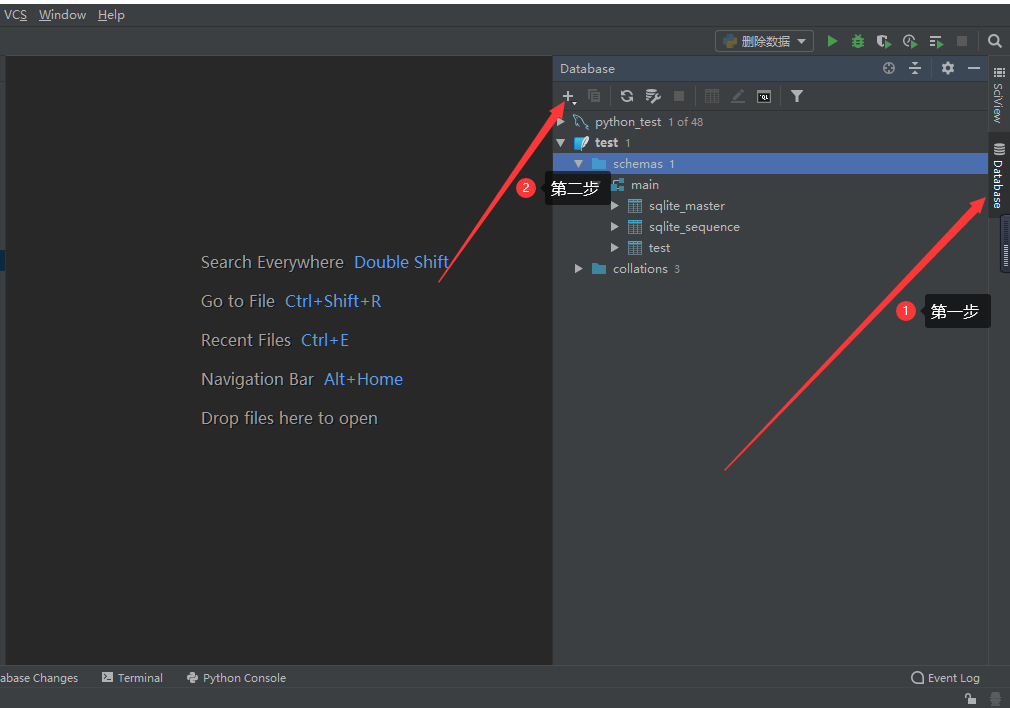
- 1.打开pycharm->右端database->点击+号
2.第二步:
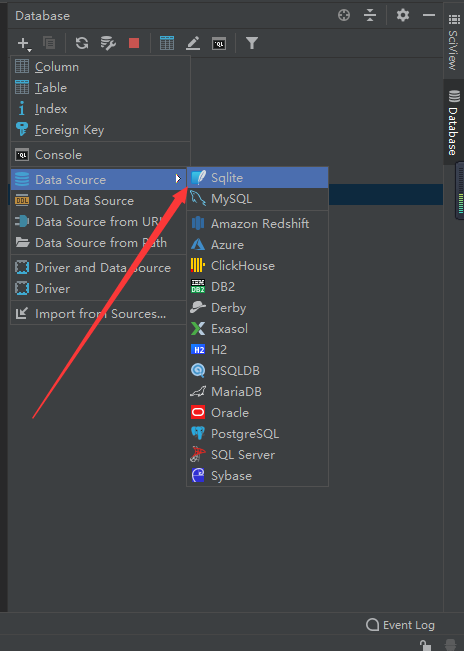
3.第三步
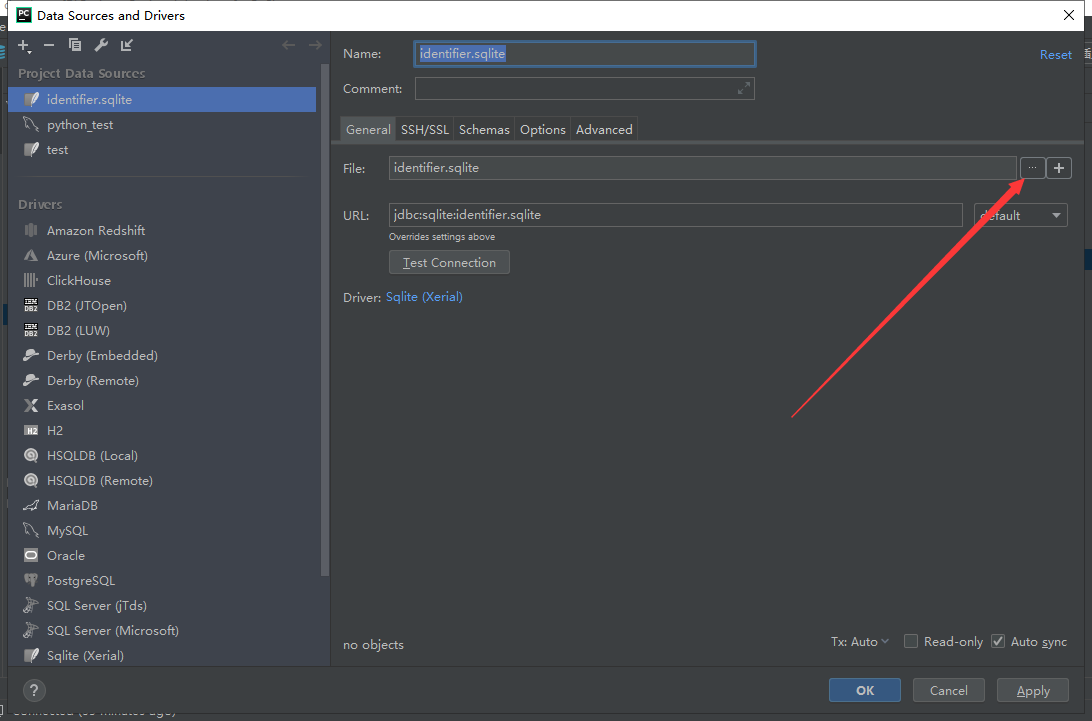
4.选择pycharm工作环境下新创建的数据库,比如我的在这里
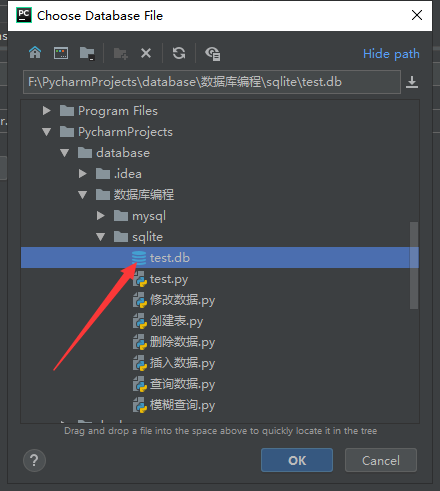
点击ok即可,注意:
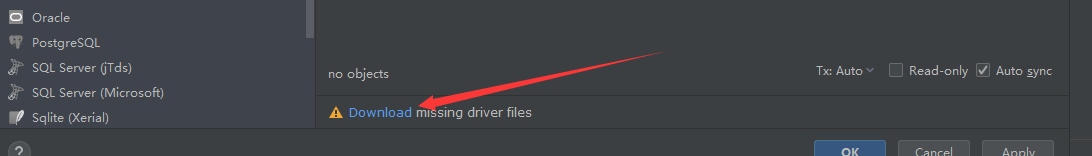
若第三步出现这个,点击Download先进行下载。。。
2.创建数据库和表
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect("test.db")
#cur = conn.cursor()
sql = """
CREATE TABLE test(
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY autoincrement,
name TEXT,
age INTEGER
)
"""
try:
#cur.execute(sql)
conn.execute(sql)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
finally:
#cur.close()
conn.close()
注意:
可以看到,此处并没有使用游标,而是直接conn.execute(sql),值得说明的是,对sqlite来说(mysql却不是),增删改以及创建表都可以不用游标,但查询一定需要,往下看
3.插入数据
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('test.db')
# cur = conn.cursor()
sql = """
insert into test(name, age) VALUES (%s,%s)
"""%("'王五'",22)
sql1 = """
insert into test(name, age) VALUES (?,?)
"""
try:
print("sql:"+sql)
print("sql1:" + sql1)
#conn.execute(sql)
#conn.execute(sql1, ('张三', 20))添加单条数据
conn.executemany(sql1,[('李四',18),('王五',28),('赵六',38)])
conn.commit()
print("插入成功")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print("插入失败")
conn.rollback()
finally:
conn.close()
显示结果:

插入数据中使用了两种方法,见sql和sql1,分别使用%s和?占位符
以下我就不一一展示显示结果了。。。
4.修改数据
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('test.db')
# cur = conn.cursor()
sql = """
update test set name = ? , age = ? where id = ?
"""
sql1 = """
update test set name = %s , age = %s where id = %s
"""%("'曹操'", 24, 11)
try:
#conn.execute(sql, ('曹操', 24, 4))
conn.execute(sql1)
print("成功")
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print("失败")
conn.rollback()
finally:
conn.close()
修改数据中使用了两种方法,见sql和sql1,分别使用%s和?占位符
5.删除数据
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('test.db')
#cur = conn.cursor()
sql = """
delete from test where name = ?
"""
sql1 = """
delete from test where name = %s
"""%("'曹操'",)
try:
conn.execute(sql1);
#conn.execute(sql,('曹操',));
#若执行conn.execute(sql,('曹操'));会报错Incorrect number of bindings supplied. The current statement uses 1, and there are 2 supplied.
#使用('曹操',)或[曹操]
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback()
print(e)
finally:
conn.close()
6.查询数据
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('test.db')
cur = conn.cursor()
sql = """
select * from test
"""
try:
cur.execute(sql);
# print(cur.fetchall())#查询所有数据
print(cur.fetchone()) # 查询第一条数据
# print(cur.fetchmany(3))#查询几条数据,从开头开始
except Exception as e:
print(e)
finally:
cur.close()
conn.close()
可以看到,查询数据必须要用游标,按条件进行查询可参照上面的占位符进行测试
7.模糊查询
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('test.db')
cur = conn.cursor()
sql = "select * from test where name like '%%%s%%'"%"王"
#sql1 = "select * from test where name like ?"
try:
print(sql)
cur.execute(sql);
#cur.execute(sql1, ("%王%",));
print(cur.fetchall()) # 查询所有数据
# print(cur.fetchone()) # 查询第一条数据
# print(cur.fetchmany(3))#查询几条数据,从开头开始
except Exception as e:
print(e)
finally:
cur.close()
conn.close()
模糊查询中使用了两种方法,见sql和sql1,分别使用%s和?占位符
注意:%s占位符模糊查询时,使用%%---%%进行转义
mysql
1.前期准备工作
导入模块:
import pymysql
连接数据库
conn = pymysql.connect(user='root',password='000000',host='localhost',
port=3306,database='python_test')
#mysql数据库不会自动创建,需要自己建立
测试是否连接数据库成功
print(conn) #打印结果为connection对象
pycharm端显示出数据库:
与sqlite操作一样,此时建立的是mysql
2.创建数据库和表
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(user='root',password='000000',host='localhost',
port=3306,database='python_test')
cur = conn.cursor()
sql = """
create table student(
id integer primary key auto_increment,
sno char(20) not null,
name char(20),
score float
)
"""
try:
cur.execute(sql)
print("建表成功")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print("建表失败")
finally:
cur.close()
conn.close()
注意:
可以看到,与sqlite不同,mysql的操作都需要游标参与
3.插入数据
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(user='root', password='000000', host='localhost', port=3306, database='python_test')
cur = conn.cursor()
sql = """
insert into student(sno, name, score)
values
(%s,%s,%s)
"""
try:
#cur.execute(sql, ('7777', 'ff', 90)) #插入一条
cur.executemany(sql,[('3333','c',3),('4444','d',4)]) #插入多条
conn.commit()
print("插入成功")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
conn.rollback()
print("插入失败")
finally:
cur.close()
conn.close()
显示结果:
mysql中使用%s做占位符
4.修改数据
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(user='root', password='000000', host='localhost', port=3306, database='python_test')
cur = conn.cursor()
sql = """
update student set name = %s where id = %s
"""
try:
cur.execute(sql,('王五',5))
#cur.executemany(sql,[('3333','c',3),('4444','d',4)])
conn.commit()
print("修改成功")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
conn.rollback()
print("修改失败")
finally:
cur.close()
conn.close()
5.删除数据
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(user='root', password='000000', host='localhost', port=3306, database='python_test')
cur = conn.cursor()
sql = """
delete from student where name = %s
"""
try:
cur.execute(sql,'d')
#cur.executemany(sql,[('3333','c',3),('4444','d',4)])
conn.commit()
print("删除成功")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
conn.rollback()
print("删除失败")
finally:
cur.close()
conn.close()
6.查询数据
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(user='root', password='000000', host='localhost', port=3306, database='python_test')
cur = conn.cursor()
sql = """
select * from student
"""
try:
cur.execute(sql)
#print(cur.fetchone())
#print(cur.fetchmany(3))
print(cur.fetchall())
except Exception as e:
print(e)
finally:
cur.close()
conn.close()
7.模糊查询
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(user='root', password='000000', host='localhost', port=3306, database='python_test')
cur = conn.cursor()
sql = """
select * from student where name like %s
"""
sql1 = "select * from student where name like '%%%s%%'"%'王'
try:
print(sql1)
cur.execute(sql1)
#print(cur.fetchone())
#print(cur.fetchmany(3))
print(cur.fetchall())
except Exception as e:
print(e)
finally:
cur.close()
conn.close()
python之数据库编程的更多相关文章
- 运用Python语言编写获取Linux基本系统信息(三):Python与数据库编程,把获取的信息存入数据库
运用Python语言编写获取Linux基本系统信息(三):Python与数据库编程 有关前两篇的链接: 运用Python语言编写获取Linux基本系统信息(一):获得Linux版本.内核.当前时间 运 ...
- python的数据库编程
数据库的基础知识 一.数据库的概念 数据库将大量数据按照一定的方式组织并存储起来,是相互关联的数据的集合.数据库中的数据不仅包括描述事物数据的本身,还包括相关数据之间的联系.数据库可以分为关系型数据库 ...
- Python学习系列(七)( 数据库编程)
Python学习系列(七)( 数据库编程) Python学习系列(六)(模块) 一,MySQL-Python插件 Python里操作MySQL数据库,需要Python下安装访 ...
- Python程序设计9——数据库编程
1 数据持久化 持久化是将内存中的对象存储在关系数据库中,当然也可以存储在磁盘文件.XML数据文件中.实现数据持久化至少需要实现以下3个接口 void Save(object o):把一个对象保存到外 ...
- python 闯关之路四(下)(并发编程与数据库编程) 并发编程重点
python 闯关之路四(下)(并发编程与数据库编程) 并发编程重点: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 并发编程:线程.进程.队列.IO多路模型 操作系统工作原理介绍.线程.进程演化史.特点.区别 ...
- python 教程 第二十章、 数据库编程
第二十章. 数据库编程 环境设置 1).安装MySQL-python http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/ MySQL-python-1.2.3.win ...
- Python黑帽编程 2.0 第二章概述
Python黑帽编程 2.0 第二章概述 于 20世纪80年代末,Guido van Rossum发明了Python,初衷据说是为了打发圣诞节的无趣,1991年首次发布,是ABC语言的继承,同时也是一 ...
- Python金融应用编程(数据分析、定价与量化投资)
近年来,金融领域的量化分析越来越受到理论界与实务界的重视,量化分析的技术也取得了较大的进展,成为备受关注的一个热点领域.所谓金融量化,就是将金融分析理论与计算机编程技术相结合,更为有效的利用现代计算技 ...
- 使用Python管理数据库
使用Python管理数据库 这篇文章的主题是如何使用Python语言管理数据库,简化日常运维中频繁的.重复度高的任务,为DBA们腾出更多时间来完成更重要的工作.文章本身只提供一种思路,写的不是很全 ...
随机推荐
- 数据库count用法
count(*)包括了所有的列,相当于行数,在统计结果的时候,不会忽略列值为NULL count(1)包括了所有列,用1代表代码行,在统计结果的时候,不会忽略列值为NULL count(列名)只包 ...
- Linux + NodeJS 常用命令
Linux系统常用命令 1.su 由当前用户切换至root用户: 2. su username 切换至某一用户: 3.chmod u+w /etc/sudoers 为/etc/sudoers文件添加写 ...
- IPV6改造?华为云如此简单
现在很多企业都在搞这个IPV6改造,说实话这个IPV6改造我这边也不是特别精通,也是通过查阅各种资料来了解IPV6这个东西,下面是我查的一些资料大家可以借鉴一下. IPv6改造三步曲--Vecloud ...
- 构建后端第2篇之---springb @ComponentScan注解使用
张艳涛写于2021-2-8日 构建后端项目的时候遇到一个问题,在zyt-auth项目的依赖定义了@Component类,这个类在项目启动的时候提示没有找到bean Field tokenService ...
- 关于maven打包与jdk版本的一些关系
最近让不同JAVA版本的容器maven打包折腾的不行,终于理出了一点头绪.在这里记录下备忘. 1. Maven与jdk版本的关系 先明确一个概念,关高版本JDK运行maven,是可以打出低版本的JAV ...
- Spring Data Commons 远程命令执行漏洞(CVE-2018-1273)
影响版本 Spring Framework 5.0 to 5.0.4 Spring Framework 4.3 to 4.3.14 poc https://github.com/zhzyker/exp ...
- Python: 解析crontab正则,增加+操作
以下是使用Python解析crontab时间格式的一个类, 同时minute和hour支持了 + 的操作. 记录一下备忘. 其中的line参数是字符串分拆后的格式, 包含了 "week&qu ...
- maze writeup
maze writeup 攻防世界的一道迷宫题,第一次接触这样的题,个人感觉很有意思,收获也挺多,做一篇笔记记录一下. 程序分析 __int64 sub_4006B0() { signed __int ...
- 2020年Android开发市场真的饱和了吗?
公司在杭州,根据我的不客观数据体验来看,最饱和的是iOS,同样发布一个职位iOS是其他技术岗位10倍的投递量. 当然Android作为一个已经市场化十余年的技术门类,它必然早已经是成熟常态.这样的技术 ...
- CMMI相关图书
Integrating CMMI and Agile Development: Case Studies and Proven Techniques for Faster Performance Im ...
