Multitier architecture
Multitier architecture - Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multitier_architecture
Common layers
In a logical multilayered architecture for an information system with an object-oriented design, the following four are the most common:
- Presentation layer (a.k.a. UI layer, view layer, presentation tier in multitier architecture)
- Application layer (a.k.a. service layer[5][6] or GRASP Controller Layer [7])
- Business layer (a.k.a. business logic layer (BLL), domain layer)
- Data access layer (a.k.a. persistence layer, logging, networking, and other services which are required to support a particular business layer)
The book Domain Driven Design describes some common uses for the above four layers, although its primary focus is the domain layer.[8]
If the application architecture has no explicit distinction between the business layer and the presentation layer (i.e., the presentation layer is considered part of the business layer), then a traditional client-server (two-tier) model has been implemented.[citation needed]
The more usual convention is that the application layer (or service layer) is considered a sublayer of the business layer, typically encapsulating the API definition surfacing the supported business functionality. The application/business layers can, in fact, be further subdivided to emphasize additional sublayers of distinct responsibility. For example, if the Model View Presenter pattern is used, the presenter sublayer might be used as an additional layer between the user interface layer and the business/application layer (as represented by the model sublayer).[citation needed]
Some also identify a separate layer called the business infrastructure layer (BI), located between the business layer(s) and the infrastructure layer(s). It's also sometimes called the "low-level business layer" or the "business services layer". This layer is very general and can be used in several application tiers (e.g. a CurrencyConverter).[9]
The infrastructure layer can be partitioned into different levels (high-level or low-level technical services).[9] Developers often focus on the persistence (data access) capabilities of the infrastructure layer and therefore only talk about the persistence layer or the data access layer (instead of an infrastructure layer or technical services layer). In other words, the other kind of technical services are not always explicitly thought of as part of any particular layer.[citation needed]
A layer is on top of another, because it depends on it. Every layer can exist without the layers above it, and requires the layers below it to function. Another common view is that layers do not always strictly depend on only the adjacent layer below. For example, in a relaxed layered system (as opposed to a strict layered system) a layer can also depend on all the layers below it.[4]
Three-tier architecture

Overview of a three-tier application.
Three-tier architecture is a client–server software architecture pattern in which the user interface (presentation), functional process logic ("business rules"), computer data storage and data access are developed and maintained as independent modules, most often on separate platforms.[10] It was developed byJohn J. Donovan in Open Environment Corporation (OEC), a tools company he founded in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Apart from the usual advantages of modular software with well-defined interfaces, the three-tier architecture is intended to allow any of the three tiers to be upgraded or replaced independently in response to changes in requirements or technology. For example, a change of operating system in the presentation tier would only affect the user interface code.
Typically, the user interface runs on a desktop PC or workstation and uses a standard graphical user interface, functional process logic that may consist of one or more separate modules running on a workstation or application server, and an RDBMS on a database server or mainframe that contains the computer data storage logic. The middle tier may be multitiered itself (in which case the overall architecture is called an "n-tier architecture").
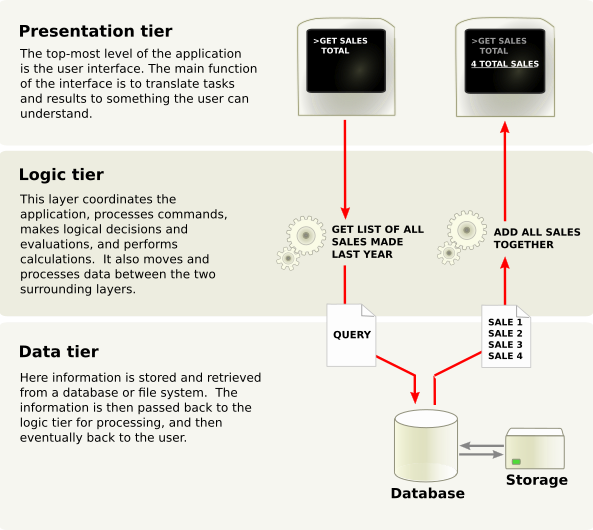
Three-tier architecture:
- Presentation tier
- This is the topmost level of the application. The presentation tier displays information related to such services as browsing merchandise, purchasing and shopping cart contents. It communicates with other tiers by which it puts out the results to the browser/client tier and all other tiers in the network. In simple terms, it is a layer which users can access directly (such as a web page, or an operating system's GUI).
- Application tier (business logic, logic tier, or middle tier)
- The logical tier is pulled out from the presentation tier and, as its own layer, it controls an application’s functionality by performing detailed processing.
- Data tier
- The data tier includes the data persistence mechanisms (database servers, file shares, etc.) and the data access layer that encapsulates the persistence mechanisms and exposes the data. The data access layer should provide an API to the application tier that exposes methods of managing the stored data without exposing or creating dependencies on the data storage mechanisms. Avoiding dependencies on the storage mechanisms allows for updates or changes without the application tier clients being affected by or even aware of the change. As with the separation of any tier, there are costs for implementation and often costs to performance in exchange for improved scalability and maintainability.
Web development usage[edit]
In the web development field, three-tier is often used to refer to websites, commonly electronic commerce websites, which are built using three tiers:
- A front-end web server serving static content, and potentially some cached dynamic content. In web-based application, front end is the content rendered by the browser. The content may be static or generated dynamically.
- A middle dynamic content processing and generation level application server (e.g., Symfony, Spring, ASP.NET, Django, Rails).
- A back-end database or data store, comprising both data sets and the database management system software that manages and provides access to the data.
Other considerations
Data transfer between tiers is part of the architecture. Protocols involved may include one or more of SNMP, CORBA, Java RMI, .NET Remoting, Windows Communication Foundation, sockets, UDP, web services or other standard or proprietary protocols. Often middleware is used to connect the separate tiers. Separate tiers often (but not necessarily) run on separate physical servers, and each tier may itself run on a cluster.
Traceability
The end-to-end traceability of data flows through n-tier systems is a challenging task which becomes more important when systems increase in complexity. The Application Response Measurement defines concepts and APIsfor measuring performance and correlating transactions between tiers. Generally, the term "tiers" is used to describe physical distribution of components of a system on separate servers, computers, or networks (processing nodes). A three-tier architecture then will have three processing nodes. The term "layers" refer to a logical grouping of components which may or may not be physically located on one processing node.
Multitier architecture的更多相关文章
- Multitier architecture-n-tier architecture
In software engineering, multitier architecture (often referred to as n-tier architecture) or multil ...
- .net架构设计读书笔记--第二章 设计体系结构
第五节 探索领域架构 一.领域驱动设计的价值与意义 最初在java中使用,.net要晚些才引入.领域驱动设计出现之初的争议.一个向导,少走弯路 1. 我们真的需要DDD吗? DDD并不适用于每个软 ...
- 翻译:wiki中的business logic词条
Business logic 业务逻辑 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia 来自Wikipedia,自由的百科全书 In computer software, ...
- Delphi 和 C++Builder 2014年及以后技术路线图
RAD Studio, Delphi 和 C++Builder 2014年及以后技术路线图 By: Embarcadero News 内容源自Embarcadero新闻组,本人水平有限,欢迎各位高人修 ...
- Parsing XML in J2ME
sun的原文,原文地址是http://developers.sun.com/mobility/midp/articles/parsingxml/. by Jonathan KnudsenMarch 7 ...
- .NET及.NET Core系统架构
三层及多层架构 Multitier Architecture ASP.NET N-Tier Architecture Schema Visual Studio N-Tier Example 来源:ht ...
- [Windows Azure] .NET Multi-Tier Application Using Storage Tables, Queues, and Blobs - 1 of 5
.NET Multi-Tier Application Using Storage Tables, Queues, and Blobs - 1 of 5 This tutorial series sh ...
- Undefined symbols for architecture arm64解决方案
在iOS开发中经常遇到的一个错误是Undefined symbols for architecture arm64,这个错误表示工程某些地方不支持arm64指令集.那我们应该怎么解决这个问题了?我们不 ...
- Optimal Flexible Architecture(最优灵活架构)
来自:Oracle® Database Installation Guide 12_c_ Release 1 (12.1) for Linux Oracle base目录命名规范: /pm/s/u 例 ...
随机推荐
- [luoguP3668] [USACO17OPEN]Modern Art 2 现代艺术2(栈)
传送门 还是一个字——栈 然后加一大堆特判 至少我是这么做的 我的代码 #include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #define N 1000 ...
- BZOJ1833 [ZJOI2010]count 数字计数 【数学 Or 数位dp】
题目 给定两个正整数a和b,求在[a,b]中的所有整数中,每个数码(digit)各出现了多少次. 输入格式 输入文件中仅包含一行两个整数a.b,含义如上所述. 输出格式 输出文件中包含一行10个整数, ...
- 创建微服务项目后,在谷歌、Safari等浏览器下无法访问的具体原因
使用SpringBoot开发了一个项目,端口随机给指定了一个,如6666. 可是奇葩的现象出现了,当在谷歌浏览器地址栏中输入localhost:6666访问的时候,提示无法访问. 检查良久,发现代码也 ...
- Error处理: “非法字符: \65279”的解决办法
将eclipse项目转为maven项目的时候,编译时遇到 “非法字符: \65279”的报错. 出错内容是: *.java:1: 非法字符: \65279 [javac] package com ...
- PXC小结
PXC使用到的端口号 3306 数据库对外服务的端口号(视具体情况而定) 4444 请求SST SST: 指数据一个镜象传输 xtrabackup , rsync ,mysqldump 4567 : ...
- 让Mac OS X专用高速移动硬盘在Linux下也能被读写
MacBook Pro以及iMac等设备都具备雷电接口和USB 3.0接口,配合使用Mac OS X格式化的专用高速移动硬盘读写数据都非常快.那么这种硬盘可以在Linux下被读写吗?其实,Mac OS ...
- springmvc中ajax处理
1.使用HttpServletResponse处理--不需要配置解析器 @Controller public class AjaxController { @RequestMapping(" ...
- mongDB的常用操作总结
目录 常用查询: 查询一条数据 查询子元素集合:image.id gte: 大于等于,lte小于等于... 查询字段不存在的数据not 查询数量: 常用更新 更新第一条数据的一个字段: 更新一条数据的 ...
- synchronized初识
作用域: 1.对象实例内--->People jack = new Jack(); ①此作用域内的synchronized锁 ,可以防止多个线程同时访问这个对象的synchronized方法 ② ...
- Unix操作系统LD_PRELOAD简介
http://blog.csdn.net/ieearth/article/details/49952047 Unix操作系统的动态链接库的知识中,这个功能主要就是用来有选择性的载入Unix操作系统不同 ...
