Python 学习第二章
本章内容
- 数据类型
- 数据运算
- 表达式 if ...else 语句
- 表达式 for 循环
- 表达式 while 循环
一、数据类型
在内存中存储的数据可以有多种类型。
在 Python 有五个标准的数据类型
- Numbers (数字)
- String (字符串)
- List (列表)
- Tuple (元组)
- Dictionnary (字典)
数字
Python 支持四种不同的数字类型
- int (有符号整数)
- long (长整型)
- float (浮点型)
- complex (复数)
字符串
字符串或串(String)是由数字、字母、下划线组成的一串字符。
print("我爱你,我的国!")
这里说一下字符串拼接,在第一章的时候最后一张图显示出字符串拼接。这里我们演示一下怎么用,先看个简单的程序如下:
#班里面有10人,来了5人,现在有多少人?
student_number=10
come_number=5
new_number=student_number+come_number
print("班级现有",new_number,"人") # 没用字符串拼接
#班里面有10人,来了5人,现在有多少人?
student_number=10
come_number=5
new_number=student_number+come_number
print("班级现有"+str(new_number)+"人") #采用字符串拼接
这里面new_number 数据类型是 int 类型,要通过 str() 转换成字符串(详见第一章介绍)。然后通过 + 号进行拼接
列表
List(列表) 是 Python 中使用最频繁的数据类型。
基本操作:
- 索引
- 切片
- 追加
- 删除
- 长度
- 切片
- 循环
- 包含
a = ["","","",""]
b = a[1]
c = a[0]
d = a[1:3] #提取列表中 a[1]和a[2] 用到切片功能,后面在详细的学
print(b) #b = 2
print(c)
print(d) #d = ["2","3"]
元组
元组是另一个数据类型,类似于List(列表)。
元组用"()"标识。内部元素用逗号隔开。但是元组不能二次赋值,相当于只读列表。
创建元组
age=(11,12,13,43,33,23)
print(age)
字典
字典(dictionary)是除列表以外python之中最灵活的内置数据结构类型。列表是有序的对象集合,字典是无序的对象集合。
两者之间的区别在于:字典当中的元素是通过键来存取的,而不是通过偏移存取。
字典用"{ }"标识。字典由索引(key)和它对应的值value组成。
person={"name":"xp","age":24}
print(person)
更多内容:猛戳这里
二、数据运算
根据这几天学的和查阅资料,整理出以下几种数据运算,当然有些我自己还没练习,先整理出来,后面用到再重点介绍。
算术运算
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
| + | 加——两个数相加 | a=1 b=2 a+b 输出结果为 3 |
| - | 减——两个数相减 | a=4 b=2 a-b 输出结果为 2 |
| * | 乘——两个数相乘 | a=1 b=2 a*b 输出结果为 2 |
| / | 除——两个数相除 | a=4 b=2 a/b 输出结果为 2 |
| % | 取模——返回除法的余数 | a=5 b=2 a%b 输出结果为 1 |
| // | 整除——返回商的整数部分 | a=5 b=2 a//b 输出结果为 2 |
| ** | 幂——返回x的y次幂 | a=5 b=2 a**b 输出结果为 25 |
比较运算
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
| == | 等于——比较对象是否相等 | a=1 b=2 a==b 返回false |
| != | 不等于——比较两个对象是否不相等 | a=1 b=2 a==b 返回True |
| > | 大于——比较两个对象谁大 | a=1 b=2 a>b 返回false |
| < | 小于——比较两个对象谁小 | a=1 b=2 a<b 返回ture |
| >= | 大于等于——比较两个对象的关系 | a=1 b=2 a>=b 返回false |
| <= | 小于等于——比较两个对象的关系 | a=1 b=2 a<=b 返回false |
逻辑运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
| and | 与 | a=false b=ture a and b =false |
| or | 或 | a=false b=ture a or b =ture |
| not | 非 | a=false b=ture nat(a and b) =ture |
逻辑运算符真值表
and 真值表
|
and |
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
1 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
or 真值表
|
or |
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
not 真值表
|
not |
1 |
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
赋值运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
| = | 简单的赋值运算符 | a=3 b=a b 的输出结果为 3 |
| += | 加法赋值运算符 | a=3 c=1 a+=c a 的输出结果为 4 等价于a=a+c |
| -= | 减法赋值运算符 | a=3 c=1 a-=c a 的输出结果为 2 等价于a=a-c |
| *= | 乘法赋值运算符 | a=3 c=2 a*=c a 的输出结果为 6 等价于a=a*c |
| /= | 除法赋值运算符 | a=4 c=2 a/=c a 的输出结果为 2 等价于a=a/c |
| %= | 取模赋值运算符 | a=9 b=5 a%=b a 的输出结果为 4 等价于a=a%b |
| //= | 整除赋值运算符 | a=49 b=5 a//=b a 的输出结果为 9 等价于a=a//b |
| **= | 幂赋值运算符 | a=2 b=3 a**=b a 的输出结果为 8 等价于a=a**b |
位运算
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
| & | 按位 与 运算符 | a=11 b=2 (a&b)=2 二进制:0000 0010 |
| | | 按位 或 运算符 | a=11 b=2 (a|b)=11 二进制:0000 1011 |
| ^ | 按位 异或 运算符 | a=11 b=2 (a^b)=9 二进制:0000 1001 (取不相同的位) |
| ~ | 按位 取反 运算符 | a=11 (~a)=-12 二进制:1000 1100 |
| << | 左移动运算符 | a=11 (<<a) =22 二进制:0001 0110 |
| >> | 右移动运算符 | a=11 (<<a) =5 二进制:1000 0101 |
注意:按位 午饭运算符,高位为1符号位为1为负数,负数在计算机以反码形式存储,反码 = 二进制取反(符号位不变)+1。所以 a = 11 二进制位:0000 1011
取反后为:1111 0100 ——> 1111 0100-1 = 1111 0011 ——> 取反: 1000 1100 = -12
问题:a = 11 c=a>>1 那么 a 的最低位移到高位上,后面的一次向右挪一位,那么高位上位1,为什么不是负数呢?结果却是5, 二进制位: 1000 0101
运算符优先级
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ** | 指数 (最高优先级) |
| ~ + - | 按位翻转, 一元加号和减号 (最后两个的方法名为 +@ 和 -@) |
| * / % // | 乘,除,取模和取整除 |
| + - | 加法减法 |
| >> << | 右移,左移运算符 |
| & | 位 'AND' |
| ^ | | 位运算符 |
| <= < > >= | 比较运算符 |
| <> == != | 等于运算符 |
| = %= /= //= -= += *= **= | 赋值运算符 |
| is is not | 身份运算符 |
| in not in | 成员运算符 |
| not and or | 逻辑运算符 |
更多内容:猛戳这里
三、表达式 if ...else 语句
缩进:缩进级别必须保持一致
Tab 键 != 4个空格
IndentationError: expected an indented block 语法错误
实例一:猜数字
ge_of_princal = 56
guess_age = int(input(">>:"))
if guess_age == age_of_princal:
print("yes")
elif guess_age > age_of_princal:
print("太大了,往小的猜")
else:
print("太小了,往大的猜")
实例二:成绩等级划分
score = int(input("score:"))
if score > 90:
print("A")
elif score > 80:
print("B")
elif score > 70:
print("C")
elif score > 50:
print("D")
else:
print("退学吧")
实例三:比较大小
#比较三个数的大小 max_number = 0
number1 = int(input("number1="))
number2 = int(input("number2="))
number3 = int(input("number3="))
if number1 > number2:
max_number = number1
if max_number > number3:
print("最大值为:",max_number)
else:
max_number = number3
print("最大值为:",max_number)
else:
max_number = number2
if max_number > number3:
print("最大值为:",max_number)
else:
max_number = number3
print("最大值为:",max_number)
四、表达式 for 循环
for x in ...:
name=['xp','qa','ws','ed']
x=0
for x in name:
print(x)
执行这段代码,会依次打印 name 的每个元素
xp
qa
ws
ed
比如我们想计算1-100的整数之和,从1写到100有点困难,利用 Python 提供的 range() 函数,可以生成一个整数序列,再通过 list() 函数转换成 list 。
sum=0
x=1
for x in range(101): # range() 函数生成(0,100)整数序列
sum=sum+x #这里一定要注意缩进
print(sum)
range() 函数 可以生成一个整数序列,通过 list() 函数转换成 list (列表)
比如:生成一个数列 [0,1,2,3,4]
list_number=list(range(5))
print(list_number)
代码打印结果:
[0,1,2,3,4]
如果生成1~100之间的奇数怎么实现呢?
for i in range(1,101,2):
if i % 2 ==1:
print("loop:",i)
也可以利用步长来实现:
for i in range(1,101,2):
print("loop:",i)
五、表达式 while 循环
实例:编写一个登陆接口,输入用户名和密码,认证成功后显示欢迎信息;输错三次后程序退出,不能再输入密码。
n = 3
user_name = "li"
pass_name = ""
while n>0:
name = input("请输入用户名:")
password=input("请输入用户名密码:")
if name == user_name and password == pass_name:
print("欢迎进入....")
break
else:
n=n-1
if n==0:
print("该用户名被锁定")
else:
print("密码输入错误,还有", n, "次机会")
while 的另外一种程序,附带解释图
_user = "li"
_passwd = ''
counter = 0
while counter <3:
username = input("Username:")
password = input("Passworld:")
if username == _user and password == _passwd:
print("Welcome %s login...."%_user)
break
else:
print("Invalid username or password!")
counter += 1
else:
print("你行不行啊")
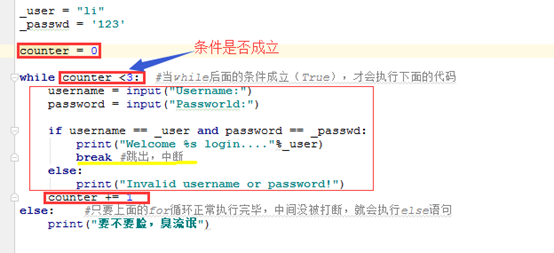
上面程序是利用while循环实现,这里我们用for循环试试
_user_name = "xp"
_user_password = ""
for i in range(3):
user_name = input("User_name:")
user_password = input("User_password:")
if user_name == _user_name and user_password == _user_password:
print("Welcome login....")
break
else:
print("Invalid username or password!")
实例打印1~100之间的偶数部分
#打印1~100之内的偶数部分
even_number = 1
while even_number <= 100:
even_number +=1
if even_number % 2 == 0:
print(even_number)
未完待续........
有什么不对的地方请大家多多指教,相互交流学习。尽量将自己学会的通过博客给大家展示出来,也希望大家不要着急。
大家也可以关注我的博客与我互动学习、交流。
Python 学习第二章的更多相关文章
- python学习第二讲,pythonIDE介绍以及配置使用
目录 python学习第二讲,pythonIDE介绍以及配置使用 一丶集成开发环境IDE简介,以及配置 1.简介 2.PyCharm 介绍 3.pycharm 的安装 二丶IDE 开发Python,以 ...
- python学习第二次笔记
python学习第二次记录 1.格式化输出 name = input('请输入姓名') age = input('请输入年龄') height = input('请输入身高') msg = " ...
- oracle学习 第二章 限制性查询和数据的排序 ——03
这里.我们接着上一小节2.6留下的问题:假设要查询的字符串中含有"_"或"%".又该如何处理呢? 開始今天的学习. 2.7 怎样使用转义(escape)操作符 ...
- Python学习-第二天-字符串和常用数据结构
Python学习-第二天-字符串和常用数据结构 字符串的基本操作 def main(): str1 = 'hello, world!' # 通过len函数计算字符串的长度 print(len(str1 ...
- [Python笔记][第二章Python序列-复杂的数据结构]
2016/1/27学习内容 第二章 Python序列-复杂的数据结构 堆 import heapq #添加元素进堆 heapq.heappush(heap,n) #小根堆堆顶 heapq.heappo ...
- [Python笔记][第二章Python序列-tuple,dict,set]
2016/1/27学习内容 第二章 Python序列-tuple tuple创建的tips a_tuple=('a',),要这样创建,而不是a_tuple=('a'),后者是一个创建了一个字符 tup ...
- [python笔记][第二章Python序列-list]
2016/1/27学习内容 第二章 Python序列-list list常用操作 list.append(x) list.extend(L) list.insert(index,x) list.rem ...
- python学习第二天 -----2019年4月17日
第二周-第02章节-Python3.5-模块初识 #!/usr/bin/env python #-*- coding:utf-8 _*- """ @author:chen ...
- Asp.Net MVC4 + Oracle + EasyUI 学习 第二章
Asp.Net MVC4 + Oracle + EasyUI 第二章 --使用Ajax提升网站性能 本文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/likeli/p/4236723.html ...
随机推荐
- Vue单页面应用
单页面应用指一个系统只加载一次资源,然后下面的操作交互.数据交互是通过router.ajax来进 行,页面并没有刷新:<1>在vue搭建的环境里面怎么有没有公用的css和js? ...
- contenteditable设置元素可编辑
需求背景 实现一个输入框,高度可以随着输入文字的增加而自动增高 有placeholder,输入为空时,显示placeholder 我们知道可以将div的contenteditable设置伪true,将 ...
- ubuntu samba共享后windows读写文件都是以nogroup问题
添加smb账号 sudo smbpasswd -a xxx 如果报错:Failed to add entry for user xxx 则是因为这个账号不存在 添加成功以后,过一会就可以重新登陆了(u ...
- 【linux轻松学】修改文件权限
用chmod修改文件权限,此命令非常重要. 用户范围:u 表示当前用户g 表示当前群组o 除u,g之外的用户和群组a 所有用户和群组 权限代号:r :读,用数字4表示w :写,用数字2表示x :执行, ...
- java web各个技术细节总结
HTML 非表单标签 1.b 粗体 u 下划线 i 斜体 del 删除效果 2.a 超链接 href target=-blank 3.img 图片 4.frameset(frame) 框架 ...
- 链栈的基本操作(C语言)
栈的链式储存结构称为链栈.链栈的节点类型与链式线性表的节点类型 定义相同,不同的是它是仅在表头进行操作的单链表.链栈通常用不带头节 点的单链表来实现,栈顶指针就是链表的头指针 ,如图所示: 代码如下: ...
- sql在最后一行添加合计
select nvl(sno,'合计') sno,sum(score) score from sc group by rollup(sno);
- sqlserver中如何将mdf文件还原到数据库
- zookeeper 单机集成部署
概述 ZooKeeper是一个分布式的,开放源码的分布式应用程序协调服务,它包含一个简单的原语集,分布式应用程序可以基于它实现同步服务,配置维护和命名服务等,是很多分布式的基础设置,比如dubbo,k ...
- Win7 VS2015环境使用SDL2-2.0.4
之前在VS中使用SDL2,如果只链接SDL2.lib,会提示 error LNK2019: unresolved external symbol _main referenced in functio ...
