touch事件的分发和消费机制
Android 中与 Touch 事件相关的方法包括:dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)、onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)、onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev);能够响应这些方法的控件包括:ViewGroup、View、Activity。继承ViewGroup的大多是容器控件,如LinearLayout等,而继承View的大部分是显示控件比如TextView,ImageView等(当然,ViewGroup本身是继承View的),显示控件没有onInterceptTouchEvent。
来看一些例子。
情形1
package com.example.toucheventdemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
public class MainActivity extends Activity
{
private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)
{
switch (ev.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_UP");
break;
}
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
{
switch (event.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_UP");
break;
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}
日志信息:

可以看到:总是先执行dispatchTouchEvent,再执行onTouchEvent.。
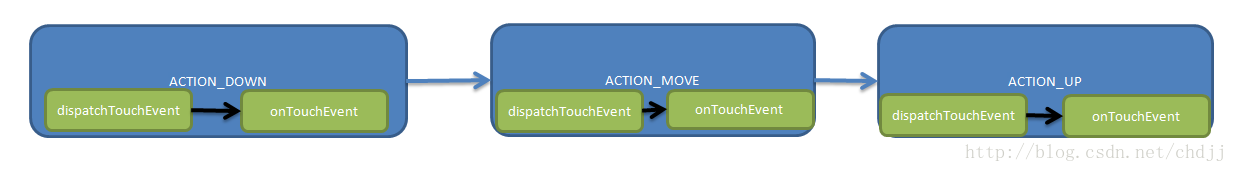
情形2:

package com.example.toucheventdemo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MyButton extends Button
{
private static final String TAG = "MyButton";
public MyButton(Context context)
{
super(context);
}
public MyButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)
{
switch (ev.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_UP");
break;
}
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
{
switch (event.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_UP");
break;
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}
mainActivity代码如下:
package com.example.toucheventdemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
public class MainActivity extends Activity
{
private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
private MyButton but = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); but = (MyButton) findViewById(R.id.but);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)
{
switch (ev.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_UP");
break;
}
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
{
switch (event.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_UP");
break;
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
} }
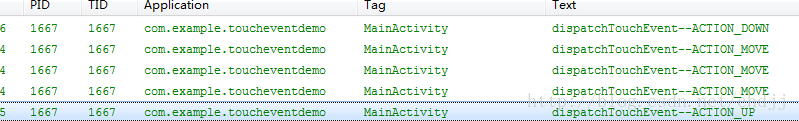
此时点击Button按钮,查看日志:

执行流程是首先由activity捕获到ACTION_DWON事件,然后调用activity的dispatchTouchEvent,接着绕开activity的onTouchEvent直接将事件传递给子控件,调用MyButton的dispatchTouchEvent,在之后调用该控件的onTouchEvent,ACTION_UP事件也是一样的流程。

情形4:
跟情形2类似,将情形3的activity的DispatchTouchEvent的返回值改为true,点击按钮,很显然,touch事件将不会被分发给Button,所以点击按钮日志是这样的:
日志信息:

情形5:
将情形3的myButton的DispatchTouchEvent的返回值改为true,点击按钮,很显然,当touch事件传递到button时,先被dispatchTouchEvent捕获,由于返回true,所以事件被消费,便不往下面传递,所以Button的onTouchEvent方法不被调用。
日志信息:


package com.example.toucheventdemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.View.OnTouchListener;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener,OnTouchListener
{
private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
private MyButton but = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); but = (MyButton) findViewById(R.id.but);
but.setOnClickListener(this);
but.setOnTouchListener(this);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)
{
switch (ev.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_UP");
break;
}
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
{
switch (event.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_UP");
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
Log.i("MyButton","ONCLICK");
}
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event)
{
switch (event.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.i("MyButton","onTouch--ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i("MyButton","onTouch--ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.i("MyButton","onTouch--ACTION_UP");
break;
}
return false;
}
}
现在点击按钮日志打印如下信息:
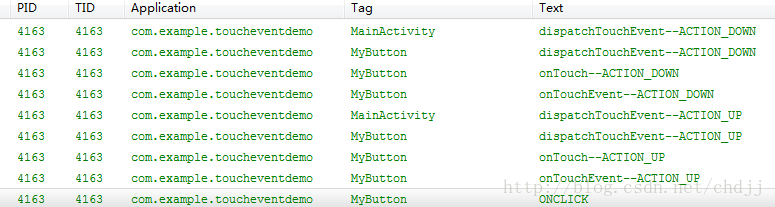
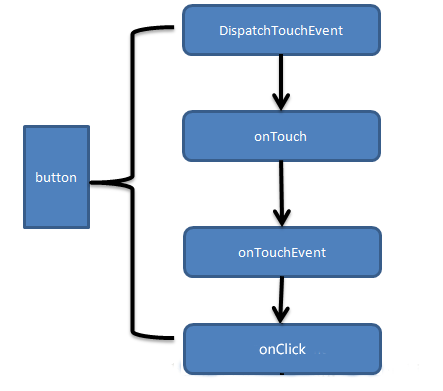
首先touch事件由activity捕获,调用activity的dispatchTouchEvent,紧接着调用Button的dispatchTouchEvent继续分发touch事件,接着并没有调用button的onTouchEvent,而是先调用了onTouch方法,这是因为button按钮注册了onTouchListener的缘故,待onTouch事件处理完之后,由于返回值为false,所以touch事件传递给了button的onTouchEvent。接着ACTION_UP事件也是类似的过程,但当Button的onTouchEvent结束后,还调用了Onclick方法。
情形8:

case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0;
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0 || prepressed) {
// take focus if we don't have it already and we should in
// touch mode.
boolean focusTaken = false;
if (isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused()) {
focusTaken = requestFocus();
}
if (prepressed) {
// The button is being released before we actually
// showed it as pressed. Make it show the pressed
// state now (before scheduling the click) to ensure
// the user sees it.
setPressed(true);
}
if (!mHasPerformedLongPress) {
// This is a tap, so remove the longpress check
removeLongPressCallback();
// Only perform take click actions if we were in the pressed state
if (!focusTaken) {
// Use a Runnable and post this rather than calling
// performClick directly. This lets other visual state
// of the view update before click actions start.
if (mPerformClick == null) {
mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
}
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {
performClick();
}
}
}
if (mUnsetPressedState == null) {
mUnsetPressedState = new UnsetPressedState();
}
if (prepressed) {
postDelayed(mUnsetPressedState,
ViewConfiguration.getPressedStateDuration());
} else if (!post(mUnsetPressedState)) {
// If the post failed, unpress right now
mUnsetPressedState.run();
}
removeTapCallback();
}
break;
在ACTION_UP分支上执行了click操作,具体由performClick方法执行:
public boolean performClick() {
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED);
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnClickListener != null) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK);
li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this);
return true;
}
return false;
}
情形9:
package com.example.toucheventdemo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
public class MyLinearLayout extends LinearLayout
{
private static final String TAG = "MyLinearLayout";
public MyLinearLayout(Context context)
{
super(context);
}
public MyLinearLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
super(context, attrs);
} @Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
{
switch (event.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.i(TAG,"onTouchEvent--ACTION_UP");
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
} @Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)
{
switch (ev.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.i(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent--ACTION_UP");
}
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
} @Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)
{
switch (ev.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.i(TAG,"onInterceptTouchEvent--ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.i(TAG,"onInterceptTouchEvent--ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.i(TAG,"onInterceptTouchEvent--ACTION_UP");
}
return super.onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
} }
此时再点击按钮,查看日志:

可以看到,由于加了一层容器控件,所以activity执行完dispatchTouchEvent之后将touch事件分发给容器控件MyLinearLayout,紧接着并不是直接将touch事件传递给button,而是先执行了onInterceptTouchEvent,这个方法返回false,并没有拦截touch事件,所以接下来会将touch事件传递给button。


- 隧道方式:从根元素依次往下传递直到最内层子元素或在中间某一元素中由于某一条件停止传递。
- 冒泡方式:从最内层子元素依次往外传递直到根元素或在中间某一元素中由于某一条件停止传递。

touch事件的分发和消费机制的更多相关文章
- Android事件分发机制(一) Touch 事件的分发和消费机制
Android 中与 Touch 事件相关的方法包括:dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev).onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev). ...
- Android 编程下 Touch 事件的分发和消费机制
Android 中与 Touch 事件相关的方法包括:dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev).onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev). ...
- Touch 事件的分发和消费机制
Android 中与 Touch 事件相关的方法包括:dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev).onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev). ...
- Android 编程下Touch 事件的分发和消费机制
1.事件分发:public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) Touch 事件发生时 Activity 的 dispatchTouchEvent(M ...
- 事件之Touch 事件的分发和消费机制
Android 中与 Touch 事件相关的方法包括:dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev).onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev). ...
- Android 编程下Touch 事件的分发和消费机制和OnTouchListener,OnClickListener和OnLongClickListener的关系
1.事件分发:public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) Touch 事件发生时 Activity 的 dispatchTouchEvent(M ...
- 通俗理解Android事件分发与消费机制
深入:Android Touch事件传递机制全面解析(从WMS到View树) 通俗理解Android事件分发与消费机制 说起Android滑动冲突,是个很常见的场景,比如SliddingMenu与Li ...
- View,ViewGroup的Touch事件的分发机制
原帖地址:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming/article/details/21696315 ViewGroup的事件分发机制 我们用手指去触摸Android手机屏幕,就会 ...
- Andriod 从源码的角度详解View,ViewGroup的Touch事件的分发机制
转自:xiaanming的博客(http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming/article/details/21696315) 今天这篇文章主要分析的是Android的事件分发机制, ...
随机推荐
- idea 项目添加web支持
选中项目添加 add - web
- 软链接ln -s以及如何解决其产生“Too many levels of symbolic links ”的错误?
Q1:如何利用ln -s来创建快捷方式? A1:ln(link,链接文件): Windows中的快捷方式,实际上快捷方式和它指向的文件是独立的两个文件,两个都占硬盘空间,只不过用户访问快捷方式时,其效 ...
- Emacs文件命令
[文件]----------------------------------------C-x C-f 读取文件到Emacs C-x r 只读的方式打开一个文件C-x C-q 清除一个窗口的只读属性 ...
- django 错误之 ImportError: No module named **
今天测试django的时候出了点问题,被坑惨了. D:\pythonCode\django\mysite>django-admin.py startproject mysite 然后创建APP ...
- kali Rolling安装之后的一些常用配置总结(更新)
原文: https://ssooking.github.io/kali-rolling-an-zhuang-zhi-hou-de-yi-xie-chang-yong-pei-zhi-zong-jie/ ...
- java---简单的ATM存取系统,
新手练手必备~ 密码账户为: 先创建账户类: package cn.Atm; /** * @author 偶my耶 */ import java.io.*; import com.project.pr ...
- Mysql 根据时间统计总数
代码写法: SELECT date_format(examinee_pay_time, '%Y-%m-%d') as payDate, COUNT(examinee_id) As realityApp ...
- [转]Oracle trunc()函数的用法
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/gengaixue/archive/2012/11/21/2781037.html 1.TRUNC(for dates) TRUNC函数为指定元 ...
- Python3 串口模块移植并使用。
想通过 Python去控制串口模块,直接上层就使用一门语言,这样虽然执行效率低一些,但是开发速度加快 通过 buildroot 先移植 Python-serial 模块 x Symbol: BR2_P ...
- 键盘 Input子系统
应用层测试代码 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <li ...
