C++Primer第五版——习题答案详解(五)
习题答案目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mered1th/p/10485695.html
第6章 函数
练习6.4
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int fact(int x) {
if (x == 1) return x;
else return x * fact(x - 1);
}
int main() {
int x;
cout << "Please input a number:\n";
while (cin >> x) {
int ans = fact(x);
cout << ans << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.5
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int abs(int x) {
return x >= 0 ? x : (-x);
}
int main() {
int x;
cout << "Please input a number:\n";
while (cin >> x) {
cout << abs(x) << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.7
size_t count_calls(){
static size_t ctr=0;
return ctr++;
}
练习6.10
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int *x, int *y) {
int temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
int main() {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
cout << x << y << endl;
swap(x, y);
cout << x << y << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.12
void swap(int &x, int &y) {
int temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
练习6.17
不相同,因为转大写需要修改传入的字符串需要加&
#include<iostream>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
bool is_upper(const string s) {
for (auto i : s) {
if (isupper(i)) return true;
}
return false;
}
void to_upper(string &s) {
for (auto &i : s) {
i = toupper(i);
}
}
int main() {
string s = "abdcedA";
if (is_upper(s)) cout << "is upper" << endl;
else cout << "Not upper" << endl;
to_upper(s);
cout << s << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.18
bool compare(matrix &a, matrix &b);
vector<int>::iterator change_val(int a, vector<int>::iterator);
练习6.19
a.不合法
b.合法
c.合法
d.合法
练习6.21
#include<iostream>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int Big(int x, int *y) {
return x > *y ? x : *y;
}
int main() {
int x = 3, y = 2;
cout << Big(x, &y) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.22
函数传参必须加引用,不加结果不正确。
#include<iostream>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void swap(int *&x, int *&y) {
int *temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
int main() {
int x = 3, y = 2;
int *px = &x, *py = &y;
swap(px, py);
cout << x << ", " << y << endl;
cout << *px << ", " << *py << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
6.23
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void print(const int *pi) {
cout << *pi << endl;
}
void print(const int *beg, const int *end) {
while (beg != end) {
cout << *beg++ << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void print(const int ia[], size_t size) {
for (size_t i = 0;i != size;i++) {
cout << ia[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void print2(const int (&arr)[2]) {
for (size_t i = 0;i != 2;i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
int i = 0, j[2] = { 0,1 };
print(&i);
print(begin(j), end(j));
print(j, 2);
print2(j);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.24
如果数组大小小于10,会造成数组越界。除此以外数组不能复制成形参。改成指针或引用。
练习6.25
用命令行当做输入,输入的argv[0]保存程序的名字,后面的才是实参
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char const **argv)
{
cout << argv[1] << endl;
cout << argv[2] << endl;
cout << string(argv[1])+string(argv[2]) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.26
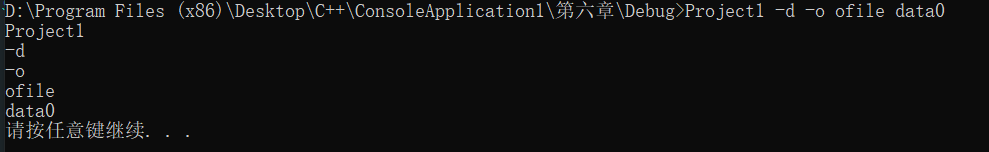
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char const **argv)
{
for (int i = 0;i < argc;i++) {
cout << argv[i] << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.27
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<initializer_list>
using namespace std;
int count_Sum(initializer_list<int> il) {
int sum = 0;
for (auto beg = il.begin();beg != il.end();beg++) {
sum += *beg;
}
return sum;
}
int main(int argc,char const **argv)
{
cout << count_Sum({ 1,2,3,4,5 }) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.28
string类型
练习6.29
如果实参个数多且占用容量大,用引用更好。
练习6.31
返回的引用是局部对象的引用时无效;返回的常量引用是局部常量对象的引用时。
练习6.32
合法,将数组重置为0-9
练习6.33
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void print(vector<int>::iterator vec_begin, vector<int>::iterator vec_end) {
if (vec_begin != vec_end) {
cout << *vec_begin << " ";
return print(++vec_begin, vec_end);
}
}
int main(int argc,char const **argv)
{
vector<int> vec = { 1,2,3,4,6 };
print(vec.begin(), vec.end());
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.34
如果传入的参数小于0,会一直调用不停止
练习6.35
会一直调用本身,无限循环
练习6.36
string (&fun(int i)[10];
练习6.39
a.合法
b.不合法
c.合法
练习6.40
a.正确
b.错误,一旦某个形参被赋予了默认值,它后面的所有形参都必须有默认值
练习6.41
a.非法,第一个形参没有默认值,必须给实参
b.合法
c.合法,'*'转换为整形
练习6.42
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
string make_plural(size_t ctr, const string &word, const string &ending = "s") {
return (ctr > 1) ? word + ending : word;
}
int main()
{
cout << make_plural(2, "success", "es") << endl;
cout << make_plural(2, "failure") << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.43
a.放在头文件中,内联函数在程序中多个定义必须完全一致。
b.放在头文件中,函数声明。
练习6.44
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
inline bool isShorter(const string &s1, const string &s2) {
return s1.size() < s2.size();
}
int main()
{
string s1 = "abc", s2 = "abcd";
cout << isShorter(s1, s2) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.46
不能,返回值不是常量表达式
练习6.47
在项目属性中设置命令行/DNDEBUG就不会出现 #ifndef....#endif、assert中的内容。
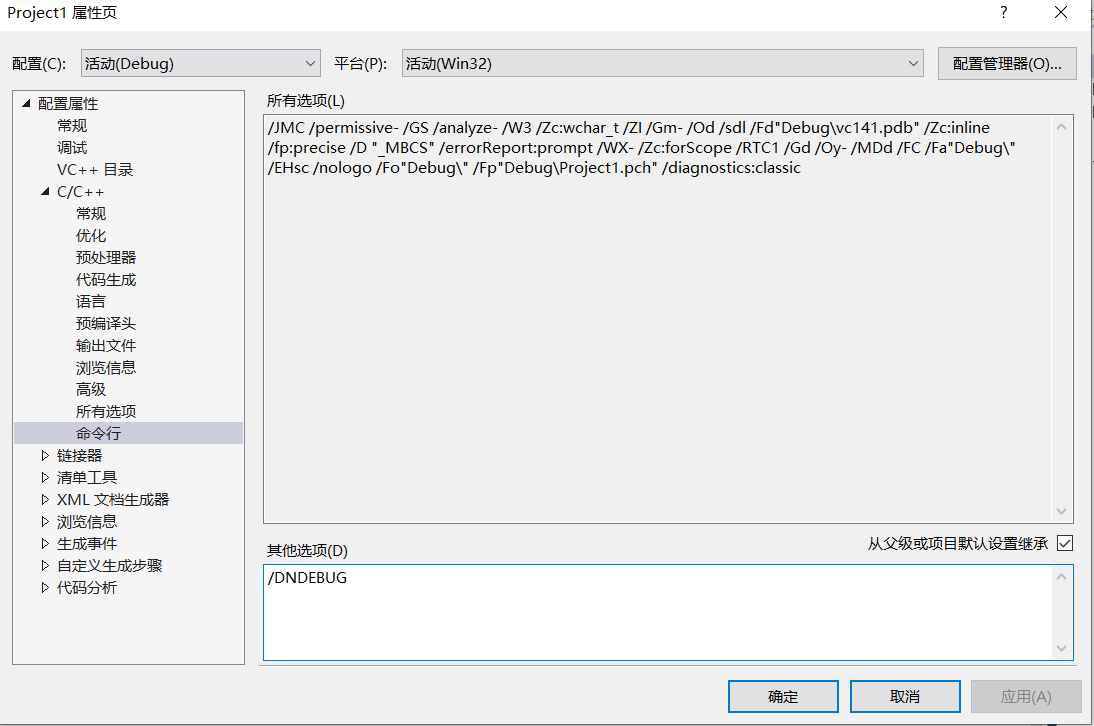
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<cassert>
using namespace std;
void read_vi(vector<int>::const_iterator iterator_begin, vector<int>::const_iterator iterator_end) {
#ifndef NDEBUG
cerr << iterator_end - iterator_begin << __func__ << " " << __FILE__ << " "
<< __LINE__ << " " << __TIME__ << " " << __DATE__ << endl;
#endif // !NDEBUG
if (iterator_begin != iterator_end) {
cout << *iterator_begin << " ";
return read_vi(++iterator_begin, iterator_end);
}
else {
cout << endl;
return;
}
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
read_vi(v.begin(), v.end());
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6.48
合理,输入结束时终止程序
练习6.50
a.非法,二义性
b.匹配void f(int)
c.匹配void f(int,int)
d.匹配void f(double,double)
练习6.53
a.合法
b.合法
c.不合法,重复定义
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int calc(int&, int&);
int calc(const int&, const int&);
char calc2(char*, char*);
char calc2(const char*, const char*);
int calc3(char*, char*);
int calc3(char* const, char* const);
int main()
{
calc(1, 2);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int calc(int&a, int&b) {
return a + b;
}
int calc(const int&a, const int&b) {
return a + b;
}
char calc2(char *a, char *b) {
return *a;
}
char calc2(const char *a, const char *b) {
return *a;
}
int calc3(char *a, char *b) {
return a - b;
}
int calc3(char* const a, char* const b) {
return a - b;
}
练习6.54
vector<int(*)(int, int)> vf;
练习6.55
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
int sub(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
int multi(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
int divide(int a, int b) {
return a / b;
}
int main()
{
vector<int(*)(int, int)> vf{ add,sub,multi,divide };
for (const auto e : vf) cout << e(4, 2) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
C++Primer第五版——习题答案详解(五)的更多相关文章
- C++Primer第五版——习题答案详解(一)
习题答案目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mered1th/p/10485695.html 第1章 开始&&第2章 变量和基本类型 练习1.3 #include&l ...
- C++Primer第五版——习题答案详解(二)
习题答案目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mered1th/p/10485695.html 第3章 字符串.向量和数组 练习3.2 一次读入一整行 #include<iost ...
- C++Primer第五版——习题答案详解(三)
习题答案目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mered1th/p/10485695.html 第4章 表达式 练习4.10 while(cin>>i&&i ...
- C++Primer第五版——习题答案详解(四)
习题答案目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mered1th/p/10485695.html 第5章 语句 练习5.9 #include<iostream> #inclu ...
- C++Primer第五版——习题答案详解(六)
习题答案目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mered1th/p/10485695.html 第7章 类 练习7.1 class Sales_data { public: std:: ...
- C++Primer第五版——习题答案详解(七)
习题答案目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mered1th/p/10485695.html 第8章 IO库 练习8.1 istream &iofunc(istream &a ...
- C++Primer第五版——习题答案详解(八)
习题答案目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mered1th/p/10485695.html 第9章 顺序容器 练习9.1 a.list,需要按字典序插入,可能插入位置在中间 b.d ...
- C++Primer第五版——习题答案详解(九)
习题答案目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mered1th/p/10485695.html 第10章 泛型算法 练习10.1 #include<iostream> #i ...
- C++Primer第五版——习题答案详解(十)
习题答案目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mered1th/p/10485695.html 第11章 关联容器 练习11.3 #include<iostream> #i ...
随机推荐
- MySQL 导出用户权限
Version <= 5.6 #!/bin/bash #Function export user privileges source /etc/profile pwd=****** expgra ...
- Hive入门学习
Hive学习之路 (一)Hive初识 目录 Hive 简介 什么是Hive 为什么使用 Hive Hive 特点 Hive 和 RDBMS 的对比 Hive的架构 1.用户接口: shell/CLI, ...
- vsCode---中文化
一直使用的是webStorm这个工具,不过由于这个工具不是那么的方便:比如我平时只是想新建一个html页面来编写一些js代码,以便测试自己的想法. 但是webStorm这个工具需要新建项目然后npm运 ...
- day057 基于对象和基于双下划线的多表查询
单表查询和多表查询的添加与查询 上述关系:author-authordetail是一对一的关系(外键在author上名为authors), book-publis ...
- POST形式 soapUI调用WebService的restful接口,传入json参数,并且返回json
第一次使用POST形式传JSON字符串,怎么都调不到后台方法,只是因为注解没加对…… CXF的WebService接口类 package com.zit.webservice.main; import ...
- C语言函数的存储类别
函数默认的隐含存储类型是extern auto:只能用于局部变量 extern:允许被其他文件调用 static:只能被本源程序文件调用
- scrapy框架初级
scrapy入门教程:https://scrapy-chs.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/0.24/intro/tutorial.html 一.安装 python模块网站,应用文件放置在s ...
- 数组的高级API-sort
按升降序排列数组项.本身存在的问题:只能通过第一位排列.解决方法:通过回调函数进行规制设置. a - b 升序. b - a 降续. 其内部运用了冒泡排序 <!DOCTYPE html> ...
- Fragment跳转至Activity片段随笔
首先需要了解Fragment的生命周期 @Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, ...
- 使用vector<vector<int>>实现的一个二维数组
本文为大大维原创,最早于博客园发表,转载请注明出处!!! 1 #include<iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; ...
