阿里2021年春季实习笔试题(最后一道大题)(2020 China Collegiate Programming Contest, Weihai Site) (C. Rencontre codeforces.com/gym/102798)
实验室的慕师弟phd马上要毕业了,正准备先找个实习,投了阿里2021年春季实习的招聘,遇到最后一道编程大题没有思路事后找到了该题的最原始出处,即
2020 China Collegiate Programming Contest, Weihai Site,(https://ccpc.io/)
后来在codeforces上发现了原题: https://codeforces.com/gym/102798/problem/C
于是花了半天多时间,在看了解析后给出了python3的代码。
================================================
原题如下:
2 seconds
1024 MB
standard input
standard output
Located at the easternmost tip of Shandon Peninsula, Weihai is one of the most famous tourist destinations all over China. There are beautiful hills, seas, bays, springs, islands, and beautiful beaches in Weihai. It is also a coastal city abundant in seafood, including prawn, sea cucumber, abalone, shellfish, and algae.
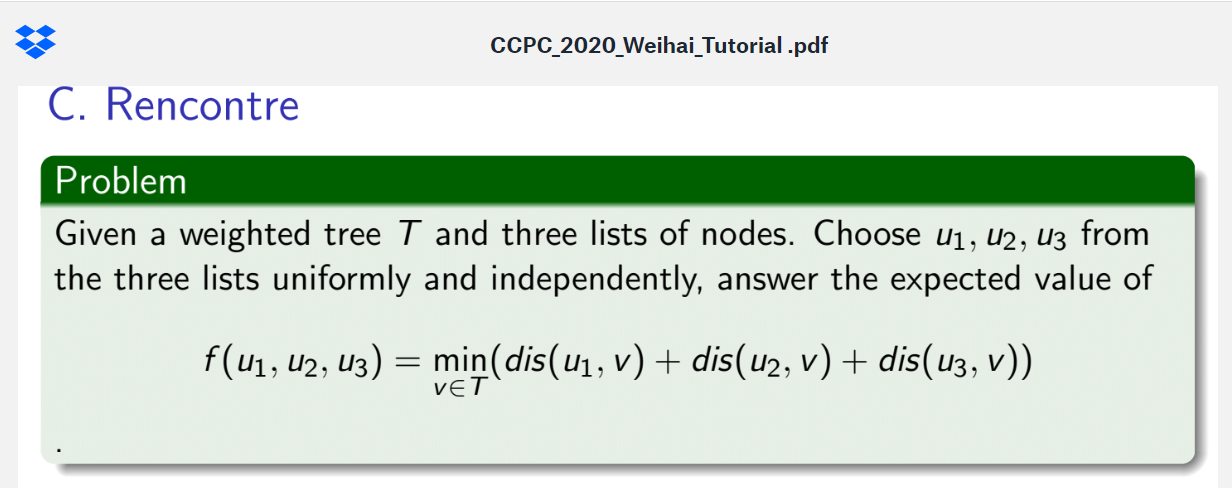
Attracted by the distinctive scenery and pleasant environment, three theoretical computer scientists plan to have a trip to Weihai. However, they cannot reach a consensus on accommodation, since some people prefer some hotels while other people like others. They decide to stay in possibly different hotels at night and meet in one hotel the next day. The hotel they meet may not necessarily be one of the hotels they stay in.
There are some roads connecting the hotels in Weihai. The roads are specially designed such that there is a unique path between every pair of hotels. Every theoretical computer scientist has prepared a list of candidate hotels before their trip starts. When they arrive in Weihai, each of them will uniformly and independently choose one hotel from the candidate hotel list. Also, they will meet in a hotel such that the total length of their routes is minimized. As a member of the theoretical computer science group, can you tell the expected total length of their routes?
The first line of the input contains a single integer nn (1≤n≤200000)(1≤n≤200000), denoting the number of hotels in Weihai. Then follow n−1n−1 lines, describing the roads connecting the hotels. Each of the n−1n−1 lines contains three integers u,v,wu,v,w (1≤u,v≤n,u≠v,1≤w≤1000)(1≤u,v≤n,u≠v,1≤w≤1000), denoting a road of length ww connecting the hotels numbered uu and vv. It is guaranteed that there is a unique path between every pair of hotels.
The last three lines of the input specify the candidate hotel lists, one for each theoretical computer scientist. Each line begins with a single integer mm (1≤m≤n)(1≤m≤n) and mm distinct integers a1,a2,⋯,ama1,a2,⋯,am (1≤ai≤n)(1≤ai≤n), meaning that the candidate hotel list contains the hotels numbered a1,a2,⋯,ama1,a2,⋯,am.
Print the expected total length of their routes within an absolute or relative error of no more than 10−6 .
==================================================


====================================================
3
1 2 1
2 3 2
1 1
1 2
1 3
3
5
1 2 3
1 3 5
2 4 7
2 5 11
3 2 4 5
4 1 2 3 5
2 1 3
13.958333333333
===========================================
这题研究了好久也没有什么靠谱的思路,于是寻找了一下题解:
https://www.dropbox.com/s/sledygvxfcqijv2/CCPC_2020_Weihai_Tutorial%20.pdf?dl=0


===================================================
这个题的第一个难点就是能分析出这n个宾馆以及宾馆之间的n-1条连接线所构成的连接所需使用的数据结构应该是图,也就是说我们首先需要确定code时所使用的数据结构。
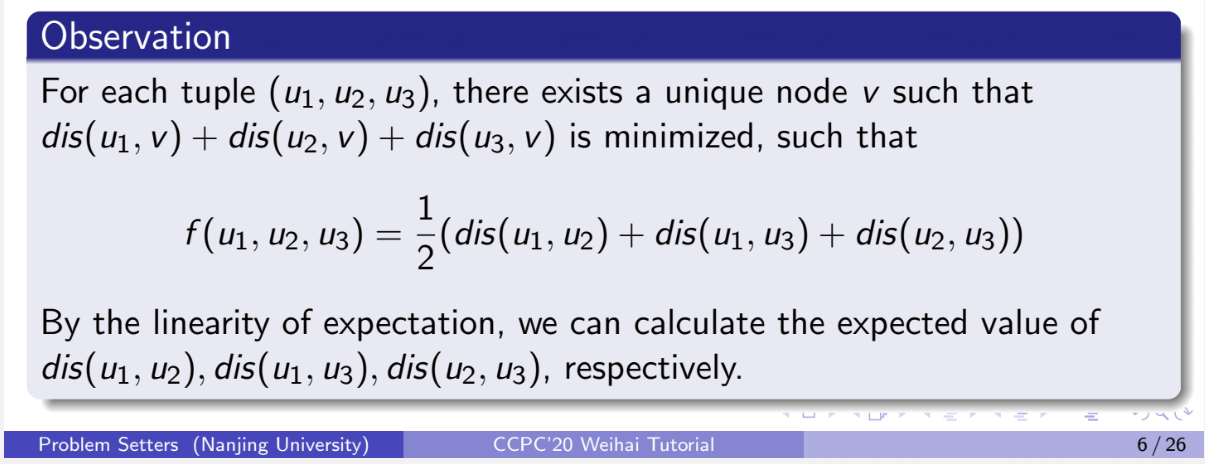
第二个难点就是要知道到一个图上的某三点的距离和的最短距离(从图上某点出发到固定三点的和的最小值)其实就是这三个固定点所组成的最小子图的总长。因为一共有n个宾馆,而这n个宾馆是有n-1个路径所连接的,而且两个宾馆如果有一条线连接的话则只有这一条线连接,这也就说明两个点之间的路径(不走重复路的情况)是唯一的。
图上的三个点(宾馆,红色点)可以看做是两种拓扑结构的子图,如下:

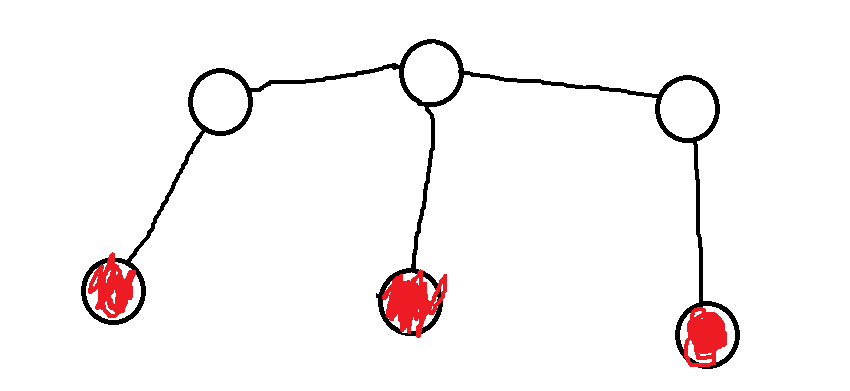
不难发现这两种结构下,子图上到这三个红点的最短路径和其实就是这个子图的所有路径之和。上面第一个图中到这个三个点路径之和最短的点就是中间的红点,上面第二个图中到这三个点最短的路径和就是中间红点上面直连的那个点,也是同时在左右两个红线相连接的那个非红色点。
不管哪种结构,到三个点距离之和的最小值就是三个点连通的最小子图内所有路径之和。但是我们难以计算最小子图到底是哪个,同时又因为图的结构性(没有回路),两点之间在不走重复路径的情况下路径是唯一的,那么这个最小连通子图也是唯一的,而这个子图的所有路径之和其实又可以表示为这三个点中任意两点距离之和的一半,也就是:
原问题:
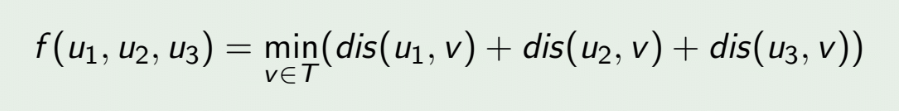
转换为:
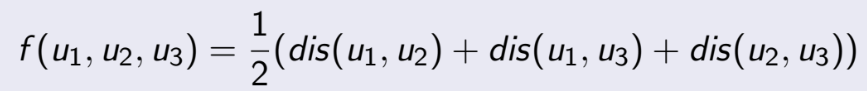
第三个难点: 把计算两点距离的期望转换计算两点之间所有连通的两点间距离的期望之和。
如何计算点u1, u2之间的距离也是一个极为困难的问题。
计算f的期望可以变成计算dis(u1,u2), dis(u1, u3), dis(u2, u3) 的期望之和的1/2。
如果u1所属的集合和u2所属的集合较大我们是无法使用穷举法来计算没两个点之间的距离的,这时候我们发现图上任意两点的组合虽然很多,甚至在点数量较多时是海量的,但是不管这些组合有再多每个组合(每种两点点路径)所经历过的路径(两点间直连的线段)的集合都是固定的,即图中的n-1条连接,那么我们可不可以把计算图上某些点之间的路径期望转换为计算图上这n-1条线段的期望呢。这样就解决了海量计算的问题,直接计算某条线段出现的概率而不是穷举的逐次计算路径的期望,这也是有些类似动态规划的做法,就是避免重复计算,以免出现海量计算和存储的问题。
因为 dis(u1,u2) 与 dis(u2,u3) , dis(u1,u3) 之间是独立的不相关的:
E(f) = 1/2 * ( E(dis(u1, u2) + E(dis(u2, u3) + E(dis(u2, u3) )
意思就是说(u1,u2)之间的连接不影响(u2, u3)之间的连接。
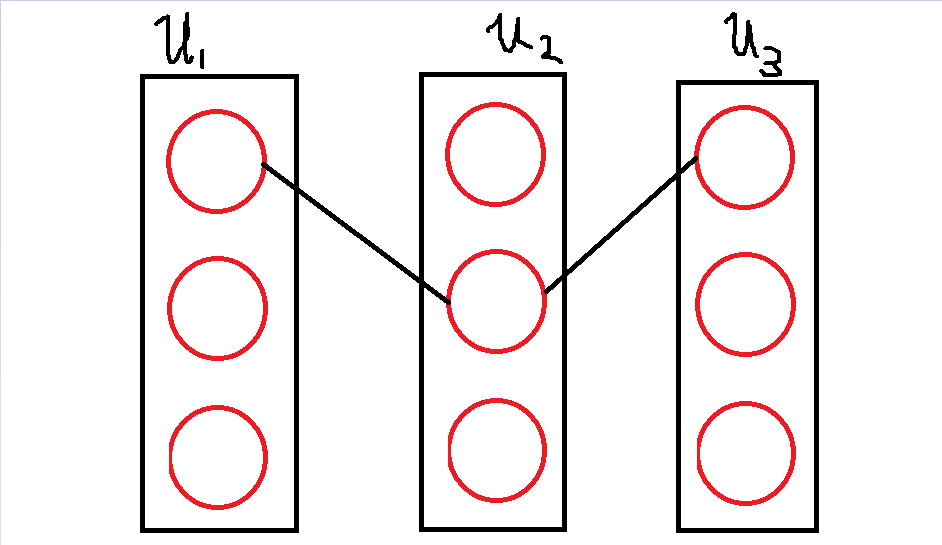
同理,dis(u1, u2)的期望也可以用u1,u2之间路径上任意两点之间的直连线段的期望和来表示。
这里我们先考虑一条线段为u1,u2路径上的一段的情况:
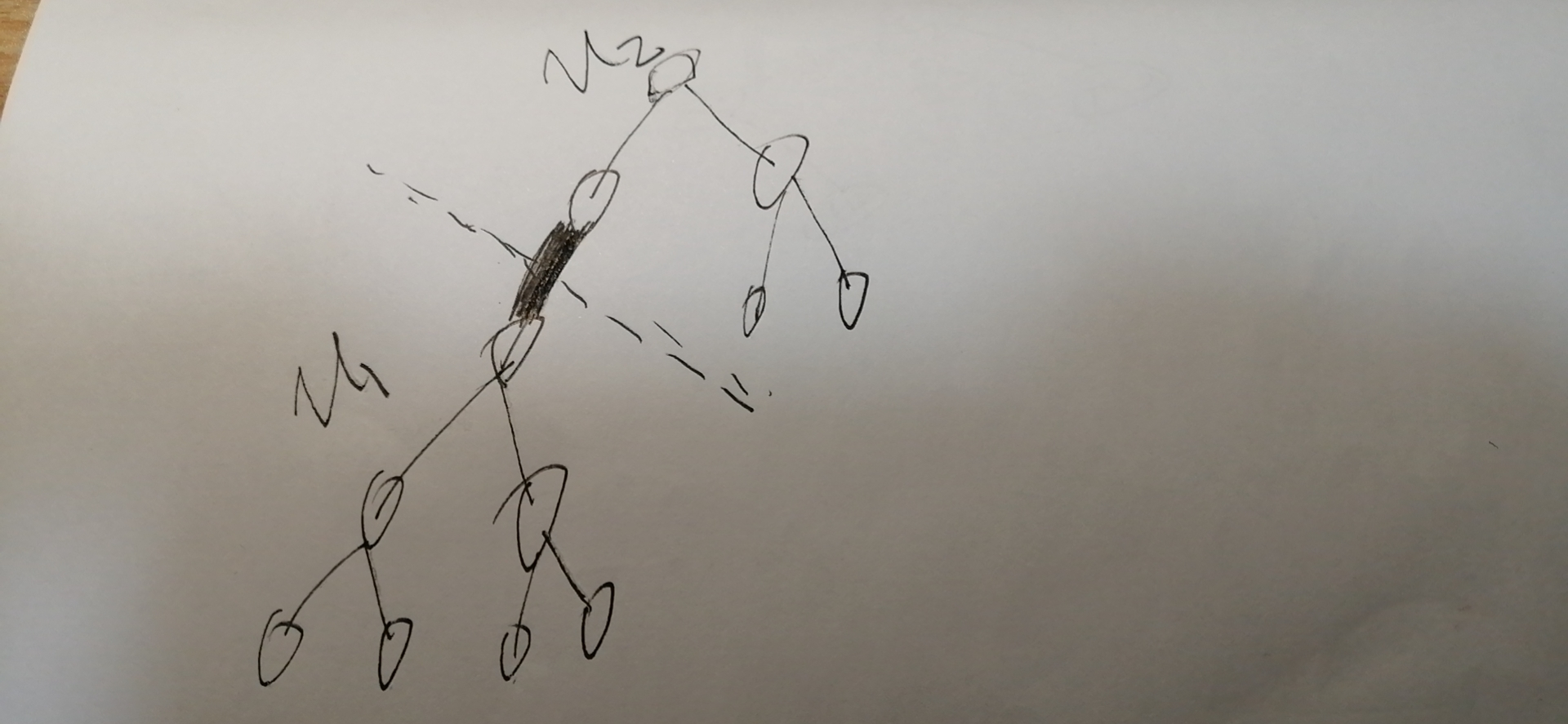

上图加粗的那个线段就是我们要计算期望的那条线段。那条线段把整个图隔成了两个子图,如果这个线段为u1,u2路径上的一部分,那么必有u1,u2分别属于两个子图。
也就是说u1在图左下部分,u2在图右上部分,也或者是u1在图右上部分,u2在图左下部分, 这里我们以u1在图左下部分,u2在图右上部分举例。
图左下部分共7个点,假设u1可能为这7个点中的三个,而总的u1待选个数假设为5,那么在整个图中u1在左下图的可能性为3/5,
也就是:
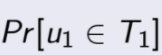
右上部分图共5个点,假设右上部分可能为u2的点为2个,而u2的总个数为4, 那么u2出现在右上部分图的可能性为2/4 ,也就是:
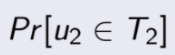
那么上图加粗那条线段在u1存在于左下图,u2存在于右上图的概率为:
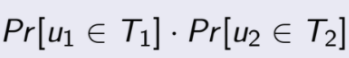
那么上图加粗那条线段在整个计算dis(u1,u2)期望中出现的概率为:
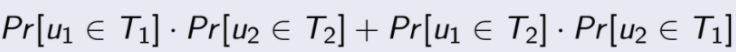
该种情况下,该条线段的期望为:
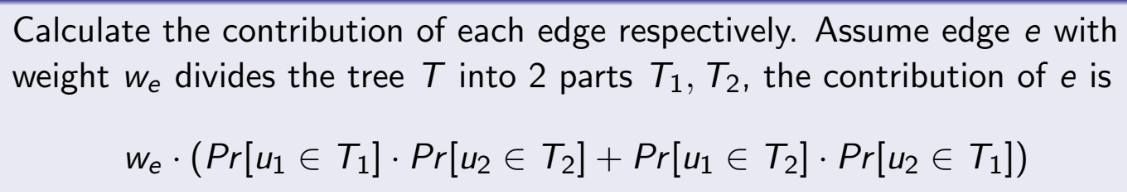
这样整个问题也就突然明晰了,原问题变成了计算每个线段的期望,线段的大小是已知的,出现的概率分别为p(u1,u2)+p(u2,u3)+p(u1,u3),
p(u1,u3)为该线段属于u1,u3之间的概率。
为了减少内存的占有及计算开销我们对所有节点都只进行一次遍历,在遍历的同时计算出两点间线段出现的概率及期望。这里使用深度优先遍历。由于每个节点我们都要计算出节点下面连接的节点有哪些因此深度优先更能节省内存。

========================================================
给出个人的python代码:
###
answer = 0
route_weight = {} #per route weight , route is the length that from v1 to v2,
graph = {}
u1_set = None
u2_set = None
u3_set = None
def init():
global u1_set, u2_set , u3_set
hotels_num = int(input())
if hotels_num == 1:
return 0
for _ in range(hotels_num-1):
route = [int(i) for i in input().split()]
if route[0]>route[1]:
route[0], route[1] = route[1], route[0]
route_weight[(route[0], route[1])] = route[2] #set route weight dict
graph.setdefault(route[0], []).append(route[1]) #set graph dict
u1_set = set([int(i) for i in input().split()][1:]) #set user1 candidate hotels
u2_set = set([int(i) for i in input().split()][1:]) #set user2 candidate hotels
u3_set = set([int(i) for i in input().split()][1:]) #set user3 candidate hotels
"""
print(route_weight)
print(graph)
print(u1_set)
print(u2_set)
print(u3_set)
""" def sum_weight(node_tuple, node_set):
global answer
w = route_weight[node_tuple] u1_T1 = len(u1_set.intersection(node_set))
u1_T2 = len(u1_set) - u1_T1 u2_T1 = len(u2_set.intersection(node_set))
u2_T2 = len(u2_set) - u2_T1 u3_T1 = len(u3_set.intersection(node_set))
u3_T2 = len(u3_set) - u3_T1 p12 = u1_T1/len(u1_set) * u2_T2/len(u2_set) + u1_T2/len(u1_set) * u2_T1/len(u2_set)
p23 = u2_T1/len(u2_set) * u3_T2/len(u3_set) + u2_T2/len(u2_set) * u3_T1/len(u3_set)
p13 = u1_T1/len(u1_set) * u3_T2/len(u3_set) + u1_T2/len(u1_set) * u3_T1/len(u3_set) #print(node_tuple)
#print(p12, p23, p13)
answer += w*(p12+p23+p13) def depth_search(node):
"""node: input number"""
after_nodes = graph[node]
history_nodes = {} for after_n in after_nodes:
if after_n in graph: #not end node
history_nodes[after_n] = depth_search(after_n)
else: #end node
history_nodes[after_n] = set([after_n])
#print(node, after_n, history_nodes[after_n])
sum_weight((node, after_n), history_nodes[after_n]) all_set = set()
for s in history_nodes.values():
all_set.update(s)
#print(s, all_set)
all_set.add(node)
#print(all_set)
return all_set if __name__=="__main__":
init()
depth_search(1)
print(0.5*answer)
测试结果:

=======================================
阿里2021年春季实习笔试题(最后一道大题)(2020 China Collegiate Programming Contest, Weihai Site) (C. Rencontre codeforces.com/gym/102798)的更多相关文章
- 剑指Offer——京东实习笔试题汇总
剑指Offer--京东实习笔试题汇总 编程题1 题目的详细信息已经记不住,只能大致描述一下,就是求最有价值的的委托信息. n.s.B.S其中n代表委托信息,s要求的最有价值的委托信息的个数,B代表买入 ...
- 2015小米暑期实习笔试题_风口的猪-中国牛市(dp)
风口之下.猪都能飞.当今中国股市牛市,真可谓"错过等七年". 给你一个回想历史的机会,已知一支股票连续n天的价格走势,以长度为n的整数数组表示,数组中第i个元素(prices[i] ...
- C++笔试题2(基础题)
温馨提醒:此文续<C++笔试题(基础题)> (112)请写出下列程序的输出内容 代码如下: #include <iostream> using namespace std; c ...
- SQLServer 常见SQL笔试题之语句操作题详解
SqlServer 常见SQL笔试题之语句操作题详解 by:授客 QQ:1033553122 测试数据库 CREATE DATABASE handWriting ON PRIMARY ( name = ...
- js作用域之常见笔试题,运行结果题
笔试题中经常有运行结果题,而大多体型都是围绕作用域展开,下面总结了几种相关的题: 外层的变量函数内部可以找到,函数内部的变量(局部变量)外层找不到. function aaa() { var a = ...
- 003_C/C++笔试题_分享大汇总
(一)感谢:lhzstudio 01_C++经典面试题全集 50~100道 都附带有参考答案 02_C++开发工程师面试题库 100~150道 03_C++笔试题库之编程.问答题 150~200道 0 ...
- 阿里2014校招笔试题(南大)——利用thread和sleep生成字符串的伪随机序列
引言:题目具体描述记不大清了,大概是:Linux平台,利用线程调度的随机性和sleep的不准确性,生成一个各位均不相同的字符数组的伪随机序列.不得使用任何库函数.(这句记得清楚,当时在想线程库算不算, ...
- 【面试笔试算法】Problem 9: 腾讯2016年研发实习笔试题:最长回文子串
(一)题目 问题:求给定字符串s的回文(palindrome)子串中,长度最大的回文子串的长度. 回文(palindrome)是指从左往右读和从右往左读字符串,看到的字符串都是一样的.比如" ...
- Java笔试题库之选题题篇【1-70题】
1.下面中哪两个可以在A的子类中使用:( ) class A { protected int method1 (int a, int b) { return 0; } } A. public int ...
- Java笔试题库之选题题篇【141-210题】
141.Struts框架可以支持以下哪种程序开发语言? A.C B.C++ C.Java D.C# 解答:C 142.在Servlet处理请求的方式为. A.以进程的方式 B.以程序的方式 C.以线程 ...
随机推荐
- 使用 Java 客户端通过 HTTPS 连接到 Easysearch
Easysearch 一直致力于提高易用性,这也是我们的核心宗旨,然而之前一直没有官方的 Java 客户端,也对用户使用造成了一些困扰,现在,我们正式发布了第一个 Java 客户端 Easysearc ...
- 腾讯手游助手 WIN11 蓝屏 DPC_WATCHDOG_VIOLATION
DPC_WATCHDOG_VIOLATION 退出QQ,或者下载最新版本QQ.
- k8s数据持久化
前面的学习,我们已经基本完成了在k8s中部署一个web服务,运行pod.创建service.创建ingress对外提供域名的七层代理. 下一个环境就得去关注应用部署后的数据存储问题,容器化如何管理,k ...
- 使用Vagrant创建CentOS虚拟机
使用Vagrant创建CentOS虚拟机 Vagrant是一款由HashiCorp公司提供的,用于快速构建虚拟机环境的软件.本节我们将使用Vagrant结合Oracle VM VirtualBox快速 ...
- 用typescript实现一个event bus
一个简单event bus的实现 发布订阅者模式 type emitKey = number | string | symbol; type func = (...args: any) => v ...
- Golang支持重试的http客户端ghttp
简介 官方仓库:https://github.com/GuoFlight/ghttp 重试的逻辑依赖了github.com/avast/retry-go 入门 client := ghttp.Clie ...
- MoneyPrinterPlus:AI自动短视频生成工具-腾讯云配置详解
MoneyPrinterPlus可以使用大模型自动生成短视频,其中的语音合成和语音识别部分需要借助于一些第三发云厂商的语音服务. 很多小伙伴可能不知道应该如何配置,这里给大家提供一个详细的腾讯云语音服 ...
- 02-HTML知识点
01 元素的介绍 02 元素的属性 03 元素的嵌套关系 04 HTML结构分析 4.1 文档声明[这个不叫元素] 4.2 html元素 4.3 head元素 主要用来写文档的配置信息 05 HTML ...
- GuavaCache、EVCache、Tair、Aerospike 缓存框架比较
Guava Cache.EVCache.Tair.Aerospike 是不同类型的缓存解决方案,它们各有特点和应用场景.下面我会逐一分析这些缓存系统的优势.应用场景,并提供一些基本的代码示例. Gua ...
- 一文为你深度解析LLaMA2模型架构
本文分享自华为云社区<[云驻共创]昇思MindSpore技术公开课 大咖深度解析LLaMA2 模型架构>,作者: Freedom123. 一.前言 随着人工智能技术的不断发展,自然语言处理 ...
