角点检测和匹配——Harris算子
一、基本概念
角点corner:可以将角点看做两个边缘的交叉处,在两个方向上都有较大的变化。具体可由下图中分辨出来:
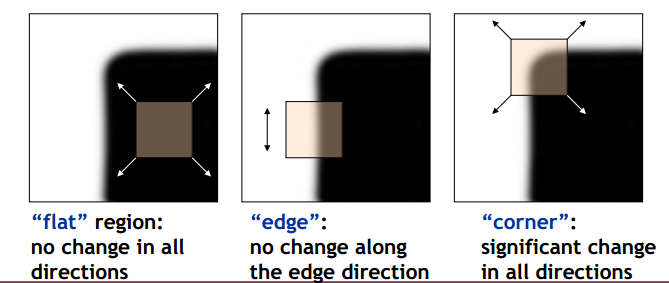
兴趣点interest point:兴趣点是图像中能够较鲁棒的检测出来的点,它不仅仅局限于角点. 也可以是灰度图像极大值或者极小值点等
二、Harris角点检测
Harris 算子是 Haris & Stephens 1988年在 "A Combined Corner and Edge Detector" 中提出的 提出的检测算法, 现在已经成为图像匹配中常用的算法.
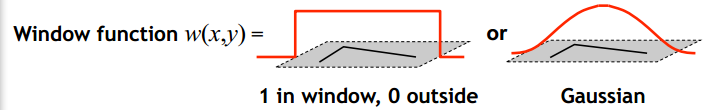
对于一幅RGB图像我们很很容易得到corner 是各个方向梯度值较大的点, 定义 函数WSSD(Weighted Sum Squared Difference)为:
$$S(x,y) = \sum_{u} \sum_{v}w(u,v)(I((u+x,v+y)-I(u,v))^2 (1)$$
其中$w(u,v)$可以看作采样窗,可以选择矩形窗函数,也可以选择高斯窗函数:
$I(u+x,v+y)-I(u,v)$可以看作像素值变化量(梯度):
使用泰勒展开:$I(u+x,v+y) \approx I(u,v)+I_x(u,v)x+I_y(u,v)y (2)$
(1)代入(2) $S(x,y) \approx \sum_u \sum_v w(u,v) (I_x(u,v)x + I_y(u,v)y)^2$
写成$S(x,y) \approx (x,y) A (x,y)^T $
其中 A 为 二阶梯度矩阵(structure tensor/ second-moment matrix)
$$A = \sum_u \sum_v w(u,v) \begin{bmatrix} I_x^2& I_x I_y \\ I_x I_y & I_y^2 \end{bmatrix} $$
将A定义为Harris Matrix,A 的特征值有三种情况:
1. $\lambda_1 \approx 0, \lambda_2 \approx 0$,那么点$x$不是兴趣点
2. $\lambda_1 \approx 0, \lambda_2$为一个较大的正数, 那么点$x$为边缘点(edge)
3. $\lambda_1, \lambda_2$都为一个较大的正数, 那么点$x$为角点(corner)
由于特征值的计算是 computationally expensive,引入如下函数
$M_c = \lambda_1\lambda_2 - \kappa(\lambda_1+\lambda_2)^2 = det(A) - \kappa trace^2(A) $
为了去除加权常数$\kappa$ 直接计算
$M_{c}^{'} = \frac{det(A)}{trace(A)+\epsilon}$
三、角点匹配
Harris角点检测仅仅检测出兴趣点位置,然而往往我们进行角点检测的目的是为了进行图像间的兴趣点匹配,我们在每一个兴趣点加入descriptors描述子信息,给出比较描述子信息的方法. Harris角点的,描述子是由周围像素值块batch的灰度值,以及用于比较归一化的相关矩阵构成。
通常,两个大小相同的像素块I_1(x)和I_2(x) 的相关矩阵为:
$$c(I_1,I_2) = \sum_x f(I_1(x),I_2(x))$$
$f函数随着方法变化而变化,c(I_1,I_2)$值越大,像素块相似度越高.
对互相关矩阵进行归一化得到normalized cross correlation :
$$ncc(I_1,I_2) = \frac{1}{n-2} \sum_x \frac{(I_1(x)-\mu_1)}{\sigma_1} \cdot \frac{(I_2(x)-\mu_2)}{\sigma_2}$$
其中$\mu$为像素块的均值,\sigma为标准差. ncc对图像的亮度变化具有更好的稳健性.
四、python实现
python版本:2.7
依赖包: numpy,scipy,PIL, matplotlib
图片:
trees_002.jpg

trees003.jpg

from PIL import Image
from scipy.ndimage import filters
from numpy import *
from pylab import * def compute_harris_response(im,sigma=3):
"""Compute the Harris corner detector response function for each
pixel in a graylevel image.""" #derivative
imx = zeros(im.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(im,(sigma,sigma),(0,1),imx) imy = zeros(im.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(im,(sigma,sigma),(1,0),imy) #compute components of the Harris matrix Wxx = filters.gaussian_filter(imx*imx,sigma)
Wxy = filters.gaussian_filter(imx*imy,sigma)
Wyy = filters.gaussian_filter(imy*imy,sigma) #determinant and trace Wdet = Wxx*Wyy-Wxy**2
Wtr = Wxx+Wyy
return Wdet/Wtr def get_harris_points(harrisim,min_dist=10,threshold=0.1):
"""Return corners from a Harris response image min_dist is the
minimum number of pixels separating corners and image boundary.""" #find top corner candidates above a threshold
corner_threshold = harrisim.max()*threshold
harrisim_t = 1*(harrisim>corner_threshold) #get coordiantes of candidate
coords = array(harrisim_t.nonzero()).T #...and their valus
candicates_values = [harrisim[c[0],c[1]] for c in coords] #sort candicates
index = argsort(candicates_values) #sort allowed point loaction in array
allowed_location = zeros(harrisim.shape)
allowed_location[min_dist:-min_dist,min_dist:-min_dist] = 1 #select the best points taking min_distance into account
filtered_coords = []
for i in index:
if allowed_location[coords[i,0],coords[i,1]]==1:
filtered_coords.append(coords[i])
allowed_location[(coords[i,0]-min_dist):(coords[i,0]+min_dist),
(coords[i,1]-min_dist):(coords[i,1]+min_dist)]=0
return filtered_coords def plot_harris_points(image,filtered_coords):
"""plots corners found in image."""
figure
gray()
imshow(image)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords],[p[0] for p in filtered_coords],'*')
axis('off')
show() def get_descriptors(image,filter_coords,wid=5):
"""For each point return pixel values around the point using a neihborhood
of 2*width+1."""
desc=[]
for coords in filter_coords:
patch = image[coords[0]-wid:coords[0]+wid+1,
coords[1]-wid:coords[1]+wid+1].flatten()
desc.append(patch) # use append to add new elements
return desc def match(desc1,desc2,threshold=0.5):
"""For each corner point descriptor in the first image, select its match
to second image using normalized cross correlation.""" n = len(desc1[0]) #num of harris descriptors
#pair-wise distance
d = -ones((len(desc1),len(desc2)))
for i in range(len(desc1)):
for j in range(len(desc2)):
d1 = (desc1[i]-mean(desc1[i]))/std(desc1[i])
d2 = (desc2[j]-mean(desc2[j]))/std(desc2[j])
ncc_value = sum(d1*d2)/(n-1)
if ncc_value>threshold:
d[i,j] = ncc_value ndx = argsort(-d)
matchscores = ndx[:,0] return matchscores def match_twosided(desc1,desc2,threshold=0.5):
"""two sided symmetric version of match()."""
matches_12 = match(desc1,desc2,threshold)
matches_21 = match(desc2,desc1,threshold) ndx_12 = where(matches_12>=0)[0]
print ndx_12.dtype
# remove matches that are not symmetric
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[matches_12[n]] !=n:
matches_12[n] = -1
return matches_12 def appendimages(im1,im2):
"""Return a new image that appends that two images side-by-side.""" #select the image with the fewest rows and fill in enough empty rows
rows1 = im1.shape[0]
rows2 = im2.shape[0] if rows1<rows2:
im1 = concatenate((im1,zeros((rows2-rows1,im1.shape[1]))),axis=0)
elif rows1<rows2:
im2 = concatenate((im2,zeros((rows1-rows2,im2.shape[1]))),axis=0)
return concatenate((im1,im2),axis=1)
def plot_matches(im1,im2,locs1,locs2,matchscores,show_below=True):
"""show a figure with lines joinging the accepted matches
Input:im1,im2(images as arrays),locs1,locs2,(feature locations),
metachscores(as output from 'match()'),
show_below(if images should be shown matches)."""
im3 = appendimages(im1,im2)
if show_below:
im3 = vstack((im3,im3)) imshow(im3) cols1 = im1.shape[1]
for i,m in enumerate(matchscores):
if m>0:
plot([locs1[i][1],locs2[m][1]+cols1],[locs1[i][0],locs2[m][0]],'c')
axis('off') """
im = array(Image.open('F:/images/lena.bmp').convert('1'))
harrisim = compute_harris_response(im)
filtered_coords = get_harris_points(harrisim,6)
plot_harris_points(im,filtered_coords)
""" im1 = array(Image.open('trees_002.jpg').convert('L'))
im2 = array(Image.open('trees_003.jpg').convert('L')) wid = 5 harrisim = compute_harris_response(im1,5)
filtered_coords1 = get_harris_points(harrisim,wid+1)
d1 = get_descriptors(im1,filtered_coords1,wid) harrisim = compute_harris_response(im2,5)
filtered_coords2 = get_harris_points(harrisim,wid+1)
d2 = get_descriptors(im2,filtered_coords2,wid) print 'starting matching'
matches = match_twosided(d1,d2) figure()
gray()
plot_matches(im1,im2,filtered_coords1,filtered_coords2,matches)
show()
运行结果:

角点检测和匹配——Harris算子的更多相关文章
- 【Computer Vision】角点检测和匹配——Harris算子
一.基本概念 角点corner:可以将角点看做两个边缘的交叉处,在两个方向上都有较大的变化.具体可由下图中分辨出来: 兴趣点interest point:兴趣点是图像中能够较鲁棒的检测出来的点,它不仅 ...
- 第十一节、Harris角点检测原理(附源码)
OpenCV可以检测图像的主要特征,然后提取这些特征.使其成为图像描述符,这类似于人的眼睛和大脑.这些图像特征可作为图像搜索的数据库.此外,人们可以利用这些关键点将图像拼接起来,组成一个更大的图像,比 ...
- opencv-角点检测之Harris角点检测
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/29356187 先看看程序运行截图: 一.引言:关于兴趣点(interest point ...
- OpenCV计算机视觉学习(13)——图像特征点检测(Harris角点检测,sift算法)
如果需要处理的原图及代码,请移步小编的GitHub地址 传送门:请点击我 如果点击有误:https://github.com/LeBron-Jian/ComputerVisionPractice 前言 ...
- OpenCV-Python:Harris角点检测与Shi-Tomasi角点检测
一.Harris角点检测 原理: 角点特性:向任何方向移动变换都很大. Chris_Harris 和 Mike_Stephens 早在 1988 年的文章<A CombinedCorner an ...
- OpenCV教程(43) harris角的检测(1)
计算机视觉中,我们经常要匹配两幅图像.匹配的的方式就是通过比较两幅图像中的公共特征,比如边,角,以及图像块(blob)等,来对两幅图像进行匹配. 相对于边,角更适合描述图像特征, ...
- Harris角点及Shi-Tomasi角点检测(转)
一.角点定义 有定义角点的几段话: 1.角点检测(Corner Detection)是计算机视觉系统中用来获得图像特征的一种方法,广泛应用于运动检测.图像匹配.视频跟踪.三维建模和目标识别等领域中.也 ...
- 【OpenCV】角点检测:Harris角点及Shi-Tomasi角点检测
角点 特征检测与匹配是Computer Vision 应用总重要的一部分,这需要寻找图像之间的特征建立对应关系.点,也就是图像中的特殊位置,是很常用的一类特征,点的局部特征也可以叫做“关键特征点”(k ...
- 角点检测:Harris角点及Shi-Tomasi角点检测
角点 特征检测与匹配是Computer Vision 应用总重要的一部分,这需要寻找图像之间的特征建立对应关系.点,也就是图像中的特殊位置,是很常用的一类特征,点的局部特征也可以叫做“关键特征点”(k ...
随机推荐
- java集合(2)- java中HashMap详解
java中HashMap详解 基于哈希表的 Map 接口的实现.此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用 null 值和 null 键.(除了非同步和允许使用 null 之外,HashMap 类与 H ...
- java虚拟机学习-JVM调优总结(6)
1.Java对象的大小 基本数据的类型的大小是固定的,这里就不多说了.对于非基本类型的Java对象,其大小就值得商榷. 在Java中,一个空Object对象的大小是8byte,这个大小只是保存堆中一个 ...
- PATH menu
先上效果图 主界面布局文件 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" ...
- PC端网页的基本构成
首先,一个前端最基本的就是排网页,有人会看不起拍页面,认为不就是排一个页面嘛,有啥的,分分钟的事,可是他不知道的是,一个网页中也包含了很多内容,像我们如果不理解margin,padding,会经常对我 ...
- HIVE安装配置
Hive简介 Hive 基本介绍 Hive 实现机制 Hive 数据模型 Hive 如何转换成MapReduce Hive 与其他数据库的区别 以上详见:https://chu888chu888.gi ...
- 【Windows 10 应用开发】如何防止应用程序被截屏
今天老周只想跟大伙们分享一个小技巧,是的,小小的技巧,很简单,保证你能学会的,要是学不会,可以考虑跳泰山. 有些时候,我们可能会想到不要让应用程序界面上显示的内容被截屏,要阻止应用界面呈现在截图上,可 ...
- 关于JS跨域问题的解决
这里不提供什么高深的代码了,只说明一个解决跨域问题的方法,个人觉得这个方法是最方便也是最有效的. 那就是一用不同源的JS,虽然JS不允许不同源的访问,但是可以引用不同源的JS,用这样的方法我们可以引用 ...
- git clone https://github.com/istester/ido.git ,确提示“Failed to connect to 192.168.1.22 port 8080: Connection refused” 的解决办法 。
不知道是否有同学遇到如下的问题: p.p1 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 11.0px Menlo } span.s1 { } git clone ...
- Python3实现简单的http server
前端的开发的html给我们的时候,由于内部有一些ajax请求的.json的数据,需要在一个web server中查看,每次放到http服务器太麻烦.还是直接用python造一个最方便. 最简单的,直接 ...
- iOS工程师常用的命令行命令总结
感觉有点标题党了. 作为一个iOS工程师,没有做过服务端,主要用的是mac电脑,此篇博文是记录我在工作,学习的过程中用的命令行命令的记录和归纳总结 一. mac命令行 1. cd /Users/xxx ...
