CentOS下搭建VNC/TEAMVIEW/SSH无密码登录
VNC
配置桌面
# 安装gnome桌面环境
yum groupinstall Desktop -y
# 安装中文语言支持包(可选)
yum groupinstall 'Chinese Support' -y
# 设置系统默认语言为中文(可选)
sed -i '/LANG/c\LANG="zh_CN.UTF-8"' /etc/sysconfig/i18n
source /etc/sysconfig/i18n
配置VNC Server
#安装vncserver包
yum install tigervnc tigervnc-server –y
#开启自启动
chkconfig vncserver on
你可以通过UltraVNC Viewer、TigerVNC Viewer或者RealVNC Viewer访问远程桌面了。
#确认vncserver包已经安装
[root@su172 ~]# rpm -qa | egrep -i vnc
tigervnc-server-1.1.0-16.el6.centos.x86_64
[root@su172 ~]#
#确认rpm包配置文件路径
[root@su172 ~]# rpm -ql tigervnc-server-1.1.0-16.el6.centos.x86_64
/etc/rc.d/init.d/vncserver
/etc/sysconfig/vncservers
/usr/bin/Xvnc
/usr/bin/vncconfig
/usr/bin/vncpasswd
/usr/bin/vncserver
/usr/bin/x0vncserver
/usr/share/man/man1/Xvnc.1.gz
/usr/share/man/man1/vncconfig.1.gz
/usr/share/man/man1/vncpasswd.1.gz
/usr/share/man/man1/vncserver.1.gz
/usr/share/man/man1/x0vncserver.1.gz
#root用户启动vncserver
#输入以root用户登录vncserver时的密码
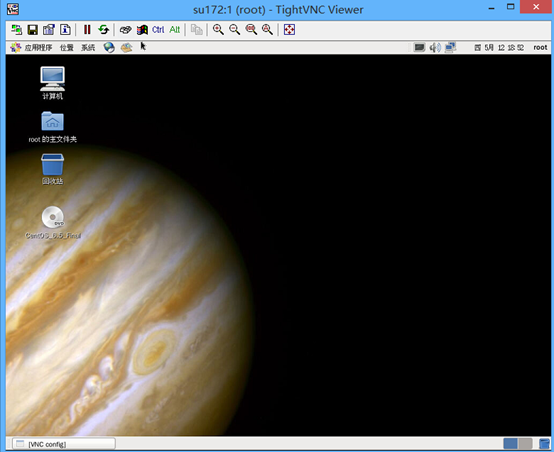
[root@su172 ~]# vncserver
You will require a password to access your desktops.
Password:
Verify:
xauth: (stdin):1: bad display name "su172:1" in "add" command
New 'su172:1 (root)' desktop is su172:1
Creating default startup script /root/.vnc/xstartup
Starting applications specified in /root/.vnc/xstartup
Log file is /root/.vnc/su172:1.log
[root@su172 ~]# cd .vnc/
[root@su172 .vnc]# ls
passwd su172:1.log su172:1.pid xstartup
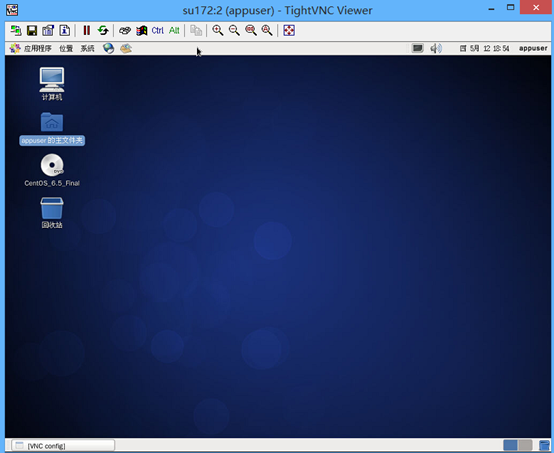
#普通用户启动vncserver
[appuser@su172 ~]$vncserver
#普通用户需要手工改密码
[appuser@su172 ~]$ vncpasswd
Password:
Verify:
#root验证

#普通user验证


#在Server端进行端口验证
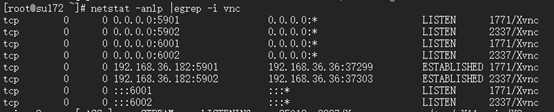
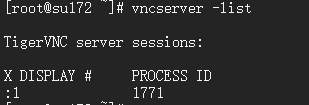
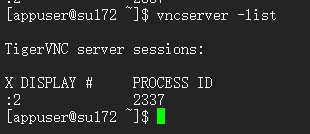
#确认vcn进程
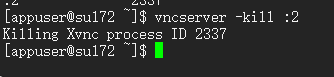
#kill vnc进程验证

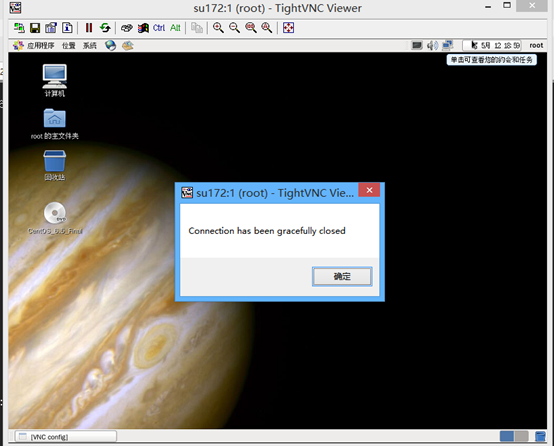
#参考
http://www.centoscn.com/image-text/config/2014/1120/4151.html
Teamview
下载
wget https://download.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer.i686.rpm
安装依赖包
yum install teamviewer_11.0.57095.i686.rpm -y
cd /opt/teamviewer/tv_bin
teamviewer --setup console #设置启动方式为控制台启动
teamviewer --daemon restart #重启teamview服务
teamviewer --info #查看teamview信息
teamviewer --passwd [PASSWD] #设置密码
teamviewer --help #查看帮助
ssh无密码登录
CentOS系统之间有可能需要无密码验证登录,方便拷贝东东,例如oracle rac安装时就有这个东西。所以提前了解很有必要。
node1执行以下步骤:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -P ''
scp /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@192.168.36.182:/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub181
node2执行以下步骤:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -P ''
scp id_rsa.pub root@192.168.36.181:/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub182
node1执行:
cat id_rsa.pub182 >>authorized_keys
node2执行
cat id_rsa.pub181 >>authorized_keys
验证
node1验证
ssh 192.168.36.182
node2验证
ssh 192.168.36.181
扩展
-v跟踪
[root@su171 .ssh]# ssh -v 192.168.36.182
OpenSSH_5.3p1, OpenSSL 1.0.1e-fips 11 Feb 2013
debug1: Reading configuration data /etc/ssh/ssh_config
debug1: Applying options for *
debug1: Connecting to 192.168.36.182 [192.168.36.182] port 22.
debug1: Connection established.
debug1: permanently_set_uid: 0/0
debug1: identity file /root/.ssh/identity type -1
debug1: identity file /root/.ssh/identity-cert type -1
debug1: identity file /root/.ssh/id_rsa type 1
debug1: identity file /root/.ssh/id_rsa-cert type -1
debug1: identity file /root/.ssh/id_dsa type -1
debug1: identity file /root/.ssh/id_dsa-cert type -1
debug1: identity file /root/.ssh/id_ecdsa type -1
debug1: identity file /root/.ssh/id_ecdsa-cert type -1
debug1: Remote protocol version 2.0, remote software version OpenSSH_5.3
debug1: match: OpenSSH_5.3 pat OpenSSH*
debug1: Enabling compatibility mode for protocol 2.0
debug1: Local version string SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_5.3
debug1: SSH2_MSG_KEXINIT sent
debug1: SSH2_MSG_KEXINIT received
debug1: kex: server->client aes128-ctr hmac-md5 none
debug1: kex: client->server aes128-ctr hmac-md5 none
debug1: SSH2_MSG_KEX_DH_GEX_REQUEST(1024<1024<8192) sent
debug1: expecting SSH2_MSG_KEX_DH_GEX_GROUP
debug1: SSH2_MSG_KEX_DH_GEX_INIT sent
debug1: expecting SSH2_MSG_KEX_DH_GEX_REPLY
debug1: Host '192.168.36.182' is known and matches the RSA host key.
debug1: Found key in /root/.ssh/known_hosts:1
debug1: ssh_rsa_verify: signature correct
debug1: SSH2_MSG_NEWKEYS sent
debug1: expecting SSH2_MSG_NEWKEYS
debug1: SSH2_MSG_NEWKEYS received
debug1: SSH2_MSG_SERVICE_REQUEST sent
debug1: SSH2_MSG_SERVICE_ACCEPT received
debug1: Authentications that can continue: publickey,gssapi-keyex,gssapi-with-mic,password
debug1: Next authentication method: gssapi-keyex
debug1: No valid Key exchange context
debug1: Next authentication method: gssapi-with-mic
debug1: Unspecified GSS failure. Minor code may provide more information
Cannot determine realm for numeric host address
debug1: Unspecified GSS failure. Minor code may provide more information
Cannot determine realm for numeric host address
debug1: Unspecified GSS failure. Minor code may provide more information
debug1: Unspecified GSS failure. Minor code may provide more information
Cannot determine realm for numeric host address
debug1: Next authentication method: publickey
debug1: Trying private key: /root/.ssh/identity
debug1: Offering public key: /root/.ssh/id_rsa
debug1: Server accepts key: pkalg ssh-rsa blen 277
debug1: read PEM private key done: type RSA
debug1: Authentication succeeded (publickey).
debug1: channel 0: new [client-session]
debug1: Requesting no-more-sessions@openssh.com
debug1: Entering interactive session.
debug1: Sending environment.
debug1: Sending env LANG = en_US.UTF-8
Last login: Thu May 12 23:51:22 2016 from 192.168.36.181
[root@su172 ~]#
CentOS下搭建VNC/TEAMVIEW/SSH无密码登录的更多相关文章
- CentOS 下SSH无密码登录的配置
CentOS 下SSH无密码登录的配置 最近学习Hadoop.它要求各节点之间通过SSH无密码登录,配置SSH的时候费了一番功夫,记录下来,以备忘. 配置SSH无密码登录需要3步: 1.生成公钥和私钥 ...
- CentOS下SSH无密码登录的配置
1.确认本机sshd的配置文件(需要root权限) $ gedit /etc/ssh/sshd_config 找到以下内容,并去掉注释符"#" RSAAuthentication ...
- CentOS配置ssh无密码登录
CentOS配置ssh无密码登录的注意点 前提配置:使用root登录修改配置文件:/etc/ssh/sshd_config,将其中三行的注释去掉,如下: 然后重启ssh服务:service s ...
- ssh-keygen+ssh-copy-id 在linux下实现ssh无密码登录访问(转)
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/pennyliang/article/details/8556662 ssh-keygen+ssh-copy-id 在linux下实现ssh无密码登录访 ...
- CentOS系统实现SSH无密码登录的方法
一.环境配置 1.服务端:CentOS release 5.3 IP:222.73.115.198 2.客服端:CentOS release 5.8 IP:192.168.4.244 二.配置SSH无 ...
- ssh 无密码登录
ssh 无密码登录要使用公钥与私钥.linux下可以用用ssh-keygen生成公钥/私钥对,下面我以CentOS为例. 有机器A(192.168.1.155),B(192.168.1.181).现想 ...
- Linux SSH无密码登录
Linux服务器常见的登录方式有两种:密码登录.秘钥登录.工作中我们最常使用的是用秘钥登录的方法,因为使用秘钥登录更高效.更安全. 如何实现SSH无密码登录: 原理:无密码ssh登录的主要操作为将本机 ...
- ssh 无密码登录要使用公钥与私钥
ssh 无密码登录要使用公钥与私钥.linux下可以用用ssh-keygen生成公钥/私钥对,下面我以CentOS为例. 有机器A(192.168.1.155),B(192.168.1.181).现想 ...
- CentOS下搭建LNMP+WordPress+http2.0教程
此文是本人CentOS下搭建WordPress的一些笔记,环境搭建时间::将看过的几篇文章总结下来,形成一条龙长文.不用大家再找来找去. 本文大概分为此几部分: 一.基础命令更新: 二.服务器加速(非 ...
随机推荐
- Java学习的第二十三天
1.今天学习了用log4j记录日志 综合实例 2.不知道日志什么时候用到 3.明天学习12章
- Python3网络学习案例三:编写web server
1. 写在前面 这里总结的并不够详细,有时间了再进行补充. 2. 设计思路 HTTP协议是建立在TCP上的1. 建立服务器端TCP套接字(绑定ip,port),等待监听连接:listen(2. 打开浏 ...
- Python3网络学习案例二:traceroute详解
1. 写在前面 本文是基于上一篇"ping详解"写的: 不同操作系统下的命令也不同,本文仅针对windows系统,命令为"tracert xxx",效果如下 2 ...
- .netcore跨域设置
跨域 广义上讲,跨域是指一个域下的文档或者脚本试图去请求访问另一个域下的资源(像我们直接通过代码使用http请求资源,或者是使用辅助工具(例如postman)是可以直接访问的,没有跨域的概念):而我们 ...
- 3.6 栈 ADT - 3.7 队列 ADT
3.6 栈 ADT 栈是限制插入和删除只能在一个位置上进行的表,叫做栈的顶部.对栈的基本操作有进栈和出栈,进栈在顶部插入元素,出栈删除最后插入的元素. 栈是一个表,因此任何实现表的方法都能实现栈.显然 ...
- MySQL日期函数与日期转换格式化函数大全
Mysql作为一款开元的免费关系型数据库,用户基础非常庞大,本文列出了MYSQL常用日期函数与日期转换格式化函数 1.DAYOFWEEK(date) 1 2 SELECT DAYOFWEEK('201 ...
- php之4个坐标点判断是否为矩形和正方形
代码 <?php $a=[0,0]; $b=[0,1]; $c=[1,1]; $d=[1,0]; $ar=array($a,$b,$c,$d); $a1=[]; // 0 1 2 3 forea ...
- leetcode4:sort-list
题目描述 在O(n log n)的时间内使用常数级空间复杂度对链表进行排序. Sort a linked list in O(n log n) time using constant space co ...
- SU+GIS,让SketchUp模型在地图上活起来
一.SU+GIS的场景展示 skp与卫星地图和倾斜摄影模型相结合人工模型与实景模型完美融合 这么一看是不是直接秒杀了单纯看看skp后联想的规划效果? 二.如何快速把草图大师的结果和GIS结合呢?在图新 ...
- 微信三方平台开发上传base64格式图片至临时素材
1 public string UploadImgByB64(string b64) 2 { 3 //access_token 需要自己获取 4 string access_token = getTo ...
