Scala高级语法
一、隐式
implicit分类:
(1)隐式参数
(2)隐式转换类型
(3)隐式类
特点:让代码变得更加灵活
(一)隐式参数
1、ImplicitTest
object ImplicitTest {
//此参数
def sleep(how:String):Unit = {println(how)}
//此参数如果被implicit修饰的话,调用可以不写参数 直接sleep2
def sleep2(implicit how:String = "香啊") = {println(how)}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
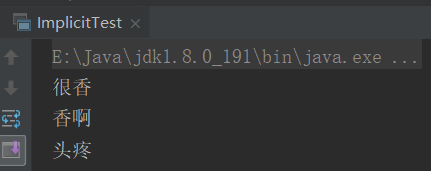
sleep("很香")
sleep2
implicit val how = "头疼"
sleep2
}
}
结果:
2、ImplicitTest1
//隐式转换类型
object ImplicitTest1 {
//类型转换
implicit def double2Int(d:Double) = {d.toInt} def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
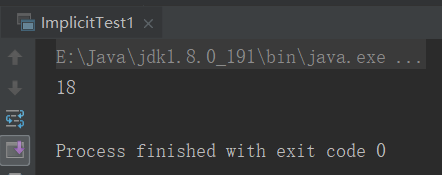
val a:Int = 18.8
println(a)
}
}
结果:
3、KelihuaImplicit
object KelihuaImplicit {
//柯理化
def sum(a:Int)(implicit b:Int) = {a + b}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//定义隐式值
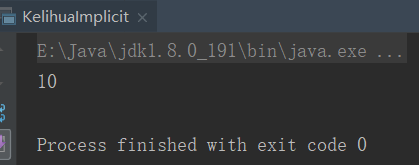
implicit val b = 9
println(sum(1))
}
}
结果:
(二)隐式转换类型
4、FileMain
import java.io.File //扫描文件的数据条数
object FileMain { //定义隐式转换
implicit def file2RichFile(file:File) = new RichFile(file) def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//1.加载文件
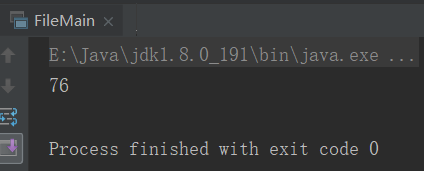
val file = new File("e:/weblog.log") //2.打印条数
println(file.count())
}
}
5、RichFile
import java.io.{BufferedReader, File, FileReader}
class RichFile(file:File) {
def count():Int = {
//读取数据
val fileReader = new FileReader(file)
val bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader)
//计数器
var sum = 0
try {
while (bufferedReader.readLine() != null){
sum += 1
}
} catch {
case _:Exception => sum
} finally {
bufferedReader.close()
fileReader.close()
}
sum
}
}
结果:
(三)隐式类
6、ReadImplicit
import scala.io.Source
object ReadImplicit {
//定义隐式类
implicit class FileRead(file:File){
//读取文件
def read = Source.fromFile(file).mkString
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val file = new File("e:/weblog.log")
println(file.read)
}
}
结果:

二、泛型
type
如何定义scala中的泛型?
1、Anything
//加入泛型 T代表任意类型
abstract class Anything[T](m:T)
2、Intthing
class Intthing[Int](m:Int) extends Anything(m) {
}
3、Stringthing
class Stringthing[String](m:String) extends Anything {
}
4、Person
class Person[A,B,C](val age:A,val high:B,val face:C) {
}
5、ScalaTest
object ScalaTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
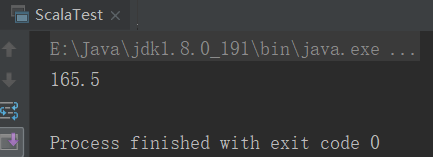
val p = new Person[Int,Double,Double](18,165.5,99)
println(p.high)
}
}
结果:
三、类型约束
java中Comparable
Scala中的比较的特质:
Ordered 上界(upper Bounds)
<T extends Person>表示T类型是Person的子类型
<? extends Person>
[T <: Person]此时T是Person的子类,这种形式是上界
[_ <: Person] def pr(list:List[_<:Any]){
list.foreach(print)
} 下界(lower Bounds)
<T super Person>
<? super Person> [T >: Person]
[_ >: Person] 视图界定(View Bounds)
<%
视图界定发生了隐式转换 上下文界定
comparator
scala->ordering
上下文界定发生了隐式转换
(一)java中Comparable
1、Person1
public class Person1 implements Comparable<Person1>{
//定义属性
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Person1(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person1 o) {
//升序
return this.age - o.age;
}
}
2、ComTest
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List; public class ComTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
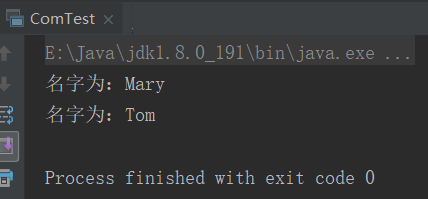
Person1 p1 = new Person1("Tom",18);
Person1 p2 = new Person1("Mary",16); List<Person1> person = new ArrayList<Person1>();
person.add(p1);
person.add(p2); Collections.sort(person);
for (Person1 p : person) {
System.out.println("名字为:" + p.getName());
}
}
}
结果:
(二)Scala中类型约束
1、上届UpperBounds
//定义一个比较的方式
class CompareInt(a:Int,b:Int){
def compare = if(a > b) a else b
} //定义比较类型
class CompareC[T <: Comparable[T]](o1:T,o2:T){
def compare = if(o1.compareTo(o2) > 0) o1 else o2
} object UpperBounds {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
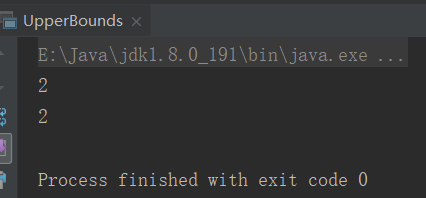
val big = new CompareInt(1,2)
System.out.println(big.compare) val comc = new CompareC(Integer.valueOf(1),Integer.valueOf(2))
System.out.println(comc.compare)
}
}
结果:
2、视图界定ViewsBounds
//视图界定
class CompareCC[T <% Comparable[T]](o1:T,o2:T){
def big = if(o1.compareTo(o2) > 0) o1 else o2
} object ViewBounds {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//视图界定发生了隐式转换
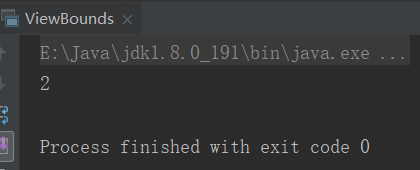
val comc = new CompareCC(1,2)
println(comc.big)
}
}
结果:
3、上下文界定ContextBounds
class Compp[T:Ordering](o1:T,o2:T)(implicit comt:Ordering[T]){
def big = if(comt.compare(o1,o2) > 0) o1 else o2
}
class Personss(val name:String,val age:Int){
override def toString: String = this.name + "," + this.age
}
//上下文界定 同样发生了隐式转换
object ContextBounds {
//比较器定义 比较规则
implicit val comparatorPersonss = new Ordering[Personss]{
override def compare(x: Personss, y: Personss): Int = x.age - y.age
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val p1 = new Personss("Tom",18)
val p2 = new Personss("John",15)
val comc = new Compp(p1, p2)
println(comc.big)
}
}
结果:

Scala高级语法的更多相关文章
- Scala进阶之路-Scala高级语法之隐式(implicit)详解
Scala进阶之路-Scala高级语法之隐式(implicit)详解 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 我们调用别人的框架,发现少了一些方法,需要添加,但是让别人为你一 ...
- 大数据之scala高级语法学习
协变 案例一: class Animal {} class Bird extends Animal {} class Animal {} class Bird extends Animal {} // ...
- scala基本语法和单词统计
scala 基本语法 1.声明变量 (1)val i = 1 使用val声明的变量值是不可变的,相当于java里final修饰的变量,推荐使用. (2)var i = "hello" ...
- 【Scala学习之一】 Scala基础语法
环境 虚拟机:VMware 10 Linux版本:CentOS-6.5-x86_64 客户端:Xshell4 FTP:Xftp4 jdk1.8 scala-2.10.4(依赖jdk1.8) spark ...
- scala 高级编程
一.函数式编程 Scala中的函数可以独立存在, 不需要依赖任 何类和对象 def 放在类中就是方法:放在外边就是函数 1.将函数赋值给变量 Scala中的函数是一等公民, 可以独立定义, 独立存在 ...
- 02.Scala高级特性:第6节 高阶函数;第7节 隐式转换和隐式参数
Scala高级特性 1. 课程目标 1.1. 目标一:深入理解高阶函数 1.2. 目标二:深入理解隐式转换 2. 高阶函数 2.1. 概念 Scala混合了面向对象和函数式的特 ...
- Scala基础语法 (一)
如果你之前是一名 Java 程序员,并了解 Java 语言的基础知识,那么你能很快学会 Scala 的基础语法. Scala 与 Java 的最大区别是:Scala 语句末尾的分号 ; 是可选的. 我 ...
- tn文本分析语言(三):高级语法
标签(空格分隔): 未分类 高级操作 1.脚本表达式 用双引号包含的脚本被称为脚本表达式,目前支持嵌入Python. 脚本表达式只能在顺序表达式中使用.代码可以在三个位置存在: |位置|功能|例子| ...
- Swift高级语法学习总结(转)
Swift高级语法学习总结 1.函数 1.1 func funcNmae()->(){} 这样就定义了一个函数,它的参数为空,返回值为空,如果有参数和返回值直接写在两个括号里就可以了 1.2 参 ...
随机推荐
- html学习笔记五
关于服务端和client的校验问题 上述的表格信息填写后发现,即使有些信息不添,依旧能够提交 所以针对此问题,我们要在client进行数据填写信息的增强型校验(必添单元,必须填写有效信息,否则无法提交 ...
- linux下安装dovecot
Dovecot是一个开源的,为Linux/Unix-like系统提供IMAP,POP3服务的软件.主要是为了安全产生的,不管大小应用,Dovecot都是一个非常优秀的选择.它非常快,配置简单,不需要专 ...
- C# 基础小知识之yield 关键字
对于yield关键字我们首先看一下msdn的解释: 如果你在语句中使用 yield 关键字,则意味着它在其中出现的方法.运算符或 get 访问器是迭代器. 通过使用 yield 定义迭代器,可在实现自 ...
- JavaScript匿名函数和回调函数
匿名函数的自调函数格式: (function(){ //代码 })(); <script type="text/javascript"> (function(){ al ...
- mysql数据库中,查看某个数据库下的表的存储类型都有哪些
需求描述: 在备份数据库的时候,使用mysqldump进行数据库的备份,如果库中仅仅有innodb存储引擎, 那么使用--single-transaction就可以,如果还有其他的存储引擎类型就要使用 ...
- oracle 无效索引
错误信息:ORA-01502: index 'VOX_ID' or partition of such index is in unusable state 原因:将表的表空间做了更改,导致索引失效. ...
- EOF ---shell编程
转自:http://blog.163.com/njut_wangjian/blog/static/1657964252013112152418345/ 在shell编程中,”EOF“通常与”<& ...
- Linux ulimit 命令
ulimit命令用来限制系统用户对 shell 资源的访问,常见用法如下: [root@localhost ~]$ ulimit -a # 查看当前所有的资源限制 [root@localhost ~] ...
- 使用ASIHTTPRequest xcode编译提示找不到"libxml/HTMLparser.h"
使用ASIHTTPRequest xcode编译提示找不到"libxml/HTMLparser.h",解决方法如下: 1>.在xcode中左边选中项目的root节点,在中间编 ...
- C++异常 将对象用作异常类型
通常,引发异常的函数将传递一个对象.这样做的重要有点之一是,可以使用不同的异常类型来区分不同的函数在不同情况下引发的异常.另外,对象可以携带信息,程序员可以根据这些信息来确定引发异常的原因.同时,ca ...
