自定义用户认证(继承django的)
1、在app下创建一个自己用户认证文件,文件名随意,记得为.py文件
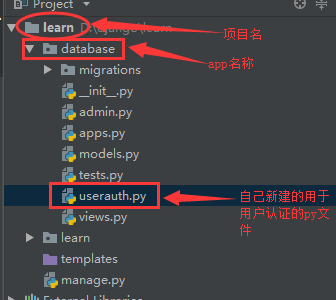
2、编辑该userauth.py文件
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding:utf-8
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import (
BaseUserManager, AbstractBaseUser
)
import django class UserManager(BaseUserManager):
def create_user(self, email, name, password=None):
"""
Creates and saves a User with the given email, date of
birth and password.
"""
if not email:
raise ValueError('Users must have an email address') user = self.model(
email=self.normalize_email(email),
name=name,
#token=token,
#department=department,
#tel=tel,
#memo=memo, ) user.set_password(password)
user.save(using=self._db)
return user def create_superuser(self, email, name ,password):
"""
Creates and saves a superuser with the given email, date of
birth and password.
"""
user = self.create_user(email,
password=password,
name=name,
#token=token,
#department=department,
#tel=tel,
#memo=memo,
)
user.is_admin = True
user.save(using=self._db)
return user class UserProfile(AbstractBaseUser):
email = models.EmailField(
verbose_name='email address',
max_length=255,
unique=True,
) is_active = models.BooleanField(default=True)
is_admin = models.BooleanField(default=False) name = models.CharField(u'名字', max_length=32)
token = models.CharField(u'token', max_length=128,default=None,blank=True,null=True)
department = models.CharField(u'部门', max_length=32,default=None,blank=True,null=True) mobile = models.CharField(u'手机', max_length=32,default=None,blank=True,null=True) memo = models.TextField(u'备注', blank=True,null=True,default=None)
date_joined = models.DateTimeField(blank=True, auto_now_add=True)
valid_begin_time = models.DateTimeField(default=django.utils.timezone.now)
valid_end_time = models.DateTimeField(blank=True,null=True) USERNAME_FIELD = 'email' #定义email为用户名
#REQUIRED_FIELDS = ['name','token','department','tel','mobile','memo']
REQUIRED_FIELDS = ['name'] def get_full_name(self):
# The user is identified by their email address
return self.email def get_short_name(self):
# The user is identified by their email address
return self.email def __str__(self): # __unicode__ on Python 2
return self.email def has_perm(self, perm, obj=None):
"Does the user have a specific permission?"
# Simplest possible answer: Yes, always
return True
def has_perms(self, perm, obj=None):
"Does the user have a specific permission?"
# Simplest possible answer: Yes, always
return True
def has_module_perms(self, app_label):
"Does the user have permissions to view the app `app_label`?"
# Simplest possible answer: Yes, always
return True @property
def is_staff(self):
"Is the user a member of staff?"
# Simplest possible answer: All admins are staff
return self.is_admin class Meta:
verbose_name = u'用户信息'
verbose_name_plural = u"用户信息"
def __unicode__(self):
return self.name objects = UserManager()
3、在models中导入该文件中的UserProfile类

4、admin中注册
编辑admin.py文件
#_*_coding:utf8_*_
from django.contrib import admin # Register your models here. from django import forms
from django.contrib import admin
from django.contrib.auth.models import Group
from django.contrib.auth.admin import UserAdmin
from django.contrib.auth.forms import ReadOnlyPasswordHashField
import models from userauth import UserProfile
from django.contrib.auth import forms as auth_form class UserCreationForm(forms.ModelForm):
"""A form for creating new users. Includes all the required
fields, plus a repeated password."""
password1 = forms.CharField(label='Password', widget=forms.PasswordInput)
password2 = forms.CharField(label='Password confirmation', widget=forms.PasswordInput) class Meta:
model = UserProfile
fields = ('email','token') def clean_password2(self):
# Check that the two password entries match
password1 = self.cleaned_data.get("password1")
password2 = self.cleaned_data.get("password2")
if password1 and password2 and password1 != password2:
raise forms.ValidationError("Passwords don't match")
return password2 def save(self, commit=True):
# Save the provided password in hashed format
user = super(UserCreationForm, self).save(commit=False)
user.set_password(self.cleaned_data["password1"])
if commit:
user.save()
return user class UserChangeForm(forms.ModelForm):
"""A form for updating users. Includes all the fields on
the user, but replaces the password field with admin's
password hash display field.
"""
password = ReadOnlyPasswordHashField(label="Password",
help_text=("Raw passwords are not stored, so there is no way to see "
"this user's password, but you can change the password "
"using <a href=\"password/\">this form</a>.")) class Meta:
model = UserProfile
fields = ('email', 'password','is_active', 'is_admin') def clean_password(self):
# Regardless of what the user provides, return the initial value.
# This is done here, rather than on the field, because the
# field does not have access to the initial value
return self.initial["password"]
class UserProfileAdmin(UserAdmin):
# The forms to add and change user instances
form = UserChangeForm
add_form = UserCreationForm # The fields to be used in displaying the User model.
# These override the definitions on the base UserAdmin
# that reference specific fields on auth.User.
list_display = ('id','email','is_admin','is_active')
list_filter = ('is_admin',)
fieldsets = (
(None, {'fields': ('email', 'password')}),
('Personal info', {'fields': ('department','name','mobile','memo')}),
('API TOKEN info', {'fields': ('token',)}),
('Permissions', {'fields': ('is_active','is_admin')}),
('账户有效期', {'fields': ('valid_begin_time','valid_end_time')}),
)
# add_fieldsets is not a standard ModelAdmin attribute. UserAdmin
# overrides get_fieldsets to use this attribute when creating a user.
add_fieldsets = (
(None, {
'classes': ('wide',),
'fields': ('email', 'password1', 'password2','is_active','is_admin')}
),
)
search_fields = ('email',)
ordering = ('email',)
filter_horizontal = () # Now register the new UserAdmin...
admin.site.register(models.UserProfile,UserProfileAdmin)
admin.site.unregister(Group)
#这里需注意,第51行
"using <a href=\"password/\">this form</a>.")) #这是django1.8的写法,如果>1.8的话需要修改成
"using <a href=\"../password/\">this form</a>."))
否则在admin后台点击修改密码的话会提示404找不到页面
5、在settings告诉django使用我们自己定义的用户认证系统
修改settings,结尾添加
AUTH_USER_MODEL = 'database.UserProfile'
#database为app名称
#UserProfile为我们刚才在userauth.py中创建的类名称
6、同步数据库
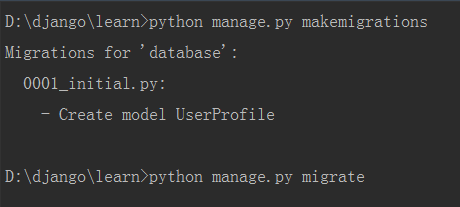
可以看到创建了UserProfile表,这样就可以直接使用django的用户认证功能
7、创建超级用户
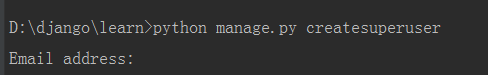
可以看到提示已经跟django默认的不一样了,以email地址作为用户名
8、此时访问django admin
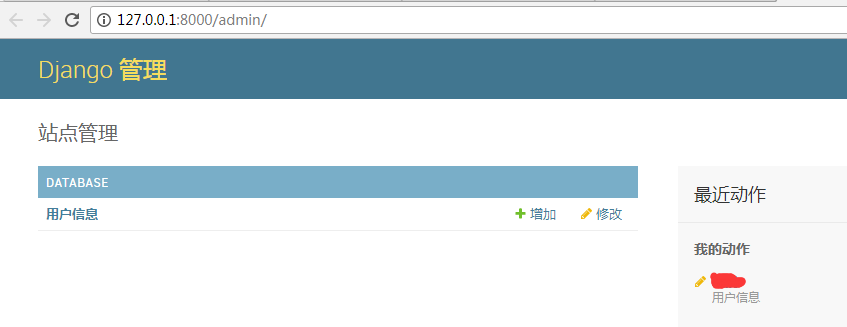
自定义用户认证(继承django的)的更多相关文章
- 使用django实现自定义用户认证
参考资料:https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.10/topics/auth/customizing/ 直接拉到最后看栗子啦 django自定义用户认证(使用自 ...
- Django自定义用户认证
自定义一个用户认证 详细参考官方文档: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.9/topics/auth/customizing/#django.contrib.au ...
- Django自定义用户认证系统之自定义用户模型
参考文档:http://python.usyiyi.cn/django/topics/auth/customizing.html Django 自带的认证系统足够应付大多数情况,但你或许不打算使用现成 ...
- CMDB资产管理系统开发【day25】:Django 自定义用户认证
官方文档:https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.10/topics/auth/customizing/#substituting-a-custom-user-mode ...
- Django--分页器(paginator)、Django的用户认证、Django的FORM表单
分页器(paginator) >>> from django.core.paginator import Paginator >>> objects = ['joh ...
- 43)django-用户认证,授权,自定义用户认证
##用户认证 django自带用户认证系统,包括认证和授权.用户认证系统由用户,权限,用户组,密码,cookie和session给组成. ###用户认证系统设置 #settings.py INSTAL ...
- YII2中自定义用户认证模型,完成登陆和注册
有些时候我们需要自已定义用户类,操作自已建的用户表,来完成登陆和注册功能. 用户表结构如下,当然可以根据自已的需要添加或删除: CREATE TABLE `tb_user` ( `id` int(11 ...
- spring Security的自定义用户认证
首先我需要在xml文件中声明.我要进行自定义用户的认证类,也就是我要自己从数据库中进行查询 <http pattern="/*.html" security="no ...
- Django自定义用户认证系统Customizing authentication
扩展已有的用户模型Extending the existing User model 有两种方法来扩展默认的User Model而不用重写自己的模型.如果你不需要改变存储在数据库中的字段,而只是需要改 ...
随机推荐
- (Tomcat)服务器之web应用的虚拟目录映射和主机搭建
首先来了解一下web的虚拟目录映射和主机搭建的知识 第一:web的虚拟目录映射 首先我们要知道什么叫做web的虚拟目录映射,这个很好理解的,就是将我们本地硬盘上的web应用映射出一个供外界用户访问的地 ...
- 【一天一道LeetCode】#100. Same Tree(100题大关)
一天一道LeetCode 本系列文章已全部上传至我的github,地址:ZeeCoder's Github 欢迎大家关注我的新浪微博,我的新浪微博 欢迎转载,转载请注明出处 (一)题目 Given t ...
- Eclipse插件 - FindBugs 检查代码隐藏的 Bug
简介 FindBugs 是一个在 Java 程序中查找 bug 的程序,它可以查找可能出错的代码,注意 FindBugs 是检查 Java 字节码,也就是*.class文件.其实准确的 ...
- 工作中常用的Linux命令
1.从其他机器拷贝文件夹 格式: scp -r 文件夹名 用户名@机器名:/路径 范例: scp -rsearch work@zjm-testing-ps23.zjm.baidu.com:/home/ ...
- Property属性, KVC键值编码OC…
1.属性:帮你自动生成setter 和 getter 方法 属性的声明:(写在.h中) 格式: @property 数据类型 属性名 属性的实现:(写在.m中) ...
- java 如何自定义异常 用代码展示 真心靠谱
先建两个自定义的异常类 ChushufuException类 class ChushufuException extends Exception { public ChushufuException( ...
- jQuery插件AjaxFileUpload文件上传实现Javascript多文件上传功能
Ajax file upload plugin是一个功能强大的文件上传jQuery插件,可自定义链接.或其它元素庖代传统的file表单上传结果,可实现Ajax动态提示文件上传 过程,同时支撑多文 ...
- Unity3D学习笔记(四)Unity的网络基础(C#)
一 网络下载可以使用WWW类下载资源用法:以下载图片为例WWW date = new WWW("<url>");yield return date;texture = ...
- HBase写数据
1 多HTable并发写 创建多个HTable客户端用于写操作,提高写数据的吞吐量,一个例子: static final Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration ...
- Java 条形码生成(一维条形码)
utl:http://mianhuaman.iteye.com/blog/1013945 在这里给大家介绍一个java 生成条形码 jbarcode.jar 生成条形码 支持EAN13, EAN8, ...
