Linux - D-Bus
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/D-Bus
D-Bus is a free and open-source inter-process communication (IPC) system, allowing multiple, concurrently-running computer programs (processes) to communicate with one another. It is mainly used by components of the freedesktop implementations such as GNOME, KDE SC or Xfce.
Heavily influenced by the DCOP system used by versions 2 and 3 of KDE, D-Bus has replaced DCOP in the KDE 4 release. An implementation of D-Bus supports most POSIX operating systems, and a port for Windows exists. It is used by Qt 4 and GNOME. In GNOME it has gradually replaced most parts of the earlier Bonobo mechanism.
D-Bus is developed as part of the freedesktop.org project.
Design[edit]
D-Bus is a message-bus system, a way for applications to talk to one another. D-Bus supplies both a system daemon (for events such as "new hardware device added" or "printer queue changed") and a per-user-login-session daemon (for general inter-process communication needs among user applications). The message bus builds on a general one-to-one message passing framework, which any two apps can use to communicate directly (without going through the message bus daemon). Most systems implement a privileged system channel, plus a private channelfor each logged-in user, so that available information in the D-Bus registry can be restricted.
D-Bus works with unix sockets between applications and daemons (applications communicate with each other through a fork of the D-Bus daemon), but work has started to create a "peer-to-peer" socket-type in the Linux kernel able to route messages between applications, leaving the daemon as a top-level manager.[3] The new approach improves speed by halving the number of memory-copy operations.
Architecture[edit]
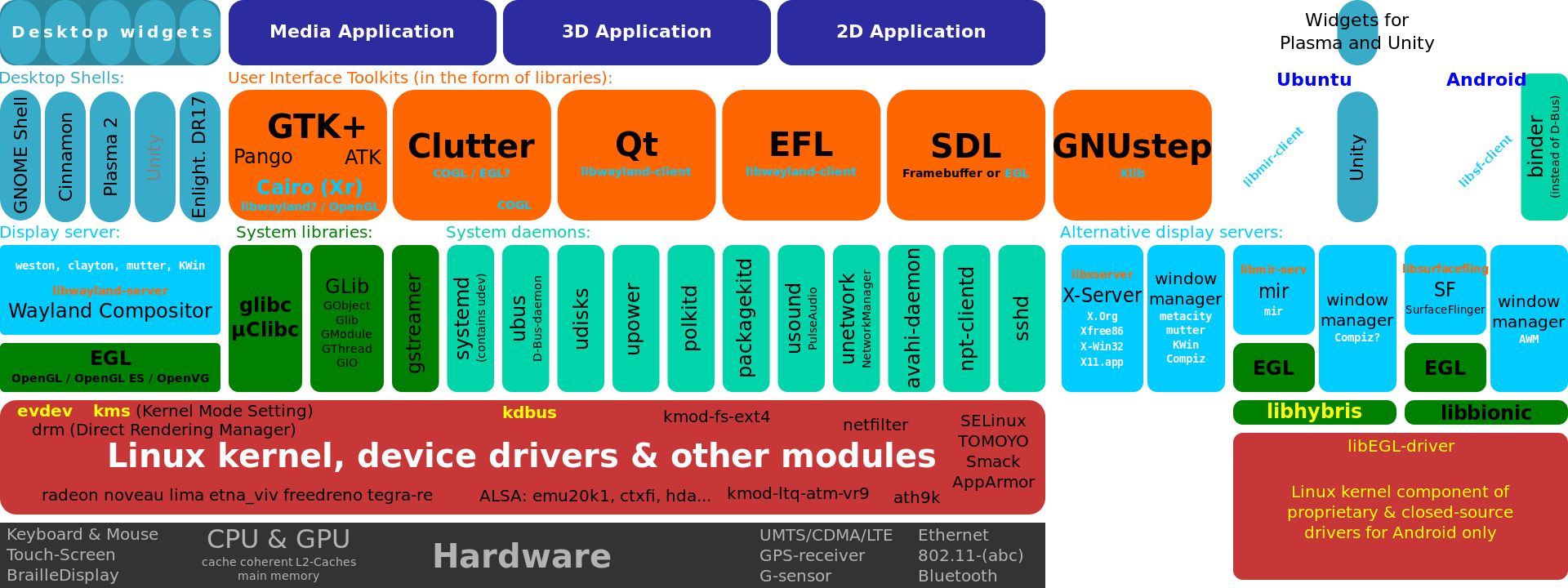

Example of usage in Linux-based systems. The dbus-daemon (named ubus in the illustration) is essentially at the core of the modern Linux graphical desktop environment. Binder is the counterpart used on Android.
D-Bus has three architectural layers:[4]
- libdbus - a library that allows two applications to connect to each other and exchange messages; in 2013 the systemd project rewrote libdbus in an effort to simplify the code, but it turned out to significantly increase the performance of D-Bus as well. In preliminary benchmarks, BMW found that the systemd D-Bus library increased performance by 360%.[5]
- dbus-daemon - a message-bus daemon executable, built on
libdbus, that multiple applications can connect to. The daemon can route messages from one application to zero or more applications, thereby implementing the publish/subscribe paradigm. - wrapper libraries based on particular application frameworks
The design of D-Bus addresses two specific cases:
- communication between desktop applications in the same desktop session; to allow integration of the desktop session as a whole, and address issues of the process lifecycle
- communication between the desktop session and the operating system, where the operating system would typically include the kernel and any system daemons or processes
Mechanisms[edit]
Each application using D-Bus contains objects that usually map to GObject, QObject, C++ objects, or Python objects. Each D-bus object operates as an instance rather than as a type. Messages received over a D-Bus connection get routed to a specific object, not to the application as a whole. In this way, D-Bus resembles software componentry, as it appears to clients as if they are interacting with an object across the IPC connection, whether or not there is an object on the other side.
To allow messages to specify their destination object, the system needs a way to identify and address an object. For this purpose, D-Bus defines a name for each object. The name looks like a filesystem path, for example an object could have the name /org/kde/kspread/sheets/3/cells/4/5. D-Bus encourages human-readable paths, but developers are free to create an object named (e.g.) /com/mycompany/c5yo817y0c1y1c5b if it makes sense for their application.
The D-Bus objects' names are namespaced to help with independently developing code modules[citation needed]. Namespaces are generally prefixed with the developer's reversed domain namecomponents (e.g. /org/kde).
http://www.cnblogs.com/wzh206/archive/2010/05/13/1734901.html
DBUS基础知识
1. 进程间使用D-Bus通信
D-Bus是一种高级的进程间通信机制,它由freedesktop.org项目提供,使用GPL许可证发行。D-Bus最主要的用途是在Linux桌面环境为进程提供通信,同时能将Linux桌面环境和Linux内核事件作为消息传递到进程。D-Bus的主要概率为总线,注册后的进程可通过总线接收或传递消息,进程也可注册后等待内核事件响应,例如等待网络状态的转变或者计算机发出关机指令。目前,D-Bus已被大多数Linux发行版所采用,开发者可使用D-Bus实现各种复杂的进程间通信任务。
注:Linux中的IPC通信机制还包括,管道(fifo),共享内存,信号量,消息队列,Socket等。
2. D-Bus的基本概念
D-Bus是一个消息总线系统,其功能已涵盖进程间通信的所有需求,并具备一些特殊的用途。D-Bus是三层架构的进程间通信系统,其中包括:
接口层:接口层由函数库libdbus提供,进程可通过该库使用D-Bus的能力。
总线层:总线层实际上是由D-Bus总线守护进程提供的。它在Linux系统启动时运行,负责进程间的消息路由和传递,其中包括Linux内核和Linux桌面环境的消息传递。
包装层:包装层一系列基于特定应用程序框架的Wrapper库。
D-Bus具备自身的协议,协议基于二进制数据设计,与数据结构和编码方式无关。该协议无需对数据进行序列化,保证了信息传递的高效性。无论是libdbus,还是D-Bus总线守护进程,均不需要太大的系统开销。
总线是D-Bus的进程间通信机制,一个系统中通常存在多条总线,这些总线由D-Bus总线守护进程管理。最重要的总线为系统总线(System Bus),Linux内核引导时,该总线就已被装入内存。只有Linux内核、Linux桌面环境和权限较高的程序才能向该总线写入消息,以此保障系统安全性,防止有恶意进程假冒Linux发送消息。
会话总线(Session Buses)由普通进程创建,可同时存在多条。会话总线属于某个进程私有,它用于进程间传递消息。
进程必须注册后才能收到总线中的消息,并且可同时连接到多条总线中。D-Bus提供了匹配器(Matchers)使进程可以有选择性的接收消息,另外运行进程注册回调函数,在收到指定消息时进行处理。匹配器的功能等同与路由,用于避免处理无关消息造成进程的性能下降。除此以外,D-Bus机制的重要概念有以下几个。
对象:对象是封装后的匹配器与回调函数,它以对等(peer-to-peer)协议使每个消息都有一个源地址和一个目的地址。这些地址又称为对象路径,或者称之为总线名称。对象的接口是回调函数,它以类似C++的虚拟函数实现。当一个进程注册到某个总线时,都要创建相应的消息对象。
消息:D-Bus的消息分为信号(signals)、方法调用(method calls)、方法返回(method returns)和错误(errors)。信号是最基本的消息,注册的进程可简单地发送信号到总线上,其他进程通过总线读取消息。方法调用是通过总线传递参数,执行另一个进程接口函数的机制,用于某个进程控制另一个进程。方法返回是注册的进程在收到相关信息后,自动做出反应的机制,由回调函数实现。错误是信号的一种,是注册进程错误处理机制之一。
服务:服务(Services)是进程注册的抽象。进程注册某个地址后,即可获得对应总线的服务。D-Bus提供了服务查询接口,进程可通过该接口查询某个服务是否存在。或者在服务结束时自动收到来自系统的消息。
Linux - D-Bus的更多相关文章
- linux下bus,device,driver三者关系
linux下bus,device,driver三者关系 1.bus: 总线作为主机和外设的连接通道,有些总线是比较规范的,形成了很多协议.如 PCI,USB,1394,IIC等.任何设备都可以选择合适 ...
- linux SPI bus demo hacking
/********************************************************************** * linux SPI bus demo hacking ...
- linux下bus、devices和platform的基础模型
转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20672257-id-3147337.html 一.kobject的定义:kobject是Linux2.6引入的设备管理机制,在内核 ...
- linux下bus、devices和platform的基础模型 【转】
转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20672257-id-3147337.html 一.kobject的定义:kobject是Linux2.6引入的设备管理机制,在内核 ...
- linux设备驱动程序--bus
linux 中bus驱动解析 总线(bus)是linux发展过程中抽象出来的一种设备模型,为了统一管理所有的设备,内核中每个设备都会被挂载在总线上,这个bus可以是对应硬件的bus(i2c bus.s ...
- Linux 驱动开发
linux驱动开发总结(一) 基础性总结 1, linux驱动一般分为3大类: * 字符设备 * 块设备 * 网络设备 2, 开发环境构建: * 交叉工具链构建 * NFS和tftp服务器安装 3, ...
- Video for Linux Two API Specification Revision 2.6.32【转】
转自:https://www.linuxtv.org/downloads/legacy/video4linux/API/V4L2_API/spec-single/v4l2.html Video for ...
- Video for Linux Two API Specification revision0.24【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/jmq_0000/article/details/7536805#t136 Video for Linux Two API Specification ...
- Linux内核最顶层文档
Linux 内核文档 该文件是 Linux 内核文档树中最顶层的,会随着内核一起更新:其目的是把散乱的文档集成为一个逻辑清晰的完整版,非常欢迎改善文档,如果想做出自己的贡献,加入vger.kernel ...
- Libpci库的调用
这几天发现在Redhat AS6.5 X86_64下用outl(index, 0xcf8)和inl(0xcfc)下读取PCIe配置空间是系统有时性的会hang, 于是去寻找解决方案,首先想到的是用/d ...
随机推荐
- log4net配置分析
appender 附加器 RollingFileAppender 滚动文件appender MaxSizeRollBackups 最大尺寸回滚 ConversionPatter ...
- 九度oj 题目1363:欢乐斗地主
题目描述: 如果大家玩过欢乐斗地主这个游戏,就一定知道有一个具有“提示”功能的按钮.如果你不知道你现在手里的牌有没有比上家大的牌,并且你也懒得去一张一张地看你手中的牌.这时候你就可以点“提示”按钮,系 ...
- [luoguP1129] [ZJOI2007]矩阵游戏(二分图最大匹配)
传送门 每一行的1和每一列的1不管怎么换还是在同一行和同一列 目标状态中有n个1是不同行且不同列的 那么就是能否找出n个不同行不同列的1 就是每一行选一个不同列的1 如果矩阵中位置i,j为1,那么点i ...
- BZOJ1227 [SDOI2009]虔诚的墓主人 【树状数组】
题目 小W 是一片新造公墓的管理人.公墓可以看成一块N×M 的矩形,矩形的每个格点,要么种着一棵常青树,要么是一块还没有归属的墓地.当地的居民都是非常虔诚的基督徒,他们愿意提前为自己找一块合适墓地.为 ...
- Excel VBA基础教程
https://www.w3cschool.cn/excelvba/excelvba-basics.html Excel VBA语言基础 VBA语言的基础认识 详解VBA编程是什么 excel处理录制 ...
- fullpage在vue单页面当中使用会出现的问题以及解决办法
在 vue 单页面当中发现fullpage会报错,报错信息大概意思为,fullpage不允许初始化多次. 解决办法,在使用fullpage的组件跳转路由进入销毁组件之前的生命周期的时候对fullpag ...
- Repeated Substrings(UVAlive 6869)
题意:求出现过两次以上的不同子串有多少种. /* 用后缀数组求出height[]数组,然后扫一遍, 发现height[i]-height[i-1]>=0,就ans+=height[i]-heig ...
- c++函数学习-关于c++函数的林林总总
本文是我在学习c++过程中的一些思考和总结,主要是c++中关于函数的林林总总.欢迎大家批评和指正,共同学习. os version: ubuntu 12.04 LTS gcc version: gcc ...
- .net IntPtr ==interoperable pointer
调用system.runtime.interopservice,可以用dllimport; API函数主要在“kernel32.dll”.“user32.dll”.“GDI32.dll”, kerne ...
- unix网络编程第2章
time_wait状态 可靠地实现tcp全双工连接的终止; (假设客户端先关闭).服务端再关闭,服务端将发送fin ,客户端此时进入time_wait状态.客户端接收到fin.将回一个ack.如果这 ...
