DOM节点中属性nodeName、nodeType和nodeValue的区别 < Delphi >
http://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/vstudio/hf9hbf87.aspx
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<books>
<book>
<author>Carson</author>
<price format="dollar">31.95</price>
<pubdate>05/01/2001</pubdate>
</book>
<pubinfo>
<publisher>MSPress</publisher>
<state>WA</state>
</pubinfo>
</books>
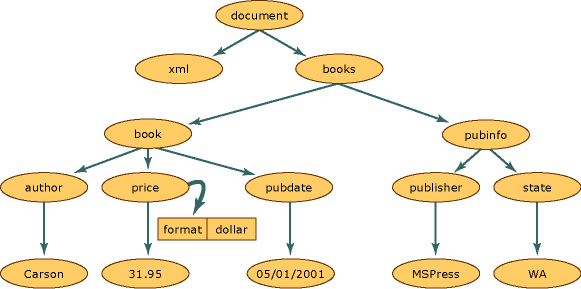
在 XML 文档结构中,此图中的每个圆圈表示一个节点(称为 XmlNode 对象)。
XmlNode 对象是 DOM 树中的基本对象。
XmlDocument 类(扩展XmlNode)支持用于对整个文档执行操作(例如,将文档加载到内存中或将 XML 保存到文件中)的方法。
此外,XmlDocument 提供了查看和处理整个 XML 文档中的节点的方法。 XmlNode 和 XmlDocument 都具有性能和可用性增强,并通过方法和属性执行下列操作:
访问和修改 DOM 特定的节点,如元素节点、实体引用节点等。
除检索节点包含的信息(如元素节点中的文本)外,还检索整个节点。
Node 对象具有一组方法和属性以及基本的和定义完善的特性。其中的某些特性包括:
节点有单个父节点,父节点是与节点相邻的上一级节点。唯一没有父级的节点是文档根,因为它是顶级节点,包含了文档本身和文档片段。
大多数节点可以有多个子节点,子节点是与节点相邻的下一级节点。以下是可以有子节点的节点类型列表。
Document
DocumentFragment
EntityReference
Element
Attribute
XmlDeclaration、Notation、Entity、CDATASection、Text、Comment、ProcessingInstruction 和 DocumentType 节点没有子节点。
处于同一级别、在关系图中由 book 和 pubinfo 节点表示的节点是同级。
DOM 的一个特性是处理属性的方式。属性是不属于父子关系和同级关系的节点。属性被视为元素节点的属性,由名称和值对组成。
例如,如果存在由与元素price 关联的 format="dollar" 组成的 XML 数据,则单词 format 是名称,format 属性的值是 dollar。
为检索 price 节点的 format="dollar" 属性,可以在游标位于 price 元素节点时调用 GetAttribute 方法。有关更多信息,请参见访问 DOM 中的属性。
http://linder0209.iteye.com/blog/1458823
http://www.css88.com/archives/5017
(一)nodeName 属性含有某个节点的名称。
元素节点的 nodeName 是标签名称
属性节点的 nodeName 是属性名称
文本节点的 nodeName 永远是 #text
文档节点的 nodeName 永远是 #document
注释:nodeName 所包含的 XML 元素的标签名称永远是 大写 的
nodeName 属性含有某个节点的名称。
- 元素(element)节点的 nodeName 是标签名称
- 属性(attribute)节点的 nodeName 是属性名称
- 文本(text)节点的 nodeName 永远是 #text
- 文档(document)节点的 nodeName 永远是 #document
(二)nodeValue
对于文本节点,nodeValue 属性包含文本。
对于属性节点,nodeValue 属性包含属性值。
nodeValue 属性对于文档节点 <document> 和元素节点 <element> 是不可用的。
(三)nodeType
nodeType 属性可返回节点的类型。
最重要的节点类型是:
元素类型 节点类型
元素element 1
属性attr 2
文本text 3
注释comments 8
文档document 9
http://www.w3schools.com/dom/dom_nodetype.asp
Node Types
The following table lists the different W3C node types, and which node types they may have as children:
| Node type | Description | Children |
|---|---|---|
| Document | Represents the entire document (the root-node of the DOM tree) | Element (max. one), ProcessingInstruction, Comment, DocumentType |
| DocumentFragment | Represents a "lightweight" Document object, which can hold a portion of a document | Element, ProcessingInstruction, Comment, Text, CDATASection, EntityReference |
| DocumentType | Provides an interface to the entities defined for the document | None |
| ProcessingInstruction | Represents a processing instruction | None |
| EntityReference | Represents an entity reference | Element, ProcessingInstruction, Comment, Text, CDATASection, EntityReference |
| Element | Represents an element | Element, Text, Comment, ProcessingInstruction, CDATASection, EntityReference |
| Attr | Represents an attribute | Text, EntityReference |
| Text | Represents textual content in an element or attribute | None |
| CDATASection | Represents a CDATA section in a document (text that will NOT be parsed by a parser) | None |
| Comment | Represents a comment | None |
| Entity | Represents an entity | Element, ProcessingInstruction, Comment, Text, CDATASection, EntityReference |
| Notation | Represents a notation declared in the DTD | None |
Node Types - Return Values
The following table lists what the nodeName and the nodeValue properties will return for each node type:
| Node type | nodeName returns | nodeValue returns |
|---|---|---|
| Document | #document | null |
| DocumentFragment | #document fragment | null |
| DocumentType | doctype name | null |
| EntityReference | entity reference name | null |
| Element | element name | null |
| Attr | attribute name | attribute value |
| ProcessingInstruction | target | content of node |
| Comment | #comment | comment text |
| Text | #text | content of node |
| CDATASection | #cdata-section | content of node |
| Entity | entity name | null |
| Notation | notation name | null |
NodeTypes - Named Constants
| NodeType | Named Constant |
|---|---|
| 1 | ELEMENT_NODE |
| 2 | ATTRIBUTE_NODE |
| 3 | TEXT_NODE |
| 4 | CDATA_SECTION_NODE |
| 5 | ENTITY_REFERENCE_NODE |
| 6 | ENTITY_NODE |
| 7 | PROCESSING_INSTRUCTION_NODE |
| 8 | COMMENT_NODE |
| 9 | DOCUMENT_NODE |
| 10 | DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE |
| 11 | DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE |
| 12 | NOTATION_NODE |
http://www.w3school.com.cn/xmldom/dom_nodes_nodelist.asp
<bookstore>
<book category="children">
<title lang="en">Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
<book category="cooking">
<title lang="en">Everyday Italian</title>
<author>Giada De Laurentiis</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>30.00</price>
</book>
<book category="web" cover="paperback">
<title lang="en">Learning XML</title>
<author>Erik T. Ray</author>
<year>2003</year>
<price>39.95</price>
</book>
<book category="web">
<title lang="en">XQuery Kick Start</title>
<author>James McGovern</author>
<author>Per Bothner</author>
<author>Kurt Cagle</author>
<author>James Linn</author>
<author>Vaidyanathan Nagarajan</author>
<year>2003</year>
<price>49.99</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
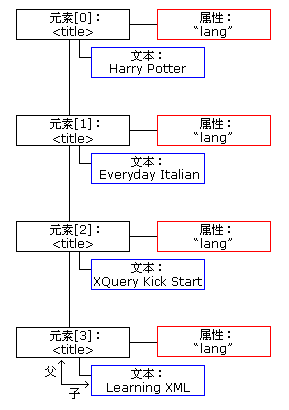
下面的图像表示 "books.xml" 中 <title> 元素的节点列表:
Xml.XMLIntf.IXMLNode.NodeType
Indicates the type of the node.
Read NodeType to determine the type of the node. The type reflects the way the node is used in the XML document.
TNodeType = (
ntReserved,
ntElement,
ntAttribute,
ntText,
ntCData,
ntEntityRef,
ntEntity,
ntProcessingInstr,
ntComment,
ntDocument,
ntDocType,
ntDocFragment,
ntNotation);
Xml.XMLIntf.IXMLNode.NodeName
Indicates the node name.
NodeName is the name of the underlying DOM node.
The node's name depends on the type of the node, as indicated in the following table:
| NodeType | NodeName |
|---|---|
|
ntAttribute |
The attribute name |
|
ntElement |
The tag name |
|
ntText |
'#text' |
|
ntCData |
'#cdata-section' |
|
ntEntityRef |
The name of the entity reference. |
|
ntEntity |
The entity name |
|
ntProcessingInstr |
the target of the processing instruction |
|
ntComment |
'#comment' |
|
ntDocument |
'#document' |
|
ntDocType |
The document type name |
|
ntDocFragment |
'#document-fragment' |
|
ntNotation |
The notation name |
Xml.XMLIntf.IXMLNode.NodeValue
Specifies the value of this node.
Use NodeValue to get or set the value of the node. The meaning of a node's value depends on the type of the node, as indicated in the following table:
| NodeType | Value |
|---|---|
|
ntAttribute |
The attribute value |
|
ntElement |
If the element contains only text, this is that text value. Otherwise, trying to read or set NodeValue causes an exception. |
|
ntText |
The text |
|
ntCData |
The content of the CDATA section. |
|
ntProcessingInstr |
The content of the processing instruction except for the target. |
|
ntComment |
The value (text) of the comment. |
Xml.XMLIntf.IXMLNode.IsTextElement
Indicates whether the node has a single text value.
Read IsTextElement to determine whether this node represents a single text value. For example, if the node represents the following:
<Title> Understanding XML </Title>
IsTextElement is true, because the node represents a tagged element and the text that is its value.
Note:
In the underlying DOM implementation, nodes for which IsTextElement is true are element nodes that have a single child node that is a text node.
IXMLNode flattens this out so that you can use the element node to work with the text value (through the Text property),
rather than requiring you to use a separate node for the text value.
DOM节点中属性nodeName、nodeType和nodeValue的区别 < Delphi >的更多相关文章
- DOM节点中获取文本易混淆的属性
DOM 节点中对于获取文本易混淆的属性,innerText, innerHTML, outerHTML, textContent, nodeValue. 一个实例: <!DOCTYPE html ...
- js:获取节点相关的 nodeName,nodeType,nodeValue
getElementById() getElementsByName() getElementsByTagName() hasChildNodes() nodeName nodeType=1元素节点/ ...
- DOM节点的属性和方法
DOM DOM 是 JavaScript 操作网页的接口,全称为“文档对象模型”(Document Object Model).它的作用是将网页转为一个 JavaScript 对象,从而可以用脚本进行 ...
- js中属性和方法的类型和区别
对象的属性:私有属性(var).类属性(静态属性).对象属性(this).原型属性(prototype). 对象的方法: 私有方法(funtion).类方法(静态方法).对象方法(this).原型方法 ...
- js中属性节点的应用
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- JS中的DOM— —节点以及操作
DOM操作在JS中可以说是非常常见了吧,很多网页的小功能的实现,比如一些元素的增删操作等都可以用JS来实现.那么在DOM中我们需要知道些什么才能完成一些功能的实现呢?今天这篇文章就先简单的带大家入一下 ...
- HTML DOM节点
在 DOM 树中,基本上一切都是节点.每个元素在最底层上都是 DOM 树中的节点.每个属性都是节点.每段文本都是节点.甚至注释.特殊字符(如版权符号 ©).DOCTYPE 声明(如果 HTML 或者 ...
- jacascript DOM节点——节点关系与操作
前言:这是笔者学习之后自己的理解与整理.如果有错误或者疑问的地方,请大家指正,我会持续更新! 节点关系 DOM可以将任何HTML描绘成一个由多层节点构成的结构.每个节点都拥有各自的特点.数据和方法,也 ...
- 深入理解DOM节点操作
× 目录 [1]创建节点 [2]插入节点 [3]移除节点[4]替换节点[5]复制节点 前面的话 一般地,提起操作会想到“增删改查”这四个字,而DOM节点操作也类似地对应于此,接下来将详细介绍DOM的节 ...
随机推荐
- $FFT$(快速傅里叶变换)
- 概念引入 - 点值表示 对于一个$n - 1$次多项式$A(x)$,可以通过确定$n$个点与值(即$x$和$y$)来表示这唯一的$A(x)$ - 复数 对于一元二次方程 $$x^2 + 1 = 0 ...
- 以应用带动SDN发展(CDN峰会 工信部杨崑)(转)
以应用带动SDN发展(CDN峰会 工信部杨崑) SDNAP推荐:这是在亚太全媒体SDN峰会由工信部研究院秘书长杨崑做的关于SDN的一个演讲,本人认为主讲者通过对整 个信息服务体系的精简归纳总结,剥 ...
- Android通过NTP服务器取得UTC标准时间
1. http://hi-android.info/src/android/net/SntpClient.java.html 利用这个类调用NTP函数. 2. 通过函数client.requestTi ...
- HDU3974 Assign the task(多叉树转换为线段+线段树区间染色)
题目大意:有n个人,给你他们的关系(老板和员工),没有直属上司的人就是整个公司的领导者,这意味着n个人形成一棵树(多叉树).当一个人被分配工作时他会让他的下属也做同样的工作(并且立即停止手头正在做的工 ...
- Ecshop二次开发修改
所有的错误,根据下面这个帖子修改 http://bg.artuion.com/328.html 修改错误: 第300行 原有内容: //return preg_replace("/{([^\ ...
- csu 1757(贪心或者树状数组)
1757: 火车入站 Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 209 Solved: 51[Submit][Status][Web Board] ...
- mysql数据库和oracle数据库之间互相导入备份
把从Oracle数据库导出的数据导入到MySql数据库中1. 使用默认的结束符号导入到MySql数据库中: LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE 'd:/oracle.txt' IGNO ...
- python进行des加密解密,而且可以与JAVA进行互相加密解密
import binasciifrom pyDes import des, CBC, PAD_PKCS5import uuidimport time # pip install -i https:// ...
- 在go中连接mysql
5.访问数据库 5.1 database/sql接口 5.2 使用MySQL数据库 5.3 使用SQLite数据库 5.4 使用PostgreSQL数据库 5.5 使用Beego orm库进行ORM开 ...
- IEEEXtreme 10.0 - Game of Stones
这是 meelo 原创的 IEEEXtreme极限编程大赛题解 Xtreme 10.0 - Game of Stones 题目来源 第10届IEEE极限编程大赛 https://www.hackerr ...
