CompletableFuture的入门
runAsync 和 supplyAsync
runAsync接受一个Runable的实现,无返回值
CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->System.out.println("无返回结果的运行"));
supplyAsync接受一个Supplier的实现,有返回值
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("有返回结果的运行");
return 1;
});
获取结果的get和join
都是堵塞,直到返回结果
get方法抛出是经过处理的异常,ExecutionException或**InterruptedException **,需要用户手动捕获
try {
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("有返回结果的运行");
return 1;
}).get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
join方法抛出的就不用捕获,是经过包装的**CompletionException **或 CancellationException
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("有返回结果的运行");
return 1;
}).join());
常用方法
获取结果的get\join\getNow
get():一直等待
get(timeout,unit):等待,除非超时
getNow(valueIfAbsent):计算完返回计算的结果,未计算完返回默认的结果
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 1;
});
System.out.println("立即获取:"+completableFuture.getNow(9999));
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println("doing");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("等一会获取:"+completableFuture.getNow(9999));
join() 同get()
thenApply\handle
执行完前面的,前面返回的结果返回,然后传给后面再,执行完后面任务,一步一步来。
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("step 1");
return 1;
}).thenApply(a -> {
System.out.println("step 2");
return a + 2;
}).thenApply(a -> {
System.out.println("step 3");
return a + 3;
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
执行结果:
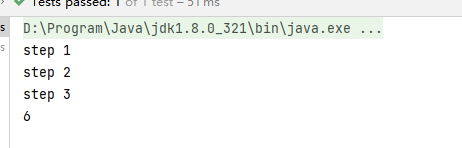
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("step 1");
int a=1/0;
return 1;
}).handle((a,b) -> {
System.out.println("step 2");
if (b!=null) {
System.out.println(b.getMessage());
return 0;
}
return a + 2;
}).handle((a,b) -> {
System.out.println("step 3");
if (b!=null) {
System.out.println(b.getMessage());
return 0;
}
return a + 3;
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
执行结果:
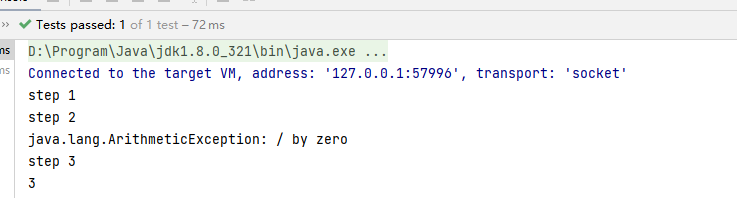
thenApply和handle的区别:
thenApply执行的时候,有异常的则整个执行链会中断,直接抛出异常。

handle有异常也可以往下一步走,根据带的异常参数可以进一步处理
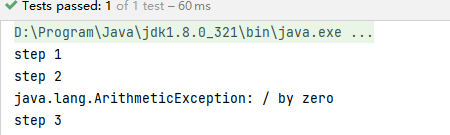
thenAccept
接收前面任务的返回结果,当前节点处理,并不返回结果。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("step 1");
return 10;
}).thenAccept(a->{
System.out.println("res "+a);
});
applyToEither
在多个任务段同时执行时,哪个任务段用时最少,就返回哪个
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("step 1");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 1;
}).applyToEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("step 2");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 2;
}), a -> {
return a;
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
执行结果:
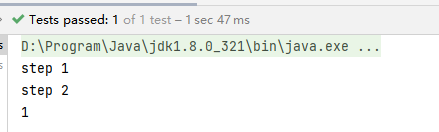
thenCombine
合并多个任务段的返回结果
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("step 1");
return IntStream.range(1, 11).sum();
}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("step 2");
return IntStream.range(11, 21).sum();
}), (a, b) -> a + b)
.thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("step 3");
return IntStream.range(21, 31).sum();
}), (a, b) -> a + b);
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
CompletableFuture的入门的更多相关文章
- CompletableFuture用法介绍
一.CompletableFuture用法入门介绍 入门介绍的一个例子: package com.cy.java8; import java.util.Random; import java.util ...
- 一条数据的HBase之旅,简明HBase入门教程-Write全流程
如果将上篇内容理解为一个冗长的"铺垫",那么,从本文开始,剧情才开始正式展开.本文基于提供的样例数据,介绍了写数据的接口,RowKey定义,数据在客户端的组装,数据路由,打包分发, ...
- Spring Reactor 入门与实践
适合阅读的人群:本文适合对 Spring.Netty 等框架,以及 Java 8 的 Lambda.Stream 等特性有基本认识,希望了解 Spring 5 的反应式编程特性的技术人员阅读. 一.前 ...
- Angular2入门系列教程7-HTTP(一)-使用Angular2自带的http进行网络请求
上一篇:Angular2入门系列教程6-路由(二)-使用多层级路由并在在路由中传递复杂参数 感觉这篇不是很好写,因为涉及到网络请求,如果采用真实的网络请求,这个例子大家拿到手估计还要自己写一个web ...
- ABP入门系列(1)——学习Abp框架之实操演练
作为.Net工地搬砖长工一名,一直致力于挖坑(Bug)填坑(Debug),但技术却不见长进.也曾热情于新技术的学习,憧憬过成为技术大拿.从前端到后端,从bootstrap到javascript,从py ...
- Oracle分析函数入门
一.Oracle分析函数入门 分析函数是什么?分析函数是Oracle专门用于解决复杂报表统计需求的功能强大的函数,它可以在数据中进行分组然后计算基于组的某种统计值,并且每一组的每一行都可以返回一个统计 ...
- Angular2入门系列教程6-路由(二)-使用多层级路由并在在路由中传递复杂参数
上一篇:Angular2入门系列教程5-路由(一)-使用简单的路由并在在路由中传递参数 之前介绍了简单的路由以及传参,这篇文章我们将要学习复杂一些的路由以及传递其他附加参数.一个好的路由系统可以使我们 ...
- Angular2入门系列教程5-路由(一)-使用简单的路由并在在路由中传递参数
上一篇:Angular2入门系列教程-服务 上一篇文章我们将Angular2的数据服务分离出来,学习了Angular2的依赖注入,这篇文章我们将要学习Angualr2的路由 为了编写样式方便,我们这篇 ...
- Angular2入门系列教程4-服务
上一篇文章 Angular2入门系列教程-多个组件,主从关系 在编程中,我们通常会将数据提供单独分离出来,以免在编写程序的过程中反复复制粘贴数据请求的代码 Angular2中提供了依赖注入的概念,使得 ...
随机推荐
- Jx.Cms开发笔记(二)-系统登录
界面 此界面完全抄了BootstrapAdmin css隔离 由于登录页面的css与其他页面没有什么关系,所以为了防止其他界面的css被污染,我们需要使用css隔离. css隔离需要在_Host.cs ...
- 使用Lua 脚本实现redis 分布式锁,报错:ERR Error running script (call to f_8ea1e266485534d17ddba5af05c1b61273c30467): @user_script:10: @user_script: 10: Lua redis() command arguments must be strings or integers .
在使用SpringBoot开发时,使用RedisTemplate执行 redisTemplate.execute(lockScript, redisList); 发现报错: ERR Error run ...
- python基础练习题(题目 字母识词)
day22 --------------------------------------------------------------- 实例031:字母识词 题目 请输入星期几的第一个字母来判断一 ...
- git详情、git工作流程、常用命令、忽略文件、分支操作、gitee远程仓库使用
今日内容概要 git详情 git工作流程 git常用命令 过滤文件 分支操作 git远程仓库使用 可参照:https://www.cnblogs.com/liuqingzheng/p/15328319 ...
- C#/VB.NET 获取Excel中图片所在的行、列坐标位置
本文以C#和vb.net代码示例展示如何来获取Excel工作表中图片的坐标位置.这里的坐标位置是指图片左上角顶点所在的单元格行和列位置,横坐标即顶点所在的第几列.纵坐标即顶点所在的第几行.下面是获取图 ...
- zookeeper篇-watch命令
点赞再看,养成习惯,微信搜索「小大白日志」关注这个搬砖人. 文章不定期同步公众号,还有各种一线大厂面试原题.我的学习系列笔记. 每个路径节点都有一个watcher监控,当该节点数据改变时(CRUD), ...
- [AcWing 68] 0到n-1中缺失的数字
点击查看代码 class Solution { public: int getMissingNumber(vector<int>& nums) { if (nums.empty() ...
- Shell脚本实战:日志关键字监控+自动告警
一个执着于技术的公众号 该程序使用场景说明:主要用于Linux服务器监控程序日志,如出现关键字异常则触发相应的动作或告警操作,通知到邮件联系人. 一.安装邮件服务 1.解压 tar -jxf mail ...
- react 疑问集锦
在 setState 后未 re-render function component 初始化调用接口
- SylixOS——虚拟机网络配置
网络配置 点击设置按钮 新建虚拟网络适配器 输入IP地址(注意:IP地址必须和SylixOS在同一个子网内) 点击确定等待,虚拟网络适配器建立完成后效果如下(多了一个名为"以太网2" ...
