谣言检测(DUCK)《DUCK: Rumour Detection on Social Media by Modelling User and Comment Propagation Networks》
论文信息
论文标题:DUCK: Rumour Detection on Social Media by Modelling User and Comment Propagation Networks
论文作者:Lin Tian, Xiuzhen Zhang, Jey Han Lau
论文来源:2022,NAACL
论文地址:download
论文代码:download
1 Introduction
本文的模型研究了如何充分利用用户和评论信息,对比之前的方法,有以下不同:
(1) we model comments both as a:
(i) stream to capture the temporal nature of evolving comments;
(ii) network by following the conversational structure (see Figure 1 for an illustration);
(2) our comment network uses sequence model to encode a pair of comments before feeding them to a graph network, allowing our model to capture the nuanced charac- teristics (e.g. agreement or rebuttal) exhibited by a reply;
(3) when modelling the users who engage with a story via graph networks, we initialise the user nodes with encodings learned from their profiles and characteristics of their “friends” based on their social networks.
2 Problem Statement
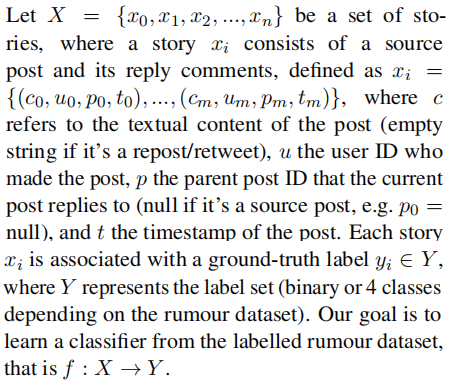
3 Methodology
总体框架:
包括如下几个部分:
(1) comment tree: models the comment network by following the reply-to structure using a combination of BERT and graph attentional networks;
(2) comment chain: models the comments as a stream using transformer-based sequence models;
(3) user tree: incorporates social relations to model the user network using graph attentional networks;
(4) rumour classifier: combines the output from comment tree, comment chain and user tree to classify the source post.
请注意,user tree 的网络结构不同于 comment tree 的网络结构,因为前者同时捕获 comment 和 reposts/retweets,但后者只考虑 comment(Figure 1)。
3.1 Comment Tree
基于 GNN 的建模 comment 之间的关系的模型通常使用的是简单的文本特征(bag-of-words),忽略了 comment 之间的微妙关系("stance" or "deny")关系。
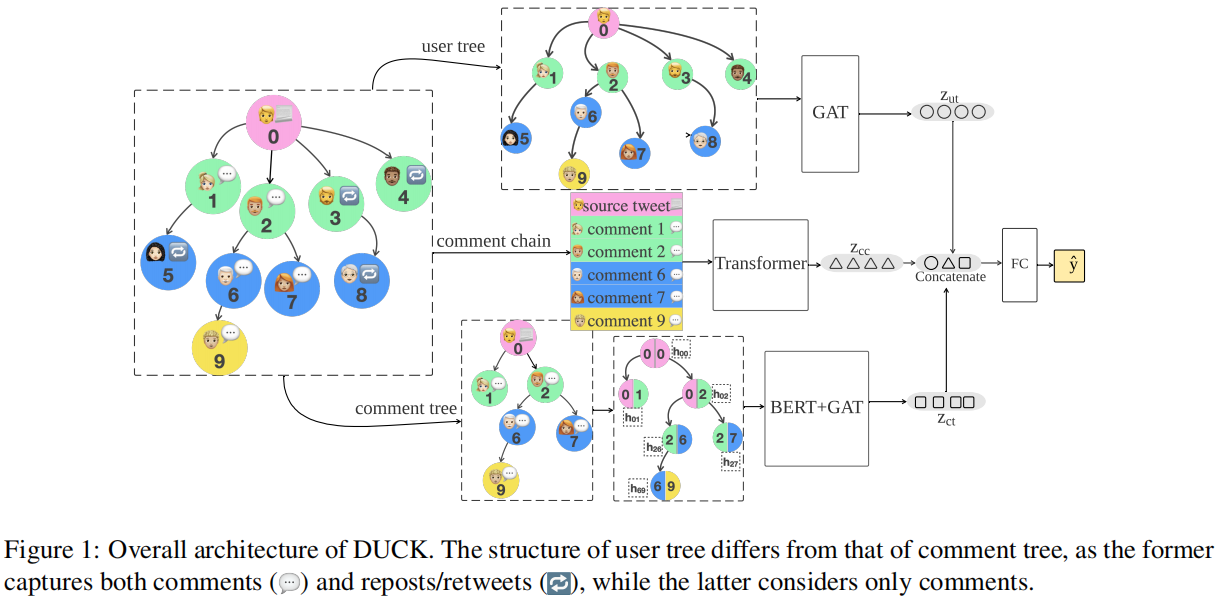
所以,本文采用预训练语言模型 BERT 和 GAT 去建模 comment tree ,具体参见 Figure 2:
首先,使用 BERT 去处理一对 parent-child posts ,然后使用 GAT 去建模整个 conversational strucure 。( self-attention 在 parent-child 之间的词产生细粒度的分析)
以 Figure 2 中的 comment tree 为例,这意味着我们将首先使用 BERT 处理以下几对 comments {(0, 0),(0, 1),(0, 2),(2, 6),(2, 7),(6, 9)}:
$h_{p+q}=\mathrm{BERT}\left(\mathrm{emb}\left([C L S], c_{p},[S E P], c_{q}\right)\right)$
其中,$c$ 表示 text,$emb()$ 表示 embedding function,$h$ 表示由 BERT 产生的 [CLS] 标记的上下文表示。
为了模拟 conversational network structure ,本文使用图注意网络 GAT。为了计算 $h_{i}^{(l+1)}$,在迭代 $l+1$ 次时对节点 $i$ 的编码:
$\begin{array}{l}e_{i j}^{(l)} &=&\operatorname{LR}\left(a^{(l)^{T}}\left(W^{(l)} h_{i}^{(l)} \oplus W^{(l)} h_{j}^{(l)}\right)\right) \\h_{i}^{(l+1)} &=&\sigma\left(\sum\limits _{j \in \mathcal{N}(i)} \operatorname{softmax}\left(e_{i j}^{(l)}\right) z_{j}^{(l)}\right)\end{array}$
为了聚合节点编码以得到一个图表示($\left(z_{c t}\right)$),探索了四种方法:
root:Uses the root encoding to represent the graph as the source post
$z_{c t}=h_{0}^{L}$
$\neg root$: Mean-pooling over all nodes except the root:
$z_{c t}=\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m} h_{i}^{L}$
where $m$ is the number of replies/comments.
$\Delta$ : Mean-pooling of the root node and its immediate neighbours:
$z_{c t}=\frac{1}{|\mathcal{N}(0)|} \sum_{i \in \mathcal{N}(0)} h_{i}^{L}$
all: Mean-pooling of all nodes:
$z_{c t}=\frac{1}{m+1} \sum_{i=0}^{m} h_{i}^{L}$
3.2 Comment Chain
本文按照它们发布的顺序将这些帖子建模为一个流结构,而不是一个树结构,处理 comment chain 考虑了三种模型:
(1) one-tier transformer
(2) longformer
(3) two-tier transformer
3.2.1 One-tier transformer
给定一个源帖子 $\left(c_{0}\right)$ 和 comment $\left(\left\{c_{1}, \ldots, c_{m}\right\}\right)$,我们可以简单地将它们连接成一个长字符串,并将其提供给 BERT:
$z_{c c}=\operatorname{BERT}\left(\mathrm{emb}\left([C L S], c_{0},[S E P], c_{1}, \ldots, c_{m^{\prime}}\right)\right)$
其中,$m^{\prime}(<m)$ 是我们可以合并的不超过 BERT 的最大序列长度的 comment(实验中是384个)。
3.2.2 Longformer
为规避序列长度的限制,实验使用了一个 Longformer,它可以处理多达4096个子词,允许使用大部分 comment,如果不是所有的评论。
Longformer 具有与 one-tier transformer 类似的架构,但使用更稀疏的注意模式来更有效地处理更长的序列。我们使用一个预先训练过的 Longformer,并遵循与之前相同的方法来建模 comment chain:
$z_{c c}=\mathrm{LF}\left(\operatorname{emb}\left([C L S], c_{0},[S E P], c_{1}, \ldots, c_{m^{\prime \prime}}\right)\right)$
其中,$m^{\prime \prime} \approx m$
3.2.3 Two-tier transformer
解决序列长度限制的另一种方法是使用 two tiers of transformers 对 comment chain 进行建模:一层用于独立处理帖子,另一种用于使用来自第一个 transformer 的表示来处理帖子序列。
$\begin{array}{l}h_{i} &=&\operatorname{BERT}\left(\mathrm{emb}_{1}\left([C L S], c_{i}\right)\right) \\z_{c c} &=&\operatorname{transformer}\left(\operatorname{emb}_{2}([C L S]), h_{0}, h_{1}, \ldots, h_{m}\right)\end{array}$
其中,BERT 和 transformer 分别表示 first-tier transformers 和 second-tier transformers。econd-tier transformers 具有与 BERT 类似的架构,但只有 2 层,其参数是随机初始化的。
3.3 User Tree
我们探索了三种都是基于 GAT 建模 user network 的方法,并通过 mean-pooling 所有节点来聚合节点编码,以生成图表示:
$z_{u t}=\frac{1}{m+1} \sum\limits_{i=0}^{m} h_{i}^{L}$
这三种方法之间的主要区别在于它们如何初始化用户节点 $\left(h_{i}^{(0)}\right)$:
第一种 $\mathbf{G A T_{\text {rnd }}}$ :用随机向量初始化用户节点。
$h_{i}^{0}=\operatorname{random}\left[v_{1}, v_{2}, \ldots, v_{d}\right]$
第二种 $\mathbf{GAT _{\text {prf: }}}$ : 来自他们的 user profiles :username, user screen name, user description, user account age 等。因此,static user node $h_{i}^{0}$ 由 $v_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{k}$ 给出
$h_{i}^{0}=\left[v_{1}, v_{2}, \ldots, v_{k}\right]$
前者捕捉使用源帖子的用户,而后者是互相关注的用户网络。
$\begin{array}{l}Z &=\operatorname{enc}(\mathbf{X}, \mathbf{A}) =\operatorname{GCN}\left(f\left(\operatorname{GCN}\left(\mathbf{A}, \mathbf{X} ; \theta_{1}\right)\right) ; \theta_{2}\right) \\\hat{A} &=\operatorname{dec}\left(Z, Z^{\top}\right)=\sigma\left(Z Z^{\top}\right)\end{array}$
$h_{i}^{(0)} \in \mathbb{R}^{d}$ 通过下述方法计算:
$h_{i}^{(0)}=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}\operatorname{ReLU}\left(W \cdot\left[v_{1}, \ldots, v_{k}\right]\right), & \text { if } \operatorname{user}_{i} \notin G_{s} \\Z_{i}, & \text { if } \operatorname{user}_{i} \in G_{s}\end{array}\right.$
其中,$W_{i}$ 是全连接参数,$v_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{k}$ 是 user profiles。
3.4 Rumour Classifier
使用 comment tree、comment chain、user tree 分别生成的图表示 $z_{c t}$、$z_{c c}$、$z_{u t}$ 进行谣言分类:
4 Experiments and Results
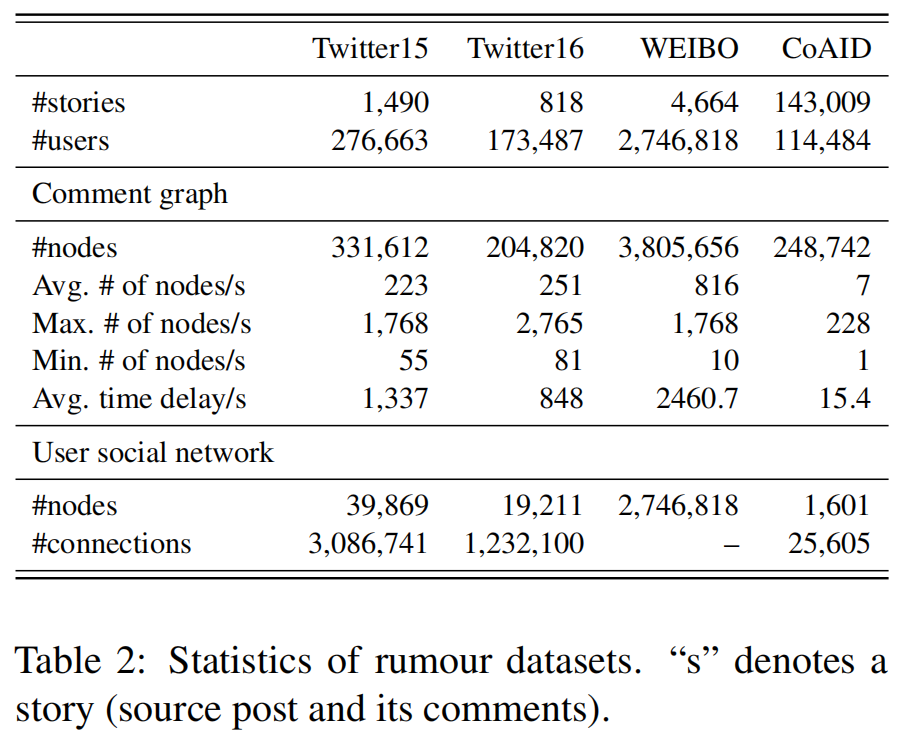
4.1 Datasets
数据集统计如下:
we report the average performance based on 5-fold cross-validation.
we reserve 20% data as test and split the rest in a ratio of 4:1 for training and development partitions and report the average test performance over 5 runs (initialised with different random seeds).
4.2 Results
本文实验主要回答如下问题:
- Q1 [Comment tree]: Does incorporating BERT to analyse the relation between parent and child posts help modelling the comment network, and what is the best way to aggregate comment-pair encodings to represent the comment graph?
- Q2 [Comment chain]: Does incorporating more comments help rumour detection when modelling them as a stream of posts?
- Q3 [User tree]: Can social relations help modelling the user network?
- Q4 [Overall performance]: Do the three different components complement each other and how does a combined approach compared to existing rumour detection systems?
4.2.1 Comment Tree
为了理解使用BERT处理一对 parent-child posts 的影响,我们提出了另一种替代方法(“unpaired”),即使用 BERT 独立处理每个帖子,然后将其 [CLS] 表示提供给GAT。
$h_{p}=\operatorname{BERT}\left(\operatorname{emb}\left([C L S], c_{p}\right)\right)$
其中,$h$ 将用作 GAT 中的初始节点表示($h^{(0)}$)。这里报告了这个替代模型(“unpaired”)及不同的聚合方法(“root”、“¬root”、“$\bigtriangleup $” 和 “all”)的性能。
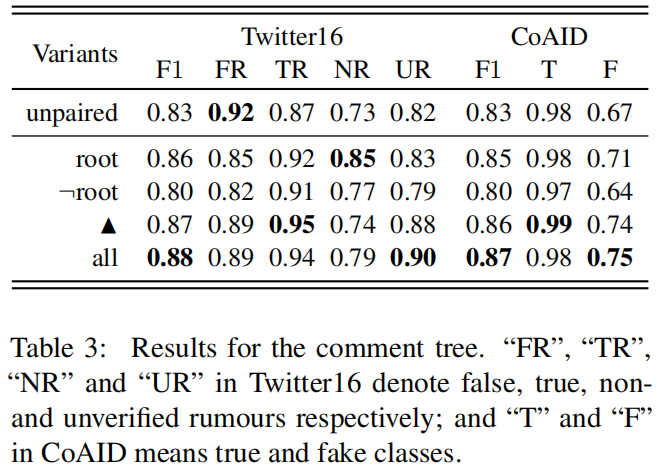
Comparing the aggregation methods, "all" performs the best, followed by "$\boldsymbol{\Delta}$ " and "root" (0.88 vs . 0.87 vs. 0.86 in Twitter16; 0.87 vs. 0.86 vs. 0.85 in CoAID in terms of Macro-F1). We can see that the root and its immediate neighbours contain most of the information, and not including the root node impacts the performance severely (both Twitter16 and CoAID drops to 0.80 with $\neg$ root).
Does processing the parent-child posts together with BERT help? The answer is evidently yes, as we see a substantial drop in performance when we process the posts independently: "unpaired" produces a macro-F1 of only 0.83 in both Twitter16 and CoAID. Given these results, our full model (DUCK) will be using "all"' as the aggregation method for computing the comment graph representation.
4.2.2 Comment Chain
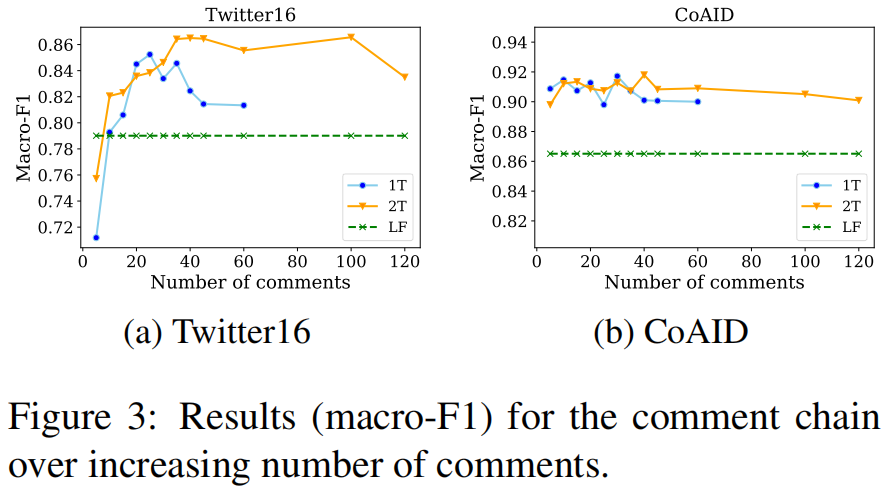
Fig. 3 绘制了我们改变所包含的评论数量来回答 Q2 的结果:
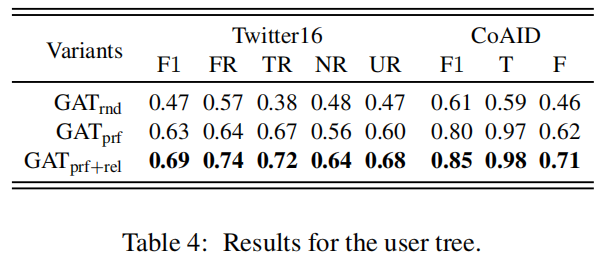
4.2.3 User Tree
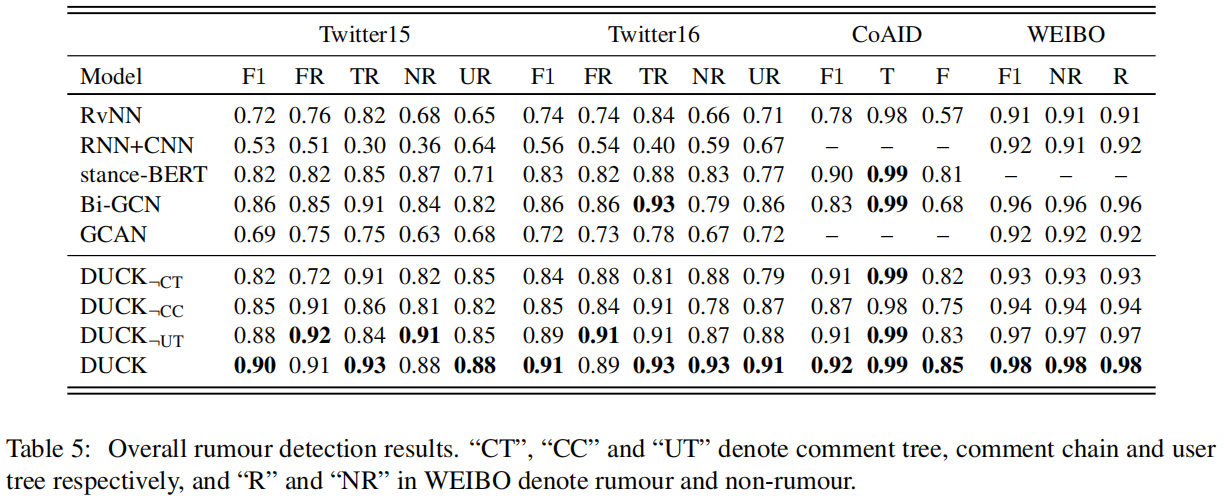
4.2.4 Overall Rumour Detection Performance
谣言检测(DUCK)《DUCK: Rumour Detection on Social Media by Modelling User and Comment Propagation Networks》的更多相关文章
- 谣言检测(PSIN)——《Divide-and-Conquer: Post-User Interaction Network for Fake News Detection on Social Media》
论文信息 论文标题:Divide-and-Conquer: Post-User Interaction Network for Fake News Detection on Social Media论 ...
- 谣言检测(GACL)《Rumor Detection on Social Media with Graph Adversarial Contrastive Learning》
论文信息 论文标题:Rumor Detection on Social Media with Graph AdversarialContrastive Learning论文作者:Tiening Sun ...
- 谣言检测(RDEA)《Rumor Detection on Social Media with Event Augmentations》
论文信息 论文标题:Rumor Detection on Social Media with Event Augmentations论文作者:Zhenyu He, Ce Li, Fan Zhou, Y ...
- 谣言检测——(GCAN)《GCAN: Graph-aware Co-Attention Networks for Explainable Fake News Detection on Social Media》
论文信息 论文标题:GCAN: Graph-aware Co-Attention Networks for Explainable Fake News Detection on Social Medi ...
- 谣言检测(RDCL)——《Towards Robust False Information Detection on Social Networks with Contrastive Learning》
论文信息 论文标题:Towards Robust False Information Detection on Social Networks with Contrastive Learning论文作 ...
- 谣言检测——《MFAN: Multi-modal Feature-enhanced Attention Networks for Rumor Detection》
论文信息 论文标题:MFAN: Multi-modal Feature-enhanced Attention Networks for Rumor Detection论文作者:Jiaqi Zheng, ...
- 谣言检测(PLAN)——《Interpretable Rumor Detection in Microblogs by Attending to User Interactions》
论文信息 论文标题:Interpretable Rumor Detection in Microblogs by Attending to User Interactions论文作者:Ling Min ...
- 谣言检测——(PSA)《Probing Spurious Correlations in Popular Event-Based Rumor Detection Benchmarks》
论文信息 论文标题:Probing Spurious Correlations in Popular Event-Based Rumor Detection Benchmarks论文作者:Jiayin ...
- 谣言检测(ClaHi-GAT)《Rumor Detection on Twitter with Claim-Guided Hierarchical Graph Attention Networks》
论文信息 论文标题:Rumor Detection on Twitter with Claim-Guided Hierarchical Graph Attention Networks论文作者:Erx ...
随机推荐
- std::hash<std::pair<int, int> >
标题是搞笑的 ! 这个问题只需要 since C++11 问题:怎么让 unordered_map 支持使用 pair 作为 key? 如果你能把两个东西压到一个基本类型里那么就不用解决这个问题了 . ...
- 精心总结十三条建议,帮你创建更合适的MySQL索引
上篇文章讲到使用MySQL的Explain命令可以分析SQL性能瓶颈,优化SQL查询,以及查看是否用到了索引. 我们都知道创建索引可以提高查询效率,但是具体该怎么创建索引? 哪些字段适合创建索引? 哪 ...
- 霜皮剥落紫龙鳞,下里巴人再谈数据库SQL优化,索引(一级/二级/聚簇/非聚簇)原理
原文转载自「刘悦的技术博客」https://v3u.cn/a_id_206 举凡后端面试,面试官不言数据库则已,言则必称SQL优化,说起SQL优化,网络上各种"指南"和" ...
- 如何让 JS 代码不可断点
绕过断点 调试 JS 代码时,单步执行(F11)可跟踪所有操作.例如这段代码,每次调用 alert 时都会被断住: debugger alert(11) alert(22) alert(33) ale ...
- B/S结构通信系统原理
本文介绍JavaWeb的B/S结构通信原理 概念: Javaweb中B/S架构是一种系统架构形式,这里的B是Browser(浏览器),S是Server(服务器),是一种系统的架构形式,有 ...
- react实战系列 —— React 中的表单和路由的原理
其他章节请看: react实战 系列 React 中的表单和路由的原理 React 中的表单是否简单好用,受控组件和非受控是指什么? React 中的路由原理是什么,如何更好的理解 React 应用的 ...
- Postfix别名邮件与SASL验证
Postfix别名邮件与SASL验证 环境简介 系统: CentOS 8.3.2011 软件包: postfix-2:3.3.1-12.el8.x86_64 cyrus-sasl-2.1.27-5.e ...
- 【Java】学习路径63-反射、类的加载-附思维导图(完结)
这一章的知识在实际开发也没有那么重要,主要是了解即可,另外掌握如何使用反射机制. 类的使用: 在虚拟机中: 类的加载->类的连接->类的初始化 类的加载 只会加载需要用到的类,加载到内 ...
- 【java】学习路径37-练习:任意文件的复制
使用字节完成复制 import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException ...
- HOSMEL:一种面向中文的可热插拔模块化实体链接工具包
HOSMEL: A Hot-Swappable Modularized Entity Linking Toolkit for Chinese ACL 2022 论文地址:https://aclanth ...
