springboot启动流程 (1) 流程概览
本文将通过阅读源码方式分析SpringBoot应用的启动流程,不涉及Spring启动部分(有相应的文章介绍)。
本文不会对各个流程做展开分析,后续会有文章介绍详细流程。
SpringApplication类
应用启动入口
使用以下方式启动一个SpringBoot应用:
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
run方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 获取应用env
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 打印banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 创建ApplicationContext
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// 一些准备工作
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// refresh ApplicationContext
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 调用listener
listeners.started(context);
// 调用ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
获取应用env
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 创建StandardServletEnvironment, 会初始化四个PropertySource:
// servletConfigInitParams, servletContextInitParams, systemProperties, systemEnvironment
// 比如-Dserver.port=8888会在systemProperties中
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 添加defaultProperties和命令行配置参数即CommandLinePropertySource
// 通常都没有这两个配置
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 使用ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource封装并暴露所有的PropertySource集
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 添加ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件并触发multicastEvent加载应用配置文件
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
// 将spring.main.xx配置加载到SpringApplication对象
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
加载配置文件的入口在ConfigFileApplicationListener类中:
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
}
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
// 添加RandomValuePropertySource
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
// 加载配置文件
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
加载配置文件的源码较多,此处不做记录,简单梳理一下流程:
- 加载active profile配置文件
- 如果配置了spring.config.additional-location或spring.config.location参数,会使用它们作为配置文件。如果这两个参数值是目录,则会从这两个目录下查找配置文件
- 默认从classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/*/,file:./config/目录下查找application-xx.properties或application-xx.yml文件
- 使用PropertiesPropertySourceLoader和YamlPropertySourceLoader解析配置文件
- 会将配置参数封装成OriginTrackedMapPropertySource类型对象,使用applicationConfig: [classpath:/application-dev.yml]之类的字符串作为PropertySource的名称
- 加载默认的application.properties或application.yml文件
- 解析出来的所有PropertySource都会添加到environment的propertySources中,propertySources是一个MutablePropertySources对象,管理着所有的PropertySource集,在这个过程中,添加的先后顺序决定了配置的优先级
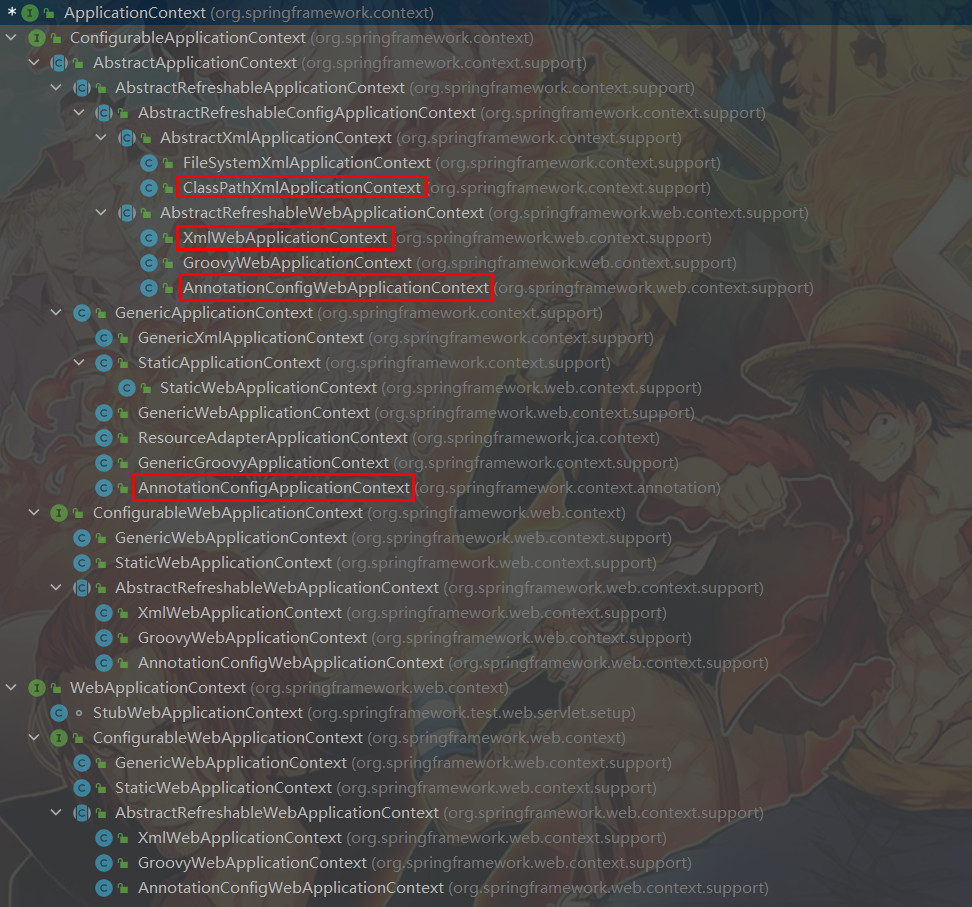
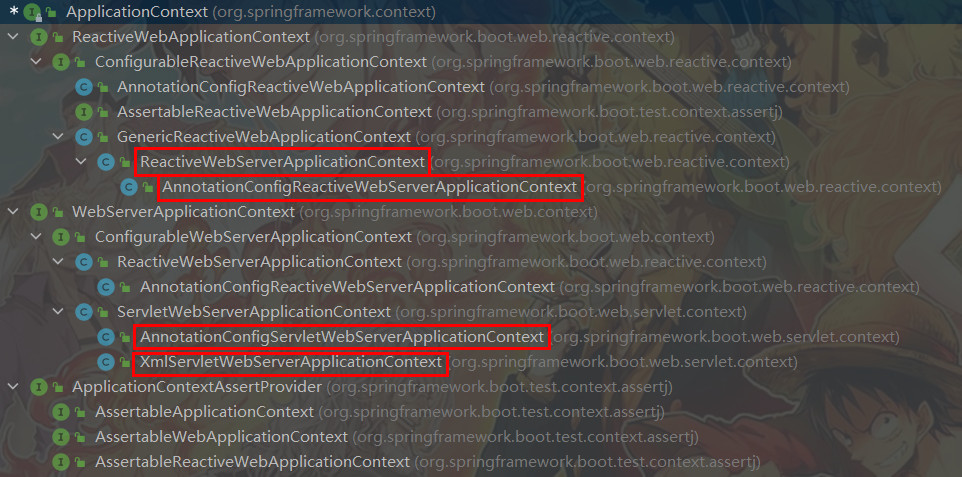
创建ApplicationContext
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
// AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext类
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
// AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext类
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
// AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
prepareContext
private void prepareContext(
ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments,
Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// Apply any ApplicationContextInitializers to the context before it is refreshed.
// ApplicationContextInitializers集是在创建SpringApplication对象的时候初始化的
applyInitializers(context);
// 触发contextPrepared事件
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// 获取BeanFactory并注册必要的Bean
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
// 注册启动参数
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
// 注册banner printer
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
// 设置是否允许Bean覆盖,使用spring.main.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding参数配置
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
// 将SpringApplication.run(Xxx.class, args)方法传入的Class注册到容器
// 使用AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader.register(Class<?>...)方法注册启动类
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
// 触发contextLoaded事件
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
refreshApplicationContext
protected void refresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.refresh();
}
调用的是ServletWebServerApplicationContext的refresh方法:
public final void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
try {
super.refresh();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
// 关闭web server
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
if (webServer != null) {
webServer.stop();
}
throw ex;
}
}
绝大多数的refresh逻辑都在AbstractApplicationContext类里面,ServletWebServerApplicationContext中会在onRefresh阶段创建webServer:
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
调用ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}
SpringBootApplication注解
指示一个配置类,该类声明一个或多个@Bean方法,并触发自动配置和组件扫描。这是一个方便的注解,相当于声明@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan注解。
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
String[] excludeName() default {};
/**
* Base packages to scan for annotated components. Use scanBasePackageClasses
* for a type-safe alternative to String-based package names.
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages")
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
/**
* Type-safe alternative to scanBasePackages for specifying the packages to
* scan for annotated components. The package of each class specified will be scanned.
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses")
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
/**
* The BeanNameGenerator class to be used for naming detected components
* within the Spring container.
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "nameGenerator")
Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class;
/**
* Specify whether @Bean methods should get proxied in order to enforce
* bean lifecycle behavior, e.g. to return shared singleton bean instances even in
* case of direct @Bean method calls in user code. This feature requires
* method interception, implemented through a runtime-generated CGLIB subclass which
* comes with limitations such as the configuration class and its methods not being
* allowed to declare final.
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = Configuration.class)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
SpringBootConfiguration注解
指示一个类提供Spring Boot application @Configuration功能。可以替代Spring的标准@Configuration注解,以便可以自动找到配置类。
应用程序应该只标注一个@SpringBootConfiguration,大多数SpringBoot应用程序将从@SpringBootApplication继承它。
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
@AliasFor(annotation = Configuration.class)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
EnableAutoConfiguration注解
启用SpringBoot自动装配功能,尝试猜测和配置可能需要的组件Bean。
自动装配类通常是根据类路径和定义的Bean来应用的。例如,如果类路径上有tomcat-embedded.jar,那么可能需要一个TomcatServletWebServerFactory(除非已经定义了自己的Servlet WebServerFactory Bean)。
自动装配试图尽可能地智能化,并将随着开发者定义自己的配置而取消自动装配相冲突的配置。开发者可以使用exclude()排除不想使用的配置,也可以通过spring.autoconfig.exclude属性排除这些配置。自动装配总是在用户定义的Bean注册之后应用。
用@EnableAutoConfiguration注解标注的类所在包具有特定的意义,通常用作默认扫描的包。通常建议将@EnableAutoConfiguration(如果没有使用@SpringBootApplication注解)放在根包中,以便可以搜索所有子包和类。
自动装配类是普通的Spring @Configuration类,使用SpringFactoriesLoader机制定位。通常使用@Conditional方式装配,最常用的是@ConditionalOnClass和@ConditionalOnMissingBean注解。
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
*/
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* 当类路径下没有指定的类时,可以使用这个属性指定排除的类
*/
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
AutoConfigurationPackage注解
Registers packages with AutoConfigurationPackages. When no base packages or base package classes are specified, the package of the annotated class is registered.
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
}
AutoConfigurationImportSelector类
DeferredImportSelector接口的实现类,处理自动装配,导出所有需要自动装配的类。
创建WebServer
SpringBoot会在onRefresh阶段创建webServer,首先从spring容器获取ServletWebServerFactory,然后调用getWebServer方法创建webServer。
getWebServer方法需要传入ServletContextInitializer集来初始化ServletContext。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ServletContextInitializer {
void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException;
}
我们开发者如果需要使用ServletContextInitializer来初始化ServletContext的话,也可以编写一个实现类,然后将其注册到spring容器即可。
另外,SpringBoot还会自动装配DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration类,这个类会创建DispatcherServlet和DispatcherServletRegistrationBean。DispatcherServlet是SpringWebMvc的最核心组件,DispatcherServletRegistrationBean实现了ServletContextInitializer接口,可以将DispatcherServlet注册到ServletContext。以TomcatServletWebServerFactory为例,这个类会通过TomcatStarter来调用所有的ServletContextInitializer,TomcatStarter实现了ServletContainerInitializer接口,Tomcat的ServletContext在启动阶段会调用ServletContainerInitializer的onStartup方法来初始化Servlet容器。
SpringBoot启动流程
- 初始化environment应用配置参数:servletConfigInitParams, servletContextInitParams, systemProperties, systemEnvironment及配置文件等
- 创建ApplicationContext对象,SpringBoot应用默认使用的是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext类
- prepareContext阶段:触发一些事件,将启动类注册到Spring容器
- refresh阶段:扫描应用组件,自动装配
- onRefresh阶段:创建并初始化WebServer
- 调用ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner
springboot启动流程 (1) 流程概览的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot源码学习3——SpringBoot启动流程
系列文章目录和关于我 一丶前言 在 <SpringBoot源码学习1--SpringBoot自动装配源码解析+Spring如何处理配置类的>中我们学习了SpringBoot自动装配如何实现 ...
- (一)SpringBoot启动过程的分析-启动流程概览
-- 以下内容均基于2.1.8.RELEASE版本 通过粗粒度的分析SpringBoot启动过程中执行的主要操作,可以很容易划分它的大流程,每个流程只关注重要操作为后续深入学习建立一个大纲. 官方示例 ...
- SpringBoot启动原理及相关流程
一.springboot启动原理及相关流程概览 springboot是基于spring的新型的轻量级框架,最厉害的地方当属自动配置.那我们就可以根据启动流程和相关原理来看看,如何实现传奇的自动配置 二 ...
- SpringBoot启动流程及其原理
Spring Boot.Spring MVC 和 Spring 有什么区别? 分别描述各自的特征: Spring 框架就像一个家族,有众多衍生产品例如 boot.security.jpa等等:但他们的 ...
- SpringBoot启动流程解析
写在前面: 由于该系统是底层系统,以微服务形式对外暴露dubbo服务,所以本流程中SpringBoot不基于jetty或者tomcat等容器启动方式发布服务,而是以执行程序方式启动来发布(参考下图ke ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(五):SpringBoot自动装配原理实现
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(六):IoC容器依赖注入
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(一):SpringApplication类初始化过程
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(二):SpringApplication的run方法
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(三):SpringApplication的run方法之prepareContext()方法
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
随机推荐
- JXNU acm选拔赛 壮壮的数组
壮壮的数组 Time Limit : 3000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 65535/32768K (Java/Other) Total Submiss ...
- 华企盾DSC忘记了数据库解锁密码
解决方法:登录数据库控制台,找到DSE所使用数据库默认名字"DSEDB",打开表"FileEncryptKey_TABLE",如下图所示: 第一行,自动生成 ...
- 解决 IDEA 报错ERROR:JAVA: 无效的源发行版: 11
解决 IDEA 报错ERROR:JAVA: 无效的源发行版: 11 原因 一般都是创建工程的时候 一路next 默认选择了 Java Version 11, 而本地的jdk版本是 8 解决 File ...
- ElasticSearch之Delete index API
删除指定的索引. 同时删除索引关联的数据.分片.元数据等相关的资源,因此执行前需要慎重. 命令样例如下: curl -X DELETE "https://localhost:9200/tes ...
- STM32CubeMX教程3 GPIO输入 - 按键响应
1.准备材料 开发板(STM32F407G-DISC1) ST-LINK/V2驱动 STM32CubeMX软件(Version 6.10.0) keil µVision5 IDE(MDK-Arm) 2 ...
- Windows Server 2019/2016 配置自动更新和更换大陆更新服务器
文章原地址: 运行 > gpedit.msc -> 计算机配置 -> 管理模板 -> Windows 组件 -> Windows 更新 下面中右侧三个选项是本篇教程中会介 ...
- Pikachu漏洞靶场 Over Permission(越权)
Over Permission(越权) 文章目录 Over Permission(越权) 水平越权 垂直越权 水平越权 首先根据提示信息的账号密码登录: 点击查看个人信息: 抓包之后发现查的人是在UR ...
- Feign源码解析:初始化过程(三)
背景 前面两篇讲了下,在一个典型的引入了feign.loadbalancer.nacos等相关依赖的环境中,会有哪些bean需要创建. 其中第一篇讲了非自动配置的bean,第二篇是自动配置的bean. ...
- Langchain-Chatchat项目:1.1-ChatGLM2项目整体介绍
ChatGLM2-6B是开源中英双语对话模型ChatGLM-6B的第2代版本,引入新的特性包括更长的上下文(基于FlashAttention技术,将基座模型的上下文长度由ChatGLM-6B的2K ...
- 带你了解WDR-GaussDB(DWS) 的性能监测报告
摘要:通过本文,读者可知晓什么是WDR,如何创建性能数据快照以及生成WDR报告. 本文分享自华为云社区<WDR-GaussDB(DWS) 的性能监测报告>,作者:Zhang Jingyao ...
