Akka(19): Stream:组合数据流,组合共用-Graph modular composition
akka-stream的Graph是一种运算方案,它可能代表某种简单的线性数据流图如:Source/Flow/Sink,也可能是由更基础的流图组合而成相对复杂点的某种复合流图,而这个复合流图本身又可以被当作组件来组合更大的Graph。因为Graph只是对数据流运算的描述,所以它是可以被重复利用的。所以我们应该尽量地按照业务流程需要来设计构建Graph。在更高的功能层面上实现Graph的模块化(modular)。按上回讨论,Graph又可以被描述成一种黑盒子,它的入口和出口就是Shape,而内部的作用即处理步骤Stage则是用GraphStage来形容的。下面是akka-stream预设的一些基础数据流图:
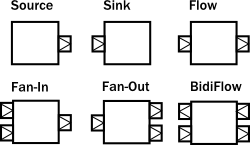
上面Source,Sink,Flow代表具备线性步骤linear-stage的流图,属于最基础的组件,可以用来构建数据处理链条。而Fan-In合并型,Fan-Out扩散型则具备多个输入或输出端口,可以用来构建更复杂的数据流图。我们可以用以上这些基础Graph来构建更复杂的复合流图,而这些复合流图又可以被重复利用去构建更复杂的复合流图。下面就是一些常见的复合流图:
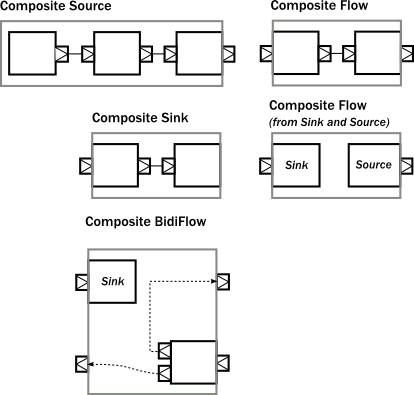
注意上面的Composite Flow(from Sink and Source)可以用Flow.fromSinkAndSource函数构建:
def fromSinkAndSource[I, O](sink: Graph[SinkShape[I], _], source: Graph[SourceShape[O], _]): Flow[I, O, NotUsed] =
fromSinkAndSourceMat(sink, source)(Keep.none)
这个Flow从流向来说先Sink再Source是反的,形成的Flow上下游间无法协调,即Source端终结信号无法到达Sink端,因为这两端是相互独立的。我们必须用CoupledTermination对象中的fromSinkAndSource函数构建的Flow来解决这个问题:
/**
* Allows coupling termination (cancellation, completion, erroring) of Sinks and Sources while creating a Flow them them.
* Similar to `Flow.fromSinkAndSource` however that API does not connect the completion signals of the wrapped stages.
*/
object CoupledTerminationFlow {
@deprecated("Use `Flow.fromSinkAndSourceCoupledMat(..., ...)(Keep.both)` instead", "2.5.2")
def fromSinkAndSource[I, O, M1, M2](in: Sink[I, M1], out: Source[O, M2]): Flow[I, O, (M1, M2)] =
Flow.fromSinkAndSourceCoupledMat(in, out)(Keep.both)
从上面图列里的Composite BidiFlow可以看出:一个复合Graph的内部可以是很复杂的,但从外面看到的只是简单的几个输入输出端口。不过Graph内部构件之间的端口必须按照功能逻辑进行正确的连接,剩下的就变成直接向外公开的界面端口了。这种机制支持了层级式的模块化组合方式,如下面的图示:
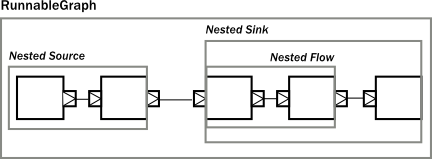
最后变成:
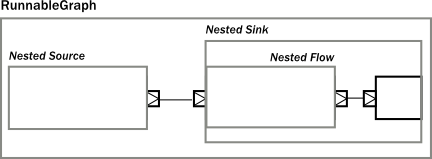
在DSL里我们可以用name("???")来分割模块:
val nestedFlow =
Flow[Int].filter(_ != ) // an atomic processing stage
.map(_ - ) // another atomic processing stage
.named("nestedFlow") // wraps up the Flow, and gives it a name val nestedSink =
nestedFlow.to(Sink.fold()(_ + _)) // wire an atomic sink to the nestedFlow
.named("nestedSink") // wrap it up // Create a RunnableGraph
val runnableGraph = nestedSource.to(nestedSink)
在下面这个示范里我们自定义一个某种功能的流图模块:它有2个输入和3个输出。然后我们再使用这个自定义流图模块组建一个完整的闭合流图:
import akka.actor._
import akka.stream._
import akka.stream.scaladsl._ import scala.collection.immutable object GraphModules {
def someProcess[I, O]: I => O = i => i.asInstanceOf[O] case class TwoThreeShape[I, I2, O, O2, O3](
in1: Inlet[I],
in2: Inlet[I2],
out1: Outlet[O],
out2: Outlet[O2],
out3: Outlet[O3]) extends Shape { override def inlets: immutable.Seq[Inlet[_]] = in1 :: in2 :: Nil override def outlets: immutable.Seq[Outlet[_]] = out1 :: out2 :: out3 :: Nil override def deepCopy(): Shape = TwoThreeShape(
in1.carbonCopy(),
in2.carbonCopy(),
out1.carbonCopy(),
out2.carbonCopy(),
out3.carbonCopy()
)
}
//a functional module with 2 input 3 output
def TwoThreeGraph[I, I2, O, O2, O3] = GraphDSL.create() { implicit builder =>
val balancer = builder.add(Balance[I]())
val flow = builder.add(Flow[I2].map(someProcess[I2, O2])) TwoThreeShape(balancer.in, flow.in, balancer.out(), balancer.out(), flow.out)
} val closedGraph = GraphDSL.create() {implicit builder =>
import GraphDSL.Implicits._
val inp1 = builder.add(Source(List(,,))).out
val inp2 = builder.add(Source(List(,,))).out
val merge = builder.add(Merge[Int]())
val mod23 = builder.add(TwoThreeGraph[Int,Int,Int,Int,Int]) inp1 ~> mod23.in1
inp2 ~> mod23.in2
mod23.out1 ~> merge.in()
mod23.out2 ~> merge.in()
mod23.out3 ~> Sink.foreach(println)
merge ~> Sink.foreach(println)
ClosedShape }
} object TailorGraph extends App {
import GraphModules._ implicit val sys = ActorSystem("streamSys")
implicit val ec = sys.dispatcher
implicit val mat = ActorMaterializer() RunnableGraph.fromGraph(closedGraph).run() scala.io.StdIn.readLine()
sys.terminate() }
这个自定义的TwoThreeGraph是一个复合的流图模块,是可以重复使用的。注意这个~>符合的使用:akka-stream只提供了对预设定Shape作为连接对象的支持如:
def ~>[Out](junction: UniformFanInShape[T, Out])(implicit b: Builder[_]): PortOps[Out] = {...}
def ~>[Out](junction: UniformFanOutShape[T, Out])(implicit b: Builder[_]): PortOps[Out] = {...}
def ~>[Out](flow: FlowShape[T, Out])(implicit b: Builder[_]): PortOps[Out] = {...}
def ~>(to: Graph[SinkShape[T], _])(implicit b: Builder[_]): Unit =
b.addEdge(importAndGetPort(b), b.add(to).in)
def ~>(to: SinkShape[T])(implicit b: Builder[_]): Unit =
b.addEdge(importAndGetPort(b), to.in)
...
所以对于我们自定义的TwoThreeShape就只能使用直接的端口连接了:
def ~>[U >: T](to: Inlet[U])(implicit b: Builder[_]): Unit =
b.addEdge(importAndGetPort(b), to)
以上的过程显示:通过akka的GraphDSL,对复合型Graph的构建可以实现形象化,大部分工作都在如何对组件之间的端口进行连接。我们再来看个较复杂复合流图的构建过程,下面是这个流图的图示:
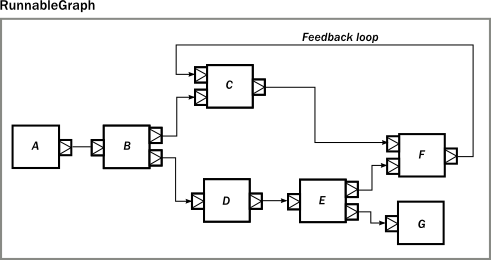
可以说这是一个相对复杂的数据处理方案,里面甚至包括了数据流回路(feedback)。无法想象如果用纯函数数据流如scalaz-stream应该怎样去实现这么复杂的流程,也可能根本是没有解决方案的。但用akka GraphDSL可以很形象的组合这个数据流图;
import GraphDSL.Implicits._
RunnableGraph.fromGraph(GraphDSL.create() { implicit builder =>
val A: Outlet[Int] = builder.add(Source.single()).out
val B: UniformFanOutShape[Int, Int] = builder.add(Broadcast[Int]())
val C: UniformFanInShape[Int, Int] = builder.add(Merge[Int]())
val D: FlowShape[Int, Int] = builder.add(Flow[Int].map(_ + ))
val E: UniformFanOutShape[Int, Int] = builder.add(Balance[Int]())
val F: UniformFanInShape[Int, Int] = builder.add(Merge[Int]())
val G: Inlet[Any] = builder.add(Sink.foreach(println)).in C <~ F
A ~> B ~> C ~> F
B ~> D ~> E ~> F
E ~> G ClosedShape
})
另一个端口连接方式的版本如下:
RunnableGraph.fromGraph(GraphDSL.create() { implicit builder =>
val B = builder.add(Broadcast[Int]())
val C = builder.add(Merge[Int]())
val E = builder.add(Balance[Int]())
val F = builder.add(Merge[Int]())
Source.single() ~> B.in; B.out() ~> C.in(); C.out ~> F.in()
C.in() <~ F.out
B.out().map(_ + ) ~> E.in; E.out() ~> F.in()
E.out() ~> Sink.foreach(println)
ClosedShape
})
如果把上面这个复杂的Graph切分成模块的话,其中一部分是这样的:
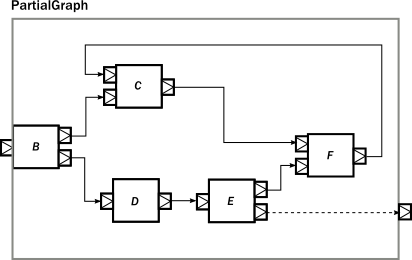
val partial = GraphDSL.create() { implicit builder =>
val B = builder.add(Broadcast[Int]())
val C = builder.add(Merge[Int]())
val E = builder.add(Balance[Int]())
val F = builder.add(Merge[Int]())
C <~ F
B ~> C ~> F
B ~> Flow[Int].map(_ + ) ~> E ~> F
FlowShape(B.in, E.out())
}.named("partial")
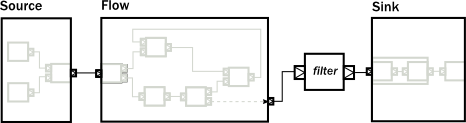
// Convert the partial graph of FlowShape to a Flow to get
// access to the fluid DSL (for example to be able to call .filter())
val flow = Flow.fromGraph(partial) // Simple way to create a graph backed Source
val source = Source.fromGraph( GraphDSL.create() { implicit builder =>
val merge = builder.add(Merge[Int]())
Source.single() ~> merge
Source(List(, , )) ~> merge // Exposing exactly one output port
SourceShape(merge.out)
}) // Building a Sink with a nested Flow, using the fluid DSL
val sink = {
val nestedFlow = Flow[Int].map(_ * ).drop().named("nestedFlow")
nestedFlow.to(Sink.head)
} // Putting all together
val closed = source.via(flow.filter(_ > )).to(sink)
返回运算结果是通过viaMat, toMat来实现的。简写的via,to默认选择流图左边运算产生的结果。
Akka(19): Stream:组合数据流,组合共用-Graph modular composition的更多相关文章
- Akka(18): Stream:组合数据流,组件-Graph components
akka-stream的数据流可以由一些组件组合而成.这些组件统称数据流图Graph,它描述了数据流向和处理环节.Source,Flow,Sink是最基础的Graph.用基础Graph又可以组合更复杂 ...
- [Python设计模式] 第19章 分公司=部门?——组合模式
github地址:https://github.com/cheesezh/python_design_patterns 组合模式 组合模式,将对象组合成树形结构以表示"部分-整体" ...
- 【题解】数字组合(NTT+组合 滑稽)
[题解]数字组合(NTT+组合 滑稽) 今天实践一下谢总讲的宰牛刀233,滑稽. \((1+x)(1+x)(1+x)\)的\(x^2\)系数就代表了有三个一快钱硬币构成的两块钱的方案数量. 很好理解, ...
- Akka(17): Stream:数据流基础组件-Source,Flow,Sink简介
在大数据程序流行的今天,许多程序都面临着共同的难题:程序输入数据趋于无限大,抵达时间又不确定.一般的解决方法是采用回调函数(callback-function)来实现的,但这样的解决方案很容易造成“回 ...
- Leetcode刷题笔记(Python 找出所有相加之和为n的k个组合,组合中只允许含有1-9的正整数,并且每种组合中不存在重复的数字。)
eg:输入:k=3,n=9 输出: [[1,2,6],[1,3,5],[2,3,4]] 输入:k=2,n=5 输出:[[1,4][2,3]] #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- c ...
- JVM垃圾收集器组合--各种组合对应的虚拟机参数实践
前言 相信很多人都看过下面这张图,(来自<深入理解Java虚拟机:JVM高级特性与最佳实践>) 在学完几种垃圾收集器类型及组合后,打算看看实际中程序用到的垃圾收集器. 但是在jconsol ...
- 剑指offer-拓展训练-字符的所有组合-全组合
/* 题目: 给定不含重复字符字符串的全组合. */ /* 思路: 递归法. 例给定abc,输出的组合长度为1,2,3. 对于长度为2的组合,分选择a(ab,ac)和不选择a的情况(bc). 选择a, ...
- [LeetCode] Moving Average from Data Stream 从数据流中移动平均值
Given a stream of integers and a window size, calculate the moving average of all integers in the sl ...
- [LeetCode] 346. Moving Average from Data Stream 从数据流中移动平均值
Given a stream of integers and a window size, calculate the moving average of all integers in the sl ...
随机推荐
- Chrome浏览器扩展开发系列之八:Chrome扩展的数据存储
Google Chrome浏览器扩展可以使用如下任何一种存储机制: HTML5的localStorage API实现的本地存储(此处略) Google的chrome.storage.* API实现的浏 ...
- Struts2+Spring+Hibernate+Jbpm技术实现Oa(Office Automation)办公系统第一天框架搭建
=============编码规范,所有文健,所有页面,所有数据库的数据表都采用UTF-8编码格式,避免乱码:===========开发环境:jdk1.7+tomcat8.0+mysql5.7+ecl ...
- win10 运行sqlplus报错“SP2-1503: 无法初始化 Oracle 调用界面”
解决方法: 1.临时方案:此时可以以“管理员身份”运行cmd,然后再执行sqlplus就行了. 长久方案: 请看原文:http://blog.csdn.net/bisal/article/detail ...
- 类 java.util.Scannar方法
类 java.util.Scannar方法 ·Scannar (InputStream ln):用给定的输人流创建一个Scanner对象. ·String nextLlne():读取输入的下一行内容. ...
- 使用Linux环境变量
bash shell用一个叫做环境变量的特性来存储有关shell会话和工作环境的信息. 全局环境变量 这对shell 会话和所有生成的子shell都是可见的.局部变量只对创建他们的shell可见. 系 ...
- 51nod_1490: 多重游戏(树上博弈)
题目链接 该题实质上是一个树上博弈的问题.要定义四种状态--2先手必胜 1先手必败 3可输可赢 0不能控制 叶子结点为先手必胜态: 若某结点的所有儿子都是先手必败态,则该结点为先手必胜态: 若某结点的 ...
- HTML中关于图像和表格,链接等的知识
下面是我分享的html中关于图像和表格,链接等知识: ①<img/>图像标签 <img/>标签中的一些常见属性:1,src是图像的路径属性,是img标签中必不可少的属性. 2, ...
- (转)OGNL表达式介绍
OGNL是Object-Graph Navigation Language的缩写,它是一种功能强大的表达式语言(Expression Language,简称为EL),通过它简单一致的表达式语法,可以存 ...
- 在Navicat 中给Mysql中的某字段添加前缀00
第一次分享心得,希望大家多多关注. 我遇到的情况是这样的,在Navicat中某表的varchar字段内容长度不够5的在内容前面添加‘0’:如字段内容是 101 我就要改成00101: 其中有2个难点: ...
- RabbitMQ入门-消息订阅模式
消息派发 上篇<RabbitMQ入门-消息派发那些事儿>发布之后,收了不少反馈,其中问的最多的还是有关消息确认以及超时等场景的处理. 楼主,有遇到消费者后台进程不在,但consumer连接 ...
