python小实例——tkinter实战(计算器)
一、完美计算器实验一
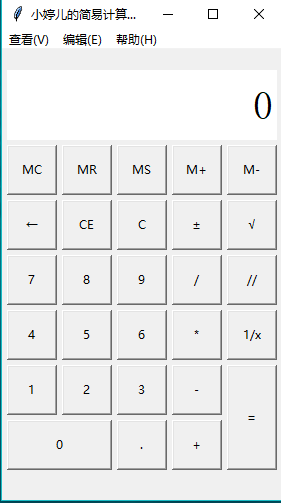
import tkinter
import math
import tkinter.messagebox class calculator:
#界面布局方法
def __init__(self):
#创建主界面,并且保存到成员属性中
self.root = tkinter.Tk()
self.root.minsize(280, 450)
self.root.maxsize(280, 470)
self.root.title('小餅餅丶的简易计算器1.0')
# 设置显式面板的变量
self.result = tkinter.StringVar()
self.result.set(0)
# 设置一个全局变量 运算数字和f符号的列表
self.lists = []
# 添加一个用于判断是否按下运算符号的标志
self.ispresssign = False
# 界面布局
self.menus()
self.layout()
self.root.mainloop() #计算器菜单界面摆放
def menus(self):
# 添加菜单
# 创建总菜单
allmenu = tkinter.Menu(self.root)
# 添加子菜单
filemenu = tkinter.Menu(allmenu, tearoff=0)
# 添加选项卡
filemenu.add_command(label='标准型(T) Alt+1', command=self.myfunc)
filemenu.add_command(label='科学型(S) Alt+2', command=self.myfunc)
filemenu.add_command(label='程序员(P) Alt+3', command=self.myfunc)
filemenu.add_command(label='统计信息(A) Alt+4', command=self.myfunc)
# 添加分割线
filemenu.add_separator()
# 添加选项卡
filemenu.add_command(label='历史记录(Y) Ctrl+H', command=self.myfunc)
filemenu.add_command(label='数字分组(I)', command=self.myfunc)
# 添加分割线
filemenu.add_separator()
# 添加选项卡
filemenu.add_command(label='基本(B) Ctrl+F4', command=self.myfunc)
filemenu.add_command(label='单位转换(U) Ctrl+U', command=self.myfunc)
filemenu.add_command(label='日期计算(D) Ctrl+E', command=self.myfunc)
menu1 = tkinter.Menu(filemenu, tearoff=0)
menu1.add_command(label='抵押(M)', command=self.myfunc)
menu1.add_command(label='汽车租赁(V)', command=self.myfunc)
menu1.add_command(label='油耗(mpg)(F)', command=self.myfunc)
menu1.add_command(label='油耗(l/100km)(U)', command=self.myfunc)
filemenu.add_cascade(label='工作表(W)', menu=menu1)
allmenu.add_cascade(label='查看(V)', menu=filemenu) # 添加子菜单2
editmenu = tkinter.Menu(allmenu, tearoff=0)
# 添加选项卡
editmenu.add_command(label='复制(C) Ctrl+C', command=self.myfunc)
editmenu.add_command(label='粘贴(V) Ctrl+V', command=self.myfunc)
# 添加分割线
editmenu.add_separator()
# 添加选项卡
menu2 = tkinter.Menu(filemenu, tearoff=0)
menu2.add_command(label='复制历史记录(I)', command=self.myfunc)
menu2.add_command(label='编辑(E) F2', command=self.myfunc)
menu2.add_command(label='取消编辑(N) Esc', command=self.myfunc)
menu2.add_command(label='清除(L) Ctrl+Shift+D', command=self.myfunc)
editmenu.add_cascade(label='历史记录(H)', menu=menu2)
allmenu.add_cascade(label='编辑(E)', menu=editmenu) # 添加子菜单3
helpmenu = tkinter.Menu(allmenu, tearoff=0)
# 添加选项卡
helpmenu.add_command(label='查看帮助(V) F1', command=self.myfunc)
# 添加分割线
helpmenu.add_separator()
# 添加选项卡
helpmenu.add_command(label='关于计算器(A)', command=self.myfunc)
allmenu.add_cascade(label='帮助(H)', menu=helpmenu) self.root.config(menu=allmenu) #计算器主界面摆放
def layout(self):
# 显示屏
result = tkinter.StringVar()
result.set(0)
show_label = tkinter.Label(self.root, bd=3, bg='white', font=('宋体', 30), anchor='e', textvariable=self.result)
show_label.place(x=5, y=20, width=270, height=70)
# 功能按钮MC
button_mc = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='MC', command=self.wait)
button_mc.place(x=5, y=95, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮MR
button_mr = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='MR', command=self.wait)
button_mr.place(x=60, y=95, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮MS
button_ms = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='MS', command=self.wait)
button_ms.place(x=115, y=95, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮M+
button_mjia = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='M+', command=self.wait)
button_mjia.place(x=170, y=95, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮M-
button_mjian = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='M-', command=self.wait)
button_mjian.place(x=225, y=95, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮←
button_zuo = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='←', command=self.dele_one)
button_zuo.place(x=5, y=150, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮CE
button_ce = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='CE', command=lambda: self.result.set(0))
button_ce.place(x=60, y=150, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮C
button_c = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='C', command=self.sweeppress)
button_c.place(x=115, y=150, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮±
button_zf = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='±', command=self.zf)
button_zf.place(x=170, y=150, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮√
button_kpf = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='√', command=self.kpf)
button_kpf.place(x=225, y=150, width=50, height=50)
# 数字按钮7
button_7 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='', command=lambda: self.pressnum(''))
button_7.place(x=5, y=205, width=50, height=50)
# 数字按钮8
button_8 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='', command=lambda: self.pressnum(''))
button_8.place(x=60, y=205, width=50, height=50)
# 数字按钮9
button_9 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='', command=lambda: self.pressnum(''))
button_9.place(x=115, y=205, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮/
button_division = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='/', command=lambda: self.presscalculate('/'))
button_division.place(x=170, y=205, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮%
button_remainder = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='//', command=lambda:self.presscalculate('//'))
button_remainder.place(x=225, y=205, width=50, height=50)
# 数字按钮4
button_4 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='', command=lambda: self.pressnum(''))
button_4.place(x=5, y=260, width=50, height=50)
# 数字按钮5
button_5 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='', command=lambda: self.pressnum(''))
button_5.place(x=60, y=260, width=50, height=50)
# 数字按钮6
button_6 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='', command=lambda: self.pressnum(''))
button_6.place(x=115, y=260, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮*
button_multiplication = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='*', command=lambda: self.presscalculate('*'))
button_multiplication.place(x=170, y=260, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮1/x
button_reciprocal = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='1/x', command=self.ds)
button_reciprocal.place(x=225, y=260, width=50, height=50)
# 数字按钮1
button_1 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='', command=lambda: self.pressnum(''))
button_1.place(x=5, y=315, width=50, height=50)
# 数字按钮2
button_2 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='', command=lambda: self.pressnum(''))
button_2.place(x=60, y=315, width=50, height=50)
# 数字按钮3
button_3 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='', command=lambda: self.pressnum(''))
button_3.place(x=115, y=315, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮-
button_subtraction = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='-', command=lambda: self.presscalculate('-'))
button_subtraction.place(x=170, y=315, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮=
button_equal = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='=', command=lambda: self.pressequal())
button_equal.place(x=225, y=315, width=50, height=105)
# 数字按钮0
button_0 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='', command=lambda: self.pressnum(''))
button_0.place(x=5, y=370, width=105, height=50)
# 功能按钮.
button_point = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='.', command=lambda: self.pressnum('.'))
button_point.place(x=115, y=370, width=50, height=50)
# 功能按钮+
button_plus = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='+', command=lambda: self.presscalculate('+'))
button_plus.place(x=170, y=370, width=50, height=50) #计算器菜单功能
def myfunc(self):
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('','程序员懒死在电脑前,打死也做不出的功能,只是装饰而已~') #数字方法
def pressnum(self,num):
# 全局化变量
# 判断是否按下了运算符号
if self.ispresssign == False:
pass
else:
self.result.set(0)
# 重置运算符号的状态
self.ispresssign = False
if num == '.':
num = '0.'
# 获取面板中的原有数字
oldnum = self.result.get()
# 判断界面数字是否为0
if oldnum == '':
self.result.set(num)
else:
# 连接上新按下的数字
newnum = oldnum + num # 将按下的数字写到面板中
self.result.set(newnum) #运算函数
def presscalculate(self,sign):
# 保存已经按下的数字和运算符号
# 获取界面数字
num = self.result.get()
self.lists.append(num)
# 保存按下的操作符号
self.lists.append(sign)
# 设置运算符号为按下状态
self.ispresssign = True #获取运算结果
def pressequal(self):
# 获取所有的列表中的内容(之前的数字和操作)
# 获取当前界面上的数字
curnum = self.result.get()
# 将当前界面的数字存入列表
self.lists.append(curnum)
# 将列表转化为字符串
calculatestr = ''.join(self.lists)
# 使用eval执行字符串中的运算即可
endnum = eval(calculatestr)
# 将运算结果显示在界面中
self.result.set(str(endnum)[:10])
if self.lists != 0:
self.ispresssign = True
# 清空运算列表
self.lists.clear() #暂未开发说明
def wait(self):
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('','功能在努力的实现,请期待2.0版本的更新') #←按键功能
def dele_one(self):
if self.result.get() == '' or self.result.get() == '':
self.result.set('')
return
else:
num = len(self.result.get())
if num > 1:
strnum = self.result.get()
strnum = strnum[0:num - 1]
self.result.set(strnum)
else:
self.result.set('') #±按键功能
def zf(self):
strnum = self.result.get()
if strnum[0] == '-':
self.result.set(strnum[1:])
elif strnum[0] != '-' and strnum != '':
self.result.set('-' + strnum) #1/x按键功能
def ds(self):
dsnum = 1 / int(self.result.get())
self.result.set(str(dsnum)[:10])
if self.lists != 0:
self.ispresssign = True
# 清空运算列表
self.lists.clear() #C按键功能
def sweeppress(self):
self.lists.clear()
self.result.set(0) #√按键功能
def kpf(self):
strnum = float(self.result.get())
endnum = math.sqrt(strnum)
if str(endnum)[-1] == '':
self.result.set(str(endnum)[:-2])
else:
self.result.set(str(endnum)[:10])
if self.lists != 0:
self.ispresssign = True
# 清空运算列表
self.lists.clear() #实例化对象
mycalculator = calculator()
来源于https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaobingbing/p/8016997.html
python小实例——tkinter实战(计算器)的更多相关文章
- Python小故事--------Tkinter的组件描述及解析
概念 Tkinter: 是Tk图形用户界面工具包标准(ctl)的Python接口,作为一个轻量级的跨平台图形用户界面(GUI)开发工具 frame: 屏幕上的一块矩形区域,多是用来作为容器(conta ...
- python小实例一:简单爬虫
本文所谓的爬虫就是通过本地远程访问url,然后将url的读成源代码形式,然后对源代码进行解析,获取自己需要的数据,相当于简单数据挖掘.本文实现的是将一个网页的图片爬出保存到本地的过程,例子很简单,用的 ...
- python小实例
一.跳动的心 love = '\n'.join([''.join([('love'[(x-y) % len('Love')] if ((x*0.05)**2+(y*0.1)**2-1)**3-(x*0 ...
- Python(五)编程小实例
Python(五)编程小实例 抓取网页信息,并生成txt文件内容! Python抓取网页技能--Python抓取网页就是我们常看见的网络爬虫,我们今天所要用到的就是我们Python中自带的模块,用这些 ...
- python+pcap+dpkt 抓包小实例
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ 网络数据包捕获与分析程序 """ imp ...
- Python数据分析实战视频教程【小蚊子数据分析实战课程】
点击了解更多Python课程>>> Python数据分析实战视频教程[小蚊子数据分析实战课程] [课程概述] Python数据分析实战' 适用人群:适合需提升竞争力.提升工作效率.喜 ...
- Python 小案例实战 —— 简易银行存取款查询系统
Python 小案例实战 -- 简易银行存取款查询系统 涉及知识点 包的调用 字典.列表的混合运用 列表元素索引.追加 基本的循环与分支结构 源码 import sys import time ban ...
- python爬取微信小程序(实战篇)
python爬取微信小程序(实战篇) 本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/HeyShHeyou/article/details/90452656 展开 一.背景介绍 近期有需求需要抓 ...
- Python GUI之tkinter窗口视窗教程大集合(看这篇就够了) JAVA日志的前世今生 .NET MVC采用SignalR更新在线用户数 C#多线程编程系列(五)- 使用任务并行库 C#多线程编程系列(三)- 线程同步 C#多线程编程系列(二)- 线程基础 C#多线程编程系列(一)- 简介
Python GUI之tkinter窗口视窗教程大集合(看这篇就够了) 一.前言 由于本篇文章较长,所以下面给出内容目录方便跳转阅读,当然也可以用博客页面最右侧的文章目录导航栏进行跳转查阅. 一.前言 ...
随机推荐
- nginx奔溃自动重启Shell脚本
# vi /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx_restart.sh 贴入一下代码: #!/bin/bash #www.xmsolink.com #Monitor nginx ser ...
- ES6深入浅出-4 迭代器与生成器-1.字面量增强
今天的内容 字面量literal 写出来就是它的值 例如字符串hello.这就是自变量. 一个空对象,也是自变量 写出来就是代表它写出来的那个意思就是自变量. 与其相反的就是构造出来的.例如下面的ne ...
- 【php】PHP制作QQ微信支付宝三合一收款码
分析 微信扫这个,支付宝扫那个,不仅要加载多张二维码,还要加css/js让它变的好看,作为一个又懒又不想写这些东西的程序猿来说,这可不行. 那能不能把QQ微信支付宝三合一,只需要扫一个收款码就行呢? ...
- 用python画 pareto front
用python画 pareto front 觉得有用的话,欢迎一起讨论相互学习~Follow Me 2D pf import os import matplotlib.pyplot as plt im ...
- ios开发将截图保存到相册
- (void)loadImageFinished:(UIImage *)image { UIImageWriteToSavedPhotosAlbum(image, self, @selector(i ...
- 安装kubernet(k8s)
简介: 需要学习的都明白,这里就不赘述了. 本文采用CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1810.iso 一:安装操作系统 本来是喜欢用fedora的,但是fedora貌似包维护的不好,就又开始用 ...
- css样式writing-mode垂直书写测试
writing-mode:控制文字的属性方向,但是不是所有的浏览器都兼容,在网页上使用时,有的浏览器显示不出该样式.该文测试的是垂直书写:网上对于测试的属性值的解释是:tb-rl:上-下,右-左.对象 ...
- LODOP打印超文本字符串拼接2 单选选择css样式表格
之前的相关字符串拼接的博文:LODOP打印超文本字符串拼接1 固定表格填充数值之前博文介绍过,字符串可以随意拼接,只要最后组织成的字符串是自己需要的超文本就可以了,前面还有一篇也是拼接样式的:Lodo ...
- 【redis】 windows 32x 64x
下载地址:http://files.cnblogs.com/files/dtdxrk/redis_win.zip
- 由于我最近搞了个wordpress搭建博客,这里我为大家分享一哈,使用wordpress过程中遇到的坑
Windows server下搭建mysql+php+apache环境参考教程: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38125058/article/details/81157865 ...
